History of Microbiology
advertisement

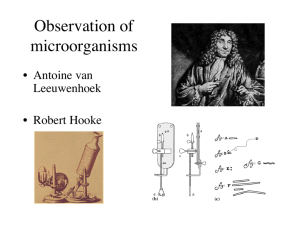
History of Microbiology JAHS Microbiology 2015 Life on Earth Ancestors of bacteria were the first inhabitants of Earth. ● Earliest evidence of life comes from 3.5 billion year old sedimentary rocks from Western Australia and Greenland ● May have chemosynthesized from outputs of hydrothermal vents ○ Miller-Urey experiments The Cell Theory In 1838, scientists Matthais Schleiden and Theodor Schwann were the main contributors to the cell theory. ● All living things are made of one or more cells. ● All cells come from preexisting cells. ● The cell is the basic unit of life. Discovery of Microbes The first microbes were observed in 1673 by Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist. ● Using a handcrafted microscope, Leeuwenhoek was the first to view and describe single-celled organisms which he called “animalcules” The Debate Over Spontaneous Generation The hypothesis that living organisms arise from nonliving matter is called spontaneous generation. According to spontaneous generation, a “vital force” forms life. ● The alternative hypothesis, that the living organisms arise from preexisting life, is called biogenesis. Evidence 1668: Francisco Redi filled six jars with decaying meat. Conditions Results Three jars covered with fine net No maggots Three open jars Maggots appeared Evidence 1745: John Needham, Roman Catholic Priest, put boiled broth into covered flasks. Conditions Nutrient Broth heated, then placed in sealed flask Results Microbial Growth Evidence 1765: Lazzaro Spallanazi boiled nutrient solutions in flasks. Conditions Nutrient Broth placed in flask, heated, then sealed Results No Microbial Growth Evidence 1861: Louis Pasteur demonstrated that microbes are present in air. Conditions Results Nutrient broth placed in flask, heated, No Microbial Growth not sealed – flask remains upright Nutrient broth placed in flask, heated, Microbial Growth no sealed – flask tilted Pasteur Pasteur’s S-shaped flask kept microbes out but let air in. The Golden Age of Microbiology: 1857-1914 Beginning with Pasteur’s work, discoveries included the relationship between microbes and disease, immunity, and antimicrobial drugs. Fermentation and Pasteurization Louis Pasteur showed that microbes are responsible for fermentation. ● Microbial growth is responsible for spoilage of food. ● Bacteria that use alcohol and produce acetic acid spoil wine by turning it to vinegar (acetic acid). ○ Pasteur demonstrated that these spoilage bacteria could be killed by heat that was not hot enough to evaporate the alcohol in wine. The Germ Theory of Disease ● 1860s: Joseph Lister used a chemical disinfectant to prevent surgical wound infections after looking at Pasteur’s work. ● 1876: Robert Koch proved that a bacterium causes anthrax and provided the experimental steps, Koch’s postulates, to prove that a specific microbe causes a specific disease. Koch’s Postulates ● The microorganism must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy organisms. ● The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in pure culture. ● The cultured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism. ● The microorganism must be reisolated from the inoculated, diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the original specific causative agent.