Radiation Detection: Geiger
advertisement

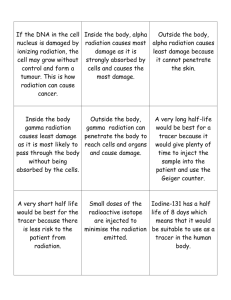
Josh Webster March 17, 2014 A Look Ahead… 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead… • History/Backstory – What is radiation? – Why detect radiation? 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead… • History/Backstory – What is radiation? – Why detect radiation? • Main Types of Detectors 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead… • History/Backstory – What is radiation? – Why detect radiation? • Main Types of Detectors • The Geiger-Müller Device: An in Depth Look 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 2 A Look Ahead… • History/Backstory – What is radiation? – Why detect radiation? • Main Types of Detectors • The Geiger-Müller Device: An in Depth Look • Building a Geiger-Müller Counter: My Spring Break Project 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 2 History Wilhem Röntgen - X-rays (1901 1st physics N.P.) Henri Becquerel - Spontaneous radioactivity (1903 N.P.) Ernst Rutherford - half-life, α, β, γ (1908 N.P.) http://s2.germany.travel/media/microsites _media/german_originality/heritage/famou speople/famouspeople_start/W-CRoentgen01_RET_1024x768.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Port rait_of_Antoine-Henri_Becquerel.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:E rnest_Rutherford_cropped.jpg Other notable contributions by: Marie & Pierre Curie, J.J. Thomson, Frederick Soddy 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 3 What is radiation? http://www.sat.dundee.ac.uk/gif/spectrum.png 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 4 What is radiation? http://www.sat.dundee.ac.uk/gif/spectrum.png • Electromagnetic waves & particle radiation 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 4 What is radiation? http://www.sat.dundee.ac.uk/gif/spectrum.png • Electromagnetic waves & particle radiation • Gamma rays and X-rays (both high energy photons) are forms of electromagnetic radiation. Alpha and beta are forms of particle radiation. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 4 What is radiation? http://www.sat.dundee.ac.uk/gif/spectrum.png • Electromagnetic waves & particle radiation • Gamma rays and X-rays (both high energy photons) are forms of electromagnetic radiation. Alpha and beta are forms of particle radiation. • Alpha particles occur in alpha decay when an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (He atom). 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 4 What is radiation? http://www.sat.dundee.ac.uk/gif/spectrum.png • Electromagnetic waves & particle radiation • Gamma rays and X-rays (both high energy photons) are forms of electromagnetic radiation. Alpha and beta are forms of particle radiation. • Alpha particles occur in alpha decay when an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (He atom). • Beta particles occur in beta decay and are electrons/positrons emitted from an atomic nucleus. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 4 Sources of Radiation • Cosmic rays from supernovae, gamma ray bursts, quasars, active galactic nuclei • The Sun - infrared, UV, X-ray (mostly blocked) http://www.technology.org/texorgwp/wpcontent/uploads/2013/07/llama-magnetic-fields.jpg 3/17/2014 http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/@api/deki/files/816/a tmosphere-nasa.gov.jpg Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 9 Sources of Radiation Continued… • α from elements Z (proton #) ≥ 52. • α, β, γ from elements with Z > 83. http://www.physics-experiments.com/photos/uranium%20radioactive%20decay.jpg 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 10 Radiation Penetration http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Alfa_beta_gamma_radiation_penetration.svg 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 11 Why detect radiation? 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 12 Why detect radiation? • For science, safety, and because it’s fun! 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 12 Why detect radiation? • For science, safety, and because it’s fun! • Determine how much of a sample will be left after a given amount of time. (i.e. radiocarbon dating) 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 12 Why detect radiation? • For science, safety, and because it’s fun! • Determine how much of a sample will be left after a given amount of time. (i.e. radiocarbon dating) • Discover new particles or learn more about known particles 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 12 Three Types of Detectors • Particle Track Devices • Ionization Detectors • Scintillation Detectors 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 16 Particle Track Device http://www.scifun.ed.ac.uk/pages/pp4ss/pp4ss-cloud_chamber.html 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 17 Ionization Detector http://spmphysics.onlinetuition.com.my/2013/08/geiger-muller-tube.html 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 18 Scintillation Detector http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Scintillation_Counter_Schematic.jpg 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 19 The Geiger-Müller Device: An in Depth Look • Townsend Avalanche Effect • Geiger Plateau • Tube Types 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 20 Townsend Avalanche Effect http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Spread_of_avalanches_in_G-M_tube.jpg 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 21 Geiger Plateau Credit: Josh Webster 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 22 Types of Geiger-Müller Tubes Tube type is critical! Alpha particles can’t pass through thick walled tubes. Glass tubes provide an alternative. http://www.cooking-hacks.com/documentation/tutorials/geiger-counter-raspberry-pi-radiation-sensor-board 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 23 Building a Geiger-Müller Counter: My Spring Break Project • What You’ll Need • Assembly • Final Touches 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 24 What You’ll Need • Kit or design for the board & parts • I bought a kit from https://sites.google.com/site/diygei gercounter/ (GK-B5 $49) • Also added the LCD ($5.50) • Geiger-Müller tube (SBM-20 @ ~$20) • Soldering iron (preferably adjustable) • 0.022” solder and solder wick • Battery and connector/wires • Digital voltmeter • Wire cutter/stripper • Mini flat head screwdriver • Flat wire cutter or finger nail clipper • Helping hands is nice • Possibly needle nose pliers and tweezers 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 25 Assembly 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 3/17/2014 2. Double check before soldering Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 3/17/2014 2. Double check before soldering Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 3. Start soldering 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 2. Double check before soldering 3. Start soldering 4. Inspect soldering 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 2. Double check before soldering 4. Inspect soldering 5. Back to soldering… 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 3. Start soldering 26 Assembly 1. Inspect parts 2. Double check before soldering 3. Start soldering 4. Inspect soldering 5. Back to soldering… 6. Inspect when done soldering 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 26 Finished Circuit Board Close-Up 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 33 Testing Connect battery, tube, and LCD. Then test with background and known source. 12-36 CPM (counts per minute) from background radiation. ~1308 CPM w/ thorium test source. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 34 Final Touches • Housing • Power switch • Other switches can be added: • Click/Mute/ Tone • Display on/off • Tube select 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 35 Conclusion 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 Conclusion • Radiation is occurring all around us. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 Conclusion • Radiation is occurring all around us. • There are various types of radiation. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 Conclusion • Radiation is occurring all around us. • There are various types of radiation. • There are varying types of detecting equipment. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 Conclusion • Radiation is occurring all around us. • There are various types of radiation. • There are varying types of detecting equipment. • Radiation detection equipment has advanced scientific knowledge and understanding. 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 Conclusion • Radiation is occurring all around us. • There are various types of radiation. • There are varying types of detecting equipment. • Radiation detection equipment has advanced scientific knowledge and understanding. • For $100 and a Saturday you can build your own detector and begin exploring radioactivity 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 36 References • DIYGeigerCounter, GK-B5 Build Instructions, Retrieved March 8, 2014 from: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/3572198/GK%20v5.3/GK%20Build% 20Instructions%20v5-2%20v5-3.pdf • Flakus, F.N., Detecting and measuring ionizing radiation – a short history, Retrieved March 10, 2014 from: http://www.iaea.org/Publications/Magazines/Bulletin/Bull234/234050431 36.pdf • Wikipedia, Geiger Counter, Retrieved March 9, 2014 from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geiger_counter#History • Wikipedia, Radiation, Retrieved March 10, 2014 from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiation#Discovery • Wikipedia, Scintillation Counter, Retrieved March 10, 2014 from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scintillation_counter • Wikipedia, Henri Becquerel, Retrieved March 11, 2014 from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henri_Becquerel 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 42 Questions? 3/17/2014 Radiation Detection - Josh Webster 43