Sheep Brain & Cow Eye Dissection Lab Report
advertisement

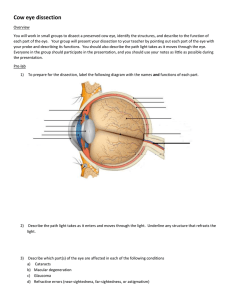
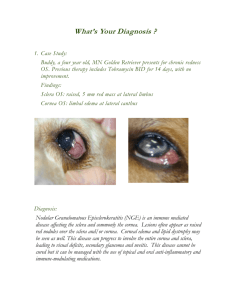
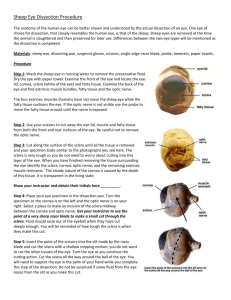
Dissection Lab Report APHY101 Athena Goulet December 11, 2012 Investigative Question How is the physiology of the sheep brain & cow eye correlated to the anatomy seen during the dissection of the two specimen? Introduction Why are the sheep brain and cow eye used to study human anatomy? These organs are similar to a human's organs and therefore we can learn a lot about human anatomy by studying the anatomy of animals, particularly other mammals. They are also easier to acquire and relatively inexpensive to acquire compared to human organs. Introduction, continued What is the significance of the investigative question? We study anatomy because understanding anatomy helps us understand physiology, or how life functions. Understanding and labeling complicated anatomical structures (anatomy) would not be useful if the purposes of those structures were unknown. Hypothesis What were your initial thoughts about the about the answer to the investigative question? I was thinking about the possible differences between a sheep eye and brain and a human's and I imagined there was a great deal of difference. I was also interested to see how much detail and how many unique structures could be discovered during the dissection. Methods What types of observations did you look at? I noticed that most of the tissue was the same color and density in the brain. The eye seemed to consist of a wide variety of tissue types, however. How were the incisions performed? Slowly, carefully, with constant pressure. I attempted to not cut any areas that might get in the way. What are some of the mini-experiments you conducted? I tested the strength of the lens by pressing on it and found it to be surprisingly strong. I am uncertain if that was from the natural structure of the lens or from the preservation process. I was also interested in distinguishing the white matter (myelinated neurons) from the gray matter (unmyelinated neurons.) I made a coronal cut in to the frontal lobe and was able to distinguish the type types very easily. Results Sheep Brain Gross Examination Results Locate the protective covering of the brain – list the meninges in order. Meninges (from outermost to innermost) ● dura mater ● arachnoid mater ● pia mater Results Locate the gyri of the brain, the sulci and the fissures – what are their differences? gyri - complex winding structures, highest ridges ● sulci - shallow grooves that separate lobes from each other ● fissures - very deep grooves such as the groove that separates the left from right hemispheres and the cerebrum from the cerebellum ● Results The blood vessels that were on the brain were very small and difficult to remove. Good effort was made to remove them from the smaller structures on the ventral side. Blood vessels are between the arachnoid layer and the pia mater – you will want to remove these vessels and the arachnoid layer if they are still present on your brain. This is done by “gross dissection” – in other words – you do not cut, you pull them away gently with the forceps. Results Locate the Brainstem which consists of the: ● ● ● Pons Medulla Cerebellum Results pituitary gland Find the Pituitary Gland if still present – if it has been removed see if you can locate its root. Results olfactory bulbs (appear to have been cut off) Examine more closely the ventral side of the brain. You should be able to see the Olfactory Bulbs – one under each lobe of the frontal cortex. Results optic nerve optic chiasm Locate and examine the Optic nerve which protrudes from the ventral side of the brain. Can you see where the nerves from the right and left eye meet in the center to form the Optic Chiasm? Results Locate now the 4 lobes of the Cerebrum: parietal occipital temporal frontal Results Sheep Brain Dissection Results Make a midsagittal cut by holding the brain level and flat – cut along the longitudinal fissure. You should be able to locate the ventricles of the brain. Results Try to locate the Lateral Ventricles, the Septum, the Third Ventricle and the Cerebral Aqueduct. lateral ventricles septum pellucidum third ventricle cerebral aquaduct Results pineal gland Try to locate the following structures: Corpus Callosum – Genu, Splenium, and the body of Corpus Callosum massa intermedia or interthalamic adhesion Hypothalamus Results cerebellum Locate the Cerebellum. Notice it resembles a tree like structure. Results Basal Ganglia Locate the Basal Ganglia: Putamen, Globus Pallidus, and Caudate Nucleus Results Unable to locate the trapezoid body and decussating fibers deep in the brain fourth ventricle Cut into the Cerebellum and the Brain stem. See if you can locate the Trapezoid Body and the Decussating Fibers – how about the fourth ventricle? It should be seen clearly now. Results Sheep Eye Gross Examination and Dissection Results cornea adipose tissue sclera optic nerve remnant of an extrinsic eye muscle Examine the external surface of the eye, noticing the thick cushion of adipose tissue. Identify the optic nerve as it leaves the eyeball, the cut remnants of the extrinsic eye muscles, the conjunctiva, the sclera, and the cornea. The normally transparent cornea is opalescent or opaque if the eye has been preserved. Results conjunctiva Examine the external surface of the eye, noticing the thick cushion of adipose tissue. Identify the optic nerve as it leaves the eyeball, the cut remnants of the extrinsic eye muscles, the conjunctiva, the sclera, and the cornea. The normally transparent cornea is opalescent or opaque if the eye has been preserved. Results Trim away most of the fat and connective tissue but leave the optic nerve intact. Holding the eye with the cornea facing downward, carefully make an incision with a sharp scalpel into the sclera, about ¼ inch above the cornea. The sclera of the preserved eyeball is very tough so you will have to apply substantial pressure to penetrate it. But work gingerly because some of the fluid may squirt out of the eyeball when the sclera is pierced. Then, using scissors, cut around the circumference of the eyeball, paralleling the corneal edge. Results choroid and tapetum lucidum cornea vitreous body posterior part anterior part Carefully lift the anterior part of the eyeball away from the posterior portion. Conditions being proper, the vitreous body should remain with the posterior part of the eyeball. Move some of the vitreous humor aside to view the pigmented choroid coat and tapetum lucidum. Results lens ciliary zonule lens anterior of cornea removing the lens iris ciliary body Examine the anterior part of the eye and identify the ciliary body, lens ciliary zonule, iris and cornea. Results vitreous humor (clear sac) retina (appears to have come off with the vitreous humor and it was attached at the optic disk to the posterior of the eye Examine the posterior portion of the eyeball. Remove the vitreous humor, and identify the retina. Discussion Was your hypothesis correct? Why or why not? The two organs were more similar to human organs than I thought so my hypothesis that the organs would be very different was incorrect. However, there were some small differences. The sheep had a differently shaped iris, but the lens was the same shape behind it. And the shape of the brain seemed more football-shaped than that of a human's with a more prominent brainstem and cerebellum. Discussion, continued What were some of the evidences you found in your autopsy that answered the investigative question? The back of the eye had an additional structure that the human eye lacks called the tapetum lucidum and it was very prominent. The cerebellum also appeared to be much larger than a human's would be. However, for the most part, I could identify many of the areas of each organ from my studies of the human body. Discussion, continued What are further questions for investigation that you still have? As I mentioned previously, the hardness of the lens interested me. The lens changes shape to focus on different visual targets, and I imagined it would be more flexible. The ventricles also seemed quite close together. Again, I wonder if this was from the preservation process, or if the ventricles are more prominent when the animal is alive. The End