Ohio’s State Tests
ANSWER KEY &
SCORING GUIDELINES
SPRING 2015
GRADE 5
SCIENCE
PART 1
Table of Contents
Questions 1 – 7: Content Summary and Answer Key ..........................1
Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines ......................................3
Question 1: Sample Responses ..............................................................6
Question 2: Question and Scoring Guidelines ....................................11
Question 2: Sample Responses ............................................................15
Question 3: Question and Scoring Guidelines ....................................25
Question 3: Sample Responses ............................................................28
Question 4: Simulation for Questions 5 and 6 ....................................33
Question 5: Question and Scoring Guidelines ....................................35
Question 5: Sample Responses ............................................................39
Question 6: Question and Scoring Guidelines ....................................49
Question 6: Sample Responses ............................................................52
Question 7: Question and Scoring Guidelines ....................................59
Question 7: Sample Responses ............................................................63
Grade 5 Science
PBA Practice Test
Content Summary and Answer Key
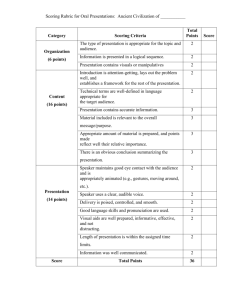
Question
No.
Item
Type
Content
Strand
Content
Statement
Answer
Key
Points
1
Matching
Life Science
All of the processes that take
place within organisms require
energy.
---
1 point
2
Short
Response
Earth and
Space
Science
Most of the cycles and patterns
of motion between the Earth
and sun are predictable.
---
2 points
3
Table
Physical
Science
The amount of change in
movement of an object is based
on the mass* of the object and
the amount of force exerted.
---
1 point
4
Simulation* Life Science
Organisms perform a variety of
roles in an ecosystem.
---
---
5
Short
Answer
Life Science
All of the processes that take
place within organisms require
energy.
---
2 points
6
Graphic
Response
Life Science
Organisms perform a variety of
roles in an ecosystem.
---
2 points
7
Short
Response
Physical
Science
Light and sound are forms of
energy that behave in
predicable ways.
---
2 points
*The Simulation is numbered but not scored.
1
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 1
Question and Scoring Guidelines
3
Question 1
20032
Points Possible: 1
See Alignment for more detail.
Scoring Guidelines
For this item, a full-credit response includes
• “Fungi” selected for “Uses dead matter for energy”
AND
• “Rabbit” selected for “Uses energy gained from plants”
AND
• “None” selected for “Uses energy directly from water”
AND
• “Grass” selected for “Uses energy directly from the sun” (1 point).
4
Alignment
Content Strand
Life Science
Content Statement
All of the processes that take place within organisms require energy.
Content Elaboration
The content statements for fifth-grade life science are each partial components of a
larger concept. The parts have been isolated to call attention to the depth of
knowledge required to build to one of biology’s foundational theories: dynamic
relationships within ecosystems. It is recommended that the content statements be
combined and taught as a whole. For example, it is important that the ecological role
of organisms is interwoven with a clear understanding that all living things require
energy. Virtual simulations and investigations can help demonstrate energy flow
through the trophic levels.
Energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction, from photosynthetic organisms to
consumers (herbivores, omnivores to carnivores) and decomposers.
Cognitive Demand
Recalling Accurate Science (R)
Requires students to provide accurate statements about scientifically valid facts,
concepts and relationships. Recall only requires students to provide a rote response,
declarative knowledge or perform routine mathematical tasks. This cognitive demand
refers to students’ knowledge of science fact, information, concepts, tools,
procedures (being able to describe how) and basic principles.
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the student to identify an organism, if any, that performs certain
energy actions in an ecosystem. Fungi are decomposers. Grass is a producer and
rabbits are consumers.
5
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 1
Sample Responses
6
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly matched each organism with its
energy action. Fungi use dead matter for energy. Grass
gets its energy directly from the sun. The rabbit gets
energy from plants and no organisms use water for
energy. Water is essential for life but it does not provide
energy. This item is an all-or-nothing for credit.
7
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response does not match the organisms to the
correct energy action and earns no credit.
8
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response accurately matches the fungi to its
energy action but the rest of the organisms are
incorrectly matched. This response receives no credit.
9
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 2
Question and Scoring Guidelines
11
Question 2
18465
Points Possible: 2
See Alignment for more detail.
12
Scoring Guidelines
Score Point
Description
2 points
The response correctly identifies the season for location X AND
correctly explains what causes the season.
1 point
The response correctly identifies the season at location X OR correctly
explains what causes the season.
0 points
The response fails to demonstrate any understanding of the causes of
seasons. The response does not meet the criteria required to earn one
point. The response indicates inadequate or no understanding of the
task and/or the idea or concept needed to answer the item. It may
only repeat information given in the test item. The response may
provide an incorrect solution/response and the provided supportive
information may be totally irrelevant to the item, or possibly, no other
information is shown. The student may have written on a different
topic or written, “I don’t know.”
Alignment
Content Strand
Earth and Space Science
Content Statement
Most of the cycles and patterns of motion between the Earth and sun are
predictable.
Content Elaboration
Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5°. This tilt, along with Earth’s revolution around
the sun, affects the amount of direct sunlight that the Earth receives in a single day
and throughout the year. The average daily temperature is related to the amount of
direct sunlight received. Changes in average temperature throughout the year are
identified as seasons.
Cognitive Demand
Interpreting and Communicating Science Concepts (C)
Requires students to use subject-specific conceptual knowledge to interpret and
explain events, phenomena, concepts and experiences using grade-appropriate
scientific terminology, technological knowledge and mathematical knowledge.
Communicate with clarity, focus and organization using rich, investigative scenarios,
real-world data and valid scientific information.
13
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the student to interpret a diagram of Earth to determine the season
at location X. The axis of the Earth is tilted 23.5o away from the direction of sunlight.
When the axis is pointed away from the sun, it is winter. Winter has fewer hours of
sunlight.
14
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 2
Sample Responses
15
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
The response receives two points. The response
correctly identifies the season “Location X is having
winter right now.” It also explains how the diagram
illustrates winter “because it is getting indirect rays of
light…caused by a hemisphere that is tilted away from
the sun.”
16
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response receives two points. It correctly identifies
the season as winter and provides a correct
explanation, “location X is winter because the sunlight
is less direct on that spot due to the 23.5 degree tilt.”
17
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response receives two points for the correct
identification of season with a correct explanation.
“The season is Winter because the Southern
Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun,” which implies the
northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun.
18
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response receives one point for the correct
identification of the season in the diagram, “location X
is winter.” The response fails to provide a correct
explanation. Being on the “opposite side of the sun”
implies the difference between night and day and is
not accepted for credit. “Does not get any heat from
the Sun” is inaccurate.
19
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response receives one point for “season in location
X it is winter.” The explanation receives no credit
because it is not clear or complete.
20
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response receives one point for the correct
identification of season, “it is winter.” The explanation
provided is incorrect. Eastern and western hemisphere
would be used to reference day and night, not the
seasons.
21
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response receives no credit because no season is
identified and the explanation provided is incorrect,
“location x is darker than the location Y because the
moon is on the X location.”
22
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response incorrectly identifies the season as fall and
fails to provide an accurate explanation. This response
receives no credit.
23
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 3
Question and Scoring Guidelines
25
Question 3
19931
Points Possible: 1
See Alignment for more detail.
Scoring Guidelines
For this item, a full-credit response includes
• 2 in the E box
AND
• 3 in the F box
AND
• 4 in the G box
AND
• 1 in the H box (1 point).
26
Alignment
Content Strand
Physical Science
Content Statement
The amount of change in movement of an object is based on the mass* of the object
and the amount of force exerted.
*While mass is the scientifically correct term to use in this context, the NAEP 2009
Science Framework (page 27) recommends using the more familiar term "weight"
in the elementary grades with the distinction between mass and weight being
introduced at the middle school level. In Ohio, students will not be assessed on the
differences between mass and weight until Grade 6.
Content Elaboration
Movement can be measured by speed. The speed of an object is calculated by
determining the distance (d) traveled in a period of time (t).
Movement is measured by speed (how fast or slow the movement is). Speed is
measured by time and distance traveled (how long it took the object to go a
specific distance). Speed is calculated by dividing distance by time. Speed must
be investigated through testing and experimentation. Real-world settings are
recommended for the investigations when possible. Virtual investigations and
simulations also can be used to demonstrate speed.
Cognitive Demand
Interpreting and Communicating Science Concepts (C)
Requires students to use subject-specific conceptual knowledge to interpret and
explain events, phenomena, concepts and experiences using grade-appropriate
scientific terminology, technological knowledge and mathematical knowledge.
Communicate with clarity, focus and organization using rich, investigative scenarios,
real-world data and valid scientific information.
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the student to compare the speeds of different cars from distance
and time data for each car. Since the times are different, the easiest way to
determine the relative speeds is to calculate it for each car. Speed can be
calculated by dividing the distance by the time. For Car E this gives 2 m/2 s or 1 m/s.
For Car F this gives 8 m/4 s or 2 m/s. For Car G this gives 4 m/1 s or 4 m/s. For Car H this
gives 0 m/ 2 s or 0 m/s. Ranking these in order from lowest average speed to highest
average speed gives Car H (0 m/s), Car E (1 m/s), Car F (2 m/s) and Car G (4 m/s).
27
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 3
Sample Responses
28
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly ranks the average speed of
each car from 1 being the lowest to 4 being the
highest average speed.
29
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response incorrectly ranks the average speed of
each car from the lowest to the highest average
speed.
30
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response incorrectly ranks the average speed of
each car from the lowest to the highest average
speed.
31
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 4
Simulation for Questions 5 and 6
33
Question 4 (Simulation for Questions 5 and 6)
16938
34
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 5
Question and Scoring Guidelines
35
Question 5
16954
Points Possible: 2
See Alignment for more detail.
Scoring Guidelines
Score Point
Description
2 points
Correct response for the best solution to control the tamarisk may
include one of the following:
• Beetles
• Control 3
• 3
• Measure 3
• Control measure 3
36
Correct response for an observation that supports the identification
may includes one of the following:
• Only eat tamarisk
• Only eat invasive plants
• Beetles have a predator
• Permanent solution
1 point
Response includes the following:
• a correct best solution to control the tamarisk
OR
• a correct observation that supports the identification
0 points
The response does not meet the criteria required to earn one point.
The response indicates inadequate or no understanding of the task
and/or the idea or concept needed to answer the item. It may only
repeat information given in the test item. The response may provide
an incorrect solution/response and the provided supportive
information may be irrelevant to the item, or possibly, no other
information is shown. The student may have written on a different
topic or written, “I don’t know.”
Alignment
Content Strand
Life Science
Content Statement
All of the processes that take place within organisms require energy.
Content Elaboration
Satellite imaging, remote sensing or other digital-research formats can be used to
help visualize what happens in an ecosystem when new producers (e.g., Tamarisk
plants) are introduced into an ecosystem. The information gained should be used to
determine the relationship between the producers and consumers within an
ecosystem.
37
Cognitive Demand
Designing Technological/Engineering Solutions Using Science Concepts (T)
Requires students to solve science-based engineering or technological problems
through application of scientific inquiry. Within given scientific constraints, propose or
critique solutions, analyze and interpret technological and engineering problems, use
science principles to anticipate effects of technological or engineering design, find
solutions using science and engineering or technology, consider consequences and
alternatives, and/or integrate and synthesize scientific information.
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the selection of a control measure that limits the invasive tamarisk
plant with the least impact of the entire ecosystem based on observations made in a
simulation. The control measures include mowing down the ecosystem, spraying
herbicides and introducing beetles. Mowing down the ecosystem and spraying
herbicides destroys both the tamarisk and native plants that destroy the habitat for
many animals. This solution is not permanent. The tamarisk plant can grow back. The
beetles eat the tamarisk plant and there is a natural predator of the beetle to keep
their numbers in check. This control measure provides the least impact on the
ecosystem because only the tamarisk plants are impacted and the natural habitat
remains unharmed.
38
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 5
Sample Responses
39
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly identifies control #3, the beetles.
It also states the “beetles only eat the tamarisk plant
leaves and not the native plants.” The correct
identification of the control measure and support for
that measure earns this response two points.
40
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response earns two points by correctly identifying
the control measure, “Number three,” and describing
how “the beetles only eat the tamarisk and is eaten by
birds.” The response also compares how the other two
measures negatively impact the environment “in
number two the trucks would destroy the ground and
kill habitat for native animals” and “in number one it
only kills the tamarisk temporarily.”
41
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly identifies control measure three,
which earns one point. The response also describes the
observation that supports this measure, “beetles only
eat tamarisk plant leaves,” for the second point.
42
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response identifies that the best control measure
that “limits the tamarisk plant with the least impact is
#3.” The response fails to provide an observation to
support why control measure three is the best option
for the least impact on the ecosystem.
43
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response earns one point for correctly identifying
the beetles as the best control measure. There is no
information provided to support why the beetles have
the least impact on the environment. “I know that if
you have too many plants that there will be too little
animals” is too vague to receive credit.
44
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response earns one point for “beetles are eating
the plants.” The rest of the response is too vague to
receive credit.
45
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response incorrectly identifies the control measure
and provides inaccurate information about the
tamarisk plants.
46
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response fails to identify a control measure and is
not responsive to the task because it lists all measures
provided in the simulation.
47
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 6
Question and Scoring Guidelines
49
Question 6
16950
Points Possible: 2
See Alignment for more detail.
Scoring Guidelines
For this item, a full-credit (2 point) response includes
• Only “Producer” selected (1 point)
AND
• “Providing poor habitat for native animals” AND “Competition with native plants
for resources” are selected (1 point).
50
For this item, a partial-credit (1 point) response includes
• “Producer” AND “Providing poor habitat for native animals” OR “Competition
with native plants for resources” are selected (1 point)
OR
• Only “Providing poor habitat for native animals” AND “Competition with native
plants for resources” are selected (1 point).
Alignment
Content Strand
Life Science
Content Statement
Organisms perform a variety of roles in an ecosystem.
Content Elaboration
Plants and some microorganisms are producers. They are the foundation of the food
web. Producers transform energy from the sun and make food through a process
called photosynthesis. Animals get their energy by eating plants and other animals
that eat plants. Animals are consumers and many form predator-prey relationships.
Decomposers (primarily bacteria and fungi) are consumers that use waste materials
and dead organisms for food. Decomposers also return nutrients to the ecosystem.
Cognitive Demand
Interpreting and Communicating Science Concepts (C)
Requires students to use subject-specific conceptual knowledge to interpret and
explain events, phenomena, concepts and experiences using grade-appropriate
scientific terminology, technological knowledge and mathematical knowledge.
Communicate with clarity, focus and organization using rich, investigative scenarios,
real-world data and valid scientific information.
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the student to interpret the results of the investigation and
communicate the role and relationship of the invasive species in the ecosystem. The
tamarisk plant is a producer that is an invasive species that has no natural predators
in this ecosystem. It also competes with native plants and destroys the natural habitat
for other organisms in this ecosystem.
51
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 6
Sample Responses
52
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly identifies the role of the tamarisk
plant as being a producer. Plants are producers. The
impact of the tamarisk plant on the ecosystem is also
correctly selected. Tamarisk plants are extremely
competitive and destroy natural habitats.
53
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
The response correctly identifies the role of tamarisk
plant and one correct impact of destroying the habitat
for native animals for one point. The response
incorrectly selects the second impact of increasing
available water in the rivers and streams. Tamarisk
plants use water in excess and would actually deplete
water in rivers and streams.
54
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly identifies the role of the tamarisk
plant as a producer and selects one correct impact for
one point. The incorrect impact of decreasing chances
of drought was selected. The tamarisk plant actually
increases the chances of drought in an area because
of its use of water. In some cases it can contribute to
fires in the ecosystem.
55
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response receives a partial credit of one because it
correctly selects the impact on the ecosystem even
though the role is incorrect.
56
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response receives no credit because it incorrectly
identified the role and ecological impacts of the
tamarisk plants.
57
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 7
Question and Scoring Guidelines
59
Question 7
17722
Points Possible: 2
See Alignment for more detail.
60
Scoring Guidelines
Score Point
Description
2 points
The response correctly provides two conclusions that can be made
based on the data.
1 point
The response correctly provides one conclusion that can be made
based on the data.
0 points
The response fails to demonstrate any understanding of the properties
of sound. The response does not meet the criteria required to earn
one point. The response indicates inadequate or no understanding of
the task and/or the idea or concept needed to answer the item. It
may only repeat information given in the test item. The response may
provide an incorrect solution/response and the provided supportive
information may be irrelevant to the item, or possibly, no other
information is shown. The student may have written on a different
topic or written, “I don’t know.”
Alignment
Content Strand
Physical Science
Content Statement
Light and sound are forms of energy that behave in predicable ways.
Content Elaboration
Sound must travel through a material (medium) to move from one place to another.
This medium may be a solid, liquid or gas. Sound travels at different speeds through
different media.
Cognitive Demand
Interpreting and Communicating Science Concepts (C)
Requires student to use subject-specific conceptual knowledge to interpret and
explain events, phenomena, concepts and experiences using grade-appropriate
scientific terminology, technological knowledge and mathematical knowledge.
Communicate with clarity, focus and organization using rich, investigative scenarios,
real-world data and valid scientific information.
61
Explanation of the Item
This item requires the student to evaluate two tables of data about sound traveling
through different media and draw conclusions about the properties of sound based
on that data. Based on the data, one conclusion that could be made is that sound
travels through liquids faster than it travels through gases. Evidence that supports this
conclusion is that the speeds of sound in water (1,526 m/s, 1,481m/s, and 1,403m/s)
greatly exceed the speeds of sound in air (356m/s, 343m/s, and 331 m/s). Another
conclusion that could be made is that sound travels faster in warmer temperatures
than it does in cooler temperatures. Evidence for this conclusion is that for air, sound
travels 356 m/s at 40oC, which is faster than 331m/s at 0oC.
62
Grade 5
Science
PBA Practice Test
Question 7
Sample Responses
63
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response correctly concludes “that sound travels
faster in water” for one point. The second point is
awarded for concluding “The colder the temp. the
slower the speed of sound.”
64
Sample Response: 2 points
Notes on Scoring
This response earns a point for concluding “sound
travels faster in water and slauer in air.” The second
point comes from the conclusion “sound travels fastest
in water when the temperature is high.”
65
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response earns one point for the conclusion “it
goes slower when it colder.” The first sentence “not as
far when it cold” is vague and does not impact the
points earned. This response lacks a second conclusion
that would compare the media in which sound travels.
66
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response earns one point for providing a conclusion
on the speed of sound in different media. “Sound
moves faster in water...Sound moves slower in air.” The
response does not address different temperatures.
67
Sample Response: 1 point
Notes on Scoring
This response earns one point for “sound travels slower
in air.” The statements “sound travels faster in places
more dense” and “because air particles are so loosely
packed in” are supporting arguments for sound
traveling slower in air. Neither of these statements is a
second conclusion based on information provided in
the data. The response does not address temperature.
68
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response earns no credit because it incorrectly
states that “sound in air moves faster than sound in
water.” The data in the table supports the opposite
conclusion. Sound travels faster in water than air.
69
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response earns no credit because it is not
responsive to the task. “Sound is in water and air. There
is more sound in water then air and less in air.” is too
vague to receive credit.
70
Sample Response: 0 points
Notes on Scoring
This response earns no credit because it is not
responsive to the task. It fails to provide any conclusion
about the speed of sound based on the data.
71
The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex,
religion, age, or disability in employment or the provision of services.
Copyright © 2014 by the Ohio Department of Education. All rights reserved.