Quick Orientation To APA Style (5th Edition)
advertisement

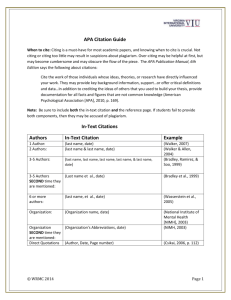
Quick Orientation To APA Style (5th Edition) The models presented in this section are illustrative of the APA Style for citations and references. For further information pertaining to the Norms of the APA, we recommend consulting the following publication: American Psychological Association (APA). (2001). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author. This quick guide for references and citations are in compliance with the Norms of the APA according to information obtained from the following websites: http://www.lib.usm.edu/research/guides/apa.html and http://www.dianahacker.com/resdoc/social_sciences/intext.html Citations An in-text citation names the author of the source (often in a signal phrase), gives the date of publication, and at times includes a page number in parentheses. At the end of the paper, a list of references provides publication information about the source; the list is alphabetized by authors' last names (or by titles for works without authors). There is a direct connection between the intext citation and the alphabetical listing. In the following example, that connection can be seen in the last author’s name and the date, which are the same in the in-text citation and in the list of references. IN-TEXT CITATION Rumbaugh (1995) reported that "Kanzi's comprehension of over 600 novel sentences of request was very comparable to Alia's; both complied with requests without assistance on approximately 70% of the sentences" (p. 722). ENTRY IN THE LIST OF REFERENCES Rumbaugh, D. (1995). Primate language and cognition: Common ground. Social Research, 62, 711-730. APA in-text citations The APA's in-text citations provide at least the author's last name and the date of publication. For direct quotations and some paraphrases, a page number is given as well. The following models illustrate the APA style of in-text citation. NOTE: In the models in this section, notice that APA style requires the use of the past tense or the present perfect tense in signal phrases introducing cited material: Smith reported, Smith has argued. 1 Basic format for a quotation Ordinarily, introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses. Put the page number (preceded by "p.") in parentheses after the quotation. Hart (1996) wrote that some primatologists "wondered if apes had learned Language, with a capital L" (p. 109). If the signal phrase does not name the author, place the author's last name, the year, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation. Use commas between items in the parentheses: (Hart, 1996, p. 109). Basic format for a summary or a paraphrase Include the author's last name and the date either in a signal phrase introducing the material or in parentheses following it. A page number is not required for a summary or a paraphrase, but include one if it would help readers find the passage in a long work. According to Hart (1996), researchers took Terrace's conclusions seriously, and funding for language experiments soon declined Researchers took Terrace's conclusions seriously, and funding for language experiments soon declined (Hart, 1996). A work with two authors Name both authors in the signal phrase or parentheses each time you cite the work. In the parentheses, use "&" between the authors' names; in the signal phrase, use "and." Greenfield and Savage-Rumbaugh (1990) have acknowledged that Kanzi's linguistic development was slower than that of a human child (p. 567). Kanzi's linguistic development was slower than that of a human child (Greenfield & SavageRumbaugh, 1990, p. 567). A work with three to five authors Identify all authors in the signal phrase or parentheses the first time you cite the source. The chimpanzee Nim was raised by researchers who trained him in American Sign Language by molding and guiding his hands (Terrace, Petitto, Sanders, & Bever, 1979). In subsequent citations, use the first author's name followed by "et al." in either the signal phrase or the parentheses. Nim was able to string together as many as 16 signs, but their order appeared quite random (Terrace et al., 1979). A work with six or more authors Use only the first author's name followed by "et al." in the signal phrase or the parentheses. 2 The ape language studies have shed light on the language development of children with linguistic handicaps (Savage-Rumbaugh et al., 1993). Unknown author If the author is unknown, mention the work's title in the signal phrase or give the first word or two of the title in the parenthetical citation. Titles of articles and chapters are put in quotation marks; titles of books and reports are italicized. Chimpanzees in separate areas of Africa differ in a range of behaviors: in their methods of cracking nuts, for example, or in their grooming rituals. An international team of researchers has concluded that many of the differing behaviors are cultural, not just responses to varying environmental factors ("Chimps," 1999). NOTE: In the rare case when "Anonymous" is specified as the author, treat it as if it were a real name: (Anonymous, 2001). In the list of references, also use the name Anonymous as author. Organization as author If the author is a government agency or other corporate organization, name the organization in the signal phrase or in the parenthetical citation the first time you cite the source. According to the Language Research Center (2000), linguistic research with apes has led to new methods of treating humans with learning disabilities such as autism and dyslexia. If the organization has a familiar abbreviation, you may include it in brackets the first time you cite the source and use the abbreviation alone in later citations. FIRST CITATION (National Institute of Mental Health [NIMH], 2001) LATER CITATIONS (NIMH, 2001) Two or more works in the same parentheses When your parenthetical citation names two or more works, put them in the same order that they appear in the reference list, separated by semicolons. Researchers argued that the apes in the early language experiments were merely responding to cues (Sebeok & Umiker-Sebeok, 1979; Terrace, 1979). Authors with the same last name To avoid confusion, use initials with the last names if your reference list includes two or more authors with the same last name. Research by E. Smith (1989) revealed that . . . Personal communication Interviews, letters, e-mail, and other person-to-person communications should be cited as follows: 3 One of Patterson's former aides, who worked with the gorilla Michael, believes that he was capable of joking and lying in sign language (E. Robbins, personal communication, January 4, 2000). Do not include personal communications in your reference list. An electronic document When possible, cite an electronic document as you would any other document (using the authordate style). R. Fouts and D. Fouts (1999) have explained one benefit of ape language research: It has shown us how to teach children with linguistic disabilities. Electronic sources may lack authors' names or dates. In addition, they may lack page numbers (required in some citations). Here are APA's guidelines for handling sources without authors' names, dates, or page numbers. UNKNOWN AUTHOR If no author is named, mention the title of the document in a signal phrase or give the first word or two of the title in parentheses. According to a BBC article, chimpanzees at sites in West Africa, Tanzania, and Uganda exhibit culture-specific patterns of behavior when grooming one another ("Chimps," 1999). UNKNOWN DATE When the date is unknown, APA recommends using the abbreviation "n.d." (for "no date"). Attempts to return sign-language-using apes to the wild have had mixed results (Smith, n.d.). NO PAGE NUMBERS APA ordinarily requires page numbers for direct quotations, and it recommends them for summaries or paraphrases from long sources. When an electronic source lacks stable numbered pages, your citation should include—if possible—information that will help readers locate the particular passage being cited. When an electronic document has numbered paragraphs, use the paragraph number preceded by the symbol ¶ or by the abbreviation "para.": (Hall, 2001, ¶5) or (Hall, 2001, para. 5). If neither a page nor a paragraph number is given and the document contains headings, cite the appropriate heading and indicate which paragraph under that heading you are referring to: According to Kirby (1999), some critics have accused activists in the Great Ape Project of "exaggerating the supposed similarities of the apes [to humans] to stop their use in experiments" (Shared Path section, para. 6). NOTE: Electronic files using portable document format (PDF) often have stable page numbers. For such sources, give the page number in the parenthetical citation. Indirect source If you use a source that was cited in another source (a secondary source), name the original source in your signal phrase. List the secondary source in your reference list and include it in your parenthetical citation, preceded by the words "as cited in." In the following example, Booth is the secondary source. 4 Linguist Noam Chomsky has dismissed the studies on Kanzi with a flippant analogy: "To maintain that Kanzi has language ability is like saying a man can fly because he can jump in the air" (as cited in Booth, 1990, p. A3). Two or more works by the same author in the same year When your list of references includes more than one work by the same author in the same year, use lowercaser letters ("a," "b," and so on) with the year to order the entries in the reference list. Use those same letters with the year in the citation. Research by Kennedy (2000b) has yielded new findings about the role of gender in the functioning of small groups. Do not include personal communications in your reference list. References Books Typical book entry -- single author Arnheim, R. (1971). Art and visual perception. Berkeley: University of California Press. Publishing information - Spell out the publishing names of associations and university presses, but omit superfluous terms such as "Publishers," "Co.," or "Inc." If two or more locations are given, give the location listed first or the publisher's home office. When the publisher is a university and the name of the state (or province) is included in the university name, do not repeat the name of the state/province in the publisher location. When the author and publisher are identical, use the word "Author" as the name of the publisher. American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author. Multiple authors When a work has up to (and including) six authors, cite all authors. When a work has more than six authors cite the first six followed by "et al." Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. Roeder, K., Howdeshell, J., Fulton, L., Lochhead, M., Craig, K., Peterson, R., et.al. (1967). Nerve cells and insect behavior. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. When a work has up to (and including) six authors, cite all authors. When a work has more than six authors cite the first six followed by "et al." Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. 5 Roeder, K., Howdeshell, J., Fulton, L., Lochhead, M., Craig, K., Peterson, R., et.al. (1967). Nerve cells and insect behavior. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Corporate authorship Institute of Financial Education. (1982). Managing personal funds. Chicago: Midwestern. No author identified Experimental psychology. (1938). New York: Holt. Citing items in an anthology/chapter in edited book Rubenstein, J.P. (1967). The effect of television violence on small children. In B.F. Kane (Ed.), Television and juvenile psychological development (pp. 112-134). New York: American Psychological Society. Reprinted or republished chapter Freud, S. (1961). The ego and the id. In J. Strachey (Ed. and Trans.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 19, pp. 3-66). London: Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1923) Following the entry, enclose "Original work published" in parentheses, noting the original date. Chapter in a volume in a series Maccoby, E.E., & Martin, J. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In P.H. Mussen (Series Ed.) & E.M. Hetherington (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 4. Socialization, personality, and social development (4th ed., pp. 1-101). New York: Wiley. Citing multivolume works Wilson, J. G., & Fraser, F. C. (Eds.). (1977-1978). Handbook of teratology (Vols. 1-4). New York: Plenum Press. In listing a multivolume work, the publication dates should be inclusive for all volumes. The volumes should be identified, in parentheses, immediately following the book title. Do not use a period between the title and the parenthetical information; close the entire title, including the volume information, with a period. Edited collections Higgins, J. (Ed.). (1988). Psychology. New York: Norton. or Grice, H. P., & Gregory, R. L. (Eds.). (1968). Early language development. New York: McGraw-Hill. Citing specific editions of a book (when the edition used is not the first edition) Brockett, O. (1987). History of the theatre (5th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. Immediately after the book's title, note the edition information in parentheses (for example, "5th ed." or "rev. ed."). Do not use a period between the title and the parenthetical information. Translated works 6 Freud, S. (1970) An outline of psychoanalysis (J. Strachey, Trans.). New York: Norton. (Original work published 1940) The original publication date is the last portion of the entry and should be in parentheses with the note "Original work published" followed by the date. Proceedings Deci, E.L., & Ryan, R.M. (1991). A motivational approach to self: Integration in personality. In R. Dienstbier (Ed.), Nebraska Symposium on Motivation: Vol. 38. Perspectives on motivation (pp. 237-288). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. or Cynx, J., Williams, H., & Nottebohm, F. (1992). Hemispheric diffences in avian song discrimation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 89, 1372-1375. Journals Citing articles in journals with continuous pagination Passons, W. (1967). Predictive validities of the ACT, SAT, and high school grades for first semester GPA and freshman courses. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 27, 11431144. Citing articles in journals with non-continuous pagination Sawyer, J. (1966). Measurement and prediction, clinical and statistical. Psychological Bulletin, 66 (3), 178-200. Because pagination begins anew with each issue of this journal, it is necessary to include the issue number in parentheses after the volume number. Note that there is a comma between the issue number and the page numbers, but no comma between the italized volume number and the issue number. If the periodical does not use volume numbers, include "pp." before the page numbers so the reader will understand that the numbers refer to pagination. Use "p." if the source is a page or less long. Citing articles in monthly periodicals Chandler-Crisp, S. (1988, May) "Aerobic writing": a writing practice model. Writing Lab Newsletter, pp. 9-11. Citing articles in weekly periodicals Kauffmann, S. (1993, October 18). On films: class consciousness. The New Republic, p.30. Newspaper articles Monson, M. (1993, September 16). Urbana firm obstacle to office project. The ChampaignUrbana News-Gazette, pp. A1,A8. No author identified Clinton puts 'human face' on health-care plan. (1993, September 16). The New York Times, p. B1. Reprinted or republished articles 7 Clark, G., & Zimmerman, E. (1988). Professional roles and activities as models for art education. In S. Dobbs (Ed.), Research readings for discipline-based art education. Reston, VA: NAEA. (Reprinted from Studies in Art Education, 19 (1986), 34-39.) Following the entry, enclose "Reprinted from" in parentheses, noting the original publication information. Close with a period. ERIC Documents (Report available from the Educational Resources Information Center) Mead, J.V. (1992). Looking at old photographs: Investigating the teacher tales that novice teachers bring with them (Report No. NCRTL-RR-92-4). East Lansing, MI: National Center for Research on Teacher Learning. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED346082) Dissertations Dissertation obtained from Dissertation Abstracts International (DAI) Bower, D.L. (1993). Employee assistant programs supervisory referrals: Characteristics of referring and nonreferring supervisors. Dissertation Abstracts International, 54 (01), 534B. (UMI No. 9315947) Dissertation obtained from the university Ross, D. F. (1990). Unconscious transference and mistaken identity: When a witness misidentifies a familiar but innocent person from a lineup (Doctoral dissertation, Cornell University, 1990). Dissertation Abstracts International, 51, 417. Give the university and year of the dissertation as well as the volume and page numbers from the Dissertation Abstract International. Unpublished Dissertation Wilfley, D. E. (1989). Interpersonal analyses of bulimia: Normal-weight and obese. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Missouri, Columbia. Unpublished Master´s Degree Dissertation obtained from a no American university Almeida, D. M. (1990). Father´s participation in family work: Consequences for father´s stress and father child relations. Unpublished Master's degree dissertation, University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada. Other Media Citing interviews Archer, N. (1993). [Interview with Helen Burns, author of Sense and Perception]. Journal of Sensory Studies, 21, 211-216. In this example, the interview lacks a title, so a description of the interview is given in brackets. If the interview has a title, include the title (without quotation marks) after the year, and then give a further description in brackets if necessary. 8 Unpublished interviews do not need a reference page entry because they are what the Publication Manual of the APA calls "personal communications" and so "do not provide recoverable data." Here, the entry consists of the first initial and last name of the interviewee, the type of communication, and the date of the interview. (N. Archer, personal interview, October 11, 1993) Citing films or videotapes Weir, P.B. (Producer), & Harrison, B.F. (Director). (1992). Levels of consciousness [Motion picture]. Boston, MA: Filmways. Here, the main people responsible for the videotape are given, with their roles identified in parentheses after their names. After the title, the medium is identified (here, a motion picture). The distributor's name and location comprises the last part of the entry. Citing recordings Writer, A. (Date of copyright). Title of song [Recorded by artist if different from writer]. On Title of album [Medium of recording: CD, record, cassette, etc.]. Location: Label. (Recording date if different than copyright) Goodenough, J. B. (1982). Tails and trotters [Recorded by G. Bok, A. Mayo, & E. Trickett]. On And so will we yet [CD]. Sharon, CT: Folk-Legacy Records. (1990) Shocked, M. (1992). Over the waterfall. On Arkansas traveler [CD]. New York: Polygram Music. McFerrin, Bobby (Vocalist). (1990). Medicine music [Cassette Recording]. Hollywood, CA: EMI-USA. Electronic Information The type of medium can be, but is not limited to the following: aggregated databases, online journals, Web sites or Web pages, newsgroups, Web- or e-mail based discussion groups or Web or e-mail based newsletters. Pagination in electronic references is unavailable in many cases, thus left out of the citation. The APA Manual has a short section demonstrating the format for electronic references on pp. 268-281. For other examples, visit http://www.apastyle.org/elecref.html Citing computer software Arend, Dominic N. (1993). Choices (Version 4.0) [Computer software]. Champaign, IL: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Research Laboratory. (CERL Report No.CH7-22510) If an individual(s) has proprietary rights to the software, their name(s) are listed at the head of the entry, last names first, followed by a period. Otherwise, treat such references as unauthored. Do not italize the title. Specify in brackets that the source is computer software, program or language. List the location and the organization's name that produced the program. Add any other necessary information for identifying the program (in this example, the report number) in parentheses at the entry's conclusion. To reference a manual, follow the same as above but add "manual" as the 9 source in the bracketed information. Do not add a period at the end of a citation if it ends in a web address. Full-Text Database (i.e., book, magazine, newspaper article or report) The second date which follows is the date the user retrieved the material. No period follows an Internet Web address. Schneiderman, R. A. (1997). Librarians can make sense of the Net. San Antonio Business Journal, 11, 58+. Retrieved January 27, 1999, from EBSCO Masterfile database. Article in an Internet-only journal Kawasaki, J. L., & Raven, M.R. (1995). Computer-administered surveys in extension. Journal of Extension, 33, 252-255. Retrieved June 2, 1999, from http://joe.org/joe/index.html Article in an Internet-only newsletter Waufton, K.K. (1999, April). Dealing with anthrax. Telehealth News, 3(2). Retreived December 16, 2000, from http://www.telehearlth.net/subscribe/newslettr_5b.html#1 Internet technical or research reports University of California, San Francisco, Institute for Health and Aging. (1996, November). Chronic care in America: A 21st century challenge. Retrieved September 9, 2000, from the Robert Wood Foundation Web site: http://www.rwjf.org/library/chrcare Document created by private organization, no page numbers, no date Greater Hattiesburg Civic Awareness Group, Task Force on Sheltered Programs. (n.d.). Fundraising efforts. Retreived November 10, 2001, from http://www.hattiesburgcag.org Sometimes authors are not identified, and there is no date showing for the document. Date website was accessed should be used and efforts should be made to identify the sponsoring author/organization of the website. If none is found, do not list an author. Document from university program or department McNeese, M.N. (2001). Using technology in educational settings. Retrieved October 13, 2001, from University of Southern Mississippi, Educational Leadership and Research Web site: http://www-dept.usm.edu/~eda/ E-Mail, newsgroups, online forums, discussion groups and electronic mailing lists Personal communications, which are not archived, should not included in reference lists and cited within the text only: Smith, Fred ("personal communication," January 21, 1999) If archived Hammond, Tl (2000, November 20). YAHC: Handle Parameters, DOI Genres, etc. Message posted to Ref-Links electronic mailing list, archived at http://www.doi.org/mail-archive/reflink/msg00088.html 10