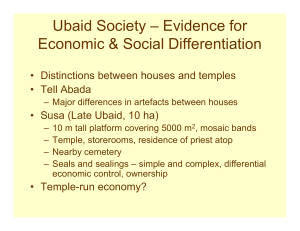
Household Archaeology and the Uruk Phenomenon
advertisement

Household Archaeology and the Uruk Phenomenon: A Case Study from Kenan Tepe, Turkey by Catherine Painter Foster B.A. (University of California, San Diego) 2001 M.A. (University of California, Berkeley) 2003 A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Near Eastern Studies in the Graduate Division of the University of California, Berkeley Committee in charge: Associate Professor Marian H. Feldman, Chair Assistant Professor Benjamin Porter Professor Rosemary Joyce Associate Professor Bradley J. Parker Spring 2009 Household Archaeology and the Uruk Phenomenon: A Case Study from Kenan Tepe, Turkey © 2009 by Catherine Painter Foster Abstract Household Archaeology and the Uruk Phenomenon: A Case Study from Kenan Tepe, Turkey by Catherine Painter Foster Doctor of Philosophy in Near Eastern Studies University of California, Berkeley Associate Professor Marian H. Feldman, Chair This dissertation examines the household–level economic and social networks at Kenan Tepe, an ancient village community in the upper Tigris region of southeast Turkey, to incorporate the study of daily lives into broader examinations of state formation in Mesopotamia during the Late Chalcolithic (3600–3000 BCE). This was a period of fundamental social change that witnessed the rise of more complex economic systems of trade and exchange on an interregional level as evident in the proliferation of similar architecture, ceramic styles, and accounting practices across the Near East. In accessing the mechanisms behind this network of interaction, generally referred to as the “Uruk Expansion” or “Uruk Phenomenon,” archaeologically the focus has remained on centralized institutions such as the administrators of temples, public buildings and storehouses that supposedly governed this overarching bureaucratic network. Notably the domestic economy, defined as the daily production and consumption activities of households, has been overlooked in favor of top–down theoretical approaches that place control of resources and labor in the hands of small elite factions or specialized trading guilds that monitored the flow of goods. 1 This dissertation instead highlights the important role that household groups play in the structuring of community and regional economies. As a microcosm of society at large, households and their daily activities are also shown to be a sensitive indicator of broader sociopolitical change. The domestic modes of production and consumption for four chronologically distinct fourth millennium households at the case study site of Kenan Tepe are identified through the analysis of domestic artifact trends and intensive microdebris sampling. These data are then interpreted within a framework of regional interaction methodology and household archaeology with a holistic focus on domestic dwellings and complex social systems at the village level. The results show shifts in domestic economies that reflect a unique combination of economic degradation, internal household decision making, and restructuring of household labor to subvert new economic demands instigated by emerging systems of exchange that fueled the Uruk Phenomenon. 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures List of Tables Acknowledgments iv ix x INTRODUCTION 1 CHAPTER 1. URUK SOCIETY: SOCIAL, CULTURAL AND ECONOMIC PERSPECTIVES 12 Uruk-Warka: Key Site of the Period and the Problem Eanna and Anu The Uruk Countryside A City Set Apart 15 16 32 35 Beyond the Uruk Heartland 37 The “Expansion” of Uruk Culture: Models and Theories Setting the Stage The Uruk World System Trading Diasporas and Entrepreneurs Political Collapse and Fragmentation 44 44 47 52 57 Conclusion 61 CHAPTER 2. HOUSEHOLD ARCHAEOLOGY AND THE URUK PHENOMENON 63 Household Archaeology in Theory and Practice Definitions and Development What is a House? Household Anthropology in Action Household Archaeology in the Near East 64 64 70 75 80 The Domestic Mode of Production and Consumption Definitions and Uses DMPC and the Uruk Phenomenon: Applications and Implications 91 91 96 Conclusion 98 i CHAPTER 3. MICRODEBRIS ANALYSIS AT KENAN TEPE 101 Microarchaeology Theoretical Foundations Practical Applications in Near Eastern Archaeology 102 102 108 The Household Archaeology Protocol at Kenan Tepe Excavation Methods and Procedures for Sample Collection Microartifact Recovery and Analysis Procedures Microartifact Preservation and Identification: Some Issues 118 119 121 134 Conclusion 137 CHAPTER 4. DOMESTIC MODES OF PRODUCTION AND CONSUMPTION AT KENAN TEPE 139 The Upper Tigris River Valley Geography and the Natural Environment Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age Settlement and Material Culture 140 140 146 Kenan Tepe: A Brief Settlement History Introduction Areas A, C, D, E and G Area F 152 152 155 160 Late Chalcolithic House Lots House Lot 1 House Lot 2 House Lot 3 House Lot 4 178 179 183 185 189 Household Level Production and Consumption Agriculture Food and Eating Stone Tools Industry Symbolism 191 191 204 237 244 256 Conclusion 260 ii CHAPTER 5. DOMESTIC ECONOMY AND REGIONAL RELATIONS 265 Stability and Change on the Household Level Thematic Elements Diachronic Shifts in the Domestic Economy Conspicuous Absence 265 265 268 275 Mechanisms for Change Sedentarization and Seasonality Economic Degradation Regional Considerations 278 279 280 283 Conclusion 293 CONCLUSION. KENAN TEPE HOUSEHOLDS AND THE URUK PHENOMENON 295 APPENDIX. LATE CHALCOLITHIC/LATE URUK SITES, SETTLEMENT HISTORIES AND MATERIAL CULTURE 302 302 Iraq Susiana/Khuzistan Luristan 313 313 319 Tabqa Dam Tishrin Dam Khabur Balikh Valley and Beyond 322 322 330 334 343 Iran Syria Turkey Birecik and Carchemish Dams Atatürk Dam Keban Dam and Beyond Upper Tigris 347 347 351 355 362 Egypt and the Levant 366 References 370 iii LIST OF FIGURES Chapter 1 1.1 Map of the ancient Near East featuring selected sites mentioned in the text (adapted from Nissen 1988, fig. 14). 13 1.2 The site of Uruk-Warka (adapted from Lenzen 1965, pl. 27). 14 1.3 The primary architecture of Eanna Levels V-IVb (adapted from Heinrich 1982, fig. 118; Lenzen 1968, pl. 27; Strommenger 1964, fig. 4). 18 The primary architecture of Eanna Level IVa (adapted from Lenzen 1968, pl. 27). 22 Beveled-rim bowl from Eanna Level IVa (adapted from Lenzen 1965, pl. 23 n). 26 1.6 Stone inlay from Eanna Levels IVa-III (from Heinrich 1936, pl. 32a). 27 1.7 Sculpture and reliefs from Eanna Level III, believed to date to Level IVa (from Strommenger 1964, pl. 18-19; Moortgat 1967, pl. 26). 27 Cylinder and stamp seal impressions from Eanna levels IV. Scale taken from original publication (adapted from Heinrich 1936, pl. 17a, 18b, 19a, c, e). 28 Tablet with archaic signs and numerical notations from Eanna level IVa (from Falkenstein 1936, pl. 27 #323). 29 The Anu ziggurat and White Temple, Levels B (in outline) through D (adapted from Heinrich 1982, fig. 83). 30 Settlement patterns in the hinterlands of Uruk-Warka and Nippur-Adad: A, Early–Middle Uruk; B, Late Uruk (from Adams 1981, figs. 12 and 13). 33 Archways from Nineveh, “Vaulted Tombs 4 and 5” (from Campbell Thompson 1932: pl. XLVIII no. 3). 39 Domestic architecture from Habuba Kabira-Süd, 1:200 (from Strommenger 1980, 38 Abb. 16). 41 1.4 1.5 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 Chapter 3 3.1 HAP sample before excavation (UTARP Digital Archive). 119 3.2 Isometric drawing of Siraf-type flotation machine (from Nesbitt 1995, 128, fig. 1). 121 Ramazan Uĝur and Yosef Uĝur operating the flotation machine (UTARP Digital Archive). 122 3.3 iv 3.4 Drying of flotation material (UTARP Digital Archive). 124 3.5 Microartifact recording sheet. 126 3.6 Examples of microceramics: A, coarse ware; B, medium ware; C, fine ware. 127 3.7 Examples of microlithic: A, chert; B, obsidian. 129 3.8 Examples of microshell. 129 3.9 Examples of microbone: A, rodent including lower jaw of subfamily Gerbillinae (far left); B, burned bone; C, fish vertebrae (left) and scale (right); D, bird; E, unidentified mammal. 131 Examples of A, microgrindstone; B, microcharcoal; C, microseed. 133 3.10 Chapter 4 4.1 Modern regions and provinces of Turkey (adapted from Dewdney 1971, fig. 41). 141 4.2 Topography of southeast Turkey (adapted from Dewdney 1971, fig. 52). 141 4.3 Kenan Tepe facing east (UTARP Digital Archive). 144 4.4 Detail of Upper Tigris region with sites mentioned in text (adapted from Algaze et al. 1991, fig. 2b). 148 Kenan Tepe facing northeast with Tigris River in foreground (UTARP Digital Archive). 153 Topographic map of Kenan Tepe (UTARP Digital Archive, prepared by Andrew Creekmore). 154 Fortification or retaining wall from Area A: A, cobblestone foundation; B, mud brick superstructure (UTARP Digital Archive). 157 Late Chalcolithic ovens from Area D: A, trench D5; B, trench D9 (UTARP Digital Archive). 158 Late Chalcolithic architecture from Area E trench 2: A, whole vessels in situ adjacent to mud brick wall; B, large wall dissecting trench (UTARP Digital Archive). 159 4.10 Top view of tandır oven from Area G trench 9 (UTARP Digital Archive). 160 4.11 Levels 6 and 7 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 3). 161 4.12 Late Chalcolithic oven from Levels 6 and 7; “House Lot 1” (UTARP Digital Archive). 162 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 v 4.13 Architecture from Level 7 in trench F1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 162 4.14 Level 5 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 3). 164 4.15 Architecture from Level 5 in trench F1: A, phase A; B, phase B (UTARP Digital Archive). 165 4.16 Packed mud pisé building in trench F9 (UTARP Digital Archive). 165 4.17 Level 4 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 2). 167 4.18 Mud brick structure from Level 4 phase B in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). 168 4.19 Mud brick constructions from Level 4 phase A in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). 168 4.20 Sunken hearth or fire pit from Level 4 phase E in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). 169 Mud brick wall from Level 4 phase D in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). 169 Brick-lined burial and pit from Level 4 phase C in trench F7: A, before excavation; B, detail of burial (UTARP Digital Archive). 170 Magazine structure from Level 4 phase B in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). 171 Structure from Level 4 phase A in trench F7, facing southwest (UTARP Digital Archive). 171 Brick-lined burial of an adult female adjacent to Phase B magazine building in Trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). 172 4.26 Level 3 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 2). 174 4.27 Mud brick structure in trench F7, Level 3 (UTARP Digital Archive). 174 4.28 Levels 1 and 2 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 1). Note: two burials from trench F6 not pictured. 175 Detail of Level 2 cobblestone surface and oven in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). 176 Tandır ovens from Area F Level 2: A, trench F2 L2002; B, trench F8 L8002 (UTARP Digital Archive). 176 Level 1 pit burials from Area F: A, trench F5 L5000/5005; B, trench F7 L7006 (UTARP Digital Archive). 177 4.21 4.22 4.23 4.24 4.25 4.29 4.30 4.31 4.32a House Lot 1, phase 1. 180 vi 4.32b House Lot 1, phases 2 and 3. 181 4.33 House Lot 2. 183 4.34 Sunken bowl feature in House Lot 2 (UTARP Digital Archive). 184 4.35 House Lot 3. 186 4.36 Large plastered pit in House Lot 3: A, before excavation; B, after excavation (UTARP Digital Archive). 186 Top view of heavily damaged structure from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive). 187 Partially preserved male individual south of Cell 1 in House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 188 4.39 House Lot 4. 190 4.40 Brick oven from House Lot 4 (UTARP Digital Archive). 190 4.41 Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 1. 197 4.42 Seed count density compared across all house lots. 199 4.43 Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 3. 203 4.44 Example of andiron from House Lot 1 (F4.4023.4225; UTARP Digital Archive). 207 4.45 Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by material type. 208 4.46 Percentage of microceramic based on count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by fabric type. 210 Percentage of microbone based on count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by species. 211 4.48 Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 2. 214 4.49 Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 2 by material type. 216 4.50 Percentage of microartifact types for House Lot 2 based on count and weight densities. 217 Fish net weight from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawing by Marie Hopwood). 220 Pierced andiron from House Lot 3 (F7.7155.7; UTARP Digital Archive). 221 4.37 4.38 4.47 4.51 4.52 4.53a Microartifact count density for House Lot 3 by material type. 222 4.53b Microartifact weight density for House Lot 3 by material type. 223 vii 4.54a Percentage of microceramic based on count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by fabric type. 225 4.54b Microceramic count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by fabric type. 226 4.55 Microartifact densities through time based on count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by type. 227 4.56 Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 4 by material type. 230 4.57 Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 4. 234 4.58 Percentage of microartifact types for House Lot 4 based on count and weight densities. 235 4.59 Weight density of microcharcoal across all house lots. 236 4.60 Pair of tripartite chert blades embedded within a compacted pebble walkway in House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 238 Percentage of microlithic based on count and weight densities across all house lots. 240 4.62 Selection of spindle whorls from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 244 4.63 Weights and diameters of whorls from House Lot 1. 246 4.64 Pierced stones from House Lot 1 as possible loom weights (UTARP Digital Archive). 247 Cylinder seal impression depicting a ground loom and weavers (from Le Breton 1957, 106 fig. 20 #20. No scale in original). 248 4.66 Bone pins or needles from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 249 4.67 Selection of shell and stone beads from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 250 Ceramic cylinder seal from House Lot 1, multiple views (UTARP Digital Archive, drawing by Marie Hopwood). 251 4.69 Bronze pin from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 252 4.70 Various small finds from House Lot 2 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Marie Hopwood). 253 4.71 Microbead from House Lot 3. 254 4.72 Various small finds from House Lot 4 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawing by Marie Hopwood). 255 Microslag from House Lot 4. 256 4.61 4.65 4.68 4.73 viii 4.74 4.75 Zoomorphic figurines from all house lots (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Marie Hopwood and Jennifer Henecke). 258 Miniature ceramic vessels from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Jennifer Henecke and Diana Backus). 260 LIST OF TABLES Chapter 1 1.1 Late fifth and early fourth millennium chronological scheme for greater Mesopotamia (adapted from Wright 2001). 16 Chapter 4 4.1 Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze calibrated carbon dates from Kenan Tepe. 155 Summary of Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age material culture at Kenan Tepe. 156 Summary of Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age architectural features in Area F at Kenan Tepe. 162 Late Chalcolithic house lots with their corresponding trenches and dates from Area F. 178 4.5 Contextual information for botanical sample data presented in table 4.6. 193 4.6 Botanical sample data across Late Chalcolithic house lots based on relative abundance. 194 Percentages of species across Late Chalcolithic Period house lots at Kenan Tepe based on NISP of identified bones. 205 4.8 Composition of chert assemblage by house lot based on absolute counts. 237 4.9 Composition of obsidian assemblage by house lot based on absolute counts. 239 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.7 ix ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This dissertation would not have been possible without the academic, financial and moral support of many people and organizations. First I wish to extend my sincerest gratitude to my advisor Marian Feldman for her guidance, support and unwavering patience throughout my graduate career. I am also especially grateful to Bradley Parker who was instrumental in giving me the opportunity to excavate at Kenan Tepe as part of the Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP) and for allowing me unrestricted access to the archaeological data. I extend my thanks to the rest of my committee, Carol Redmount, Rosemary Joyce, and Benjamin Porter, for their guidance in a number of arenas including examinations, grant proposals, writing, and the academic field in general. I offer my sincere thanks as well to Aaron Brody, Director of the Badè Museum of Biblical Archaeology, for ample laboratory space and steady employment. My experiences as Curator at the Badè have been truly wonderful. I also wish to thank Christine Hastorf who graciously read and provided comments for chapters 2 and 3. Finally, though not an official member of my dissertation committee, David Stronach has been an influential part of my graduate career. With three phone calls he single–handedly secured me a job, a position in the UTARP team and introduced me to the archaeology of Mesopotamia in general and Anatolia in particular. There are many people I wish to thank whose efforts in the field and laboratory were essential for this project. I am especially grateful to all past and present members of UTARP who excavated, photographed, drew, and washed pottery over eight seasons at Kenan Tepe. While the total list of participants is extensive, I wish to thank a few x individuals in particular for their hard work and assistance: Diana Backus, Marco Baldi, Peter Cobb, Kris Butler, Liz Clark, Lynn Dodd, Andy Creekmore, Melissa Eppihimer, Jenni Henecke, Dave Hopwood, Marie Hopwood, Mila Hover, Jason Kennedy, Bradley Parker, Ashely Sands, Sibel Torpil, Barış Uzel, and Jon Vidar. I also extend my thanks to Lynn Rainville for her guidance with microarchaeological methods and procedures early in the project. I am grateful to Rachel Marks and LaTasha Johnson who spent a year sorting microsamples through the Undergraduate Research Apprentice Program (URAP) at UC Berkeley. My deepest gratitude is reserved for the UTARP specialists whose analyses were vital to my project: Sarah W. Kansa (faunal), Elizabeth Healey (lithics), Alexia Smith (botanical), Lynn Dodd (metals and ceramics), Bradley Parker (ceramics), Andy Creekmore (mapping, ceramics), and Marie Hopwood (ground stone). Finally, this project would not have been possible without the kind permissions offered by the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism and staff of the Diyarbakır Museum, in particular Necdet Đnal, Nevin Soyukaya, and Mehmet Arif Bilici. I would also like to thank a host of individuals who, among other things, have provided me with lasting friendship, academic growth, inspiration, and comic relief: my colleague and friend Brian A. Brown, Rebecca Hisiger, Stephanie Langin-Hooper, Jean Li, Dana DePietro, Cindy Ausec, Elizabeth Minor, Roy Fisher, Sabrina Maras, Terri Tanaka, Anaita Khudonazar, Emily Chung, Sedigheh Keshavarzi, and Dan Thompson. In addition my thanks to Sharon Steadman and Jennifer Ross for opening the doors to the Anatolian Archaeology session at ASOR and allowing me to present my work. Thank you as well to John Hayes for the steady semesters of teaching and to Jan Eklund and Samantha Zhu at the UC Berkeley History of Art slide library for gainful employment xi and a quiet corner. Last but not least, a large amount of gratitude is owed to my family who has always supported my decision to pursue archaeology and have remained a constant source of love and encouragement. This is especially true of my parents, Charles and Carol Painter, and my husband Brandon for whom this dissertation is dedicated. There are several funding agencies I wish to thank who provided financial assistance for all stages of this project. My primary fieldwork at Kenan Tepe between 2004 and 2008 was made possible by generous grants from the UC Berkeley Graduate Division, the Stahl Endowment Fund for Archaeological Research, the American Research Institute in Turkey, and the American Schools of Oriental Research. This research was also funded in part by a National Endowment for the Humanities Collaborative Research Grant (#RZ-50222-04). Funding for laboratory equipment and analysis was provided by the Paul J. Alexander Memorial Fellowship and the George Franklin Dales Foundation. Because of the Dorot Foundation and UC Berkeley Center for Middle Eastern Studies, I was able to present preliminary and final results of this project at the annual meetings of the American Schools of Oriental Research and Society for American Archaeology. Finally several grants from the UC Berkeley Near Eastern Studies department made it possible for me to research and compose the majority of this study. While several comments and suggestions have been made by a number of patient reviewers to earlier drafts of this document, any errors that remain are solely my responsibility. xii INTRODUCTION This dissertation examines theoretical models for social complexity established by scholars investigating the Uruk Phenomenon—a designation that refers to the archaeologically attested distribution throughout much of the Near East of distinctive categories of material culture associated with southern Mesopotamian civilization or, more specifically, the site of Uruk–Warka during the Late Chalcolithic period (3600– 3000 BCE). These models, including World–Systems Theory (Algaze 1993), trade diasporas (Stein 1999a), and political upheaval (Johnson 1988/89), focus on the fundamental social changes this material culture represents and the various mechanisms by which it supposedly spread throughout the region via trade, colonization, occupation, or conquest. While these models support large–scale economic systems controlled by a bureaucratic elite both in the core state of Uruk–Warka and its hinterland (a macroregional approach), little has been done to explore the ways in which local exchange networks functioned during this time (a microregional approach) or how this larger Uruk Phenomenon affected the fundamental units of society: households. By applying the theoretical approach of household archaeology and the methodological framework of microarchaeology, I provide an alternative view to the traditional conceptions of the Uruk Phenomenon by charting the complex economic and social relationships that exist between households and regional/interregional economies. My goal is to highlight the various levels at which different societies simultaneously interact, paying close attention to changes in the domestic economy at the case study site of Kenan 1 Tepe, located in the upper Tigris River valley of southeast Turkey, as an indicator for large sociopolitical shifts occurring throughout Mesopotamia during this time. As stated previously, the Uruk Phenomenon is characterized by the distribution of a distinctive material culture assemblage. This includes architectural styles, ceramics, accounting practices, artistic conventions, and the earliest writing and pre–literary forms like bullae, impressed clay balls, and tokens. These categories appear together as a complete assemblage, or separately at a number of ancient sites stretching from the southern alluvial plains of Iraq, east to Susiana and the Iranian plateau, northwest to the semi–arid desert and steppe lands of northern Iraq and eastern Syria, and further north into the Euphrates and Tigris River valleys of southeastern Turkey. The degree or amount to which this distinctive cultural assemblage is present at sites has characterized for various scholars the amount of cultural interaction present between these peripheral polities and the southern alluvial urban centers, the largest being Uruk–Warka. Distinguished by a stratified government, multifaceted economy, urbanization, and an interregional trading network, fourth millennium BCE Uruk–Warka (discussed in detail in chapter 1) has occupied a pivotal position for scholars interested in the emergence of complex societies both in the Middle East and around the world.1 Yet the exact nature of this early state—how the political and economic administration was organized, the role of religion in government, and the degree of foreign relations with neighboring communities—continues to be highly debated. For example, any discussion regarding the Uruk Phenomenon is often centered on elucidating the exact nature or, 1 For example, Andean scholar Terence D’Altroy (2001, 445; original emphasis) has stated that, “because of the precocious sociopolitical and economic formations of Greater Mesopotamia and the ingenuity of the scholars who have worked to explain them, Uruk has stood as the model for the rise of state society for several decades.” 2 more specifically, degree of interregional interaction, how these cultural and social trends developed, for what reasons these interactions took place and the causes for their apparent downfall in the early part of the third millennium BCE.2 The central theory explaining the motivations for this interaction focuses on the dichotomy in the distribution of natural resources between the core of southern Iraq and its neighboring territories, whereby the establishment of colonial enterprises in these periphery regions was crucial to the procurement of resources such as wood, stone, and metals (see chapter 1 and Algaze 1993). This model favors a passive periphery whose sociopolitical and cultural development derived not from indigenous factors, but through contact via cross–cultural interaction with a more advanced Uruk system. The terms core and periphery themselves imply a certain level of Uruk–centrism when applied to analyses of late fourth millennium BCE cultural interactions. However research in these outlying regions, specifically southeast Turkey and the Tigris and Euphrates River basins, has uncovered a tapestry of advanced social networks that both interacted with, and were independent of, interregional trading systems penetrating from the south. For example, work at Hacınebi on the Euphrates River suggests distinct groupings of households based on material culture assemblages that attest to a dynamic system of interaction with possible foreign traders along with a fairly complex economic system that predates contact by an Uruk network (see chapter 1 and Stein 1999a, 1999b, 2002a, 2002b; Stein et al. 1996a). Another example is the site of Arslantepe, a five hectare mound roughly fifteen kilometers outside the modern city of 2 Since arguments abound as to what exactly this distribution of material culture or ideas is to be called— Uruk Phenomenon (Collins 2000), Uruk Expansion (Algaze 1989a; Emberling 2002; Steadman 1996; Stein 2002b) or “informal empire” (Algaze 1986a, 1993)—in this dissertation I retain the most recent and widely used designation of Uruk Phenomenon that carries less undertones and implications of meaning than “expansion” or “empire” (see also Postgate 2002; Rothman 2001). 3 Malatya, where monumental local style architecture, mass produced bowls, and a developed economic system reflects a fairly well developed indigenous system of accounting, centralized production, and large building projects (see chapter 1 and Frangipane 1997a, 1997b). More recently, a large urban center has been uncovered at Hamoukar on the upper Khabur River along with hundreds of stamp and cylinder seals displaying north Syrian artistic styles, industrial–sized ovens, and most remarkable, evidence for early warfare that brought about the demise of the Late Chalcolithic settlement there (see appendix and Gibson et al. 2002a). Many more examples are discussed in greater detail in chapter 1. Despite this new and exciting research, the traditional picture of cultural development and exchange during the late fourth millennium BCE remains unbalanced in three ways. First, the majority of surveys and excavations in southeast Turkey focus on the upper Euphrates River valley and Urfa Plain. This geographic imbalance is partly due to the scheduling of dam projects that threaten archaeological sites in these areas. For example, many of the archaeological and historical sites in the Euphrates River valley are already flooded by the Birecik, Atatürk, and Keban dams, thus necessitating initial research in these areas (see appendix). However the upper Tigris system of southeast Turkey remains archaeologically unknown for the Late Chalcolithic period. Because of this, data from the Euphrates valley sites have been used as a type set for the material cultural of the entire region. This is a dangerous assumption as the community organization and economy of the Tigris River valley may have been uniquely different from surrounding areas due to environmental factors or differential access to natural resources. Without comparative examinations from both riverine systems, an inherent 4 bias exists that skews interpretations of ancient trade routes (Algaze et al. 1994), regional ceramic styles, even the role of villages and rural populations in the rise of social complexity (Bermann 1994; Schwartz and Falconer 1994). Second, in attempting to elucidate the nature and degree of cross–cultural interaction during this time, scholars studying the Uruk Phenomenon have rarely discussed in detail ancient settlements that, throughout their history of occupation, did not share any characteristics with southern Mesopotamia—that is, show no evidence for colonization, trade, exchange, or interaction visible in the archaeological record (for exceptions, see Rothman 2004; Steadman 1996). Though these indigenous settlements may appear outside the Uruk system or sphere of influence, they serve as key elements for understanding the function of this trade system by highlighting the multifaceted nature of interaction between communities of various sizes and levels of complexity throughout the Near East. Third, in most investigations concerning the Uruk Phenomenon, the primary focus has been the elite, understanding the overarching processes of state formation, and elucidating interregional economic systems that seem deterministic at best and hegemonic at worst. This focus overshadows the actions and participation by nonelite individuals within local community networks in shaping these larger processes. As Reinhard Bernbeck and Susan Pollock (2002, 178) note, “almost all narratives about the fourth millennium are concerned with large scale institutions and whole social groups and classes…viewing them from a functional perspective—of people who are at the apex of a political, religious or other hierarchy.” This imbalance has also been identified by other scholars who have called for more multivocal analyses from both bottom–up and top– 5 down perspectives (Rothman 2004, 106; Stein 2002a). This would include recognizing individuals, human agency, and most importantly, the diverse network of economic, social, and political relationships that exist within any one community. In order to combat these shortcomings in the current scholarship of the Uruk Phenomenon, this dissertation examines a smaller–scale indigenous settlement in Upper Mesopotamia: Kenan Tepe. This site was chosen as the primary case study for a number of reasons. First, although the area has been thoroughly surveyed (Algaze 1989b; Algaze et al. 1991, 1994; Ay 2001), Kenan Tepe is the first Late Chalcolithic settlement to be systematically excavated in the upper Tigris River valley of southeast Turkey. Second, the material culture assemblage excavated at Kenan Tepe reflects a strong affiliation with local southeast Anatolia with little intrusive elements. This is interesting since, based on the generally accepted model of resource procurement and colonization (chapter 1 and Algaze 1989a, 1993, 2001b), Kenan Tepe should have occupied a prime niche within the sphere of southern Mesopotamian contact. The site lies in an important resource zone; not far from the vast copper mines at Ergani Madden, in an area that was heavily forested in antiquity and contained sources of semiprecious stones. Likewise the site lies on a major thoroughfare for transportation and communication, the Tigris River, making it easily accessible to foreign and local traders alike. Kenan Tepe could be one example of how trade for natural resources, as is most often suggested (Algaze 1993; Kohl 1987; Weiss and Young 1975) was not the only reason for contact. Third, Kenan Tepe is also ideal for conducting a nonelite examination of the daily activities carried out by households of the Late Chalcolithic through the application of microarchaeological techniques. The striking preservation of several multiphase, superimposed architectural units (“houses”) as well as 6 open courtyard areas, animal pens or barns, allow for analysis of long term use of space and household–level economic development. The theoretical foundation for this research is drawn from the anthropology of the house or domestic sphere, whose characteristics have been adopted by archaeologists and applied to ancient contexts in the form of household archaeology (chapter 2). This specialized form of spatial analysis provides archaeologists with a way to study past peoples whose activities and behaviors have left behind residues in the form of material artifacts, such as charred bone from a feast or pieces of obsidian discarded during tool making (Allison 1999; Kent 1984; Wilk and Ashmore 1988; Wilk and Rathje 1982). Yet material culture has a richer function than simply a passive reflection of human behavior (Tringham 1991, 1995). Houses and public areas serve as spaces in which social relationships and identities are defined, created and negotiated. Furthermore household relationships and actions are not isolated from the rest of society, nor do they merely react passively to changes imposed from outside (Hendon 1996, 47). My research considers the active role that households play in shaping social relationships, both internally within local Late Chalcolithic communities in southeast Anatolia, and externally with regional neighbors. This dissertation is further theoretically informed by the seminal work of Richard Wilk and William Rathje (1982, 618) who emphasize that households are the level in which adaptation can be directly studied because, as social groups, households articulate directly with economic and ecological processes. My research project builds on this notion by analyzing Late Chalcolithic households along with the more visible administrative and religious evidence (“elite” contexts) that typically constitute the major 7 body of evidence in studies on the Uruk Phenomenon. I assert that only when microlevel approaches that incorporate evidence from households are taken into consideration, can cultural processes occurring during this crucial phase of social and economic development be fully understood. Methodologically I use an integrated approach that draws from artifact patterning and macroartifacts analyzed within a household archaeological framework. I also build upon the work of Wendy Matthews (1995a, 2001b, 2005), Arlene Rosen (1989) and Lynn Rainville (2005)—three pioneers in the scientific application of microdebris analysis and micromorphology to ancient Near Eastern sites (chapter 3). These techniques are based on the recovery of microartifacts, minute pieces of bone, stone, ceramics and shell that represent primary refuse from past activities like cooking or tool making. Because of their size, microartifacts are less affected by the cultural and natural formation processes that alter archaeological deposits such as cleaning, artifact removal during abandonment, and erosion. Microarchaeological research in general is still relatively underutilized and has never before been applied to examinations of the Uruk Phenomenon. For example, though an unprecedented amount of domestic buildings were uncovered at the famous Late Chalcolithic/Late Uruk period site of Habuba Kabira-Süd in Syria (chapter 1; Kohlmeyer 1996; Strommenger 1980), discussions of houses and households were limited to purely architectural descriptions and final use patterns for spaces based on visible archaeological evidence or macroartifacts found within rooms. To summarize, this dissertation is motivated by three concerns. First, to provide a counterpoint to traditional studies of the Uruk Phenomenon that focus on evidence derived from the Euphrates and lower Tigris River basins, leaving the upper Tigris a 8 veritable terra incognita for Late Chalcolithic period research. My first goal therefore is to allow for comparative examinations of material culture between the Euphrates and Tigris River valleys. Second, it is my intention to investigate the development of an indigenous community in a resource–rich zone that, based on archaeological evidence, did not fall within the Uruk system of colonization or trade. Kenan Tepe as a case study will emphasize the vital role that villages and other small–scale settlements played in the development of social complexity in Upper Mesopotamia. Third, I wish to complement data derived from elite contexts that are cited as evidence for expansion, colonization, and trade with data on household–level social relations. This dissertation highlights small scale institutions—households—to underscore the variety of social and economic networks operating within any population. I will show that understanding domestic economies and localized networks is imperative to adequately interpret large–scale developments, such as state formation, which are often shaped by community–based cultural norms. To introduce this research, in chapter 1 I first explore the primary evidence from which all discussions of the Uruk Phenomenon derive, the site of Uruk–Warka itself, to highlight the severe limitations in terms of scope and detail inherent in this particular dataset for discussing interregional trade and interaction. I then discuss the archaeological evidence beyond the Uruk heartland and critique the various theories and archaeological data surrounding issues of the Uruk Phenomenon.3 Within this discussion I highlight the collective shortcomings of these approaches, namely the reinforcement of top–down views of social, political and economic histories and developments, the exclusion of 3 While the archaeological data is discussed only in brief and for a small selection of ancient sites, a full accounting of the settlement histories and material culture are presented in the appendix. 9 evidence from sites outside the Uruk sphere of influence/interaction, and the neglect of multiscalar approaches that draw from villages, households and individuals, not just the core and subsidiary settlements. In chapter 2 I discuss the methodological foundation for my research beginning with the overarching framework of household archaeology. This includes its conceptual and methodological development as a subfield, definitions of house and household, the history of household–based research in Near Eastern archaeology, and the relationship between household economies and regional interaction spheres. I then define and discuss the development of microarchaeological techniques, their theoretical foundations and practical applications in chapter 3. I conclude this chapter by outlining the procedures used to conduct a microarchaeological examination of households at Kenan Tepe including excavation methods, sampling, and microartifact recovery, identification and analysis. In chapter 4 I present general background on the site of Kenan Tepe: its environmental context, occupational history, and general settlement patterns and material culture for Late Chalcolithic sites in the upper Tigris River valley. I then discuss the architectural data of four chronologically distinct Late Chalcolithic house lots. Next I chart the domestic mode of production and consumption—the domestic economy—in terms of types of activities and degree to which they were practiced in these spaces. This economy is generated from multiple activities including agriculture, food preparation and eating, chipped stone technologies, cottage industry and symbolic systems. In chapter 5 I interpret this unsynthesized evidence within a collective framework designed to incorporate all aspects of the archaeological remains found within the 10 household contexts at Kenan Tepe. I primarily rely on a diachronic approach that evaluates core elements and significant shifts in the domestic modes of production and consumption between the four household groups. The mechanisms behind these changes in the domestic economy will be considered within the scope of indigenous conditions and circumstances and also within a wider system of socioeconomic trends by comparing archaeological data retrieved from Kenan Tepe with neighboring sites. The results show that the domestic economy of these household groups experienced economic degradation and production restructuring, specifically in terms of diet and animal husbandry, to circumvent the centralization of resources—a hallmark of state/Uruk economy—that occurred at the end of the fourth millennium at Kenan, likely instigated by local elites. 11 CHAPTER 1. URUK SOCIETY: SOCIAL, CULTURAL AND ECONOMIC PERSPECTIVES Uruk Mesopotamia has been a topic of study in the archaeological community for over one hundred years since the Deutsche Orient–Gesellschaft first broke ground at ancient Warka at the beginning of the twentieth century. Since then Uruk–Warka, 1 located three hundred kilometers south of Baghdad in the alluvial lowlands of southern Mesopotamia (figures 1.1, 1.2), has remained the focus of scholarly attention due in part to its links with the development of key attributes that, to both modern and ancient minds,2 are the building blocks for civilization. These include, among other things, urbanism and cities, the first writing, advanced economic systems, huge agricultural yields, and specialized crafts. Due to these preconceived notions and the fact that it was one of the earliest sites to be excavated in the Near East,3 Uruk–Warka has remained the touchstone for understanding Mesopotamia in the fourth millennium BCE, reinforced by both the naming of an entire archaeological phase after the site (“Uruk Period”) and 1 The modern name for Uruk is Warka and you will often see, as in this dissertation, the ancient city referred to as Uruk–Warka. This is done for several reasons, the most important of which is to distinguish the ancient city/site from that of the archaeological period by the same name (Uruk Period) and references to the general culture and people “of Uruk.” 2 The Standard Version of the Epic of Gilgamesh (George 1999) features Uruk–Warka as the center of civilized life. The city measured “[three square miles] and a half” ( Tablet I, I23), was surrounded by a baked brick wall with a “parapet that none could copy” (Tablet I, I14) and was the location “where [men] are engaged in labors of skill” (Tablet II, P63). 3 Uruk–Warka has enjoyed a lengthy period of excavations stretching for over one hundred fifty years since 1849 when the Englishman William K. Loftus first began work at the site (Loftus 1857). In 1912 the directorship was handed over to Julius Jordan by Robert Koldewey, then director of the excavations at Babylon, on behalf of the Deutsche Orient–Gesellschaft. This would signal the beginning of a long term interest and commitment by the Deutsche Orient–Gesellschaft (later renamed the Deutsche Archäologische Institut) at Uruk–Warka and expand on their already flourishing excavation and financing activities at Hattuşa, Tell el–Amarna, Jericho, Babylon and Aššur (Jordan 1913, 1914). Excavations by Jordan and his colleagues after World War I (1928–1939) and Heinrich J. Lenzen (1953–1967) and H.J. Schmidt (1967– 1977) after World War II are the most relevant campaigns for this discussion, though not the latest, as the archaeological discoveries from these years were foundational in establishing Uruk–Warka as the premier site of ancient cultural development. 12 especially as material culture related to Uruk–Warka was uncovered in sites throughout the region during the last fifty years. Figure 1.1. Map of the ancient Near East featuring selected sites mentioned in the text (adapted from Nissen 1988, fig. 14). 13 Figure 1.2. The site of Uruk-Warka (adapted from Lenzen 1965, pl. 27). As briefly described in the introductory chapter to this dissertation, that material evidence—in the form of architectural styles, ceramic assemblages, economic and administrative paraphernalia, and iconography—coupled with theoretical foundations for interregional interactions, social hybridization, and cultural dominance have formed the foundations by which scholars currently conceive of society in late fourth millennium Mesopotamia in general, and Uruk society in particular. My goals for this chapter are to 14 present in more detail how exactly these data are used to formulate the sociocultural character of Uruk Mesopotamia, an exercise that will reveal certain avenues of approach to this subject that remain untested in the current scholarly literature. In this chapter I argue that studies involving the Uruk Phenomenon have not addressed the issue from multiscalar view points. As I will show below, the primary evidence from Uruk–Warka itself and many sites in the periphery are limited both in excavated area and overall scope such that the domestic modes of production and consumption have received little attention. The inclusion of household archaeological approaches can help fill this gap by bringing into focus sociopolitical and economic systems of the nonelite. Uruk–Warka: Key Site of the Period and the Problem My title for this section has been purposefully drawn from Hans Nissen (2002) to underscore a major point: Uruk–Warka stands as both a key site for the development of state–level societies during the late fourth millennium and poses a serious problem for truly understanding that radical development in human history. I contend that is because three major issues surround the excavation and interpretation of the material from Uruk– Warka: 1) only centralized elite contexts have been analyzed, 2) survey data has been used to support the supremacy of Uruk–Warka within the southern alluvium and by extension the larger region and 3) at the time of initial excavations in the early twentieth century the material culture of Uruk–Warka was considered unique. These underlying problems have skewed in many ways the identification of an Uruk Phenomenon and to a larger extent the models by which scholars seek to understand it. 15 Eanna and Anu Perhaps the greatest gift for, and likewise detriment to, understanding Uruk society is the fact that the primary evidence from Uruk–Warka derives from only a relatively small portion of the overall large site (250 hectares by the LC 5 period; table 1.1).4 This portion is what may be considered a primarily elite context, 5 and the nature of its deposition creates problems for interpreting function and meaning. SAR Phase Name Chronological Date LC 1 Terminal ‘Ubaid ca. 4300—4150 BCE LC 2 Early Uruk ca. 4150—3800 BCE LC 3 Middle Uruk ca. 3800—3500 BCE LC 4 Middle Uruk ca. 3500—3350 BCE LC 5 Late Uruk ca. 3350—3100 BCE Table 1.1. Late fifth and early fourth millennium chronological scheme for greater Mesopotamia (adapted from Wright 2001). 4 For the fourth millennium BCE, the academic literature presents a host of chronological schemes and labels that include the traditional southern Mesopotamia Uruk Period (Porada 1965), protoliterate period (Delougaz and Lloyd 1942), the Amuq sequence phases A through J (Braidwood and Braidwood 1960), Chalcolithic sequence (Vértesalji 1987), a northern Mesopotamia chronology (Gut 1995), Late Chalcolithic I and II (Rova 1999–2000), Northern Uruk chronology (D. Oates and J. Oates 1994), the School of American Research (SAR) LC 1–5 (Rothman 2001), and standard calibrated dates. In this dissertation I retain the use of SAR’s chronological framework LC 1–5 whose dates derive from the most recent 14C dates from various sites throughout Mesopotamia. Thus they are not solely contingent upon Uruk–Warka and the south, nor purely a northern chronological system (see table 1.1). 5 However the most recent work at Uruk–Warka involving aerial photography, geophysical survey, and geomorphologic analysis of drill cores (Boehmer 1991; Becker and Fassbinder 2001; Fassbinder et al. 2003) is allowing scholars to answer long–standing questions about the city of Uruk, not just the religious/administrative center found at the Eanna precinct and Anu Ziggurat area (discussed in the following pages). The evidence current researchers are finding is exciting and includes residential city planning, traffic routes along streets, and water channel systems. With the onset of the Second Gulf War in 2003 however, the progress of work at the site remains speculative and seriously dependent on the future political situation in Iraq. 16 Levels dating to the fourth and early third millennium BCE were excavated in two main areas located in the center of the site: the so–called Eanna6 precinct dedicated to the goddess Inanna, and the area of the Anu Ziggurat dedicated to the sky god. These two areas were most likely separate mounds in antiquity but joined together by the end of the fourth millennium to create what was then the heart of the Uruk–Warka urban landscape. The architecture uncovered in the Eanna precinct covers an area of 80 by 50 meters with the most relevant occupational levels being Level V (ca. 3600 BCE; LC 3), IVb (3500– 3200 BCE; LC 4)7 and IVa (ca. 3200–3000 BCE; LC 5). Eanna Level V begins the late fourth millennium sequence, built atop at least twelve earlier levels of ‘Ubaid period constructions. This level, as with subsequent ones, is characterized by monumental architecture that most likely represents public buildings as opposed to private dwellings although this fact is debated. For example, while many of the buildings uncovered in Eanna were named by the excavators as temples, there is little contextual information to support this claim. The largest of these Level V buildings was the so–called Limestone Temple (Kalksteintempel) that measured 76 by 30 meters and was constructed of large whitish gray limestone slabs 10 centimeters thick on a mud brick foundation (figure 1.3; Lenzen 1974a, 112). Limestone is not local to Uruk–Warka or its environs, in which case it had to be imported from outcroppings that lay approximately 70 kilometers away. This building was of the Mittelsaal–type, so called by the excavators because it featured a tripartite floor plan consisting of a long central hall flanked on either side by a series of 6 In Sumerian, meaning “House of Heaven.” Based on wood samples from Temple C (Level IVb; discussed in the following pages) that provided a calibrated date of 3545–3295 BCE based on a 14C half–life of 5,730. See Adams 1981, 348 note 2 for this correction of the originally published date of 2815 ± 85 BCE (Lenzen 1965, 20). 7 17 Figure 1.3. The primary architecture of Eanna Levels V-IVb (adapted from Heinrich 1982, fig. 118; Lenzen 1968, pl. 27; Strommenger 1964, fig. 4). four smaller rooms. These rooms were accessible from the exterior as well as the interior and it was through these series of lateral doorways that one entered the structure. In two of these rooms there was evidence for staircases. An additional set of three rooms was located at the far southwest end of the building that lay at a perpendicular (right) angle to the rest of the structure. These rooms were only accessible through the long central space. The limestone superstructure was corrugated with niches and buttressing on both the interior and exterior of the building—a decorative feature that will come to symbolize Mesopotamian architecture. 18 A second monumental building lay at the far western end of the precinct. Called the Stone Cone Temple (Steinstifttempel),8 this building also spans Eanna Levels V through IVb (figure 1.3).9 The 28 by 19 meter building stood within a specially built court with a limestone enclosure wall that was recessed with deep niches. This building also carried a tripartite plan with a long central hall or courtyard with a fireplace flanked by subsidiary rooms and topped on the northeast by a narrow perpendicular room. The structure was composed of a limestone block foundation sealed with bitumen that supported a molded brick superstructure made of mud and crushed gypsum plaster. Stuck into this brickwork were elaborate mosaics composed of brightly colored cones made of slate blue, pink and white stones.10 Excavations in 1989 of a 50–meter–long trench stratigraphically link the Steinstifttempel with a nearby square feature—the Great Court (Grosser Hof)—whose edges were also sealed with bitumen (Boehmer 1991, 468).11 These two large buildings were accompanied in Level IVb by two smaller temples (A and B) and a poorly preserved corridor of a building (the Red Temple) constructed atop the remains of the Kalksteintempel that yielded a wealth of inscribed clay tablets that will be discussed below.12 The most extensive architectural feature for Level IVb was a large building complex located southwest of the Red Temple. Called by various names in 8 Also called the Stone Cone Mosaic Temple by Roaf (1989, 61) and Stone Mosaic Temple by Nissen (1988, 97). 9 I have found great confusion in the literature as to which level this building belongs. Collins (2000, 34) discusses the Steinstifttempel in the context of Level V but does not note that it continues into later levels. Both Roaf (1989, 61) and Nissen (1988, 98) place it with Level IVb and IVa respectively. Based on the architectural drawings and discussion by Lenzen (1950, 1974a, 112) and others (UVB XV, 8 if., taf. 36, 37), the Steinstifttempel is shown to have foundations within Level V that continued into Level IVb, but not beyond, as suggested by the construction of the so–called Riemchengebäude on top of it (discussed later this chapter). 10 Bitumen–colored (black) limestone, red sandstone and white limestone and alabaster respectively (Lenzen 1974a, 115). 11 This use of bitumen to render the building foundations watertight have led to the interpretation of the “Stone Cone Temple” as the seat of an early water cult (Boehmer 1990, 1991). 12 The Red Temple and Temple A are not depicted in figure 1.3. 19 the literature,13 the Cone Mosaic Building (Stiftmosaikgebaude) and/or Round Pillar Hall (Rundpfeilerhalle) consisted of a raised terrace with two rows of columns bordering a rectangular sunken court (figure 1.3 and Nöldeke 1932, 12, pl. 8; Lenzen 1974a, 116). These features were built of small square–sectioned, sun–dried mud bricks, called Riemchen bricks by the excavators, which were characteristic of Uruk period southern Mesopotamia and used in the majority of building constructions during this period.14 The bricks were thickly coated with mud plaster into which small baked clay cones, whose heads were painted in black, red and white, were positioned and arranged into intricate diamond, zigzag and triangular patterns. The final building of note for Level IVb is a huge square construction, called variously Temple E or Palace E (Lenzen 1974a; “Empfangspalastes”) that measured 30 meters square in size and was made of mud brick on a limestone foundation (figure 1.3).15 The floor plan was unique with a central courtyard (20 meters square) surrounded by pillared porticos that led to sets of three small rooms, each of which opened to the outside (Lenzen 1974a, 121 pl. XVI; 1974b pl. 31). The pillars, doorways and exterior façade were all richly decorated with niche and recessed designs reminiscent of other Eanna constructions like the Kalksteintempel and enclosure wall of the Steinstifttempel, though for the square building it is niched brickwork and not stone. 13 Called the Mosaic Court or, confusingly, the Pillar Temple by Roaf (1989, 61) and incorrectly the Steinmosaikgebäude (“Stone Mosaic Building”) by Leick (1988, 234) despite the fact that the cones used in the decorations here are made of clay and not stone. She is perhaps confusing this building complex with either the Steinstifttempel (“Stone Cone Temple”) of Levels V/IVb or the Pfeilerhalle (“Pillared Hall)” of Level IVa. 14 Except of course for the stone buildings discussed above for Levels V–IVb. Riemchen bricks are highly distinct of the period, much like the “plano–convex” bricks used in constructions of the Early Dynastic period in Mesopotamia (see Delougaz 1933). 15 This building has also been called simply “Square Building” in Roaf (1989, 63). 20 At the conclusion of Eanna Level IVb there was a radical architectural shift within the precinct. A wall was built that partially enclosed the area with access through a gateway in the southeast. While two buildings continued into at least the beginning of the following Level IVa (“Palace E” and the Steinstifttempel),16 the Stiftmosaikgebaude and precinct, including the mosaic courtyard, and Temples A and B were systematically filled in and leveled to created a huge platform on which two new buildings were erected for Level IVa. The most complete of these was Temple C with a distinctive cruciform floor plan composed of two parts (figure 1.4). The first was a central hall (Rumpfbau) with three fireplaces: two round and one panhandle in shape.17 This hall was flanked by two series of small rooms with doorways on either side allowing access from the outside into the inner hall. The second part was an upper hall (Kopfbau) set on a perpendicular axis from the central hall.18 The Kopfblau was also flanked by subsidiary rooms, one of which was designated as the long, narrow cella. Some niching decorated the brickwork inside this structure, but none was visible on the exterior. This is in contrast to a larger neighboring building, designated as Temple D, that featured elaborate niching and buttressing to its exterior (figure 1.4). This building, although only partially preserved, likely measured 80 by 52 meters and lay at an angle perpendicular to Temple C, encompassing the platform on which the Stiftmosaikgebaude and courtyard once stood for Level IVb and the east corner of Palace E. The excavators reconstructed Temple D 16 The stratigraphic relationship of these buildings to the rest of the complex is quite perplexing, due in part to the early excavation styles and the confusing nature of building and re–building of monumental architectural works over centuries in the same location. Suffice to say, it appears that Palace E and the Steinstifttempel appear at the beginning of Level IVa and are later cut into (and hence, go out of use) by later Temple D and the Riemchengebäude respectively (see Lenzen 1974a,1974b). The most visual example of this comes from UVB vol. XXV pl. 31 where Palace E is labeled as “Uruk IVb – IVa.” 17 UVB XXI, 16 f., pl. 31, 32. 18 It is possible that these halls were actually two stand–alone units (Lenzen 1974a, 123). 21 also with a cruciform floor plan, though the surrounding rooms were only accessible from the central hall. Figure 1.4. The primary architecture of Eanna Level IVa (adapted from Lenzen 1968, pl. 27). Northwest of Temples C and D lay two more monumental constructions collectively called the Pillar Hall and Hall Building (Pfeilerhalle und Hallenbau). The smaller Pfeilerhalle was more like an open porch with four cornerstones and eight pillars: three on the each long side and two on each short side (figure 1.4).19 The pillars were decorated with clay cone mosaics of black and red arranged in triangular, diamond, 19 UVB XXI, 19, pl. 31, 32. 22 zigzag, checkerboard, and hourglass patterns. Constructed slightly later on the north side was a larger pillared hall 40 meters long and 18 meters wide.20 The middle corridor of this building was lined by two rows of thick pillars with deep niches cut into them on the exterior side. Between these pillars were 1 meter wide corridors that allowed access from the outside into the middle hall. Southwest of the Pfeilerhalle was the Great Court (Grosser Hof), a nearly square installation whose function remains enigmatic. As with the Steinstifttempel discussed above, the Grosser Hof has been linked to some kind of structure that utilized water, such as a pool or garden, based on the presence of a preserved water pipe and baked mud brick lining set in bitumen around the edge of the square that ensured a watertight seal (Matthews and Wilkinson 1991, 182). In the far northwest corner of the precinct lay a final building called the Riemchengebäude based on its construction with the ubiquitous square–sectioned Riemchen brick. This rectangular building (18 by 20 meters) was dug into the remains of the Steinstifttempel, using the limestone blocks as a foundation. The nested floor plan consisted of a central room surrounded on all sides by a narrow corridor and bordered on the south by an additional long, narrow hall. Evidence for wall murals were uncovered (Nunn 1985) along with a huge amount of objects (discussed below) that had been packed inside and burned. The entire structure was then re–plastered and sealed. At the close of Level IVa, the entire Eanna precinct was once again filled in and leveled to make way for Level III constructions of the Jemdat Nasr period, though remains of these buildings and a large terrace are fragmentary. Debate continues as to the validity of the excavators’ initial designation of these monumental buildings as temples. No in situ artifact remains were found inside any of 20 UVB XXIV, pl. 27, 29. 23 these buildings, save for the Riemchengebäude, that can offer evidence to their function or use. With each succeeding phase of architecture within the Eanna precinct, the buildings were leveled and filled in with rubbish and other debris (derived from these buildings? from elsewhere?) in order to create a platform on which more constructions could be built (Nissen 1988, 2002). Thus any material objects discovered within these rubbish heaps are not stratigraphically connected to the building within or on top of which it was found. Seen in this light, the function of these monumental structures will perhaps never be known for sure. However their size and the labor involved in their construction belay their probable public function. The tripartite plan so common throughout these buildings and others more securely labeled as temples,21 hint at a religious connection despite the fact that no altars or obvious platforms were found inside any of the Eanna buildings. One is also reminded that domestic structures, like those at Habuba Kabira–Süd (discussed this chapter), can carry a similar tripartite arrangement complete with central fireplaces. It is also most likely that our modern categories of temple, palace and house as separate entities do not apply to the ancient Near East where there is often a blurring of religious, political and domestic spheres. As noted above, no in situ remains were discovered within the archaic level buildings leaving us only able to speak in generalities of the material culture sequence of late fourth millennium Uruk–Warka. These materials, most importantly ceramics and accounting and glyptic assemblages, have served as the primary basis of comparison for cultural assemblages outside of the Uruk–Warka heartland in terms of contact and 21 Such as the Eridu temple sequence (Safar et al. 1981) or the White Temple atop the Anu ziggurat at Uruk–Warka dated to the Jemdat Nasr period (discussed this chapter and also Heinrich 1937). 24 interaction. Yet these objects also derive from very specific elite contexts, leaving one to wonder if the same materials, ceramic forms in particular, are being used in the lower, nonelite sectors of the city? In brief, the ceramic assemblage is characterized by a combination of handmade and wheelmade vessels. When compared with earlier levels, there is a noted decline in the production or use of plain handmade pottery beginning in Level V and continuing throughout Level IV. Ceramic types range from plain–simple to red and grey wares with a number of distinctive shapes. These include spouted jars (UVB IV, 44 pl. 19Cc), bottles with slender bodies and bent spouts (“water bottles;” UVB IV pl. 19Da), four–lugged jars in which the lugs are pierced (UVB IV pl. 19Dn, o), and conical cups with string–cut bases. Decorative techniques include burnishing, incising with crosshatch or fingernail designs (UVB IV pl. 19Dw), and slips of red or cream. Reserved slip is also common, a result of either wiping the slip away or wet burnishing during production. Perhaps the most iconic of the Uruk–Warka assemblage however is the beveled– rim bowl (Glockentöpfe), a mass–produced vessel with a sloping rim made from highly coarse, often porous materials inside a mold of relatively standard size (figure 1.5; UVB IV, 43).22 The function of this vessel is highly debated in the literature with theories ranging from their use as ration containers (Nissen 1970) to holders of votive offerings (Beale 1978; Campbell Thompson and Mallowan 1933), bread molds (Millard 1988), food containers (Forrest 1987), or used in salt production (Buccellati 1990). The reasons for such keen interest in this relatively inferior ceramic type are the overwhelming 22 This standardization has been challenged by Beale (1978) who says the capacity of the bowls varies too widely both within the assemblage at Uruk–Warka and between other sites in which they are found to have been a standardized unit of measurement. 25 abundance of beveled–rim bowls at sites across the greater Mesopotamian region23 and thus, what they symbolize in terms of cultural interaction. Figure 1.5. Beveled-rim bowl from Eanna Level IVa (adapted from Lenzen 1965, pl. 23 n). Documentation by Heinrich (1936) of the small finds from Levels V–IVa in the Eanna precinct highlight a rich assemblage of arts and crafts. Several glazed relief tile fragments used to decorate furniture or walls, jewelry made of semiprecious stones, and gold leaf attest to the level of sophistication in craft production and consumption by the residents of Uruk–Warka (figure 1.6). Continuation of this artistic talent can be found in the following Level III (Jemdat Nasr period) with the most well–known examples being a life–sized stone mask representing a woman (the “Lady of Uruk”), the “Warka Vase” with a carved relief depicting plants, animals, tribute bearers, and the goddess Inanna (Heinrich 1936 pl. 2, 3), and the basalt “Lion Hunt” stela featuring a “priest–king” figure firing a bow and arrow (figure 1.7). Although these objects derive from Level III, it is 23 Interestingly beveled–rim bowls are not accounted for in the deep sounding report from Uruk–Warka for Levels V–IV (von Haller 1931), which correspond to the time this vessel type is found in abundance throughout the region. This could either be due to the actual lack of beveled–rim bowls within the deep sounding or, more likely, the failure of the excavators to record this undesirable ceramic type. 26 believed they represent heirloom pieces that originated in Level IV based on their naturalistic designs and motifs (Goff 1963). Figure 1.6. Stone inlay from Eanna Levels IVaIII (from Heinrich 1936, pl. 32a). A B C Figure 1.7. Sculpture and reliefs from Eanna Level III, believed to date to Level IVa (from Strommenger 1964, pl. 18, 19; Moortgat 1967, pl. 26). 27 Similar iconography can be found in the large corpus of stone stamp and cylinder seals from Uruk–Warka, although more seal impressions were found than actual seals. The visual representations on these devices are broad and include geometric and linear designs (figure 1.8 A), files of domestic and wild animals (figure 1.8 B), building façades (figure 1.8 C), kings or local rulers (figure 1.8 D),24 “cultic” paraphernalia (figure 1.8 E), bound captives (UVB XV pl. 28a, 30a), and images of commercial activity including boats filled with cargo and animals being herded by their caretakers. Figure 1.8. Cylinder and stamp seal impressions from Eanna levels IV. Scale taken from original publication (adapted from Heinrich 1936, pl. 17a, 18b, 19a, c, e). 24 The most distinctive being a bearded male wearing an ankle–length skirt and rounded cap with his hair gathered at a low chignon (Heinrich 1936 pl. 15b, 17a–c; Seal W14772c 1 (pl. 17a) is from the later Jemdat Nasr period [Level III]). 28 Evidence for the beginning of writing and its various stages of development also come from this assemblage including tally stones (clay balls used for counting), tokens, clay envelopes impressed with seal designs, and the earliest clay tablets with proto– cuneiform writing (figure 1.9 and Falkenstein 1936; Nissen 1986; Nissen et al. 1993). One of the more famous texts is a fragment from the Professions List, the complete form of which is found in multiple copies in the succeeding phase and is further recopied many times up until the Akkadian period. As its title might imply, the text is a collection of a grouping of signs that represent the titles of officials and names of professions. Figure 1.9. Tablet with archaic signs and numerical notations from Eanna level IVa (from Falkenstein 1936, pl. 27 #323). The second elite area from which scholars derive primary evidence about Uruk society is the Anu Ziggurat, a mud brick platform 13 meters high with buttresses, that is the culmination of continuous rebuilding since the ‘Ubaid period (figure 1.10 and Heinrich 1937, 61–63 Abb.78–90; Lenzen 1941; Perkins 1963). A ramp on the eastern side of the platform provided access to a flat open area on top occupied by a series of 29 Figure 1.10. The Anu ziggurat and White Temple, Levels B (in outline) through D (adapted from Heinrich 1982, fig. 83). temples that had been rebuilt over consecutive levels.25 The White Temple (Level B), so– called because its mud brick walls were covered with bright white gypsum plaster, represents the final phase of these buildings and likely dates to Eanna Levels IVa or III. The building measured approximately 22 by 17 meters and sat on top of a socle of asphalt 40 centimeters high. The tripartite floor plan had a central hall and two rows of rooms flanking on either side that were punctuated by three doorways. Two raised platforms in the central hall likely served as an altar and offering table while two narrow rooms on the south side likely held staircases that led to the roof. Being approximately 500 meters due west of the Eanna complex, the Anu Ziggurat and White Temple were physically and 25 These included an area demarcated by postholes for some kind of structure (“Posthole Building”) and another raised platform with a building plan marked in red paint (“Line Building”). See Perkins (1963, 110–114) and Heinrich (1982) for a detailed and comprehensive review of this architectural evidence. 30 stylistically akin to the buildings at Eanna with elaborate niching, buttressing and other decorative elements. The similar building plans signal some level of cultural continuity, leading me to hypothesize that the White Temple was the religious focal point and the buildings in the Eanna complex were public, administrative structures (or both). That the White Temple was set apart could also mean it was only used at certain times of the year for special rituals or festivals. The data presented here is the primary physical evidence by which archaeologists have traditionally interpreted the core of Uruk society. Certainly the textual evidence discussed above coupled with large, centralized administrative and/or religious structures, cylinder seals and other accounting practices, mass production of standardized vessel forms, and even the possibility of smelting workshop areas (see Nissen 1988, 82; 2001, 155) suggests that at Uruk–Warka during the fourth millennium BCE there is a ranked, well organized central administration perhaps capable of controlling a highly stratified economic system. This interpretation has been left largely unchallenged and unscrutinized allowing the above mentioned evidence, derived from limited contexts relative to the overall size of the ancient settlement, to speak for the entirety of the site and specifically for the upper echelon of Uruk society—namely those who occupied these structures and/or had the control of resources to enable their construction. Meanwhile the nature and function of nonelite Uruk society is currently unavailable to us. Focusing on the centralized areas by the early excavators was perhaps due in part to the enormity of the city itself, which during the LC 5 expanded to a size of 250 hectares with a postulated population of twenty to fifty thousand inhabitants with further expansion to 600 hectares by 2900 BCE (Nissen 2002, 7). For the initial excavators, for 31 whom the technology of geomorphological survey, GPR or resistivity was not available, the prospect of investigating domestic quarters on any broad scale was daunting at best, if not outright impossible. The attentions paid to centralized areas of the mound are also likely connected with research strategies of early twentieth century excavators (along with some modern ones) that revolved around questions involving the upper strata of ancient societies and their associated treasures so that the high mound of any site was the first (and oftentimes only) area to be heavily investigated. Thus while many strands of evidence have been used to solidify the centrality of Uruk–Warka as a social, political, economic and cultural core, without evidence from the rest of society, namely the nonelite and households, the mechanisms by which this society developed and was managed remain hidden from scholars. The Uruk Countryside The cultural milieu represented by the monumental architecture, mass–produced pottery, and higher–level accounting at Uruk–Warka has also been interpreted within a progression of larger settlement growth and distinct patterning that seemingly favored this polity to the detriment of neighboring sites. The settlement pattern in the immediate hinterlands of Uruk–Warka reflects the supremacy of that huge site as the dominant centralized entity that overshadowed and possibly stymied the growth and development of surrounding settlements. For example there is an explosion in the number of settlements, from eighteen to over one hundred, between the Early Uruk and LC 1–5 but there is a dramatic shift in the patterning of these settlements (figure 1.11 and Adams 1981; Adams and Nissen 1972). Whereas before rural villages and small towns were 32 33 B Figure 1.11. Settlement patterns in the hinterlands of Uruk-Warka and Nippur-Adad: A, Early-Middle Uruk; B, Late Uruk (after Adams 1981, figs. 12 and 13). A relatively isolated from one another and evenly dispersed, by the end of the fourth millennium they exhibit contraction and centralization into a pattern of distinct settlement size hierarchy (Adams and Nissen 1972, 11–18). This was organized into a tripartite grouping of sites that range from small (less than 8 hectares) to medium (18 to 14 hectares) to large (20 hectares or more) with Uruk–Warka, at 250 hectares by the LC 5, being set apart completely (Pollock 2001, 187).26 This clustering also shows a distinct pattern relative to Uruk–Warka, such that settlements at a distance of 15 kilometers or less from the site are consistently no larger than 2 hectares in size. Medium to large polities only existed outside of this buffer zone reinforcing what Adams and Nissen (1972, 27) suggest as the inhibiting tendency by the main center of Uruk–Warka toward urban growth among its dependencies. Interestingly this distinct settlement pattern is not reflected to the north in the Nippur–Adab area. Here instead a handful of large sites were established at least by LC 2 and coexisted with medium–sized settlements in a relatively dense conglomeration. By LC 5 however sites become increasingly isolated in a trend that is opposite of what is occurring around Uruk–Warka during the same period (Pollock 2001, 190–92). These data, coupled with the archaeological evidence discussed above, have served as the foundation for scholarly theories concerning the Uruk Phenomenon that necessarily revolve around the centralization of populations and resources, and possibly even cultural knowledge and social ideology (Collins 2000). Survey data from the Nippur–Adab region however show that the settlement situation in southern Mesopotamia during this time was not homogenous, reinforcing that Uruk–Warka is, in 26 Adams (1981, 71–75) differentiated sites into two size groupings while Johnson (1975) visualized a four–tiered hierarchical system that has been adopted by others (Algaze 1993, 2001a). 34 many respects, a unique case. Likewise the contraction and clustering of settlement groups, as viewed in the survey data of the heartland of Uruk–Warka, most likely reflect the movement of populations within the area or possibly emigration outside of it and not necessarily conglomeration within a single center (see Johnson 1988–89; Pollock 1999 and later this chapter). Research in outlying village sites, and the households contained within them, would enlighten this survey data by presenting more rigid physical evidence for the movement of populations and their changing socioeconomic positions in relation to what scholars currently perceive as centralization of communities and resources at core settlements.27 A City Set Apart A final problem that the excavations of Uruk–Warka have presented to scholars of the Uruk Phenomenon lies in the virtual isolation in which the site was excavated at a time substantially prior to the discovery of other fourth millennium sites outside of southern Mesopotamia (Nissen 1988, 110). Because of this, Uruk–Warka was treated as a site from a unique culture with its own characteristic material and unique set of problems to be solved using the field methods appropriate to it.28 This is best exemplified by the primary excavators Nöldeke, Heinrich, Lenzen, and von Haller who, as architectural historians and not trained archaeologists, paid strong attention to building forms and architectural details and less to ceramic seriation for example. Publication of the deep sounding at Uruk–Warka (von Haller 1931) does not give any indication that the ceramic 27 Apart from this dissertation, this type of research has already been done at sites like Abu Salabikh (chapter 3) in the Nippur–Adad region and Kurban Höyük in southeast Turkey (Algaze 1990; Wattenmaker 1994a; Wilkinson 1990a). 28 A similar critique of the excavation methods and recording procedures for Uruk–Warka has been offered by Hans Nissen (2002). 35 assemblages presented there represent all or most of the ceramics found. Nor is the record accurate or comprehensive. For example, second millennium sherds were included among the fourth millennium ceramics derived from Eanna Levels IV and III (Nissen 2002, 5) and only a single beveled–rim bowl is recorded for the entire 19 meter deep sounding (von Haller 1931, Taf. 18Ac); a curious fact when one considers that this vessel type is prolific in the assemblages of neighboring settlements (see appendix). The reality of this situation is that the ceramic sequence at Uruk–Warka is unreliable and incomplete for the entire fourth millennium BCE. This has obvious repercussions for debates concerning the Uruk Phenomenon since the primary phases of cultural development from which excavators at sites outside of the southern alluvium draw comparisons is not available. Nor is there any other ceramic sequence to take its place. As noted by Nissen (2002, 5), the Nippur deep sounding material has not been fully published and the sequence from Abu Salabikh is not long enough. Thus it is impossible for Uruk–Warka to stand as the type site for precise chronological considerations of the fourth millennium BCE. Instead it seems much more productive to work within regional typological and chronological schemes as many have already done. This vital shift has had the added effect of highlighting the subtle local and regional characteristics of ceramic assemblages that are, in many ways, more productive in charting sociocultural developments than focusing on interregional comparisons alone. The same can be said for iconography and glyptic styles whose primary evidence from cylinder seals and sealings derive from more 36 secure contexts at sites like Brak and Hacınebi (see appendix) and are thus more reliable chronological indicators.29 In summary it is unlikely the early excavators could have realized the significance of their findings, especially the ceramic sequence, nor foreseen the great importance this site would play in further arguments concerning the “spread of Uruk culture.” On the other hand, as will be discussed below, the very fact that Uruk–Warka was excavated first allowed its material culture and perceived social structure to set the tone for later excavations beyond the southern Mesopotamian heartland. Beyond the Uruk Heartland The physical evidence derived from several key sites beyond the Uruk heartland set the stage for what would later develop into observations, interpretations, and hypotheses about the movement of Uruk material culture, and subsequently cultural influence, throughout greater Mesopotamia. While these excavations certainly shed light on the interactions between regions, the methodological focus by which these sites were unearthed and their material assemblages examined severely altered the ways in which this Uruk Phenomenon has been traditional viewed. For example the general information we have about Uruk period occupations, especially in southern Iraq, outside of Uruk–Warka is based on limited exposures at a handful of sites and broader, more thorough investigations of a small number of key mounds. Sites like Nippur (McCown and Haines 1967; Wilson 1986), Ur (Woolley 1955), Jemdet Nasr (Matthews 1989, 1990, 2002), and Khafajeh (Delougaz and Lloyd 29 Of course stylistic data such as with seal iconography is not without problems especially in terms of heirlooms and archaizing. 37 1942) have material evidence derived solely from deep soundings, step trenches or surface surveys30 that reveals connections with their southern Mesopotamia cultural sphere especially in terms of ceramic assemblages. At more intensely excavated sites like Eridu the evidence derives primarily from the temple precinct much like at Uruk–Warka; a very narrow window in which to perceive the whole of Uruk (and Eriduan) society. Thus naturally the evidence from Eridu—massive stepped platforms of Riemchen bricks that supported two protoliterate temples (I and II) and a large plastered building of Mittelsaal–type with parabolic archways—solidified for early excavators a coherent southern Mesopotamian material culture assemblage that reflected the monumental architectural works, artistic motifs and ceramic typology from the Eanna precinct. 31 Excavations in western Iran and northern Iraq at sites like Susa32 and Nineveh further reinforced the extension of “Uruk culture” beyond the southern alluvium while relying on very limited contexts (figure 1.1). At Nineveh on Kuyunjik, one of the primary citadel areas at the site, a massive mud brick building with thick piers that supported a system of parallel archways encircling a central courtyard was built (or abandoned?) sometime at the end of the fourth millennium, based on the ceramic assemblage comprised of mostly beveled–rim bowls (figure 1.12).33 Whether this structure was truly a complex of tombs34 or served a public function is unknown, but it currently stands as the only tangible piece of architectural evidence for the Late Chalcolithic at Nineveh. 30 With the exception of Khafajeh whose remains dating to the end of the fourth millennium BCE derived from the earliest Sin Temple (I) (Delougaz and Lloyd 1942, 9–14). 31 See appendix (Iraq) for details about the excavation history, material culture, and full bibliography for Eridu. 32 To be discussed later in this chapter and in detail in the appendix. 33 See Appendix (Iraq) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Nineveh. 34 Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1931, 81; Campbell Thompson and Hamilton 1932, 78. 38 Apart from this single building, the deep sondage at Nineveh offered over 12 meters of occupational debris representing the Uruk period alone. The ceramics derived from this context not only provided the basis for the earliest northern Mesopotamian chronology, the so–called Ninevite 1 through 5 (I–V), but also solidified the presence of southern Mesopotamian Uruk ceramic forms outside of the southern alluvium. The deep sounding offered a window into diachronic change throughout the end of the fourth millennium in terms of ceramic sequence that was (and still is) not possible at Uruk– Figure 1.12. Archways from Nineveh, “Vaulted Tombs 4 and 5” (from Campbell Thompson 1932: pl. XLVIII no. 3). Warka as discussed previously. For example, while the Ninevite 3 phase (LC 4) is characterized by mostly wares and forms typical of Syria, Anatolia and local northern Iraq sites, the following Ninevite 4 (LC 5) has almost exclusively southern Mesopotamian forms including drooping spouted vessels, flat dishes, and beveled–rim 39 bowls en masse.35 But again the only evidence that can be derived from such a narrow context is the development of ceramic and glyptic typologies, and perhaps the waxing and waning of specialized elements like accounting (e.g., tablets, tokens), chipped stone technologies, and symbolic systems. Furthermore this evidence is uncontextualized within the broader scope of Ninevite society that is a crucial dataset for understanding how “Uruk” ceramic forms began to be used at the site and what exactly these data mean in terms of regional interactions and possible exchange. Finally perhaps one of the most crucial excavations outside of the Uruk heartland, and one that has offered a broader scope than the material evidence at Eridu and Nineveh, is Habuba Kabira–Süd (South) within the Tabqa Dam area of north Syria (figure 1.1). Habuba–Süd was an 18 hectare town over 900 meters long surrounded on three sides by a huge wall composed of Riemchen bricks.36 Three building levels were distinguished by excavators on this virgin site who estimated a total occupation of six to eight thousand people over a span of one hundred fifty years all carbon dated to the LC 5 (Strommenger 1985, 86). Habuba–Süd is important for several reasons and offers three major lines of evidence that other Late Chalcolithic period sites cannot. First, it is the only large–scale example of Late Uruk residential architecture with evidence for town planning and a drainage system. The densely built houses averaged 300 square meters in size and were composed solely of Riemchen bricks with most floor plans being of the Mittelsaal–type 35 The following Ninevite 5 phase exhibits another complete shift in the ceramic repertoire to elaborate painted and incised wares that will itself become the type assemblage for the Jemdat Nasr and very Early Bronze Age ceramics across the region. 36 See appendix (Syria: Tabqa Dam) for details about the excavation history, material culture, and full bibliography for Habuba Kabira–Süd. 40 seen at Uruk–Warka and elsewhere (figure 1.13 and Strommenger 1980, 36). Second, the citadel area of Habuba–Süd, called Tell Kannâs/Qannas, was the administrative and religious center for the site, on par with monumental constructions from Eanna Levels V– IVa. It included a grouping of public buildings (the North and South Temples), with tripartite floor plans, interior decorative niches, and basins (Finet 1975, 1977, 88–90). A third large building was uncovered in the central sector that was also tripartite in plan with an attached magazine filled with storage jars. Inside these structures a wealth of objects were recovered, from cylinder seal–impressed jar stoppers to traces of bitumen, and alabaster vases that resemble southern Mesopotamian forms of four–lugged jars. Figure 1.13. Domestic architecture from Habuba Kabira-Süd, 1:200 (from Strommenger 1980, 38 Abb. 16). 41 Third, along with architectural elements, the material culture assemblage at Habuba–Süd and Kannâs is completely foreign to the local Syrian assemblages seen at neighboring sites (e.g., Tell Brak), instead exhibiting the full corpus of southern Mesopotamian wares and forms along with numerical tablets, clay balls with tokens, and clay bullae with cylinder seal impressions reminiscent of designs from Godin Tepe, Susa, Chogha Mish and Uruk–Warka (see appendix and later this chapter). The broad horizontal exposures of domestic and public architecture alike at Habuba–Süd also allowed excavators to detect production and consumption activities on a general site– wide basis. Chipped stone recycling, ceramic production, metal working, storage facilities or tools for agricultural production were notably rare (Strommenger 1980, 55) and likely support the assumption that products, especially agricultural products, were provided by people from the countryside (Sürenhagen 1986, 21). These wider contextual data have allowed archaeologists to comfortably contend that Habuba–Süd was a relatively short–lived settlement founded by a group (or groups) from a non–local population that were reliant on their neighbors, but also involved in higher level recording of these or other products. The evidence derived from excavations at Habuba–Süd has offered a unique picture of Uruk society beyond the heartland derived from domestic and public/religious contexts. But this evidence has both formulated the occurrence of an Uruk Phenomenon, whereby there were interregional interactions during the last half of the fourth millennium, while at the same time only scratching the surface regarding the nature and mechanisms behind this event. For example, the houses at Habuba–Süd provided a wealth of detail about city planning and common architectural types, but little mention 42 has been made to the artifacts found within the houses and how they reflect the usage of spaces within and between them (chapter 2; Kohlmeyer 1996). This household approach to the domestic modes of production and consumption would be invaluable to assess variability between household groups and provide a more nuanced picture of daily life in the town. This microlevel approach could also help sustain (or refute) claims made about the general reliance on rural neighbors for such staple products as stone tools and agricultural goods. Finally, examinations on the individual and collective household– level at Habuba–Süd would be important for charting diachronic trends over the three occupation phases determined by the excavators. Changes in the domestic and elite economies could shed light on a number of unanswered questions like: what was the relationship between the residents of Habuba–Süd and their neighbors? Who built the enormous city wall and monumental structures of Kannâs? And perhaps most importantly, why was the site suddenly abandoned (and never reoccupied) at the close of the LC 5? The material culture assemblages derived from excavations of Uruk–Warka, later Nineveh and finally Habuba Kabira have served as the substantial beginning dataset for understanding the late fourth millennium in greater Mesopotamia.37 The material and scholarly focus on Uruk–Warka has led to its primary position as the central polity from which culture supposedly spread as exemplified in the foundation of Habuba–Süd, the product of a seemingly transplanted cultural group(s) that clung to the practices, traditions and tastes of the homeland. These excavations however have only identified contact—whether through trade, colonization, or influence—and not the holistic picture of the motivations or structure of this Uruk Phenomenon. At Uruk–Warka, Eridu, 37 The comprehensive dataset can be found in the appendix. 43 Nineveh and even Habuba–Süd, the monumentality and centrality of datasets like temples and public buildings have necessarily dictated an elite–focused agenda whereby the means of interaction were controlled by the select few. Household approaches are an appropriate and productive avenue by which to reinforce or refute the true centralization of resources or social ideologies, for example, by examining the ways that the nonelite (e.g., the majority of the population) responded to changes in their local communities. The “Expansion” of Uruk Culture Setting the Stage Early excavations at sites like Uruk–Warka, Eridu, Nineveh and Habuba–Süd have thus far provided evidence for, at some level, shared cultural practices as reflected in ceramic types, iconography, accounting practices and architecture. Continued excavations at settlements throughout greater Mesopotamia, especially in north Syria and southeast Turkey, have highlighted the extent to which these shared cultural practices stretched (see appendix). These excavations have also revealed that this sharing is neither consistent nor ordered, leaving scholars to grapple with recognition of the overall pattern(s) of interaction that define the Uruk Phenomenon.38 As Dan Potts (2004) has rightly remarked, over the last ten to twenty years there has emerged a veritable cottage industry of publications presenting various interpretations, models and hypotheses to explain the mechanisms behind, and the organizational nature of, the Uruk Phenomenon. These include long–distance exchange 38 The frustration and challenge of figuring out this pattern is best exemplified by Gregory A. Johnson (1987, 126) who whimsically remarked, “What happened? Fourth millennium specialists have a tendency to hide under their desks if they think that someone might ask them this question.” 44 by merchant colonies (with roots in the ‘Ubaid period: Alden 1982; Lebeau 1989; Lupton 1996; J. Oates 1993; Stein 1999a, 1999b; Sürenhagen 1986), immigration (Amiet 1986), political and economic expansion (Adams 1981; Nissen 2001), acculturation, emulation and hybridization (Helwing 1999; Pittman 2001; Rothman 1993; Stronach 1994), agricultural opportunities, commerce and staple finance (Frangipane 1997a, 1997b; Frangipane and Palmieri 1987; McCorriston 1997; Schwartz 1988b), social ideologies (Collins 2000), political collapse and fragmentation (Johnson 1988/89; Pollock 2001, Zagarell 1986), ecological catastrophe (Hole 1994), and core/periphery models of an Uruk world system (Algaze 1989a, 1993, 2001b).39 The reasons behind this flowering of debate concerning the Uruk Phenomenon and what it represents is likely due to an academic (and public) fascination with the social, economic, political and religious atmosphere whereby the world’s first cities, bureaucracies, and writing systems emerged. As more research is conducted it is becoming increasingly clear however that the foundations of the Uruk Phenomenon lay before the first states in the fifth millennium communities and networks of interaction (J. Oates 1993; Schwartz 1988b). This is not to say that the systems in place during the fourth millennium were identical to those in the fifth millennium, but that the groundwork had already been laid for these types of interregional interactions. So too are approaches to this subject changing as scholars realize that the primacy and trajectory of Uruk society is intricately tied to the early date in which Uruk–Warka was excavated.40 They also recognize the indigenous growth of these same elements of statehood— 39 A well–organized summary of each of these approaches along with a detailed history of the Uruk Phenomenon debate has been compiled by Pascal Butterlin (2003). 40 This primacy of excavation of Uruk–Warka, where work began in 1849 and continues intermittently to this day, has in many ways affected how archaeologists perceive the transfer of culture and social 45 centralized administration, accounting, monumental architectural works—in polities of northern Mesopotamia. Despite the wide attentions paid to the Uruk Phenomenon, many of the models and approaches to understanding the nature and mechanisms behind this interregional trade and interaction in the late fourth millennium share foundational elements that fall short of arriving at comprehensive explanations. These collective shortcomings include the reinforcement of top–down approaches to sociopolitical and economic histories in greater Mesopotamia that are essentially elite–focused. Even investigations outside of the Uruk–Warka heartland that offer evidence for indigenous development of socially and economically complex communities draw largely from centralized and elite data. Furthermore, in the quest to elucidate ethnic groups as either “Uruk” or “local,” scholars have done little to investigate the socioeconomic circumstances of smaller village communities that were decidedly outside this interregional sphere of influence and contact. A final issue is one of resolution, where truly multiscalar approaches have not been used to incorporate the domestic economies of villages and individual households into discussions of larger, centralized economic systems. Each of these shortcomings is best represented below in three distinct models used to understand the Uruk Phenomenon to which I will now turn. complexity. If for example Tell Brak had been excavated first, would scholars be instead discussing and debating the “Brak Phenomenon?” A particularly poignant quote by Robert Braidwood seems appropriate for reflection here: “I am haunted by the specter of how for years afterwards quite accidental priorities of discovery may influence culture–historical generalizations” (Braidwood 1974, 79). 46 The Uruk World System The macroscale model of an Uruk world system has been proposed by Guillermo Algaze and stands as the principle example of a top–down, elite–centered approach to the Uruk Phenomenon based on a theory of world systems. The World–Systems Theory (hereafter “WST”) is derived from the work of Immanuel Wallerstein (1974), whose primary goal was to analyze and interpret the type of economic and political system in place for European colonial expansion beginning in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries CE. Wallerstein focused on a core/periphery dichotomy to explain the nature of interaction between the “homeland” and the “colonized,” eventually highlighting an overall unequal exchange where peripheral areas—seen as underdeveloped economically, socially, and in some cases culturally—immediately benefit from the interaction with a more culturally complex core. In principle, however, this exchange system is asymmetrical and in time the periphery’s reliance on specialized goods and economic systems based on the core eventually leads to the system's downfall, either locally within the periphery community or at the core level. Despite Wallerstein’s assertions that this theory cannot be applied to ancient societies or social systems—he believes that the only true world systems were able to come about with European expansion—the WST has been widely used by many fields including Sociology, Political Science, and Archaeology. Examinations by Paynter (1981) and Kohl (1987) have considered the applicability of this theory to archaeological investigation and have found, through slight modifications, that it is a useful methodology to be employed by archaeologists. This sentiment is also expressed by Chase–Dunn and Hall (1997), who see the WST as applicable but caution against 47 applying the model wholesale. For example, a component of the WST is the exchange of bulk goods that are the most important for the generation of economic complexity within the state. However the trade of preciosities must not be overlooked as these can be politically charged elements in a growing bureaucratic system.41 As already mentioned, the WST has been used by Guillermo Algaze (1986a, 1989a, 1993, 2001a, 2001b) to explain the nature and mechanisms behind sociocultural interactions throughout Mesopotamia in the fourth millennium. In fact his 1989 Current Anthropology journal article42 spearheaded the idea of the physical movement of Uruk culture throughout the greater Mesopotamian region, an “Uruk Expansion” in this case. Hailed by some as merely an attempt to systematize old hypotheses,43 others saw Algaze’s arguments as a “rich tapestry of archaeological data within an important conceptual framework” (Lamberg–Karlovsky in Algaze 1989a, 595). That framework focused on the emergence of politically and economically distinct polities in the southern alluvium centered on the city of Uruk–Warka, whose lack of primary natural resources like stone, metals, and wood was the primary catalyst for expansion into the resource– rich, but culturally underdeveloped, periphery of the northern and eastern borders of Mesopotamia. His argument is based on a three–tiered system of enclaves, colonies, and trading posts whose locations on direct lines of north–south and east–west trade and 41 Wallerstein (1996, 294) himself concurs, saying there must be a distinction between trade in luxury and bulk goods. This is especially true for prehistoric cases where, before modern transportation capabilities, long distance trade was necessarily in low bulk, high profit goods like luxuries/preciosities. 42 This article was a condensed version of his unpublished monograph entitled, “The Uruk Expansion: ‘Momentum towards Empire’ in Early Mesopotamian Society,” a revision of his doctoral dissertation (Algaze 1986a). 43 See Burchard Brenties and other comments following Algaze 1989, 591–602. See also Lamberg– Karlovsky (1984), who also argued for the colonial implantation of periphery regions during the “First Conjuncture” of his longue durée view of ancient Near Eastern cultural development. 48 communication ensured for the Uruk core that resources could be harnessed, controlled, and applied for the welfare of urban political elites in the south. The primary evidence from which Algaze drew is first based on settlement pattern data derived from surveys both in the southern alluvium (see previously this chapter and Adams 1981; Adams and Nissen 1972) and western Iran (Johnson 1973). Second is the physical archaeological evidence that, for Algaze, pointed to a developing system of political control and cultural infiltration. Along with the evidence from Uruk–Warka itself discussed previously, Algaze looked east to sites in the Susiana/Khuzistan plain of Iran that exhibited a dramatic shift in material culture and settlement plan at the end of the fourth millennium that, for Algaze, was the result of colonization. The site of Susa, for example, during the earliest Late Chalcolithic phase (Susa I or A; dated LC 1–3) featured a monumental multi–roomed building (Bâtiment de Suse I) with 2 meter thick pisé walls on the central Apadana mound, a large low mud brick platform containing the buried remains of approximately two thousand individuals (massif funéraire) in the deep Acropole sounding and a later 10 meter high stepped mud brick platform (haute terrasse) decorated with inlaid ceramic cones, clay models of goat horns and plaque mosaics (Canal 1978; Pollock 1989).44 These unusual and seemingly local cultural traditions are disrupted in the following phase (Susa II or B; dated LC 4–5) where, after a large destruction, ceramics of southern Mesopotamian Uruk type begin to be used along with accounting elements (e.g., bullae with tokens, numerical tablets) and glyptic repertoires echoed at neighboring Uruk–Warka. 44 See appendix (Iran: Susiana/Khuzistan) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Susa. An extensive bibliography for excavations at Susa can also be found in Carter and Stolper 1984. 49 From here colonies of Uruk traders were established at newly founded settlements like Jebel Aruda and Habuba–Süd along the Euphrates River in Syria. Both of these sites are characterized by the complete suite of southern Mesopotamian material culture including Mittelsaal architectural types, ceramic forms, elaborate systems of accounting and economy, and cylinder seal motifs that hearken back to designs used at Uruk–Warka and Susa. Enclaves were also established at pre–existing sites like Nineveh (discussed previously), Tell Brak, Samsat, Carchemish and Hacınebi (discussed below). Finally a sprinkling of outposts were embedded within settlements or in remote locations close to resource locations. For example, Godin Tepe, located in the Kangavar Valley of the Zagros Mountains in Iran, contained a supposed merchant community living within a heavily fortified oval enclosure on the citadel mound above the local village that engaged in the trade of semiprecious stones and wine along the Khorasan Road (Badler 2002; Weiss and Young 1975).45 The idea of an Uruk world system has been critiqued by many (inter alia Frangipane 1997b, 2001; Joffe 1994; Pollock 1992; Rothman 2004; Stein 1999b, 2002a) for numerous reasons that I am in agreement with. There is, as yet, no physical evidence for the trade in items like metals, timber or semiprecious stones, though more recent work on organic residues is offering interesting results.46 The Uruk world system model also assumes a passive, underdeveloped periphery that has since been shown to be false as more and more excavations in north Syria and southeast Turkey reveal indigenous 45 See appendix (Iran: Luristan) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Godin Tepe. For example, Virginia Badler (1996, 2002) with her colleague Patrick McGovern (2003, 40–63) successfully identified the presence of wine in jars from buildings inside the Oval Enclosure at Godin Tepe. Similarly McGovern and others (1996) have discovered chemical evidence for wine residues at fourth millennium Uruk-Warka. 46 50 development of cultural complexity at sites like Arslantepe, Tell Brak and Hacınebi (see below and appendix). The initial work of Algaze also opens the door for critique in the use of analogy and incorporation of methodology from fields outside that of Near Eastern Archaeology for use in understanding the Uruk Phenomenon. Analogy—or drawing a comparison to show a similarity in some respect between two or more situations, occurrences, or states—has long been a contentious issue for its practical use in Archaeology where for many it is a matter of degree as to how many similarities must be present in order to justify use of a particular analogy. In the field of prehistoric Archaeology, analogy is especially attractive in spite of the fact that modern–day examples, such as Marsh Arabs in southern Iraq, would not necessarily exhibit the exact types of habits, personalities, or life choices as those in the fourth millennium BCE southern alluvium. Yet with the Uruk world system model, analogy goes hand in hand with the use of outside methodology, where the hypothesis concerning relatively modern societies (in Wallerstein’s case, fifteenth and sixteenth century Europe) in a particular sociological framework regarding colonization, indigenous development, and core/periphery relationships is being placed on fourth millennium BCE cultural communities. This idea is further reinforced by the language used not only in Algaze’s published work, but by many scholars for whom the “Uruk Expansion” equates to exactly that: an infiltration of culture materials and social structures.47 This line of analogy also places too much emphasis on the continuity and similarities of world systems throughout time, even millennia, and expects the observer to equate the European economic and political system 47 Though I have not come across any who would be so bold as to liken this expansion to early or informal empire as Algaze (1989a, 1993) does. In my mind, the term “informal empire” is never fully defined in the first place. 51 with that of a tribally based, developing urban city–state landscape. In a unique reversal of Orientalizing, Mesopotamian societies as a whole are thus turned into copies of present Western “civilization” (Bernbeck and Pollock 2002, 189). Most of all, the idea of an Uruk world system reinforces a top–down approach to sociopolitical and economic histories. A better approach to fourth millennium Mesopotamia would incorporate the microscale by examining the multitude of smaller networks of interactions and relationships that exist below this wider umbrella of a world system. It is most likely that scholars will discover that these smaller networks interweave to create a tapestry of interaction and not a single “world wide” system. Examinations on the microscale also address the need for multiscalar approaches that focus on the various levels at which humans interact: from region to village to inner communities to households (and if one is daring, even individuals). Framing the ancient world within a core/periphery dynamic inevitably presumes the passivity of groups outside of the central core and necessarily glosses over the more nuanced relationships within and between regions, communities and individuals of multiple social groups and classes. It is here that a reinsertion of the theoretical foundations of peer polity interaction (Renfrew 1986) would be most useful, if anything to remind scholars that not all interactions are based purely on economic concerns but also include aspects of culture, religion, ideology, or all of the above. Trading Diasporas and Entrepreneurs A primary reaction against the Uruk world system model has been to highlight the level of socioeconomic complexity preexisting in periphery regions before incursions of 52 Uruk peoples, material culture, and/or influence during the LC 4–5 (Frangipane 1997b, 2001; Rothman 2004; Stein 1999b, 2002a, 2002b). While these types of rebuttals and renewed frameworks have significant merit because they highlight regional (as opposed to strictly interregional) networks of interaction, most remain elite–focused with little consideration for the dynamic relationship between centralized administration and distribution of resources and domestic modes of production and consumption. Thus these approaches reinforce the elite nature of these interactions that characterize the Uruk Phenomenon while simultaneously challenging the cultural dominance of a single core state at Uruk–Warka. A primary critique against the Uruk world system (or core/periphery) model is the assumption the core holds military, technological, ideological, economic and/or organizational domination over the periphery. This type of approach to the Uruk Phenomenon focuses on an external dynamic explanatory framework that glosses over any constituent political units to favor the whole (Stein 1999b, 9). Thus the fundamental unit of social change is the world system and not the society or social groups that comprise it (Stein 1999b, 25). The asymmetrical exchange, power relations, economic influences and ideological forms inherent with a core/periphery relationship also downplay the role of the periphery in sociocultural developments, essentially rendering it as a passive recipient of more advanced culture from the core. This passivity, however, is not visible in the Uruk periphery as exemplified by a number of key sites spread throughout north Syria and southeast Anatolia that offer primary evidence for local developments of cultural complexity.48 One example is Arslantepe, a 5 hectare mound located 15 kilometers west of the Euphrates River and 6 48 See appendix for a comprehensive discussion of all relevant sites in these areas. 53 kilometers northeast of the modern city of Malatya, Turkey.49 During the earliest Late Chalcolithic phase (Period VII; dated LC 3) the site’s inhabitants built a large tripartite mud brick structure (Building XXIX) with painted walls and mud columns that contained mass–produced ceramics (Frangipane 1993; Frangipane and Balossi 2004). In the following phase (Period VIA; dated LC 4/5) they constructed a “palace–temple” complex comprised of four terraced buildings with evidence for administrative and redistribution activities, specifically stockpiles of stamp and cylinder seal–impressed bullae and clay fragments. There is also evidence for metal smelting and casting, textile weaving, and ceramic production. While there is a minimal inclusion of characteristically southern Mesopotamian elements (mostly ceramics), the general material culture assemblage at Arslantepe during this phase retains an overwhelming local Anatolian character (see appendix). Similarly at Tell Brak in north Syria there is evidence for a well developed socioeconomic system that involved higher–level accounting, localized production of specialist goods, and monumental architecture including temples (inter alia Mallowan 1947; J. Oates 2002; J. Oates and D. Oates 1997).50 This average 65 hectare site (and up to 100 hectares in LC 3) contains 10 meters of occupation that span the mid–fourth to the early third millennium. During the LC 2, there was a massive perimeter wall around the settlement with a monumental gateway and a probable temple with niched façade. The LC 3 settlement was characterized by well–built houses, some with high status goods like ivory objects, carnelian and gold beads, “eye idols,” and a tripartite–plan public building. 49 See appendix (Turkey: Keban Dam and Beyond) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Arslantepe. 50 See appendix (Syria: Khabur) for details about the excavation history, material culture, and full bibliography of Tell Brak. 54 A final example is Hacınebi, a 3 hectare site located in the Euphrates River valley north of Birecik in Turkey, where during the earliest Phase A (dated LC 2) the inhabitants built a monumental terrace and platform complex, storage buildings, and a 3–meter–wide enclosure wall with buttressing and a massive mud brick raised platform. There is also evidence for all stages of metal production including special smelting pit furnaces, crucible fragments, open–faced casting molds, and final products like copper chisels and pins. Engraved stamp seals, seal blanks and impressions whose iconography is paralleled across the piedmont zone from Değirmentepe to Gawra to the Khuzistan plain (Pittman 1999, 45) attest to higher level accounting and interactions within a local and regional sphere. These multiple levels of exchange and interaction are perhaps better explained through a model of trade diasporas as opposed to a single world system (Cohen 1971; Stein 1999). Instead of being core–centric, a trade diaspora model explains variation in exchange systems from the perspective of the participants such as foreign traders and indigenous hosts. Thus a colony can be seen instead as a kind of trade diaspora (like at Hacınebi for example), part of an interregional exchange network composed of merchant groups that are culturally distinct from their host communities, but there is no political or economic control of the periphery by the core. A trade diaspora model also encourages a more focused study of household–level activities that can help distinguish distinct groups within any one social unit such as a small village, community or city. While I admire the focused attention on the agency of local communities that the trade diaspora model introduces, it reinforces the broader perspective of a core/periphery dynamic, albeit with a less domineering political and economic agenda. The foundational 55 evidence for “complexity in the periphery” and trade diasporas derives from highly elite and centralized contexts, especially at sites like Arslantepe where the economic system coordinated through centralized administrative buildings has seemingly overshadowed any discussions of domestic modes of production and consumption that were assuredly in place at the settlement. In the case of Hacınebi, domestic modes of production and consumption have thus far been examined individually (e.g., chipped stone, spinning/weaving, agriculture), but not as a collective whole whose separate elements interlace together to form a domestic economy (see chapters 2, 4, 5). Following the trends in the domestic economies of households over time would help push examinations of the Uruk Phenomenon at this site and others beyond simply identifying cultural or ethnic minorities within indigenous populations to how these groups interacted on social, economic, and political levels. For example, Stein (2002b, 152) has claimed there was a peaceful existence and economic autonomy between the indigenous population and Uruk colony at Hacınebi with little cultural mixing between the two groups. This is based on a general picture of household activities and patterns such as diet and tool production and use across the site. However I suspect that if one was to examine these data on a minute, house by house basis and compare individual domestic economies, there would likely be evidence for differentiation based not just on ethnicity, but also gender and social and economic class defined by, for example, differential access to resources. Finally, many of the sites in the periphery regions that have been incorporated into discussions of the Uruk Phenomenon provide some kind of evidence, largely in the form of ceramics or glyptic, for interactions with Uruk–Warka, western Iran, or the southern alluvium in general. While this may seem a logical mode of examination, it has 56 become an exceedingly atomistic one. In particular while scholars have been busily deciphering the pattern behind the locations, types, and degrees to which interactions were occurring at these periphery sites, there is likewise a pattern of settlements that were not interacting with this wider network in a way that is at least visible archaeologically. My point is that sites, especially smaller villages and towns, that do not exhibit effects from the Uruk Phenomenon are just as important, if not more so, for teasing out mechanisms and motivations for interaction. In fact these interactions may be nothing more than the mobilization of staple resources between local polities naturally located on major transportation routes and have nothing to do with Uruk colonies (Rothman 1993, 173). Political Collapse and Fragmentation For a small handful of researchers, the Uruk Phenomenon and the end of the fourth millennium does not represent a blossoming of interregional interactions and explosive economies. Instead the appearance of colonies or enclaves implanted in greater Mesopotamian communities represent refugees fleeing a catastrophic political fragmentation and collapse generated in the southern alluvium.51 This approach has merit in that it deviates from more traditional economic models of burgeoning trade and interaction and loosely incorporates multiscalar evidence from villages as well as towns and centralized polities. However these village data are unfortunately treated in a cursory manner with hypotheses based on assumptions as opposed to detailed examinations of domestic economies. 51 A similar model was proposed by Frank Hole for the fifth millennium, however in this case climatic deterioration and environmental shifts (specifically rising seal levels in the Arabian/Persian Gulf) caused the scattering of ‘Ubaid communities across Mesopotamia (Hole 1994). 57 Survey data is the primary point of departure for these approaches of political collapse and fragmentation. Johnson (1988–89, 598) in particular, cautions that the settlement data for the Uruk heartland interpreted by Adams, Algaze and others as rapid growth, may instead be more the product of poor temporal resolution in the archaeological data than population movements or a high growth rate. Instead of growth, he sees severe population declines in the Late Uruk at sites like Ur (Adams 1981; Wright 1981), Nippur, and Eridu, which in fact was completely abandoned at the very end of the LC. In Susiana there is a decline in occupied area by almost half during the LC 5 (129 to 52 hectares; Johnson 1973, 70–78) and similarly in the Deh Luran plain (Wright 1981). A “buffer zone” in which no settlements of any size are present developed between Susa (discussed previously) and the rival polity of Chogha Mish signaling hostilities between the two. The 18 hectare settlement of Chogha Mish was the sister–city to Susa in terms of cultural development in the region with monumental architecture, a densely packed urban neighborhood, streets with drains, and probably a city wall (Delougaz and Kantor 1996).52 The ceramic assemblage, accounting practices, and seal iconography are closely paralleled at Susa (Levels 17/18), Uruk–Warka VII–IV, and Habuba Kabira-Süd. A hostile environment is apparent for this area as attested in military scenes on seals from Chogha Mish (Delougaz and Kantor 1969, 25) and Susa (Amiet 1961, 251) and in the increased density of sling bullets at an elite rural estate near Abu Fanduweh (Johnson 1976). According to Johnson (1987), this conflict is based on competition for control of rural labor and agricultural production, the two foundational elements that allowed one to 52 See appendix (Iran: Susiana/Khuzistan) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Chogha Mish. 58 literally build an elite status through monumental architectural constructions, surplus, and the establishment of commercial value to acquire elite commodities. The injection of state control within the rural sector is suggested through a shift in the volume of ration containers (e.g., beveled–rim bowls) that reflect attempts at standardization. At a critical juncture sometime at the middle to end of the fourth millennium, demand on rural settlements between these regional polities proved too overwhelming, forcing populations to abandon the region. Yet if peasant refugees are rushing to leave a political fallout in the south, then who built the 900 meter long city wall of Habuba–Süd? Johnson contends that these refugee groups were also composed of losing elites in the southern power struggles who felt the necessity to guard themselves while in exile from their political rivals. In critique of Johnson, huge walls do not necessarily serve as fortification nor do they denote fear from outsiders, although this can certainly be argued for some cases. Walls can be a physical manifestation of power and control over resources such as labor, raw materials and time. They can also serve as boundary markers between urban and rural, ethnic groups, and/or political entities. However the evidence at Habuba–Süd seems to indicate that the peoples who lived there were not completely cut off from their neighbors. In fact the agricultural evidence suggests they relied solely on the local population for their food. Plus the idea that powerful elites from Uruk–Warka and Susa had the resources and military prowess to pursue their (already defeated) political rivals in the northern reaches of Mesopotamia seems improbable. With that said, heated conflict does seem to be a real possibility. Warfare, the evidence for which was once only available in military scenes on cylinder seals from the 59 Late Chalcolithic, now have physical archaeological evidence from the north Syrian site of Hamoukar.53 This single hectare settlement (Ur 2002a, 2002b) reached its cultural peak during the LC 3. At this time a large city wall that included four possible gateways was built along with a monumental building complex of Mittelsaal–type with an adjacent production area (Gibson et al. 2002a, 33). One of the structures also contained a large kitchen with a series of grinding stones embedded in clay benches and a massive baking oven. The entire complex was heavily burned and collapsed, sealing thousands of in situ artifacts inside including carbonized grain, a bone facsimile of a dagger in a scabbard, whole ceramic vessels, stamp seals and impressed sealings, unbaked solid clay balls and over twelve hundred oval–shaped clay “bullets” used in hunting and combat that attest to the violent destruction of the buildings. Following the destruction of these buildings, a number of deep pits containing southern Mesopotamian Late Uruk ceramic types, such as beveled–rim bowls, strap handle cups, and four–lugged vessels, were dug into the destruction debris and along the city wall. It is possible that an incursion by peoples using these pottery styles launched the attack against the settlement at Hamoukar sometime at the end of the fourth millennium BCE or, at least seemed to have benefited from the destruction of this well– established, economically complex city. While Hamoukar currently stands as the only evidence for actual warfare during the late fourth millennium, the occurrence of sociopolitical strife is not an unfounded and unimaginable possibility. Yet the real flaw in Johnson’s approach is that the major upheavals instigated by elite factions of the population, namely the pressing of exorbitant labor and tribute demands, are not examined in detail at the level where these economic 53 See appendix (Syria: Khabur) for details about the excavation history and material culture of Hamoukar. 60 shifts supposedly took place: the rural villages and households. Greater support for this model could be garnered through a detailed examination of diachronic shifts in the domestic modes of production, consumption or distribution for households within neighboring village communities. A rapid increase in the production of specific agricultural products like cereals or ovicaprines could support the growing requirements to feed and supply emerging classes of specialist craftsmen or elites. Likewise a consistent trend of economic growth or decline could signal either the prosperity or deficiency of rural communities that could be due to any number of circumstances such as environmental degradation, social upheaval or shifts in clan–based organization. Conclusion Understanding the complexities and organization of societies during this premier phase of ancient Mesopotamian history has many challenges. One is the “type site” for the fourth millennium Near East, Uruk–Warka, offers a narrow window by which to perceive Uruk society that is limited to elite contexts like monumental buildings and temples and further hampered by an unreliable and poorly understood ceramic sequence. While surveys in the Uruk heartland have also underscored the possible centralization of populations and resources around Uruk–Warka, continued surveys in the hinterland (at Nippur–Adab in particular) have reinforced that perhaps this polity is a unique case as the settlement pattern in the southern alluvium was not homogenous and likely ever– changing. The rather limited scope by which scholars have contextualized Uruk–Warka is hampered by the limited exposures at a handful of sites in southern Mesopotamia that 61 have been excavated. Even these offer evidence for primarily the elite sectors of Uruk society and not the social, economic and religious life of Uruk households. This trend extends to sites in northern Mesopotamia at places like Nineveh and Habuba–Süd where there is more complete evidence for ceramic sequences or domestic architecture, but no specific information on the larger contexts from which both “local” and “Uruk” ceramics derived (at Nineveh) or the activities of production, consumption, and distribution that comprise a domestic economic system (at Habuba–Süd). While these and additional sets of evidence have set the stage for the identification of an Uruk Phenomenon, they have also altered the means by which to understand it. Scholars have made significant advances toward uncovering the mechanisms and motivations by which systems of interaction and exchange played out during the fourth millennium BCE, whether through an Uruk world system, trading diasporas, or political fallout. But these and other models have remained geared toward single types of interaction that are elite focused and economically driven. Studies involving the Uruk Phenomenon have not addressed the issue from multiscalar view points that incorporate the nonelite, domestic, and multifaceted networks of relationships that exist on the level of the individual, households, community, village, and broader region. In the following chapters I will discuss exactly how the nonelite and domestic contexts of Uruk society can be explored through the theoretical and methodological frameworks of household archaeology, microdebris analysis and domestic modes of production and consumption. 62 CHAPTER 2. HOUSEHOLD ARCHAEOLOGY AND THE URUK PHENOMENON As the previous chapter has shown, the problem inherent in examinations of the Uruk Phenomenon is the atomistic approach to economic and sociocultural networks that develops when one does not take into account the nonelite, specifically domestic household groups. Yet if the picture of Uruk and Late Chalcolithic society has been formulated through the analysis of religious and centralized administrative factions, how does one study the household? More specifically, how might the domestic modes of production, consumption and interaction inherent within households be uncovered for the Late Chalcolithic period? This chapter addresses these questions by providing background on the theoretical field of household studies in general and Near Eastern archaeology in particular. I then discuss the intimate ways in which household groups and local economies are intertwined as manifest in a domestic mode of production and consumption, all of which will serve as a basis for how household archaeology can be applied specifically to assessments of the Uruk Phenomenon. I argue that by examining the domestic economy of household groups, as a complement to traditional studies of Uruk and local Late Chalcolithic systems of exchange that focus primarily on centralized elites and specialist trading factions, we can arrive at a more holistic picture of the mechanisms and nature of the Uruk Phenomenon. 63 Household Archaeology in Theory and Practice Definitions and Development Household archaeology can be defined as a subdivision of settlement pattern archaeology specializing in the study of spatial patterning at the household level. As a relatively recent focus of research, household archaeology can trace its foundations to the cultural anthropological studies of family and kinship systems dominant in the early twentieth century. However these traditional approaches to define the universality of the family (Malinowski 1963 [1913]) or residence rules for the generation of household units (Murdock 1949), brought researchers to the point that household forms were not the result of variable patterns of behavior but instead simply the outcome of a system of marriage and residence rules (Netting et al. 1984, xvi), all essentially non–material. Some attempted to go beyond this to show that household structure was affected by many interlocking factors. For example, Meyer Fortes’s (1949, 1958) developmental cycle for domestic groups, defined as workshops of social reproduction, charted the evolutions in form and function that every household group undergoes during its life cycle of internal (e.g., marriage, inheritance, death) and external (e.g., conscription, public funerals) systemic events. Yet how does this materialize archaeologically? Fortes and others are quiet on this point, though indeed they are ethnographers and anthropologists, not archaeologists. Thus this way of analyzing household structure did not prove as useful to archaeologists who instead found ethnohistorical studies of domestic life and its material manifestations better suited for constructing analogies between past and present household structures. 64 The “real” birth of household archaeology coincided with the emergence of processual archaeology in the 1960s and 1970s in North America, where archaeological investigations were beginning to formulate research problems that could be tested scientifically and where material culture was used as evidence of human behavior, rather than an exercise of listing traits in an ethnographic format (Trigger 1989, 273). More detailed discussions began to materialize, for example, about forms of domestic structures and how these are determined through various internal and external systems (Rapoport 1969, Whiting and Ayres 1968). In a foundational book, Kent Flannery examined the origins of village life and households in Mesoamerica, including house structure, specialized and gender–specific activity areas within households, and exchange on village and regional levels (Flannery 1972, 1976). Early examinations of post– depositional processes, disorganization and the decay of settlements also began to emerge during this time such as Robert Ascher’s ethnographic work with the Seri in Baja California (Ascher 1968). Yet for terminology and application, the foundation of early archaeological and anthropological household studies lay on uncertain ground. In all previously mentioned studies, aspects of kinship and family structures still played a defining role in investigations. This is especially true in the work of E.A. Hammel and Peter Laslett (1974, 76) where the study of domestic groups—defined as a unit of people who share the same physical space for eating, sleeping, leisure activities, growing up, child rearing and procreation—can only be largely applied to historical examples where census information is available for nuclear family units. Also the various usages of terms like family, coresident, or domestic group was, and in many respects still is, not always 65 uniform across the anthropological field. Traditionally the family has been defined as a self–identified kinship entity while households are residential units,1 though as was often the case, the terms are used interchangeably (Bender 1967, 493). The basic assumption was that households were made up of individuals who share the same living space and a set of activities. These activities are traditionally labeled “domestic” and consist of food production and consumption, housekeeping, procreation and childrearing. This functionalist definition of the household is limited when we consider cross– culturally that not all individuals who work together or perform domestic functions share the same residence, nor do those who live together necessarily engage in collective activities (Bender 1967, 494). Thus many anthropologists strived to employ alternative designations for the groups that they were observing ethnographically. Households became domestic groups where all members acknowledge authority in domestic matters (Bulmer 1960) or budget units for a group of individuals who share a common fund and exchange goods between themselves (Seddon 1976). Donald Bender (1967, 495) substituted coresidential group for household in order to draw a clear distinction between these groups and any functions they may perform. In this way Bender, like other anthropologists, began drawing the line between kinship and propinquity as the essential features that define membership in each of these respective groups in an attempt to avoid a functionalist definition of the family. However Bender's definition of household as consisting of coresidential groups and domestic functions is equally as obtuse. Domestic activities, or in Bender's words, “the day–to–day necessities of living” (1967, 499) seem to be purposefully vague and, as pointed out by Sylvia Yanagisako (1979, 196), not 1 This is not my definition of household as used in this dissertation. See subsection “What is a House?” in this chapter. 66 cross–culturally valid. Likewise the definition of the nuclear family is not universal nor can it be assumed as the ideal family type for every society. It is from this anthropological foundation, imbued with terminological debate, that the subfield of household archaeology emerged. The term “household archaeology” was first used by Richard Wilk and William Rathje in their 1982 article in American Behavioral Scientist, “Archaeology of the Household: Building a Prehistory of Domestic Life.” They believed it was possible that a “theory of change in household organization can bridge the existing mid–level theory gap" (Wilk and Rathje 1982, 617), that separates grand theories of culture change and the pot sherds and stone tools of the archaeological record. Wilk and Rathje characterized the household in explicit terms as being composed of three elements: social, material, and behavioral. Social is the demographic unit that includes the number and relationships of the members; material are the physical dwellings, activity areas, and objects therein; and behavioral are the activities that the household performs. This generally functionalist view sought to define the household as an economically cooperative unit, distinct from a dwelling unit that is explicitly coresidential. This builds on the work of Donald Bender (1967) and Jack Goody (1972) who had previously acknowledged that groups living under a single roof can actually constitute separate households since there is no economic cooperation. Overall Wilk and Rathje were not concerned with the morphology of households per se—since this type of investigation lead back to issues of kinship systems and family composition, all of which are rarely recoverable or identifiable from the prehistoric archaeological record—but more on what households do and how they function in their individual sociocultural 67 environments.2 They determined four primary functions of the household that are applicable cross–culturally and which will serve as a baseline for investigations of households in this dissertation: 1) production, 2) distribution, 3) transmission, and 4) reproduction. Production is human activity that procures resources or increases their value (Wilk and Rathje 1982, 622). This can encompasses a number of activities like agriculture, food processing, craft specialization and manufacture of tools, ceramics, jewelry, and cloth. The level at which production activities take place within a single household can vary considerably and is very often linked with the way that labor is organized. For example, the scheduling of linear versus simultaneous tasks will determine the number of household workers needed, time allowed and cost incurred to complete a single task. Linear tasks require only a single individual to complete a sequence of operations,3 whereas simultaneous tasks require many persons performing the same operations at the same time or performing different operations (specialization) in order to complete a specific, single product. Distribution involves the moving of resources from producers to consumers within the household unit (pooling) or between households or corporate units (exchange). Often small households will find no advantage in pooling resources when production within society is generally uniform or there is a large diversity in production between individuals. In this case, producing individuals would have little incentive to pool with those who did not produce (due to lack of jobs or skills) because there would be no reciprocity in the action. Conversely large households can increase access to a broader 2 3 See also Ashmore and Wilk 1988; Wilk and Netting 1984. Wilk and Rathje give the example of lithic reduction (1982, 622). 68 variety of goods while decreasing the variability of supply by pooling when overall production is highly diversified, making the quantity of goods produced variable over time. Thus in band and urban, state–level societies there is an overall emphasis on the use of exchange between small household groups while agricultural societies and those with mixed economies pool within larger, extended household groups. Transmission concerns property, specifically the transferring between generations of rights, roles, and land (Wilk and Rathje 1982, 627). Transmission is a specialized and specific form of household distribution of assets that is determined by the accessibility of property and goods. When resources are abundant, routes of transmission follow group affiliation lines, such as residence or descent group membership. When resources are scarce, the party that controls the resources defines more narrowly the rules of transmission, specifically to households or individuals. Here we see the development of partible and impartible inheritance depending on whether there are enough resources to be split evenly between familiar heirs. It is within this context, especially with impartible succession, that marriage becomes a strategy for the transmission of property or wealth. Also household members who do no inherit become a landless class, a ready pool from which craft specialists and military establishments can draw. Reproduction is the rearing and socializing of children within the household. Pooling of labor is often the way in which this time and labor intensive activity is accomplished. This is especially true when women’s labor is most needed in an agricultural subsistence economy. Allowing childcare to be handled by a select pool of households frees female labor for production, assuming that women are the sole childcare providers in that society. This situation is different for state–level societies where the 69 government, schools and social welfare programs take partial responsibility for the childrearing from normally nuclear–sized family units. Reproduction can also apply to the reproduction and transmission of cultural knowledge. A fifth category that I would include is consumption. For households, this means the actual use of the products of production through the eating of food or using of craft goods for example. These products may have derived directly from internal household production or by the process of distribution through a local or extramural network. Overall consumption patterns offer the most information about individual domestic economies and their local spheres of interaction since consumption is the outcome of all productive activities (Hastorf and D’Altroy 2001, 8). Of these primary traits of households, one must look not for a single functionality, but spheres of household function that will vary between societies and levels on the developmental cycle (Wilk and Rathje 1982). Variability will also be found between households as every household unit is the product of a mix of strategies. This discussion serves as a theoretical base for the examination of household groups, but how is it applicable archaeologically? What is a House? Before continuing my discussion of how households can be studied archaeologically it is necessary to discuss several of the terms used in this dissertation to outline for the reader my own definitions and with them, the associated possibilities and limitations. The task of constructing precise and reduced definitions for terms like house, household, and family is challenging since these terms ultimately represent inherently complex, multifunctional institutions instilled with a diverse array of cultural principles 70 and meanings (Yanagisako 1979, 200). Perhaps for many, the easiest and most recognizable is the house itself, what I define as the physical structure that serves a myriad of functions: shelter from the elements, location of daily socioeconomic activities, boundary between the public and private spheres of society, and a focal point for family life including rituals, childrearing, education and enculturation. Just as the function of houses varies cross–culturally, so too do the forms as determined by physical and cultural forces (Rapaport 1969, 1986). Physically this includes environment, climate, location, and available building materials—one cannot build an igloo in the desert, for example. Yet the most defining factor is often culturally based and includes social organization, economics, rituals, traditions and taboos. A third factor which may also be included here is agency, both by individuals and household groups acting over generations.4 The house is not a static entity. Archaeological ethnography has demonstrated the changing form and function of both houses and their internal spaces (Kramer 1982; Watson 1979). The rate at which these changes take place varies from annually (re– plastering mud brick walls) to daily (a living room becomes a sleeping room at night) to hourly (flint knapping switches to weaving activities in the same courtyard). The house also expands and contracts with shifts in social organization, so that the transition of rooms from public to private use, addition of spaces and demolitions give each house a life cycle mirrored by the development cycle of the domestic group that uses it (Bailey 1990; Fortes 1958). As human groups shape and are shaped by their physical environments, cultural regularities will be imbued within the architecture of the house 4 As defined by Pyburn (1998) and Netting (1993). Accessing the individual in the past through the archaeological record has been a topic of continuous debate in which some contend that uncovering the ancient individual is unnecessary, if not impossible, since patterns of practices and behavior eventually transcend single organisms (Dobres and Robb 2000; Gardner 2004; Morris 2004). 71 itself, an identifiable code that is able to be “read” in order to uncover the sociocultural meanings behind these regularities (Bourdieu 1977; Hillier and Hanson 1984; Kent 1990). As mentioned previously, cultural factors do have a role in determining house form and function; however we must remember that the house is a socially constructed entity and yields a multitude of meanings for those who live, work, eat, and sleep within its walls.5 Traditionally the real difficulty is in distinguishing houses from non–houses archaeologically. If the built environment has ever changing form and function, how then does one determine a building is a house and not a temple, store room, or stable? In Near Eastern archaeology, location, size, and architectural style often separate the house from other constructions. Though not always, houses are frequently smaller, both in square footage and wall thickness, and exhibit “mundane” architectural styles free of decorational details or embellishments such as niches, molded brick, mosaic, or paint. They are located on the fringes of settlement outside the central areas or “high places.” Often the repetition of domestic architectural styles distinguishes the house from buildings that were created for a special function, and thus required a unique architectural floor plan.6 The cultural assemblage within the house largely comprises domestic activities materialized as spindle whorls, loom weights, and needles (cloth/clothing production), cooking pots, storage jars and grinders (food production), clay sickles, flint and obsidian blades (agricultural tools), and anthropomorphic and zoomorphic figurines (household religion or childrearing). Many non–portable features such as ovens, hearths, 5 Not to mention those who build, abandon, reuse, and eventually study the house (Bailey 1990, 24). Though many examples show that temple architecture likely developed from the basic house form (e.g., Eridu, Gawra). The repetition of temple forms is also visible in vernacular architecture (Habuba Kabira– Süd; see Kohlmeyer 1996). 6 72 small storage bins, and sleeping benches are also often considered staples of a typical house. Finally, the amount and grouping of these domestic objects are reflective of house– or industrial–levels of production. For example, a high concentration of obsidian debitage found in the corner of a courtyard could indicate small–scale lithic production (or at least lithic disposal patterns), but high concentrations of debitage found throughout the courtyard, along with all stages of production (e.g., raw materials, tools, finished products) could signal a workshop. Defining households is a difficult task specifically because archaeologists do not excavate households. As discussed previously, households can have a fluid composition that is affected by the organization of production, economic structures, or resource availability. Households are systems (Wilk 1989, 31) determined by the activities and relationships of their members and thus cannot be defined as bounded units.7 For this dissertation, I define households as activity groups that engage in multiple spheres of activity (Wilk and Netting 1984, 5), many of which overlap in space and time.8 Households are not necessarily kin–based or coresidential due to the fact that, especially in preliterate societies, it is difficult if not impossible to determine these aspects based on the available archaeological materials. For my investigation, households must be limited to the primary locus of activities: the house and its immediate surroundings, collectively 7 Because of this fluid, boundless nature of the household, some scholars feel the term itself is not useful (Wilk and Netting 1984) or that households are not a productive unit of analysis (Wong 1984). Others take households out of the realm of noun or something to be defined, and make them actively engaging as “householding” (Polanyi 1944) and “shareholding” (Netting 1993: 100). 8 A similar idea is proposed by Hirth (1993) where the primary unit of study is not households, but instead household series, acknowledging the successive household groups that develop and change over the course of several generations. This is an extension of Fortes’s (1958) developmental cycle and is further mirrored in Tringham’s (1995) treatment of the “use lives” of houses. 73 identified as house lots.9 However I acknowledge household groups can and often do conduct activities outside of this principal area, for example when performing agriculture or trade. The activities in which households engage are diverse and as described previously, include aspects of production, consumption, distribution, and socialization. Three of these could be characterized as economically based, thus making household activities the foundation for what we may consider a domestic economic system. This internal system governed by the actions of individuals is not only self–referential, but interacts with external economic and social networks of the larger community and even region (see below). Finally the term family is one that will be sparingly used, if at all, in this dissertation due in part to its immaterial nature. I define family as a self–identified, kin– based unit characterized by propinquity but not economics. The family is not necessarily an economic unit, though a family can make individual and group decisions about courses to take where economics are concerned, for example the selling of surplus agricultural lands, diversifying consumable food products, or pooling of resources between families. The problem with families is their identification in prehistoric contexts where specific textual documentation about kin dynamics is lacking.10 Even protohistoric texts of the Uruk IVa and III periods at Uruk–Warka are only valuable in an extramural way since their subject matter is confined to lexical lists, economic transactions, and basic accounting (Nissen 1986, Nissen et al. 1993). 9 The term house lots is primarily used in New World archaeology, specifically in reference to Mesoamerican residence units within settlements. A house lot is generally a large, often bounded, area comprised of a primary dwelling unit (the house), adjacent uncovered patio or open area, and garden zone (Alexander 1999; Deal 1985; Hayden and Cannon 1983; Manzanilla and Barba 1990). 10 Veenhof (1996, v) suggests that households, defined as a basic socioeconomic unit, can only be adequately studied on the basis of both archaeological and textual sources. This essentially discounts any use of the term household for studying preliterate societies. It is clear, based on my rendering of the term household and its anthropological implications, that I disagree with Veenhof in this respect. 74 Household Anthropology in Action The study of houses and household groups by archaeologists has been undertaken using several methodological means that, over the years, have become increasingly minute and contextually focused. This development for the application of household archaeology began with the study of activity areas or “loci at which particular human events occurred” (Kent 1984, 1) in houses to draw from the archaeological record traces of economic household production, distribution, and spatial usage. Susan Kent was especially pioneering in this effort, drawing heavily on another subfield, ethnoarchaeology, that was coalescing during the 1980s (see below). In her initial assessment, Kent (1984) tested three archaeological assumptions: 1) that activity areas could be identified through the patterning of artifacts11, 2) that most activity areas are gender–specific, and 3) that most activity areas are monofunctional.12 Through her ethnographic work in Navajo, Euroamerican and Spanish American families, and the subsequent application of these data to archaeological case studies, Kent effectively demonstrated that several factors play a role in artifact assemblage composition. These include types and materials of objects used—her example is durable, mass–produced objects such as found on historic sites—and animal disturbances such as dogs dragging away bones. These factors, along with climate, season, house type and size, influence the primary location of activity areas, but not the way they are used, which to Kent, can be recognized through predictable patterning. Activity areas are, furthermore, neither sex specific nor monofunctional when viewed cross–culturally (Kent 1984, 224–225). 11 A supplement to this is the assumption that artifacts are abandoned at their place of use (described as primary refuse by Schiffer 1972, 161). 12 See “Analyzing Household Activities” chapter section in Flannery 1976, 34–47. 75 That certain activities or behaviors performed by humans in the past leave material traces in the archaeological record was a key element in the development of activity area research, along with the study of human residue behavior (Gould 1980, 42) and the use of modern ethnographic analogy for examining uses of household space.13 The earliest and still most widely cited ethnographic works by Near Eastern archaeologists are those of Patty Jo Watson (1979) and Carol Kramer (1982) where both discussed every aspect of modern rural village life in western Iran, from population density to housing construction and waste disposal.14 This type of archaeological ethnography primarily served to aid in the identification of archaeological materials and has not been applied without criticism. Many scholars caution against one–to–one comparisons between past and present traditional societies since this assumes normalized patterns of domestic behavior that transcend temporal, cultural and spatial circumstances. They also construct a static past of human behaviors (Allison 1999, 2). Thus ethnographic data should be used as a tool, not an explanation, for archaeological inquiries much in the way that true ethnoarchaeology formulates and tests archaeologically oriented methods, models or hypotheses with ethnographic data (Hodder 1983; Kent 1987; Yellen 1977). Kent (1990, 127) attempts this by answering the question: why are some houses more segmented or partitioned than others? Her study, which uses the sociopolitical data drawn from the HRAF (Human Relations Area Files) of seventy–three different societies, is nestled within a broader look at the relationship 13 A short history of the development of ethnoarchaeology can be found in van der Kooij 2002. Hans Nissen (1968) and Frank Hole (1978) engaged in similar ethnographic work focusing on the relationship between sedentary communities and pastoral nomads. See more recent work by Kathryn Kamp (2000), Lee Horne (1994) and Jak Yakar (2000). There are also general ethnographies (such as Sweet 1960) that deal with rural communities in the Middle East, though these are not specifically for application to archaeological data. 14 76 between domestic architecture and the organization of space. Her direct correlation between increased segmentation in architecture and increased social complexity, however, draws on basic assumptions about the archaeological record; specifically that material culture is a direct reflection and passive byproduct of human actions in the past. This view differs from the more recent post–processual or interpretative approach in archaeology, which interprets material culture as active and meaningful elements of society. This view of an active material record is one that has further affected the development of household archaeology beginning in the 1990s. Many of these later developments were influenced by the bodily connection between house and individuals, which actually had its theoretical beginning in the 1960s and 1970s. The most influential work is that of Pierre Bourdieu who postulated that, especially in preliterate societies, inhabited space and specifically the house is “the principle locus for the objectification of generative schemes” (Bourdieu 1977, 89). Likened to a book, as individuals habitually move through, inhabit and relate with the physical space of the house, their bodies “read” the coded cultural messages embedded within the structure and the household social system, thus making them embodied spaces. The hierarchies, marked relationships between individuals, and internal physical/psychological divisions based on gender, age, and status found within the house reinforce the taxonomic principles underlying the greater society in which the household is situated. Phrased differently, the domestic space is the physical embodiment of the cultural order (Hanks 1990, 314). For Bourdieu (1977, 79; 1990) these encoded messages are the habitus, generally conceived of as universalizing rules in any society of how individuals should live, act, or behave. These conceptions are so unconscious and deeply embedded within the fabric of culture, it 77 makes an individual’s practices seem sensible or reasonable (i.e., the “right” way). It is through these embedded rules, ideas, and values that individuals give meaning to their social environment. The idea of embodied space was influential for later household archaeological studies (Hodder and Cessford 2004; Kuijt 2000; Tringham 1995). In particular, a critique of Claude Lévi–Strauss's influential “house societies”15 by Janet Carsten and Stephen Hugh–Jones (1995, 39) expands on the dynamic nature of the house and that houses, like people, have life cycles of birth, aging, and dying that can and should be observed. Following Bourdieu’s notion of the habitus, houses are an extension of people and as an institution, serve as the primary socializing agents. Other scholars examining the work of Lévi–Strauss highlight the importance of continuity in built space and that landscapes, dwellings, and even heirlooms are material embodiments of the continuity of the house (Joyce 2000; Tringham 2000). Yet continuity does not equate houses with static entities. Margaret Rodman (1992, 640) highlights the multilocality and multivocality of the ancient past to reinforce the idea of “place” as a politicized and cultural construct and not just a locale. Even landscapes can be imbued with mythical knowledge or history (Basso 1996) and house spaces have multiple meanings that are constructed spatially and psychologically. Most recently the incorporation of gender studies into examinations of past domestic behaviors and constructions have been influential for several household scholars including Rosemary Joyce, Ruth Tringham, Christine Hastorf , and Elizabeth Brumfiel (1991). Work by Henrietta Moore (1988) can be seen as one of the early 15 Inspired by the organization of noble houses during medieval period Europe, “house societies” are a specific social order that serves as a transition between kin–based and class–based groupings. See Lévi– Strauss 1979. 78 movements toward a more gendered look at the past. She highlights the tendency to lump “women's work” into that of general domestic labor has added to the invisibility of women and their important contribution to the household both economically and socially in the past.16 Penelope Allison (1999) and Julia Hendon (1996) have also been critical to the study of households by confronting the need for a more social approach to investigations of household production, especially approaches that are embodied, agent– centered, and concerned with understanding social identity. In their view, houses are not just neutral locations for activities, but a space where social relationships and identities are defined, created and emphasized through meaningful action (Hendon 2004, 274). As this section has shown, there are several methodologies by which households can be studied including ethnoarchaeology, activity area research, behavioral archaeology, and gendered studies. In chapter 3 I will add to this list more specific and minute methods. Yet a lingering question undoubtedly remains: why should one study households? What do they have to offer archaeologists? While the importance of household studies to examinations of the Uruk Phenomenon in particular is discussed below, I will only reinforce here the remarks made previously, that houses and households are embodied spaces that both exhibit and reinforce cultural rules, practices and beliefs. In short, they are a microcosm of the larger social group and their inclusion in any truly holistic investigations of social, cultural, political or economic developments within or between sociocultural groups is imperative. 16 Carol Meyers (2002, 2003) has similarly emphasized the undervaluing of women’s work by scholars investigating households in ancient Israel. 79 Household Archaeology in the Near East It is important at this point to discuss the ways in which household archaeology as a theoretical and methodological tool has been applied to archaeological contexts in the ancient Near East to serve as a backdrop for its use in studying the Uruk Phenomenon. The application of household archaeological investigations in Near Eastern contexts has lingered somewhat behind that of Mesoamerican and other American studies, with more theoretical emphasis being placed on large–scale economic and social systems, elite or royal participants in these systems, and general political history. That is not to say that early archaeological investigations in the eastern Mediterranean did not discuss aspects of private life, city planning, and domestic architecture (Contenau 1954; Frankfort 1950; Lampl 1968; Oppenheim 1977; Saggs 1965). In fact William Foxwell Albright was one of the earliest scholars to discuss the domestic structure of the ancient Israelite household and aspects of daily life throughout the Levant (Albright 1949) in a tradition that continues up to the present (King and Stager 2001; Schloen 2001). However a supreme focus on simply identifying cultural and ethnic groupings based on their domestic artifactual assemblages and categorizing house forms (e.g., “four–room house” or “courtyard house”) has generally directed the course of household studies in Near Eastern archaeology up until the beginning of the 1980s when researchers began to investigate what activities were happening inside those four walls. Still, as the examples listed below will show, there remains a general lack (with notable exceptions) in multiscalar approaches to household studies that bring to bear notions of depositional histories and how these affect activity areas, house lives of individual structures, 80 microanalysis of assemblages, and most importantly, how human actors can be associated and integrated into the study of households. The most prolific application of household archaeology in the ancient Near East is reserved for prehistoric periods. In particular the Neolithic period (10,000–7,000 BCE) has garnered the greatest concentration by scholars who are interested in the adoption of sedentary agricultural practices, how this affected cultural systems and worldviews and in turn, how this is manifest in the architectural remains. For example, Ian Kuijt has highlighted the relationship between social crowding17 and the construction of physical boundaries in Pre–Pottery Neolithic Jordan and Israel. These boundaries, such as enclosed domestic structures, were used to impede movement, restrict or control access and develop social barriers in interpersonal interaction (Kuijt 2000, 79). Likewise Trevor Watkins (1990) has argued that architectural changes reflect social changes at Qermez Dere, Iraq during a time of new subsistence strategies and sedentary lifestyles in the Epi– Paleolithic and the Neolithic periods (8500–7900 BCE). This transition manifested itself archaeologically through the exclusion of food processing activities within the dwelling, performance of labor–intensive cleaning, and the addition of symbolic fittings to buildings as paralleled at Çatalhöyük, Basta, ‘Ain Ghazal, and Çayönü. But there are also psychological shifts that accompanied the physical. Watkins argued the house was no longer viewed as simply shelter or the center of activities, but instead as the focus of family life and the generator of symbolic values—a home (Watkins 1990, 337). While these two studies are important for analyzing social change reflected in domestic architecture, they unfortunately do not explore the impact that post–depositional 17 Defined as tensions that occur when hunter–gatherers, horticulturalist, or agriculturalists remain in large aggregates for a long time (Cohen 1985, as cited in Kuijt 2000, 78). Social crowding can be seen as a result of population growth or density. 81 processes have on domestic artifact assemblages, variation between households, and the dynamic nature of house spaces when viewed diachronically. However at Pre–Pottery Neolithic 'Ain Ghazal excellent preservation and meticulous limestone plastering of interior floors have allowed the excavators to examine and trace renovation histories of individual houses (Banning 2003; Banning and Byrd 1981). By adopting Fortes’s (1958) developmental cycle of domestic groups, E.B. Banning and Brian Byrd suggested the reasons for variations in floor plans over the life span of the structures are due to remodeling of houses over the course of the developmental cycle of the household. These remodelings are the manifestation of responses to changes in the coresidential group brought about by multiple factors like changes in room function, subdivision of private property through inheritance, ideological purposes, or physical deterioration of the structure. While this example takes a diachronic view of Neolithic houses highlighting their impermanent layouts and uses, it only skims the surface of analyzing how household groups used the space on a day–to– day basis and the reciprocal relationship between these groups and their physical, spatial constraints. Changes in the social order affected the architecture, but how did the architecture affect the social order? A more holistic household investigation is that of the Burnt Village at Tell Sabi Abyad, Syria (Level 6, 6000 BCE) by Marc Verhoeven who examined spatial distribution of objects, depositional processes, and the function of spatial units. In this case, architecture was viewed not simply as physical constructions, but as social spaces in the Bourdieuian sense, built as culturally meaningful places by human agents in the past. By making this connection, Verhoeven is trying to bring us, “from excavated space to 82 prehistoric place” (1999, 13) to better understand how the various building types at the Burnt Village were created and used. His conclusions are that the circular tholoi were used for permanent residence and the adjacent rectangular structures served as storage facilities for permanent and nomadic groups. Echoing Kent (1990), Verhoeven believes extreme internal segmentation of rooms within the rectangular buildings signified use by multiple families or social groups. Furthermore the idea that these buildings were also used by nomadic populations are evident by the use of sealings (in a local distributional system), faunal remains that attest to seasonal pastoral movements, and that these large– scale communal storage units exceed household requirements. Finally an exceptional case of early household studies in the Near East is that by Michael Roaf at the Late ‘Ubaid site of Tell Madhhur, Iraq excavated as part of the Hamrin Dam Salvage Project (Roaf 1984, 1989). At the center of the site was a large house that had succumbed to a conflagration and subsequent deliberate infilling by the ancient inhabitants. These actions allowed for extraordinary preservation of the structure, where the walls were still standing 2 meters high with windows at the time of excavation. Roaf was able to not only record the complete plan of the house—characterized by a central rectangular room flanked by rows of smaller rooms—but also chart the various modifications that were made to the structure over the use–life of the building. By analyzing flow patterns, room sizes, and the spatial distribution of artifacts throughout the building, Roaf also discerned specific activity areas and room functions, such as cooking and eating sectors and storage and living rooms. Much of what Roaf found in the Madhhur house were items of “everyday domestic life” including unbaked clay vessels, spindle whorls, clay nail mullers, counters, bone tools, mace heads, grindstones, palettes, 83 pestles and chipped stone. Drawing from ethnographic parallels, Roaf was able to hypothesize on the social activities and social structures that could be accommodated by this new type of early architecture (the tripartite house) with implications for the structuring of family household life for millennia to come. While the depositional history of the Madhhur house may seem clear—a single, catastrophic destruction episode—Roaf’s own ethnographic observations highlight the problematic aspects of even pristine contexts. In particular, he witnessed the destruction by fire of a room in his own dig house whereby the walls were purposefully pushed down to help smother the flames and the heavy wooden roof beams were removed, lest they should fuel the fire (Roaf 1989, 101). The following day valuable and undamaged objects were collected from amongst the ashes. These types of activities, needless to say, would disrupt the artifact assemblage and spatial patterning of any archaeological context, as was noted by Roaf for Madhhur. Yet oddly this acknowledged contextual mixing of artifacts did not stop him from charting the distribution of ceramic types and small find categories to discern room function (Roaf 1989, 121). Household–based approaches are not restricted to the earliest periods of sedentary life in the Near East. Going beyond the traditional static architectural descriptions of “four–room house”–types in Iron Age Israel, James Hardin investigated the organization of daily life and activities from domestic contexts at the site of Tel Halif (Hardin 2001, 2004). Focusing exclusively on a single destroyed house, Hardin studied de facto refuse (Schiffer 1972) of macroartifacts and pattern densities of microartifacts (Rosen 1993 and below) to chart activity areas and reflect upon the economic and productive organization of both men and women within this particular household. His study is one of the few to 84 look specifically at archaeological, as opposed to purely textual (i.e., biblical), evidence for daily life in ancient Israel by examining household–level data. Another example is Elizabeth Stone who re–examined data from the site of Nippur (McCown and Haines 1967) to launch a deeper investigation into houses and households at the early second millennium BCE city (Stone 1981, 1987). Her analysis of architecture, artifact assemblages and textual sources in Areas TA and TB helped to establish the existence of neighborhoods within the city whose household structuring and life histories determined the long range social development of particular individual neighborhoods or quarters on a local scale and the city as a whole. In this case, analogy was utilized to link this ancient example with patterns of urban residence in Islamic cities of the modern Middle East such as Cairo, Damascus, Aleppo and Baghdad. This example of the fusion of textual sources and archaeology is important in that it shows the ability to reach the household and even individual (in this case, family) level in Mesopotamian cities and examine how the life histories of these families and households can affect local developmental patterns.18 As mentioned previously, there are exceptional examples of household archaeology being practiced in the Near East that incorporate multiscalar approaches, account for depositional histories, and attempt to include human agency interacting with the domestic environment. A primary example is Ian Hodder (1990, 1992, 1998) whose extensive work at the seventh to sixth millennia BCE site of Çatalhöyük in Turkey focuses on the relationship of humans to their natural (agrios) and built (domus) 18 One shortcoming of this study is that households and neighborhoods were examined with little regard to their place within the wider sociocultural context at Nippur (see Yoffee 1989). Stone has more recently explored broader issues of ancient urban planning through intensive survey and limited excavations at the southern Mesopotamian site of Mashkan–shapir, located thirty kilometers north of Nippur (Stone and Zimansky 2004). 85 environments. In short, houses become the vehicle by which wild animals and humans are domesticated. This is reflected at Çatalhöyük by the incorporation of symbols of danger—bones of vultures, foxes, and boars—into the permanent features and decorations within houses. According to Hodder (1992, 246), the bringing of wild elements into the realm of the house and including them as part of the overall domestic symbolism, provides reassurance of the human potential to control and tame nature. This is crucial as the village depends on the successful domestication of plants and animals in order to survive. The domestication of people derives in part from the burying of individuals below the house floors at Çatalhöyük. This practice emphasizes continuity across generations that simultaneously link people to the living family unit, the deceased, and the physical structure in which they all reside; a powerful relationship that creates a sense of “home.” Thus Neolithic peoples accepted the constraints of sedentary lifestyles and agricultural production because the institutions of house and home were believed to ensure continuity as well as protection against the various perceived dangers of the outside natural world (Hodder 1992, 250). On a more concrete level, work by Ruth Tringham and Mirjana Stevanovic, as part of the Berkeley Archaeologists at Çatalhöyük (BACH) team, seeks to understand not just the architectural features of houses or the spheres of activities undertaken by those who inhabited them, but to uncover the entire use–lives of these structures from construction and habitation to destruction and abandonment. Building off their highly meticulous excavation methods developed during previous work in the former Yugoslavia (Tringham et al. 1985, 1992), Tringham and Stevanovic carried out a focused investigation of a single 37 square meter house (CH Building 3) and surrounding 86 buildings at Çatalhöyük. Over seven years of painstaking work revealed every life stage of this particular house including five major phases, each with multiple subphases, which introduced change in the spatial configuration (Tringham 1997; Stevanovic 1997; Stevanovic and Tringham 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003). Throughout these phases they uncovered a range of floors, fire installations, platforms, post retrieval pits, bins and niches. The interior of the walls were painted and burials of children and adults were located beneath the floors. Residue of woven baskets, a domed clay oven and even the entire collapsed roof were excavated. Based on their findings from Building 3, the BACH team even constructed a replica Neolithic house as a form of experimental archaeology to arrive at a full experience of living in these types of dwellings. Directly relevance to the subject of Uruk Phenomenon discussed in this dissertation, Susan Pollock and her collaborators have examined economic systems at the 10 hectare Uruk mound of Abu Salabikh in the Nippur hinterland to challenge the belief that emerging state–level institutions in southern Mesopotamia had direct control over the production of staple goods at the beginning of the third millennium BCE.19 Using a combination of surface survey, surface scrape, and detailed excavation, Pollock was able to illustrate a pattern of widespread household production of ceramics and the manufacture and use of chipped stone tools across the entire community and not limited to specialist quarters or centrally administered facilities (Pollock 1987, 1990a, 2001; Pollock et al. 1991, 1996; Pope 1994). Apart from this multiscalar approach, a revolutionary application of micromorphology at Abu Salabikh, conducted by Wendy Matthews (1995a and chapter 3), allowed further interpretations regarding the preparation and laying of plaster floors, the origins and use of construction materials, the use of rugs 19 Johnson 1973, 1975, 1987; Nissen 1988; Wright and Johnson 1975. 87 and mats, and the variations in type and depth of floor occupational deposits. All these data combine to give a more detailed picture of domestic life during the late fourth millennium and how it fits into the broader scope of social and cultural changes that were occurring at this time. In general, investigations of households in the eastern Mediterranean and Near East have become more of a focus in the last twenty–five years as the importance of household–level economic and social systems are more widely seen as crucial factors in the overall development of complex political and economic systems. Yet the focus on primarily architectural elements associated with households remains in the scholarship. For example, Kay Kohlmeyer’s (1996) examination of houses at Habuba Kabira–Süd provides details about city planning and common house types at the site, but makes no mention of the artifacts found within the houses and how they reflect the usage of spaces within and between them. This information would have been not only enlightening but vital for this dissertation and any others wishing to uncover domestic lifeways during the Late Chalcolithic in greater Mesopotamia. Peter Pfälzner goes further by recovering activity areas and social organization through the study of artifact patterning in third millennium BCE households at Tall Bdēri (Pfälzner 1996). Though he makes a concerted effort to elucidate social structures on the household level, this is based on large assumptions, namely that such changes in building layout over successive phases are motivated primarily by shifts in function. He also postulates that extended family households can be detected simply by the presence of more that one hearth or grinding room within a domestic complex. Pfälzner does not take into account sociocultural factors that might influence the changing floor plans of a single 88 house, such as fluctuations in family structure, shifts in religious ideology, or changes in economic needs. As much as we would like to accurately calculate the population within any one household as Pfälzner does, this is simply not possible with square footage estimates from ethnographic data or, in the case of Bdēri, the number of permanent features associated with a domestic dwelling since these data are not cross–culturally valid. Other architectural reports by Frank Braemer (1982) and Olivier Aurenche (1981) have already been critiqued by P.M. Michèle Daviau (1993, 20–22) for their lack of discussion on associated artifact assemblages within domestic structures. However, I contend that even Daviau has not gone far enough in her own investigations of domestic structures in the southern Levant by not taking into account depositional processes and how these can affect activity areas within houses (Hardin 2001; Schiffer 1987). In fact, many of the ancient Near Eastern household studies discussed above do not account for various natural and cultural elements that affect the deposition of artifacts and thus the composition of the archaeological record. These include, but are not limited to, processes associated with destruction and/or abandonment, scavenging and squatter populations, erosion, and modern agricultural and construction activities (see chapter 3). As the examples I have presented above show, household archaeological studies are beginning to increase in number in Near Eastern archaeology although several fundamental issues remain, the most important of which involves scale. While I acknowledge that preservation and small sample size are limitations for Neolithic and ‘Ubaid period research, the investigations of these house and household examples remain too narrow. A strict focus on a particular house or household group at a site, while 89 informative is often not placed within the larger picture of socioeconomic trends that these domestic remains can reflect. Oftentimes household examinations also do not account for internal fluctuations or variation between household groups over time. Diachronic investigations are essential for gaining the entire picture of domestic life and organization. Most uses of household archaeological theory and methodology in the Near East are also heavily weighted toward prehistoric contexts where textual documentation is not available. Despite the claims of some that true household studies cannot be accomplished without textual sources (Veenhof 1996, v), I applaud the work of prehistorians to draw out the subtle nuances of ancient human behaviors, social structures, and cultural underpinnings based solely on archaeological materials. Yet as Stone, Hardin and others have shown, texts and household archaeological material can make a happy and insightful marriage. The use of household–based approaches for protohistoric and historic periods is greatly needed and can only improve our understanding of societies, like the Neo–Assyrian Empire for example, which have traditionally been analyzed through elite eyes.20 A final critique and the most important issue I see confronting those wishing to do household archaeology in the Near East is the route by which the archaeological record in houses was created and determined by natural and cultural processes. With some exceptions (Hardin 2001, 2004; Matthews 1995a), post–depositional processes are often overlooked in household investigations where there is an assumption that objects are excavated in their place of use. While this particular subject will be discussed in detail in 20 However, as a cautionary note, the overuse of texts in the study of households is possible especially when the archaeological record is made to “fit” the textual sources. 90 chapter 3, suffice to say this is a major issue when one attempts to locate the centers and types of activities in which households engaged derived from primary use contexts. The Domestic Mode of Production and Consumption Definitions and Uses Thus far I have outlined the basic theoretical underpinnings for household archaeology as a subdiscipline, tracing its intellectual and practical development and uses based on specific Near Eastern examples to answer the question of how one can study the household. While methodological issues are prevalent, forcing scholars to adjust their research strategies (see chapter 3), I contend the household remains a valid level of study based on the activities in which it engages, the most prominent for this discussion being production and consumption. Understanding the ways households produce, exchange and consume as part of a domestic economy is vital not only for distinguishing the basic structure of household groups, but also using this domestic mode of production and consumption (hereafter “DMPC”) as a diachronic window into larger sociocultural change. The seminal study on domestic modes of production is that of Sahlins (1972) who examined anthropological economic systems of hunter–gatherers and other “primitive societies.” He outlined the DMPC for family/kin–based units characterized by three primary and interconnected traits: 1) the sexual division of labor as the dominant form of economic specialization, 2) the use of elementary technology and “simple” tools on the household level and 3) the level of household production. According to Sahlins, 91 households are not usually self–sufficient because they are naturally underproductive.21 Thus the household system is not designed for surplus production or profits, but instead geared toward general livelihood. Because these three traits are systematically related and one cannot develop without the others, the households of archaic societies achieve a level of stasis that can only be overcome by external contradictions, specifically by the application of sociopolitical pressure (Sahlins 1972, 82). This summation of archaic level households considers them as a whole, a “black box” that disregards the actions and behaviors of individuals and groupings inside of it (Wilk 1989). This is echoed in the basic assumption by Sahlins (1972, 185–276) that members of a household act altruistically, their domestic behaviors governed by reciprocity and unselfish pooling of resources. Yet motivations are not always so benign or focused on the general positive gain of the household group. Aspects of social status, position on the developmental cycle, and power relations within and between households underlie the idea that these groups should not be viewed as static, monolithic entities, but instead as dynamic systems of social relations and practices. This is successfully accomplished by Richard Wilk and others who demonstrate through modern ethnographic examples decision–making within the household and how that affects the domestic economy. Wilk suggests, contra Sahlins, that equal pooling of household labor and resources may in fact increase, not decrease, production (Wilk 1989, 44). In this way the household group is seen as an active participant in a local economy, not passively adapting to changing environments. Such was the case for Late Chalcolithic households 21 Sahlins applies the work of A.V. Chayanov (1966), who studied Russian agriculture during the pre– Revolutionary period, to support this notion. “Chayanov’s Rule,” as expressed by Sahlins, states that, “intensity of labor in a system of domestic production for use varies inversely with the relative working capacity of the producing unit” (Sahlins 1972, 91). 92 at Kenan Tepe where a shift in domestic economy, specifically diet and food consumption, was accomplished to undermine increased centralization of resources (see chapters 4 and 5). This returns us to the definition of households based on a functional interpretation as producing/consuming agents in a domestic economy. Yet we must bear in mind that inside this black box is an interaction of structure and agency, larger social forms, and individual actions (Hendon 2004, 272). Thus households do not organize production, exchange, or respond to external conditions in the same way within any given society. Individuals interact within households and households in turn interact with the community at large. This interaction is based on any number of social or political elements that characterize complex societies, but it is important to note that this relationship between households and the larger community is in flux: households are not isolated from society, nor do they react passively to changes imposed from the outside.22 While the variety of elements affecting the ordering and actions of the domestic economy may seem irreconcilable to some, I however believe households are still a valid level of study because their economies are sensitive indicators of larger sociopolitical change. This has been attested archaeologically by a number of scholars as it pertains to production and consumption patterns of autonomous agricultural communities and their relationship with developing state–level societies. I offer two examples here to reinforce how shifts in domestic economies can reflect wider political changes and that these same economies can be the impetus for that change. My first example is Christine Hastorf (1990) and Terence D’Altroy (Hastorf and D’Altroy 2001) who have focused on the changes in everyday life for the Sausa (Xauxa) 22 As Sahlins (1972) would argue. See Hendon 1996, 47. 93 community of the central Andean highlands, in particular the impact of the Inka imperial economy on local Sausa food production and consumption. By examining paleoethnobotanical data derived from household floors and stable isotope data from human bones, Hastorf (1990) was able to chart the changes in agricultural crop production and diet/consumption between the periods in which the Sausa were sociopolitically independent and later when they were a part of the Inka Empire. A primary focus on, and clear increase in, the production and consumption of maize provide evidence that the Inka state purposefully intervened in household–level economies by forcing the reorganization of labor to accommodate tax levies and the widening of access to this resource in order to “level the field” of regional political elites. However these same data also suggest that other aspects of the household economy—kinship bases, technologies, and other aspects of subsistence production—remained relatively unchanged during imperial rule. This interruption of the domestic economy can thus be interpreted as an indicator for some of the motivations behind the rise and expansion of the Inka state, namely the acquisition and exploitation of human (labor) and agricultural (staple crop) resources. My second example is Patricia Wattenmaker (1994a, 1994b, 1998) who has demonstrated the relationship between household economies and the state at Kurban Höyük in Upper Mesopotamia during the late third millennium BCE. She successfully identified a shift in household–level consumption patterns that mirrored the political reorganization of the city during this time. Households became more reliant on specialist–made cloth and ceramics, particularly serving vessels, while retaining their use of internally produced, handmade cooking pots and stone tools. This reliance on products 94 made by specialists was not a result of increased tributary demands made by burgeoning elites that disrupted household–level production, but was instead an indirect result of political centralization at Kurban. This was reflected in the nature of specialist products selected by the households: tableware ceramics. The selection of serving vessels, with their high degree of social visibility, showed that nonelite domestic groups were actively involved in creating the social system in which elites were vying for status. This is because the use of prestige goods to verify rank is only effective if there is some recognition of the goods as symbolizing prestige and if there is a significant demand for them (Wattenmaker 1994b, 111). This symbolizing and demand was thus based in the household, created and determined by nonelites. Other scholars have similarly examined this relationship between specialized production of goods and domestic economies, and how it has played a role in the development of complex societies in terms of control over the production of staple goods (Pollock et al. 1996) and weaving technologies (McCorriston 1997). These case studies attest to the established importance of domestic economies and their interconnected relationship with community and regional systems of trade, exchange, production and consumption—what I call political economy. In studies of the Uruk Phenomenon, the domestic economy has been severely overlooked in favor of top– down approaches that place control of resources and labor in the hands of small elite factions or specialized trading guilds that monitored the flow of goods, all systems that are essentially extramural to the household. If the basis for the Uruk Phenomenon is economic, that is, motivated by resource procurement strategies and subjugation of the periphery through a colonial system (Algaze 1993 and chapter 1), this radical change in 95 the sociopolitical climate will be visible in the domestic economy, that is the daily production and consumption activities of households, of communities incorporated into this new system. A handful of researchers have begun to examine changes effected by the larger political economy of Uruk on household–level production (in particular Keith 1998), however these studies are often limited by the passive nature in which the domestic economy is framed. Under these new conditions, one could assume a shift in political obligations and restructuring of household labor to meet new economic demands. However individual members of the household can also make these internal adjustments or alter their daily actions to accomplish their own political ends and not simply to accommodate the needs of external elites. People can also work both sides, operating on the level of the domestic and political economy. I assert that domestic production is both affected by external pressures (as shown by Hastorf) and effects changes on the community and even regional level by several means including product selection, labor pooling and organization (as shown by Wattenmaker). In studying the Uruk Phenomenon, we must examine the ways in which the domestic economy was transformed by a shift in political economy as well as how the domestic economy helped govern the nature of that larger economy. DMPC and the Uruk Phenomenon: Applications and Implications The domestic mode of production and consumption as a sensitive indicator of socioeconomic change seems an ideal window through which to analyze the Uruk Phenomenon as it relates to systems of interactions and cultural developments and at 96 what social level these processes took place. Archaeological evidence from on–going research in the periphery areas of southern Mesopotamia—north Syria and southeast Turkey specifically—is causing much of the scholarly community to acknowledge that the system of trade and interaction that characterizes the Uruk Phenomenon is much more complex than previously envisioned and, more importantly, not the same in all areas. That is to say, the relationships between northern and southern Mesopotamia are pluralistic and dynamic. This notion, however, is typically based not on the examination of Late Uruk households, but administrative and religious contexts. Thus it is assumed that this trading network was governed by only elite groups of people who oversaw the specialization and centralization of production and distribution. The need for an alternative dataset and fresh point of view drawn from the household level is obvious and furthermore substantiated by scholars such as Susan Pollock and her colleagues at Abu Salabikh who are foundational examples of the success of household–level investigations. Household studies such as this dissertation that specifically look at how, or if, this trade affected the private sector, offers an entirely new window into the character of the Uruk Phenomenon and challenges our original assumptions about the nature of this interaction. Because the domestic economy is a sensitive indicator of larger sociopolitical change, we can use household data to support or possibly disprove the economic stimulus behind the Uruk Phenomenon as proposed by Algaze (1993). For example, a radical shift in the domestic economies of indigenous populations could signify a reorganization of labor and production schedules to accommodate newly established trading colonies or the demands of local burgeoning elites. The increased production or consumption of specific 97 goods or crafts, like semiprecious stones or metals, could also signal this shift in the domestic economy and, depending on the products in question, highlight the motivations. Likewise, a consistent trend in the domestic economy of indigenous households over a proven span of pre–Uruk and Uruk contact phases could highlight the fact that interregional exchange during this time was in fact completely governed by the elite or specialist manufacturers and traders, and did not transform the daily lives of individual nonelite households. While these scenarios do not disprove that a trading network was established for the extraction of natural resources for use in the south, they do shed light on the organization of this trade and interaction, supporting either separate and centralized colonies and trading outposts or a broad–based system that incorporated both the domestic and community economies. Conclusion In this chapter I have presented the theoretical foundation and methodological aspects of household archaeology to show the primacy households should have in studying ancient societies. Households are defined as activity groups that can engage in multiple spheres of overlapping activities in space and time and are physically anchored to the house and its immediate surroundings, collectively identified as the house lot. Households and the activities in which they engaged can and should be studied through several lines of evidence including ethnoarchaeology, activity area research, behavioral archaeology and architectural studies. In the several Near Eastern household studies I discussed, among the most resolute issues include the need for diachronic analyses to account for fluctuations within and between households over time, along with the 98 recognition that depositional and post–depositional processes drastically affect domestic archaeological assemblages. More minute methods of household archaeology such as microdebris analysis and micromorphology are two answers to these lingering problems that will be discussed in the following chapter. Why are households a worthwhile subject of archaeological inquiry? Houses and households are embodied spaces that both exhibit and reinforce cultural rules, practices and beliefs. In short, the domestic space is the physical embodiment of the cultural order, but they are also places where social relationships and identities are defined, created and emphasized through meaningful action by human actors. These actions or activities in which households engage are diverse and often include aspects of production, consumption, distribution, and socialization. The first three of these aspects could be characterized as economically based, thus making household activities the foundation for a domestic economic system. This domestic mode of production and consumption (DMPC) is recoverable archaeologically and most successfully distinguished through the combination and analysis of multiple lines of evidence that can include architecture, faunal and floral datasets, lithic assemblages, ceramics, and ground stone (see chapters 4 and 5). Much of these types of evidence have already been analyzed and presented from Late Chalcolithic household contexts (see chapter 1, appendix and Stein et al. 1996a; Pollock et al. 1996) however, in many ways, they remain unsynthesized in terms of using these data to reconstruct the DMPC for these local fourth millennium communities and in turn, the broader region. That is because apart from determining the nature, motivation and structure of household groups, the DMPC also interacts with, and serves as a reflection 99 of, external economic and social networks. These characteristics have many implications for the study of the Uruk Phenomenon which, as discussed in chapter 1, is argued to be economically based. Thus it is imperative that household–level analyses in general, and domestic economic systems in particular, be included within examinations of the Uruk Phenomenon to offer a more holistic approach to the nature and mechanisms for trade and interaction in fourth millennium BCE Mesopotamia. The ways in which household– level production and consumption was transformed, either directly or indirectly, by shifts in local economies provide a unique avenue by which to study what the primary items of trade were, how the system(s) was organized, and who benefited from these interactions. 100 CHAPTER 3: MICRODEBRIS ANALYSIS AT KENAN TEPE In chapter 2 I solidified the role that household archaeology can play as an appropriate and vital method to incorporate more detailed resolutions of analysis into examinations of local Late Chalcolithic and Uruk households that include the domestic along with public, religious and political spheres. Exploring what households do in terms of production, consumption and distribution can be studied through domestic artifact patterning and the use of ethnoarchaeological analogy. However, as discussed previously, these approaches have particular limitations, the most troublesome being depositional processes. Thankfully these can be combated through a process referred to as microarchaeology, which provides an even finer resolution of data that contributes to a study of the domestic economy. Yet how exactly does the analysis of microdebris help us understand the DMPC of Late Chalcolithic households? In this chapter I will answer this question first by presenting the theoretical and methodological foundations of microarchaeology with particular attention paid to how it has been applied to Near Eastern contexts. Then I outline the methods used for recovering microdata from Kenan Tepe, a Late Chalcolithic village located in the heart of the upper Tigris River valley.1 In chapters 4 and 5, Kenan Tepe will serve as a case study in which to establish and test diachronic changes to the DMPC and how it reflects larger sociocultural changes supposedly ushered in by the Uruk Phenomenon. 1 The geography and settlement history of Kenan Tepe are detailed in chapter 4. 101 Microarchaeology Theoretical Foundations Microarchaeology is the study of residues of human behaviors on a microscale through the recovery and interpretation of small artifacts, sediments, or trace materials. This methodology developed out of activity area research as a specialized way to uncover primary use contexts within and between domestic spaces. As a blanket term, microarchaeology includes specialized methods that vary depending on intensity, the most well known being microdebris analysis, micromorphology, soil chemistry, and microfloral studies (Cessford 2003; Manzanilla and Barba 1990; Matthews et al. 1997; Middleton and Price 1996; Özbal 2006; Özbal et al. 2004; Rainville 2005; Rosen 1989, 2007). Though these methods are often utilized and presented in the literature separately, a combination of data derived from all three can complement any traditional analysis of household studies provided appropriate time, money and resources are available. Microdebris analysis, also known as micro–refuse or heavy–residue analysis, is the examination of minute pieces of stone, bone, ceramics and other artifacts that have become embedded within the sediment matrix of archaeological loci. These microartifacts range in size from 90 to 0.25 millimeters depending on the researcher and are preserved and subsequently recovered whole or in various stages of fragmentation. Microartifacts enter the archaeological record through trampling, loss, lack of detection during cleaning episodes, or through subtractive technologies like chert knapping where microdebitage is produced. Primary investigations using this method have focused on surfaces, particularly domestic floors, since these are the locations where trampling activities can most easily incorporate microartifacts into the substrate. It is now widely 102 recognized, however, that sampling of ovens, pits, middens, and burials are crucial for the proper interpretation of microartifact densities as compared across an archaeological site (Cessford 2003; Özbal et al. 2004; Rainville 2005). What these microartifacts represent hinges on the hypothesis that natural and cultural formation processes of the archaeological record affect the presence, patterning, and preservation of traditional artifacts. For example, slow abandonment of a site will remove most, if not all, useable and valuable artifacts (e.g., tools, weapons, ceramics) from their location of use. Likewise meticulous cleaning can all but erase evidence for activities such as tool making or cooking by the removal of debris from the primary locus of use and depositing of it in secondary contexts. Because of their size, microartifacts are capable of being undetected in the cleaning process or being immediately incorporated into the surface matrix of a feature by “slipping through the cracks,” thus remaining as primary refuse (Schiffer 1987, 18 and below) resulting from an activity, practice or behavior. Small size also prevents microartifacts from succumbing to the effects of post– depositional processes like erosion and bioturbation that can further alter the artifact patterning on most archaeological sites. As a method, microdebris analysis has its origins in the earliest examinations of California shell mounds where it was recognized that smaller fraction artifacts may not necessarily be represented in the larger fractions and should thus be recorded separately (Gifford 1916). Grain size separation techniques and the quantitative analysis of material residues were later conducted on Native American sites in California as a prelude to later microartifact and geoarchaeological research (Cook and Treganza 1947). By the 1970s, researchers were beginning to examine natural and cultural formation processes evident 103 at archaeological sites especially as they relate to the deposition and preservation of macroartifacts (Ascher 1968; Baker 1978; Fehon and Scholtz 1978; Kirkby and Kirkby 1976; Schiffer 1972; Schiffer and Rathje 1973; Villa 1982). Ethnoarchaeology played a vital role in these examinations as a way to chart cultural actions, behaviors, and practices and how these are manifest physically in the archaeological record (Gifford 1978; Gould 1980; Stanislawski 1965). It was observed that the spatial distribution of macroartifacts could be used to recover activity areas and determine the functionality of spaces (Binford 1973; Bullard 1970; Whallon 1973). An important example is the study of Nunamiut Eskimo of north central Alaska by Lewis Binford (1978) who noted a relationship between human behaviors and the structured consequences of these behaviors in terms of artifact distribution and spatial segregation of activities. He also found that particular behaviors, such as trash disposal or butchering practices, will alter the types and condition of artifacts produced and their spatial patterning. At the same time, researchers also began to examine natural formation processes and the sedimentology of archaeological sites to study aspects of paleoenvironments, the formation of tells, and the ways in which non–cultural formation processes affect artifact patterning and preservation (Butzer 1982; Hassan 1978). In particular, Michael Schiffer (1972; Schiffer and Rathje 1973) was instrumental in challenging the assumption that spatial patterning of archaeological remains reflects the direct spatial patterning of past activities. He proposed that the spatial, quantitative, and associational attributes of material objects uncovered in the archaeological record are a function of both depositional processes and behaviors. Natural, or non–cultural, formation processes (Schiffer’s n–transforms) including wind and water erosion, bioturbation, and soil 104 chemical composition all combine to inherently bias the preservation and distribution of artifacts. Cultural formation processes or c–transforms can be even more destructive because they do not have predictable physical effects like natural processes.2 As described by Schiffer (1972), these c–transforms are determined by five processes through which all elements travel during their use–life in a cultural system, what he calls systemic context. These processes—procurement, manufacture, use, maintenance, and discard—are not part of a unilinear system so that objects do not necessarily pass through each phase in order. For example, objects that are introduced via trade or exchange often skip the manufacturing process and go straight to use. The way in which people abandon a site can also alter the ratios of objects in various stages of their use–life and the spatial distribution of those objects (Ascher 1968; Schiffer 1972). Macroartifacts recovered in the archaeological record together represent all stages of manufacture, use or discard and can also be an incomplete assemblage based on the conditions that mandated desertion of the location. These concepts were fundamental for later studies by Schiffer (1983, 1987) where he demonstrated that most macroartifacts recovered by archaeologists are not primary refuse, or artifacts that have been discarded at their location of use, but instead secondary or de facto refuse where objects have been removed and deposited away from their original loci of use or reached their archaeological context without the performance of discard activities respectively. Naturally this is a problem for archaeologists trying to interpret the distribution of objects inside a domestic structure for example. An experiment dealing with litter disposal on the University of Arizona campus conducted by Judith McKellar (1983) seemed to offer a 2 Though an underlying tenant of enthoarchaeological research is that human behaviors and practices can leave predictable pattering of artifacts in the archaeological record. 105 solution. Her results were that small artifacts tend to be discarded as primary refuse in activity areas. This research laid the groundwork for further development and refinement of the methodology, most notably in testing the reliability of microartifacts and microdebris analysis as a viable procedure for uncovering primary use contexts and activity areas (DeBoer 1983; Dunnell and Stein 1989; Metcalfe and Heath 1990; Newcomer and Sieveking 1980; Nielsen 1991; Schiffer 1983, 1987; Sherwood and Ousley 1995; Stein and Teltser 1989). K. R. Fladmark (1982) was one of the earliest to discuss microartifacts in regard to stone flake residue or microdebitage as a byproduct of reductive tool making activities. A similar study by Kathleen Hull (1987) at the stone circle site of Bow Bottom in the Northern Plains found that lithic activity areas can be identified by the clustering of microdebitage with or without a corresponding high density of macrodebitage. Michael Deal (1985) used the distribution of ceramics in two modern Tzeltal Maya communities to showcase the differential use, disposal, and reuse patterns for this visible microartifact category. Warren DeBoer (1983) found that light or small objects are also less likely to be obstructions to interfere with future utilization of the discard space. Finally Duncan Metcalfe and Kathleen Heath (1990) demonstrated the dramatic patterning in the types and frequencies of microartifacts within and between rooms in structures at the Nawthis Village in central Utah. During this time of methodological development there are also challenges to the notion that microartifact concentrations are simply markers of prehistoric production activity locations. For example two studies found daub was introduced into microsamples through house wall collapse (Sherwood et al. 1995, 453) 106 and differential displacement of all artifact categories and sizes occurred with various levels of trampling (Nielsen 1991). Micromorphology is another method of microarchaeological analysis that uses resin–filled thin sections of sediment samples derived from occupational surfaces to distinguish and evaluate activity areas, construction episodes, and differential use of space. The history of this technique dates to soil studies of the 1930s and to archaeological studies of palaeosols during the 1950s. After further technological and methodological developments in the 1970s and 1980s, micromorphology became a primary technique for analyzing cave deposits (Courty et al. 1991; Goldberg and Sherwood 1994) as well as settlements, specifically trampling and compaction in streets (Courty et al. 1989). The method can be seen as an extension of larger soil and formation process studies that take into account the ways in which floors and occupational surfaces are constructed through human agency as well as natural factors (Gé et al. 1993; Goldberg and Whitbread 1993). The most well known application of this technique in Near Eastern contexts has been by Wendy Matthews at a variety of sites, specifically Abu Salabikh, Tell Brak, and Çatalhöyük (discussed below). Soil chemistry and characterization studies have also been successfully employed at archaeological sites in order to recover distinctive chemical residues that particular activities can leave behind (Cook and Heizer 1965; Manzanilla and Barba 1990; Middleton and Price 1996). These methods utilize everything from simple soil acidity or pH level tests to increasingly complex techniques like inductively coupled plasma– atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP/AES) for multi–element characterization. Finally, phytolith and pollen studies can be seen as additional microarchaeological techniques 107 representing the microflora that can derive from occupational surfaces (Albert et al. 2008, Rosen 1992, 2007). Practical Applications in Near Eastern Archaeology The application of microarchaeological methods and techniques in Near Eastern archaeology is slowly gaining momentum as scholars begin to focus more intently on household–level aspects of ancient culture. Microarchaeology as a technique has been used for studying not only activity areas and the uses of space within and between structures, but also the changing functionality of rooms, choices in construction materials, and the geomorphology of tell sites themselves. However, as a yet unstandardized approach, the techniques utilized vary by researcher both in method and scope. First and foremost, the early work of Arlene Rosen has been foundational for that of later microarchaeologists. She reiterated the notion upheld by Schiffer and others that artifacts uncovered on any given surface cannot be assumed to be the primary remains of pre–abandonment activities. Most likely they have been affected by cleaning episodes, abandonment activities or some kind of post–depositional processes that altered their spatial patterning through cultural and natural forces. Microartifacts, defined by Rosen as less than 3 centimeters in diameter in size, have the ability to remain at the locus of activity because they are more subject to loss and can easily be incorporated into a surface substrate (Rosen 1986, 92). Rosen’s method involved a stratified random sampling grid system (Redman 1987) where 20 centimeter squares of sediment were cut 2 centimeters deep and then removed in toto from floors, courtyards, and streets (Rosen 1989, 1991). Mud bricks and 108 pits were also sampled for purposes of comparison. Samples were wet sieved through a 0.25 millimeter mesh to remove fine sand, silt, and clay. Once dried, the remaining clean sample was separated into size fractions (5, 2, 1, 0.50, and 0.25 millimeter). Once the weight and volume were recorded from each size fraction, the sample was examined through a binocular stereomicroscope. Artifact percentages were estimated with the aid of visual percentage charts (Bullock et al. 1985, fig. 24). Rosen applied this methodology to a number of sites in the southern Levant including Tel Halif (Lahav) and Tel Miqne– Ekron where she was able to pinpoint activity areas based on the relative frequencies of microartifacts, present evidence of dumping episodes in streets, and compare the courtyards of elite and nonelite residences. She was also interested in the general depositional processes that contributed to the creation of specific features, such as a large ash deposit at Tel Halif (Rosen 1993), or tell sites in general (Rosen 1986). These techniques and procedures have since been adopted by other microarchaeologists including Lynn Rainville, who has analyzed microartifact distributions at Titriş Höyük, Kazane, Tilbes, Tell Brak and Ziyaret Tepe (Algaze et al. 2001; Rainville 2000, 2005). Instead of a grid system, Rainville collected multiple 50 centimeters square samples from each excavated surface (i.e., floors, alleyways) as well as permanent features (i.e., ovens, benches, platforms), burials, and middens. Mud bricks and sterile soil were also sampled to account for the possibility that the breakdown of bricks added extra secondary refuse to the sample that would not be evidence for primary refuse (Rosen 1989, 568). Unlike Rosen who used wet sieving, Rainville processed samples in a mechanical float machine where a small amount of phosphate was added to the water to dissolve any remnant clay and silt after which the samples were rinsed 109 through a 1 millimeter mesh. After floatation, the remaining heavy residue was sifted through four screens into size fractions (6.3, 4.75, 2, and 1 millimeter). Rainville defined microartifacts as less than 10 millimeters in size, which is notably smaller than Rosen’s 3 centimeters maximum size threshold, and sorting them into material categories using magnifying binoculars instead of a stereomicroscope. Weight and count densities by material category were then used by Rainville for cluster and correlation analysis using SPSS and JMP statistical software that revealed patterning in the density of microartifacts, specifically relative high and low density areas of debris types and their relationship to macrodebris distribution. The ultimate goal and contribution of Rainville’s work is the establishment of correlations between microartifacts and loci such that certain locus types share similar signatures based on density of microceramics. These signatures, when complemented with macroartifact distributions and general archaeological observations, transform microdebris into a predictive, not simply descriptive, tool. For example after sampling fourteen different types of loci such as interior surfaces, hearths, and burials at Titriş Höyük, Rainville found that street contexts were highest in microceramic debris density followed by food preparation areas. Construction materials, supra–floors, and sterile soil were lowest (Algaze et al. 2001; Rainville 2005). At Tell Brak the plethora of microartifacts in trash–filled drains and scarcity in burial fills provided the baseline for numerical high and low densities that was used to determine indoor and outdoor spaces and activity areas associated with domestic structures at the site (Emberling and McDonald 2003, 64). At Ziyaret Tepe, Rainville has combined microdebris with micromorphological analyses and soil chemistry to arrive at a better understanding of 110 daily practices and consumption and production habits among and between households (Matney and Rainville 2005, 38; Matney et al. 2007). A further derivation of Rosen’s initial methodology was adopted by Rana Özbal who examined households through the lens of microdebris analysis at Tell Kurdu (Özbal et al. 2004; Yener et al. 2000).3 Özbal also sampled indoor and outdoor surfaces, supra– floor deposits, trash pits, walls, fill deposits and fire installations, processing them by wet sieving through a 1 millimeter mesh similar to Rosen (Özbal et al. 2004, 50). However, as with Rainville, the dry samples were size sorted through four screens (6, 4, 2 and 1 millimeter) and sorted using x10 magnification into five main categories: pottery, bone, lithics, shell and “other”—this final group being reserved for small finds like beads, bitumen, and sealing fragments. The primary index for Özbal’s calculations is count ratios only (counts for each size category per liter), which is applicable to her investigations of foot traffic and movement patterns reflected in fragmentation of microartifacts, especially ceramics. Densities are also charted across spaces and aid in the identification of more ephemeral activities that lack architectural correlates or permanent features.4 Finally the most recent work by Craig Cessford at Çatalhöyük will undoubtedly have an instrumental impact on the method of microdebris analysis and the types of information we can derive from these specific datasets in the future. Like previous microarchaeologists, Cessford (2003, 2005) has consistently sampled all contexts within 3 Tell Kurdu is a 15 hectare double mound located in the Amuq Valley in the province of Hatay, Turkey. The site boasts Early and Middle Chalcolithic levels (Amuq phases C–E; sixth/fifth millennium) with dense architecture, storage facilities, industrial areas, and administrative sophistication in the form of tokens, stamp seals, and clay sealings. 4 Özbal’s primary example is a “bread/food preparation” area at Kurdu, first though to be monofunctional. The microartifactual data demonstrated that a variety of activities took place in this locus like shell working, bead making and lithic tool production (Yener et al. 2000, 54). 111 his research areas (North, South, and KOPAL areas) including middens, pits, floors, ovens, and bins. Although Cessford has not been clear about how samples are collected or the average volume of each sample, he has processed them in much the same way as Rainville through flotation and size sorting (greater than 4, 2, and 1 millimeter). Fifty–six different material microartifact types exhibit the breadth of materials recoverable on the microlevel that far exceed the more limited typologies of other researchers. Cessford has also adopted many of the statistical methods, used for example by paleoethnobotanists, which include calculations of ubiquity, presence, diversity, and density.5 In general, these different analytical approaches to the data highlight certain trends in context characterization that could be said to represent “signatures” much in the way of Rainville. For example, Cessford found that most midden deposits have a significantly higher level of diversity in artifact categories than occupational fill (Cessford 2005, 51). Most importantly, Cessford’s work has brought into focus the very real limitations of microdebris analysis while at the same time questioning the underlying assumptions of the methodology. In particular he addresses the fact that samples from plastered walls at Çatalhöyük contained much of the same materials such as chipped stone and tiny fragments of animal bone found in plastered floors at the site. This indicates construction materials were drawn from sources that already contained microartifacts and that these cannot be considered primary or in situ refuse indicating discreet loci of activities. Cessford uncovered similar issues when calculating and comparing density percentages 5 Ubiquity is the percentage of the presence of material categories as they relate to the total number of samples. For example, animal bone and chipped stone were found to be quite ubiquitous as they occurred in over 50% of samples at any given size fraction, and in 80% of samples overall (Cessford 2005: 47). Presence is a binary–type analysis in which one looks for whether or not a particular material type is present (preserved or identifiable) within any given sample. Diversity is a simple count of the total number of material types found in each sample regardless of fraction size. Density, in this analysis, is a simple ratio of total material type weight divided by the total volume of the original sample. 112 between rooms or structures. He noted that the link between microartifact density and in situ activities for surface contexts is problematic since floors in various rooms of a structure can be replaced at different points in time (Cessford 2005, 57). Thus a higher density of artifacts in a floor could simply represent a longer temporal duration of that surface. He also disagrees with Rainville and others that the level of naturally occurring microartifacts within floors can be established and quantified through the sampling of walls, especially mud bricks. However this “background noise” assumes spatial and temporal consistency, something that is lacking at Çatalhöyük and most likely other sites as different floors are created with different materials at different times. Density analysis is however still particularly useful in midden and fill contexts and for sampling short– lived features such as shallow scoops and stake holes (Cessford 2003). The methods introduced by Rosen and developed by other microarchaeologists carry both positive and negative aspects. The wet sieving technique used by Rosen and Özbal to process microartifact samples essentially compromises the collection of botanical materials within the soil matrix by putting undue water pressure on the delicate seeds and charred wood that are more readily and successfully collected through traditional flotation techniques. That is not to say that botanical remains cannot be recovered from microsamples, however it is important to treat these two types of data— microartifacts and botanicals—in different ways. Thus, as with Rainville and Cessford, I have chosen to adopt the flotation technique in order to process microarchaeological samples (discussed below). Another issue is the maximum size threshold for defining a microartifact. If too high, the very essence of a microartifact as a minute physical trace of past activities able 113 to be incorporated within the sediment matrix of archaeological loci and thus not removed from the primary location of said activity will be negated. However, by setting the minimum size too low, one runs the risk of not being able to confidently identify the material category of the microartifact, while at the same time doubling or even tripling laboratory processing time. While perhaps a standardized size measurement for microartifacts may never be agreed upon, I have adopted Rainville’s more conservative size limits of less than 10 millimeters but greater than 1 millimeter to necessitate well– paced processing and accurate identification. Where there seems to be the greatest division in methodology among researchers is sorting and identification of microartifacts. While the use of stereomicroscopes surely guarantees a higher level of accuracy and less eye strain, binocular visors allow for faster processing, more portability, and are significantly less expensive. Still the utility of visual percentage charts, as shown by Rosen, can perhaps decrease sorting time when using a stereomicroscope. However relying solely on percentage is, in essence, a derivative of count density that unfortunately causes the exclusion of important weight data. In the end, I believe that microartifact processing time and accuracy in identification are very much dependent on the skill of individual researchers, which is why I have chosen to use a combination of binocular visor (for the larger size fractions) and a stereomicroscope (for the smaller size fractions). While this dissertation relies solely on microdebris analysis for reasons discussed below, there are other major methods by which microarchaeology is practiced. Micromorphology has been one of the research specializations of Wendy Matthews who studied the spatial and temporal variation in site formation processes at Abu Salabikh, 114 Tell Brak, and Çatalhöyük. By closely examining the microstratigraphy of floors and occupation debris, she has also been able to highlight activity areas, changes in space use, and micromorphological characterizations of different context types within and outside of buildings much in the same way that Rainville has distinguished locus signatures through microdebris analysis. While Matthews’s methodology has been outlined in a number of publications (Matthews 1995b, 2001a, 2001b, 2003, 2005; Matthews and Postgate 1994), I will summarize it here briefly. Block samples of undisturbed occupation sequences are cut out of the section face of excavation units and wrapped tightly in tissue and tape for transport. In the laboratory, the block samples are impregnated with a crystic polyester resin that requires six weeks to harden. Then the sample is ground and polished into large thin sections measuring 13.5 by 6.5 centimeters and 25 to 30 µm in thickness. The thin sections are examined using a field polarizing macroscope (at magnifications of x5.3 to x70) and polarizing microscope (at x40 to x400). Matthews uses area percentage charts (Bullock et al. 1985, fig. 24) to record the density of botanical and other remains in the thin sections. Matthews’s initial work at Abu Salabikh used a combination of microdebris and micromorphological techniques (Matthews 1995a; Matthews and Postgate 1994). Whole earth samples averaging 60 liters in volume were taken from various contexts so that microartifacts could be retrieved from the heavy fraction.6 These samples first underwent soaking and were then wet sieved through a 3.5 millimeter mesh. For each sample, a 1 millimeter mesh was used on the first 10 liters of soil to catch fish bones and other small, fragile remains. Matthews examined two attributes when analyzing the final microartifact 6 Botanical samples were collected from the same contexts in which the microdebris samples were collected. Botanical remains were retrieved through a standard flotation process (Matthews and Postgate 1994) 115 data: abundance, or the quantity of each class of material per liter of excavated earth, and fragmentation. When combining the results of count and weight ratios with data derived from microstratigraphy analysis, Matthews was able to distinguish patterns of trampling, placement of mats or rugs, and the process and technology by which floors were created and laid down at the site. Similar results derived from her work at Tell Brak where Matthews characterized micromorphological signatures for various discreet contexts (Matthews 2001a, 2001b, 2003). For example, she found that unenclosed or unroofed areas outside of structures contained no or poorly prepared surfaces with thick accumulations of organic and refuse– rich deposits (Matthews 2003, 387). Not surprisingly, these areas were also subject to greater post–depositional processes as evidenced by salt lenses from evaporating rain water and organic staining around faunal remains. Within structures, unroofed sectors like inner courtyards had no prepared surfaces and deposits that were rich in domestic debris such as ash from ovens or discards from sweeping. Areas of food preparation and cooking had poorly prepared floors, burnt plant and animal remains mixed with heterogeneous unburned sweepings. When these domestic or private contexts were compared with data from religious or public contexts, in particular a building designated as a mid–third millennium BCE temple at Brak, an interesting dichotomy was visible. The temple was characterized by well–prepared floors, some with finishing coats, and lenses of soot derived from repeated burning episodes in front of the altar (Matthews 2003, 382). 116 Most recently in 2004, Matthews began a new7 five–year phase of micromorphological research at Çatalhöyük where remarkable preservation of stratified sequences of sediments, microartifacts, and bioartifacts in buildings and middens make application of this methodology especially fruitful (Matthews et al. 2004). The ultimate goal, as expressed by Matthews and her fellow authors is, “to study the social and ecological strategies of individual households and neighbourhoods and the intersection of these strategies with ritual practice and cycles of burials, plastering and paintings and sculpture, in the high–resolution microstratigraphic sequences within buildings” (Matthews et al. 2004, n.p.). Incorporation of phytolith studies and the mineralogical and elemental composition of plasters is already shedding light on shifts in paleoenvironments and differential access to resources by individual households at the site. As a method, micromorphology has several constraints (as addressed in Matthews et al. 1997). A well–equipped laboratory and substantial amounts of time are necessary to produce the thin sections. Analysis is dependent upon existing visible and identifiable characteristics for remains, a similar issue for microdebris analysis. This is particularly manifest in the use of thin sections specifically because only a rough level of identification can be made. For example it is possible to distinguish bird, fish and mammal bones, but it is difficult to identify species within these categories. Plant remains are perhaps the most difficult as many seeds require multiple views in order to identify and thin sections can only offer a single traverse angle. The remaining limitation of this method is perhaps scale, in that only a small slice of occupational deposit is being 7 Her initial phase of work at Çatalhöyük spanned seven years, from 1993–1999 (yearly field summaries: Matthews 1993, 1994, 1995b, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999; synopsis: Matthews 2005). 117 analyzed. This underscores the need for a multiscalar approach to the study of ancient households and the use of space that draws from primary excavation and specialist analyses: paleoethnobotany, zooarchaeology, soil chemistry, and microdebris. These constraints underscore the primary reasons behind my not adopting micromorphology for this dissertation. However, in terms of future research, the advantages of thin section and micromorphological techniques seem to outweigh the drawbacks. As Matthews (2001b) has demonstrated, occupation sequences in thin section can often be analyzed separately as individual layers of plastering, accumulated deposits, and fill debris. Post–depositional processes such as erosion can also be detected. In sum, the primary advantage of micromorphology is the ability to simultaneously analyze diverse sediments, artifacts, and bioartifacts to arrive at a fuller picture of occupational levels, especially domestic floors. The Household Archaeology Protocol at Kenan Tepe Now that I have presented the theoretical and methodological foundations for carrying out microarchaeological research, in this section I will detail the procedures by which microsamples were collected, processed, and sorted at Kenan Tepe. As with any archaeological endeavor, the way that microartifacts are gathered and interpreted will necessarily affect the outcome of my interpretations of this very unique dataset. With this in mind I find it imperative to present this information both for critical review and as the methodological framework for the microdata discussed in the following chapter. 118 Excavation Methods and Procedures for Sample Collection The microarchaeological sampling procedure at Kenan Tepe is the Household Archaeology Protocol (hereafter “HAP”). HAP samples, which average from 20 to 50 liters in volume, consisted of multiple elements: a soil flotation sample, macroartifacts (e.g., visible pot sherds, bone fragments, lithics) and the remaining sediment containing microartifacts. In order to collect HAP samples, the best preserved segment of a feature was identified, that is, the portion of the feature that showed the least amount of effects from post–depositional disturbances like rodent burrowing or erosional wash. A 50 centimeter square was sectioned off using nails and twine or rope (figure 3.1). This sample area was then excavated down to the base of the feature (e.g., depth of the floor, not including the subfloor). The sediment obtained from this sample was not screened, Figure 3.1. HAP sample before excavation (UTARP Digital Archive). 119 but collected in toto into clean, double–bagged grain sacks. Once the HAP sample was removed, the rest of the preserved feature was excavated, measured in marked buckets to record the total volume of the locus, and then screened at a ratio of 1:1. The volumes of both the HAP sample and the feature from which the HAP was obtained were recorded to calculate the density of debris within the excavated locus and compare distribution across structures. The majority of features where microdebris samples were taken using the HAP procedure were surfaces: interior floors, exterior alleyways, and platforms. In several cases, the depth of separate superimposed surfaces was so thin that there is a possibility that bleeding between surfaces occurred. In every case, only the floor or surface was excavated and none of the subsurface, if possible. Unfortunately preservation issues often limited the number of samples that could be taken from any one surface, such that in many cases there is only a single sample to represent the locus. Naturally optimal conditions for this procedure would be the extraction of multiple samples across a single feature, in this case surfaces, in order to pinpoint higher and lower density of microartifacts that could, for example, reflect differential uses of space within a single structure. However these single samples, when complemented with samples from additional contexts and macroartifacts, should provide enough information to distinguish functionality of features and spaces. Flotation samples were also taken from ovens, hearths, pits and middens and though not collected using the protocol, the heavy fractions from these samples were processed and analyzed the same way as HAP samples (see below). Mud bricks were also sampled to record the elements from which they were comprised. These particular data are important because the breakdown of mud brick, 120 whether through destruction or decay over time, introduces elements like shell or lithic fragments into the archaeological record, thus adding extra secondary refuse to the HAP samples that would not be evidence for primary activity (Rainville 2005; Rosen 1989). Microartifact Recovery and Analysis Procedures Botanical and microartifacts were recovered from the HAP samples through a flotation process using a standard Siraf–type flotation machine (Nesbitt and Samuel 1989; Williams 1973) that incorporated an internal grid plate (following Nesbitt 1995; figure 3.2). The machine was a 50–gallon metal drum outfitted with four legs, an inlet valve, sludge outlet, weir spout and a false bottom to divert water and sediment through Figure 3.2. Isometric drawing of Siraf-type flotation machine (Nesbitt 1995, fig. 1). 121 the sludge outlet. Flotation activities were conducted by the author, Bradley Parker, Jenni Henecke, Ramazan Uĝur and Yosef Uĝur over two field seasons (2006 and 2007) adjacent to the Tigris River at the local fire station in Bismil, a few blocks adjacent to the UTARP excavation house (figure 3.3). The tank was operated on a compacted bed of Figure 3.3. Ramazan Uĝur and Yosef Uĝur operating the flotation machine (UTARP Digital Archive). level stones and low–lying vegetation in 2006 and on a level concrete walkway in 2007. Both locations were situated within a shady corner of the station yard under a copse of mulberry trees that provided adequate shade both for the samples and the operators. It was necessary to erect a small tent made of plastic tarp and rope over the tank to lessen the amount of leaves and other modern debris falling into the water and thus the samples.8 The water supply derived from an adjacent well where water was continuously 8 This modern debris would not affect the samples in any way because it is easily identifiable. For example, unburned leaves and twigs would not preserve in the archaeological record unless under very specific circumstances that are not present at Kenan Tepe. We still felt it was important to keep the samples as clean as possible. 122 pumped into a small holding tank and flushed away toward the river via a man–made sluice. A second electric generator pumped water from this holding tank into the flotation machine through a 1 inch valve. This valve was connected on the inside of the tank by a 1 inch diameter plastic tube with a wide metal shower head attached to the end and facing up. The sludge valve of the tank was positioned over the sluice so that waste water and sediment was easily rinsed away and thus eliminated the need for a settling tank. To begin flotation operations, first the upper part of the tank was lined with a 1 millimeter mesh (about the size of window screen) and secured by plastic clothespins to the lip of the tank. Next the two nested screens suspended under the outlet spout on the outside of the tank were lined with 1 millimeter and 0.25 millimeter (finely woven fabric) mesh, which was also secured by plastic clothespins to the lip of the wooden frame screens. The samples were measured in marked buckets to record the volume and then added to the tank just as it was filled with water. The sample was both stirred by hand and agitated by water streaming through the upturned shower head. This disaggregated the sample so that charred seeds and charcoal, collectively called the light fraction or flot, were separated from the rest of the sample. Because the flot material has a lighter density than that of the water, it floats to the surface and was able to be collected either by hand with the aid of metal cups or, more effectively, by overflow from the tank. This was accomplished by closing the sludge valve and opening the inlet valve so that the tank was completely filled with water, to the point of overflowing. The water and flot were siphoned into the outlet spout and fell through the side screens as a waterfall effect. The flot was collected in the dual meshes that lined the side sieves. The meshes were bundled and tied, labeled and hung up to dry on a clothesline in the shade (figure 3.4 A). The 123 remaining heavy fraction caught in the mesh within the tank, which included both microartifacts and non–cultural residues, was continually stirred until clean of all sediment. Once clean, the sludge valve was opened to drain the tank approximately halfway and the mesh holding the heavy fraction was removed. The mesh was then bundled and partially submerged in a separate plastic bucket filled with clean water to remove any lingering mud. Once properly labeled, the heavy fraction was spread out on a mat in the sun to dry (figure 3.4 B). Oftentimes this fraction took twelve to twenty–four hours to dry, so meshes had to be transported partially wet to the excavation house where they were re–laid and dried completely. A B Figure 3.4. Drying of flotation material: A, light fraction or flot; B, heavy fraction (UTARP Digital Archive). The dry light fractions or flots were carefully bagged and exported inside rigid plastic boxes to the UTARP project paleoethnobotanist, Dr. Alexia Smith, at the University of Connecticut. The dry heavy fractions were also carefully bagged and 124 exported to the Household Archaeology Laboratories at the University of Utah and the University of California, Berkeley for further processing. The laboratory procedures for the processing and examination of the heavy fractions, designated as the Microartifact Processing Protocol (MAPP), contained a number of steps. First, each heavy fraction was weighed and then sifted through a set of nested brass geologic sieves that subdivided the sample into size fractions greater than 5.6, 4, 2, and 1 millimeter. Objects that were larger than 10 millimeters were hand–sorted from the greater than 5.6 millimeter screen by visual inspection with the aid of a ruler and classified as macroartifact. The subdividing of the samples into size fractions is not only a great aid in the sorting process, as it is easier to see and sort materials of the same size, but also allowed me to monitor and record the amount of material in each size fraction. These data are crucial for charting trampling activities or the effects of post–depositional processes on the samples. The greater than 5.6, 4, and 2 millimeter size fractions were sorted using a 2.0x Optivisor® binocular magnifier and the greater than 1 millimeter size fraction was sorted using a Leica® EZ4 stereomicroscope (8x to 35x; 10x eye piece). For this dissertation, I define microartifact as any cultural object less than 10 millimeters, but greater than 1 millimeter, in size. Any item less than 1 millimeter I consider microscopic and beyond the range of this dissertation. The microartifacts were separated from rocks, sticks, dirt clods and other non–cultural debris into broad material categories: ceramics, lithic, shell, animal bone, grindstone, seeds, charcoal, and other (figure 3.5). 125 Figure 3.5. Microartifact recording sheet. Some of these categories were further subdivided and are explained below. These subdivisions are not arbitrary, but based on the macroartifacts that have been excavated and analyzed at Kenan Tepe from Late Chalcolithic contexts. Microartifacts were only placed in these subcategories if they could be positively identified with that group. I categorized microceramics based on two primary characteristics: 1) the presence of relatively smooth, flat sides or surfaces, and 2) gradation of color within the fabric as indicative of firing differential (i.e., a black core; figure 3.6). However gradation was not always present. In these cases, other traits guided my identification such as visible wheel 126 Figure 3.6. Examples of microceramics: A, coarse ware; B, medium ware; C, fine ware. striations, inability to break when applied with pressure,9 and grit or vegetal temper/inclusions within the fabric and on the exterior surface of the sherd. Color can also be distinctive; for example high fired ceramics like fine wares have a distinctive green and yellowish color in the Late Chalcolithic assemblage at Kenan Tepe. Much of the difficulty in distinguishing microceramics from mud brick is that the latter has many of the same characteristics: grit or vegetal inclusions and gradation of color (in the case of differentially fired or charred mud bricks). Thus the presence of a flat side and angular break was critical to positively identify an object as microceramic. This class of microartifact was further subdivided into type categories consisting of fine, medium, and coarse. Fine microceramics are high fired, extremely hard, and contain little to no temper or inclusions (figure 3.6 C). Based on macroceramic fine ware examples from Kenan Tepe, they also contain little to no color gradation in the fabric making them difficult to 9 Dirt clods or compacted sediment that make up a surface matrix will break apart instantly by the application of pressure from a finger tip or the end of a tiny paintbrush handle. 127 positively identify without some kind of diagnostic element, such as a rim, carinated body piece, or base. Medium microceramics exhibit relatively dense fabric with some grit or chaff inclusions (figure 3.6 B). Coarse microceramics are extremely chaffy cook pot wares with heavy vegetal inclusions (figure 3.6 A). These are more easily broken than the hard, high–fired fine wares which may affect the amount of coarse ceramics identifiable on the microlevel. I based categorization of microlithic on material (chert and obsidian) and evidence of modification (figure 3.7). On the microlevel, most of what is recoverable are flakes and other microdebitage that result as shatter during lithic manufacture or from heat breakage (Rosen 1997, 30). It is possible to recover bladelets; however, most of what is collected includes chips and microflakes. These detached pieces are often angular in shape with sharp edges and relatively shiny surfaces (Andrefsky Jr. 1998, xxii). Evidence for modification includes a visible striking platform and bulb of percussion, which is a protuberance on the ventral face of the flake, accompanied by light striations or scars. At this level one cannot distinguish between primary flakes (from a core) or reduced flakes (from the creation of a specific tool like scrapers or sickles). However, these microliths can serve as a direct reflection of stages in the lithic reduction and tool making processes, as the debitage produced becomes incrementally smaller as the artifact nears completion (Andrefsky Jr. 1998, 96).10 Both land and seashells exhibit a broad range of characterizing features. Shell may be composed of one or multiple separate pieces, thick or thin walled, colorful or colorless, opaque or translucent, smooth or scaly (Abbot 1989; Abbot and Dance 1998). 10 However Andrefsky Jr. (1998, 96) notes that smaller flakes can also be removed in order to set up the removal of a larger flake from a core. 128 Figure 3.7. Examples of microliths: A, chert; B, obsidian. Figure 3.8. Examples of microshell. Most microshell I recovered was generally whitish gray in color for freshwater shells and brown for landshells (figure 3.8). They also exhibited iridescent and/or opaque features and seemed to have several layers one on top of the other like an onion. Many of the microshell fell within the three subcategories of bivalve, gastropod, and snail. Bivalve shells are composed of two shells hinged together. They range from thick to thin–walled 129 and can exhibit either smooth or horny exterior surfaces. The diagnostic element for this shell type that is identifiable on the microlevel is the umbo or beak, defined as a knoblike protuberance near the hinge of the two shells. Gastropods have an elongated cone spirally twisted around an imaginary axis, the spiral following a clockwise course (Abbott and Dance 1998, 7). The diagnostic elements for this shell type that are identifiable on the microlevel are the apex, spire (and spiral lines), and columella or inner lip. Land snail shells are generally thin–walled, slightly opaque, and brown in color or have brown spotting. Often very light striations are visible. Unburned microbones are most recognizable by the presence of some kind of diagnostic element, such as teeth, protuberances, or articular ends (figure 3.9 E). The interior porous or spongy (cancellous) structure of the bone will often be visible due to breakage. Often the surface of the bone is shiny and in some cases has a flaky texture. Color can vary from white or milky to yellowish and often exhibits brown spotting. Burned microbone is essentially the same in structure as unburned, though in many cases the porous interior of the bone has been removed through firing (figure 3.9 B). Burned bones are extremely hard and similar in many ways to a darkened rock. However bone is distinguishable by the presence of subtle exterior ribbing, striations and/or pitting that is common to unburned faunal material. Color for burned bone ranges from black and gray to a bright white or whitish–blue for bones that have been exposed to extremely high temperatures. Much of the burned microbone was unidentifiable and therefore included within a single subcategory of “burned.” Any burned microbone that was identifiable with any of the other subcategories (bird, fish, rodent) was noted. 130 Figure 3.9. Examples of microbone: A, rodent including lower jaw of subfamily Gerbillinae (far left); B, burned bone; C, fish vertebrae (left) and scale (right); D, bird; E, unidentified mammal. The major subcategories of unburned microbone are: bird, fish, rodent, and unidentified mammals. Bird bone is characterized by a thin cortex and more angular edges than mammal bone. It is generally light and hollow with internal supportive webs that strengthen the bone structure (figure 3.9 D). Fish bone is also very thin and light, but characteristically flat with a woody internal texture (figure 3.9 C). Clean fish bone appears translucent, but for the majority of the microsamples they are brown due to staining from the soil matrix. Rodent bones are primarily identified through teeth, both fragmentary and whole, vertebrae of the spinal column and tail, and long bones with 131 articular ends (figure 3.9 A). At the microlevel, these elements naturally represent a very tiny species. Finally mammal bone is generally distinguished by rounder edges and a thicker cortex, as compared with bird bones for example. However as we are dealing with mostly microbone fragments, these elements are harder to identify outright. Thus if an unburned bone was unable to be identified as bird, fish, or rodent, it was included in the unidentified mammal subcategory. Grindstone, seeds, and charcoal are the less encountered microartifacts in the heavy fraction portion of the samples. This is due in part to the difficulty in identification and the methodologies by which the samples are processed. Identification of grindstone fragments rely heavily on the composition of macroartifact samples of this particular object. In this case, grindstones from Kenan Tepe are usually made from basaltic stone, gray or black in color that can be heavily pitted. A flat working edge, sometimes slightly indented to mirror the curve of the grinding slab, distinguishes this type of microartifact from naturally occurring rounded basalt pieces (figure 3.10 A). Most seeds and other charred organic material are collected separately in the light fraction or flot (figure 3.10 C). However if seeds become waterlogged in the flotation process, they are recoverable in the heavy fraction, though with my samples this was rare. Like seeds, most charcoal (i.e., burnt/charred wood) was collected with the light fraction material during the flotation process. Some waterlogged examples, however, were recovered from the heavy fractions. These are characterized by their wood structure comprised of faint grain lines (figure 3.10 B). In some cases, shiny surfaces on the charred material could be detected. Overall charcoal is extremely fragile and prone to breakage, thus making count densities of this particular microartifact unreliable for statistical analysis. Finally, the category 132 “other” was reserved to include any small finds such as pendants, beads, sealings or metal. Identifiable microartifacts that did not fall within any of the other categories or subcategories were also placed in the “other” category. Figure 3.10. Examples of A, microgrindstone; B, microcharcoal; C, microseed. Once the microartifacts from each size fraction had been sorted into their respective categories or subcategories, the counts and weights of materials from each grouping were calculated and recorded (figure 3.5). The same procedure was applied to any macroartifacts (greater than 10 millimeters) that were collected at the beginning of the sorting processes. These were subdivided into three material categories (i.e., ceramic, bone, and lithic), counted, and weighed. With these raw weight and count data, I was then able to calculate weight and count densities of the microartifact categories by dividing raw count or weight by the total number of liters in each of the HAP samples. When these microartifact densities were charted across the excavated spaces and compared with the 133 level and nature of macroartifacts recovered from these same locations, a complex picture of spatial usage emerged, providing evidence for the production, consumption and disposal patterns of household groups at Kenan Tepe and offering a glimpse into the everyday activities that guided their lives (see chapter 4). Microartifact Preservation and Identification: Some Issues Before concluding I wish to address several issues concerning microartifacts that have already been recognized elsewhere (Cessford 2003, 2005; Rainville 2005) and can potentially affect the dataset from which I draw my conclusions for this dissertation. These issues are primarily concerned with preservation and identification. The presence and preservation of microartifacts in surfaces and other sampled features depends on several factors: 1) cultural use of the space, by human or animal, including the objects that were utilized within this space, 2) the permeability of the soil matrix that makes up the surface or feature, 3) post–abandonment depositional processes or disturbances and 4) the material and manufacture processes of the microartifacts themselves. The way that people use and interact within a space will alter the amount and types of refuse that are recoverable.11 For example, heavy trampling such as found in hallways, courtyards, and alleyways contributes to the high amount of microartifacts for the smallest size fraction recoverable by the methodology used in this dissertation.12 This type of behavior can also be destructive, especially for less robust materials like friable cook pot wares, delicate fish bones, and fragile shell. This factors in to the limitations of 11 This of course is the primary foundation for microarchaeological investigations, especially activity area research, where different actions by people in the past will leave different distinguishable material evidence for us to interpret, recognize, and even attempt to build “signatures” around (Rainville 2005). 12 Though different firing conditions and thus the friability of the ceramic can also affect the point at which it will break down under pressure (Rainville 2005, 24). 134 only examining microartifacts that are greater than 1 millimeter or larger since some activities like knapping or trampling can produce debitage that is smaller (Fladmark 1982). The placement of furniture or permanent fixtures within a space and the use of mats or rugs will also affect the presence and more importantly, patterning of microartifacts within a space by determining the flow of movement and thoroughness of cleaning activities. Microartifacts will also be more easily incorporated into the floor or surface matrix of a feature if that matrix is relatively porous (Rosen 1986). This naturally favors trampled pebble or packed mud surfaces such as found at Kenan Tepe, as opposed to stone floors.13 Plastering of these surfaces, however, could affect the permeability. Plastering also affects the visibility of debris such that more of the larger (10 to 20 millimeters) microartifacts will be removed from the primary area of activity because of more accurate and thorough cleaning before they can be incorporated into the surface matrix. The use of plaster can also introduce microartifacts into a sample that are not derived from primary activities but are inherent to the construction material itself as demonstrated by Cessford (2003, 2005) at Çatalhöyük. At Kenan Tepe a wide range of floors and surfaces were sampled including compacted pebble alleyways, packed mud floors, and poorly prepared mud plastered floors to give a full range of surface types, and thus construction types, for household contexts. Other issues to consider are the reuse of abandoned structures by squatters or other transient groups that may introduce microartifacts through their activities. The slow abandonment and eventual decay of the structure itself may also introduce material 13 Though microartifacts could reside in the narrow gap between flagstones for example or within the cracks of the stone itself. The collection process for microsamples under these circumstances would of course differ from the methods presented here. 135 elements like mud brick into the surface that is unrelated to human activities in the past. Even the pristine example of a structure that was suddenly and violently destroyed never to be reoccupied should be approached with caution. As best demonstrated by Roaf (1989, 101), people will purposefully push down the walls of a burning house to smother the flames and remove roof beams and other sources of fuel. In the aftermath, the primary location of objects within the structure, supposedly sealed by the destruction of the building, will be altered as people haphazardly search through the rubble to remove valuable objects. While this will not affect microartifacts directly, the collapse of the structure and subsequently trampling by scavengers could incorporate secondary refuse into the sediment matrix that is later sampled. This reflects the importance of knowing the complete life history of a structure. The material and manufacture of the microartifacts themselves will mostly determine the preservation of these objects in the archaeological record. As mentioned previously, more delicate materials like shell and fish bones are more likely to be destroyed through trampling or post–depositional processes than more robust high–fired ceramics or chipped stone. Teeth preserve especially well as they are dense and hard, which allow them to survive more often than fish and bird bones that are small and light. A differentiation can also be found for ceramics where high–fired fine wares are easily broken and trampled while often retaining their shape, while low–fired coarse wares like cook pots can crumble more easily into their constituent parts. Chipped stone tools and lithic debitage seem to fare best as only highly acidic soils will hasten the breakdown of these microartifacts. 136 Last are the concerns surrounding identification. In general and in most cases the presence of some kind of diagnostic element is crucial in the identification of the microartifact, especially for shell, fine ceramics, and animal bone.14 Without these indicators, it is possible that some microartifacts will be missed in the course of sorting. As with all laboratory analyses, human error can also play a role. Size can also be an issue. As already noted by Cessford (2005, 48) some microdebris categories are impossible to visually distinguish in the smaller size fractions. In using a stereomicroscope for the smallest size fraction (greater than 1 millimeter), I have attempted to overcome this difficultly of identification. These issues involving microartifact preservation and identification are not presented here to discredit the use of microdebris analysis for studying domestic economies or the use of space. They are instead highlighted to identify some of the limiting factors of the methodology in order that we may determine appropriate types of research questions that can be answered through this technique. Conclusion Microarchaeology is an even finer resolution by which one can study Late Chalcolithic households by offering a window into primary use contexts that are generally unavailable to traditional examinations of domestic artifact patterning. Activities such as knapping, cooking or butchering leave behind residues like microflakes, ceramic chips or bone fragments that, because of their size, are generally missed in the cleaning process and are incorporated into the soil matrices of surfaces and 14 Particular issues as they relate to specific artifact classes have already been raised in my descriptions of microartifact material classification (see “Microartifact Recovery and Analysis Procedures”). 137 other features. This primary refuse thus represents the activities of production and consumption that were carried out in and around spaces used by household groups over the use–life of a domestic structure. When these microdata are used in comparison and/or as a complement to macroassemblages, one can gain a full picture of the types and degree of production and consumption within and between household groups that combine to represent a domestic economy. Microarchaeology can also help determine how (or if) domestic modes of production and consumption played a role in the larger systems of regional exchange and interaction characterized by the Uruk Phenomenon. I will now apply the methods and theoretical underpinnings of household archaeology and microarchaeology to the study of domestic economy at a village site in the upper Tigris River valley of southeast Turkey, Kenan Tepe, to establish the domestic mode of production and consumption for the house lots under consideration (and the household groups that used/inhabited them). From this examination I will evaluate shifts in the domestic economy in terms of regional relationships and the Uruk Phenomenon in chapter 5. 138 CHAPTER 4: THE DOMESTIC MODE OF PRODUCTION AT KENAN TEPE The goal of this chapter is to establish the domestic mode of production and consumption (hereafter “DMPC”) at Kenan Tepe through an examination of four specific house lot contexts. This is accomplished first through situating Kenan Tepe within the modern and ancient environment. This is essential since natural environmental conditions determine: 1) the accessibility of Kenan to other settlements in terms of communication, trade and defense, 2) the availability of local natural resources such as water, metals, stone and wood and 3) the form and nature of settlement including physical structures based on climactic conditions.1 Second, I place Kenan Tepe within the wider milieu of material culture and settlements within the Upper Tigris followed by an elucidation of Late Chalcolithic and transitional Early Bronze Age material at the site itself. Next I establish the loci of examination for the DMPC based on a largely architectural discussion of house lots and then offer the archaeological evidence for production and consumption activities within each household. In the following chapter, I will use this evidence to evaluate whether production and consumption activities on the household level changed over a span of approximately six hundred years and if so, consider the factors behind these shifts. 1 This is not to suggest that environmental conditions determine a society’s subsistence practices alone, however they do play a role in sociocultural development on a settlement and regional level. 139 The Upper Tigris River Valley Geography and the Natural Environment As already mentioned, understanding the climate and natural landscape of this unique area is essential for examining Kenan Tepe’s DMPC, especially since domestic economies are, in many respects, affected by and dependent upon local geographic and environmental conditions. For example, in a chert–rich area one may expect to find an abundance of this stone type in the lithic macro– and micro–assemblages and a much smaller percentage of, say, obsidian stone that needs to be imported. But a majority of obsidian artifacts in this same hypothetical assemblage could signal a highly developed trade network and/or easy access to this material. The Upper Tigris region of southeast Turkey was a wide, moderately forested river valley flanked by low terraces, a Mediterranean climate, and access to natural resources like copper, stone and agricultural land that will be discussed in detail below. Southeast Turkey is the smallest of the modern Republic of Turkey’s geographic regions, covering only about eight percent of the land (Enriç 1980, 74; figures 4.1, 4.2). However, this area can be considered the northernmost extension of a larger geographic region, the “Fertile Crescent,” which extends from the Zagros Mountains east of the alluvial lowlands in southern Iraq to the Amanus and Taurus mountain ranges rising two to three thousand meters in height. Today southeast Turkey is a steppe environment composed of plateaus lying along the marginal folds of the Taurus southern foothills. Most of these platforms lie 600 to 900 meters above sea level and gradually slope downward to 350 meters above sea level as one moves south from the city of Şanliurfa toward the Syrian frontier (Dewdney 1971, 202). 140 Figure 4.1. Modern regions and provinces of Turkey (adapted from Dewdney 1971, fig. 41). Figure 4.2. Topography of southeast Turkey (adapted from Dewdney 1971, fig. 52). 141 Roads, both ancient and modern, follow the smaller rivers that cut deeply through the mountains as they travel south through the foothills and empty into the Euphrates and Tigris River basins. For example, an ancient road travels through the Bitlis Gap and Rahva Pass in order to reach Lake Van and the flanks of the Nemrut volcano, an ancient obsidian source. Other roads follow the Tigris valley to cross the mountains at their lower central sector (Enriç 1980, 75). These roads meet in the Diyarbakir basin, from there going east to follow the Zagros range down to the Gulf, while another road leads from the Tigris basin to Israel/Palestine via Şanliurfa (Turkey) and Aleppo (Syria). The plateaus of the southeast region are split north to south by the Karacadağ volcanic massif, a shield–shaped volcano of Pleistocene age rising 1,938 meters and whose basaltic lavas are spread over the surrounding area for a total of 7000 square kilometers (Erinç and Tunçdilek 1952). The geography of the western half, between Şanliurfa and Gaziantep, is characterized by slightly inclined and uniform limestone plateaus that are dissected by the Euphrates River and its tributaries. Among these plateaus are karstic depressions and larger plains, such as the Harran and Suruc, which contain alluvial soil and are highly fertile when irrigated. On the east of the massif is a more rugged landscape of clastic deposits hundreds of meters thick. At the center is the Diyarbakır basin, a wide alluvial plain fed by the Tigris River that flows down from the marginal folds of the Taurus foothills and is joined by smaller tributaries (i.e., Batman, Ambar, and Garzan) south of the plain. The basin is bordered on the south by the Mardin threshold that extends into north Syria (Erinç 1980, 76; Yakar 2000, 15). The Tigris River valley begins a few kilometers south of Diyarbakır and extends for 60 kilometers until the river enters the “Tigris canyon” about 5 kilometers east of the 142 Tigris–Batman confluence (Parker 2001, 159). South of the upper Tigris River valley lies the Tur Abdin range, created by a collision of the Arabian shield with the Eurasian plate (Erentöz and Ketin 1962, 57). This area is dominated by rocky basalt flows creating a natural barrier between the fertile Upper Tigris valley and Syrian steppe 75 kilometers to the south. Within the upper Tigris River basin itself, the river is flanked by a series of low and high terraces of Late Pleistocene and Holocene date. Lower terraces on the north bank are 5 to 6 kilometers in width, creating a low relief karst plain blanketed by deep silt and clay deposits all of which overlay Lower Miocene gypsum beds (Algaze et al. 1991, 180). The south bank of the river has similar, though narrower, terraces extending from the Batman Su–Tigris River confluence in the east to the modern town of Bismil 30 kilometers to the west. Numerous broad, shallow, and inactive sinkholes dot the landscape though deep, water–filled active ones remain mostly in the northern boundaries of the plain (Algaze et al. 1991, 180). Archaeological sites tend to cluster around these sinkholes, as well as in valleys along tributary streams and the Tigris itself. This region is characterized by an extreme continental Mediterranean climate marked by heavy precipitation in the winter and extreme aridity in the summer. The mean annual rainfall is 500 to 600 millimeters, though in dry years it can dip down to less than 300 millimeters (Dewdney 1971, 39; Roberts and Wright 1993, 198). Average winter temperature varies between 1 and 5 ºC, sometimes reaching as low as –10 ºC in the Diyarbakır basin. This cold period, however, is relatively short, lasting only three months before the onset of warmer spring conditions that will eventually give way to the long, hot summer months where temperatures remain on average above 40 ºC. 143 The vegetation of the more humid foothills 700 to 800 meters above sea level is described by Dewdney (1971, 54) as “drier deciduous and mixed forest” zones dominated by oak (Quercetum) and juniper with some pine and fir. These are sparse parklands as opposed to dense forests where sizeable areas of open grassland are present. Areas below 700 meters contain steppe formations and reddish–brown steppe soils (alkaline), calcareous and rich in lime. Acanthophyllum, milk vetch (Astralagus sp.), brome grasses (Bromus) and some wild types of grain (Avena) grow rapidly here during the spring precipitation and are subsequently burnt off by the high summer heat (Erinç 1980, 78). Vegetation is poorest in those areas south of the Karacadağ and Şanliurfa where, due to mean annual rainfall of 300 millimeters or less, desert–steppe type plants prevail. Kenan Tepe is surrounded by modern farmlands and active springs on two sides of the site. Desert scrub vegetation dominates the modern environment including caper berry bushes and wild grasses. Barley, wheat, tomatoes, peppers, cotton, and watermelons are currently cultivated adjacent to the site (Parker et al. 2003, 121; figure 4.3). Figure 4.3. Kenan Tepe facing east (UTARP Digital Archive). 144 Geomorphic studies of the landscape using satellite imagery and aerial photography reveal a significantly wider upper Tigris flood plain in the ancient past that reached approximately 1 kilometer across at Kenan Tepe (Matney et al. 2003, fig. 1) suggesting perhaps an even more diverse aquatic environment in terms of flora and fauna than today. While the environmental data is lacking for the immediate area, sediment and pollen core samples from Lake Van northeast of the Upper Tigris region show a gradual increase in values such that desert–steppe was gradually replaced by oak forest between 4300–1600 BCE. This was most likely due to increased humidity in the region from higher precipitation levels (van Zeist and Bottema 1982).2 Overall the natural environment in the upper Tigris at the end of the fourth millennium was characterized by a wide, moderately forested river valley that provided a suitable environment for hunting and gathering. Adequate precipitation levels allowed for the sustainable practice of dry farming as well. Ancient foot paths and passes between the river valley, the obsidian–rich mountains to the north and east, and the copper mines of Ergani Madden to the northwest provided steady communication and trade. Despite this the Upper Tigris was seemingly isolated in terms of trade and interaction with neighboring regions to the south as we will see below when discussing the Late Chalcolithic material culture at Kenan. The rocky basalt flows of the Tur Abdin range serve as a natural barrier between the valley and the Syrian steppe lands to the south and the Taurus foothills enclose the valley on the north. These mountainous features could have been a deterrent to trade, especially smaller donkey caravans moving 2 Butzer (1995, 136) reports different findings from Lake Van sediment samples: a phase of low precipitation around 3800–1000 BCE, with intensely low levels between 3200–2900 BCE or at the close of the Late Chalcolithic. Pollen cores from Lake Van and Lake Zeribar in the Zagros mountains also show a long period of moderate decline in oak woodland between 3250–2750 BCE. 145 north. However the Tigris River is a major feature connecting the Upper Tigris with surrounding regions, provided that the river was navigable in the past. As the material culture from the Upper Tigris will show below, the region was largely populated with small communities engaged in local ceramic production, agriculture, and some interregional trade. Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age Settlement and Material Culture The settlement pattern for the Late Chalcolithic period reflects an increase in occupations of relatively similar size that suggest either an influx of populations or the conglomeration of previously semi–nomadic groups into centralized villages. This pattern, coupled with a relatively uniform material culture assemblage, supports the hypothesis that mainly localized interactions took place between numerous homogenous groups; a pattern that is most likely reflective of the domestic economy at Kenan. Most data for settlement in the Upper Tigris during the late fourth and early third millennia derive from extensive surveys and limited excavations. While this region has been of interest to researchers since the mid–nineteenth century CE,3 more recent 3 J.G. Taylor (1865) made three trips to the Upper Tigris between 1861 and 1863 to gather statistical information for the British government and record several Neo–Assyrian stelae and rock reliefs near Eğil and Kurkh (Üçtepe). Between 1889 and 1899, C.F. Lehmann–Haupt and W. Belck followed the route of Xenophon and his “Ten Thousand” Greek mercenaries who crossed the confluence of the Bohtan Su and Tigris in 401/400 BCE (Belck 1899; Lehmann–Haupt 1910, 337–350; Lightfoot 1986; Xenophon 1998). E. Huntington (1903) studied Hittite rock cut chamber tombs, cisterns, reliefs, and inscriptions at Hilar (modern Sesverenpınar) southwest of Ergani. Đ. Kiliç Kökten, under the auspices of the Turkish Historical Society (Türk Tarih Kurumu), carried out one of the earliest surveys in the Diyarbakır province, focusing specifically on the Bismil, Silvan and Ergani districts (Günay and Whallon 1980, 96; Kökten 1947). Finally surveys by the Joint Istanbul–Chicago Prehistoric Project (1963–1972) resulted in the excavations at Çayönü Tepesi and Girikihacıyan (Braidwood and Çambel 1980; Braidwood et al. 1981; Braidwood and Braidwood 1982; Watson and LeBlanc 1990). 146 explorations in the 1980s and 1990s have been more fruitful.4 The most extensive of these was the Tigris–Euphrates Archaeological Reconnaissance Project directed by Guillermo Algaze (Algaze 1989b; Algaze et al. 1991, 1994). Between 1988 and 1990, the project identified over 490 sites in the survey areas that included the plains of the Batman Su and Bohtan Su, Cizre–Silopi Plain, Upper Tigris basin from Batman to Bismil, and the lower Euphrates basin within the Birecik and Carchemish dam areas.5 Late Chalcolithic sites were identified by the presence of chaff–tempered assemblages that have parallels in forms and wares in the Amuq F sequence (Braidwood and Braidwood 1960). Based on the published survey data, there is a radical increase in settlements both in size and number during the Late Chalcolithic period as compared to the previous Late Ubaid/Middle Chalcolithic in the Upper Tigris region especially along tributaries of the Tigris such as the Batman Su (Algaze et al. 1989b).6 Following the Late Chalcolithic however, there is a realignment and constriction of settlements where populations seem to inhabit only sites within the Tigris River valley proper. This is most evident along the Batman, Garzan and Bohtan Su where no evidence for Early Bronze Age settlements has been detected (Benedict 1980; Rosenberg and Togul 1991), while the Cizre–Silopi region has a decline in occupied hectares from the 4 These surveys coincided with the Turkish government’s initiation of a huge development program called the Güneydoğu Anadolu Bölgesi or Southeast Anatolia Project (GAP) that includes the construction of 22 dams, 19 hydraulic power plants and irrigation systems on the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers and their major tributaries totally over 1.7 million hectares in area. 5 Other regional surveys were carried out in the valleys of the Batman Su tributaries (Rosenberg and Togul 1991), the Tigris River valley between Tepe Beldesi and the Batman Su (Ay 2001), and Adıyaman province (Blaylock et al. 1990, 1998) to complete the previous survey work of Mehmet Özdoğan (1977) in the lower Euphrates Basin. 6 The size for these Late Chalcolithic settlements are not given in a definitive way in Algaze’s report. Mainly he refers to these sites as “numerous hamlet–sized and a few larger occupations” (Algaze et al. 1991, 182). 147 Late Chalcolithic to the Ninevite 5 periods (Algaze et al. 1991).7 As Algaze (et al. 1991, 182) has noted, this pattern stands in sharp contrast to the emergence of Early Bronze Age urban settlements in the Khabur–Sinjar plains due south of the Tigris River in northern Syria and Iraq (Wilkinson 1990b). While a relationship between these two settlement pattern shifts remain to be identified and discussed, one could consider the possibility that larger, more urban sites were possible in the Khabur due to access to wider tracts of agriculturally viable land. In terms of settlement size, this information can only be garnered from the few Late Chalcolithic sites that have been excavated and published along the Upper Tigris basin (see figure 4.4 and below). No hierarchy is evident as all excavated sites range from only 1 to 2 hectares, but no larger than 4 hectares, in total size. Based on survey reports (Rosenburg and Togul 1991, 243), this trend is also evident in the Cizre–Silopi plain Figure 4.4. Detail of Upper Tigris region with sites mentioned in text (adapted from Algaze et al. 1991, fig. 2b). 7 There is, however, no shift in the settlement pattern (i.e., the placement of sites), between the Late Chalcolithic and EBA (Algaze et al. 1991, 196). 148 (Algaze et al. 1991, fig. 21) and upper Batman River with a few notable exceptions like 10 hectare Ikiztepe and Gre Migro (Algaze 1989, fig. 2a-b). From these few examples from the Upper Tigris we find that regional architecture was characterized by sun–dried mud brick constructions with or without stone foundations and floors of beaten earth or prepared mud plaster. At Aşağı Salat, a low–lying mound 20 kilometers east of Bismil at the confluence of the Tigris and Salat Çayı, a two–roomed building with a three course stone foundation was uncovered along with a square platform composed of stone posts, grinding stones, and cobbles (Şenyurt 2004, 661). At Salat Tepe, a 30–meter–high mound approximately 14 kilometers east of Bismil, small architectural units were uncovered with mud brick walls and foundations along with large hearths and work surfaces (Ökse 1999, 2004; Ökse et al. 2001, 2002). Pits 2 meters in diameter with mud plastered floors were uncovered at Kavuşan Höyük, 10 kilometers southeast of Bismil, which contained handmade and well–fired thin metallic ware ceramics, animal bones, zoomorphic figurines, and chert tools (Building Level V in Trench No. III; Kozbe et al. 2004, 499). At neighboring Giricano, excavations on the south side of the mound produced well preserved architectural remains of a large (at least 6 meters long) building whose associated painted ceramics and stamp seal impressed clay bulla date it relatively to the middle of the fourth millennium (Level 06; Schachner 2003, 2004; Schachner et al. 2002). The majority of the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age ceramic assemblage in this region is locally made and characterized by chaff and/or grit tempered coarse handmade wares, some with chaff facing paralleled in the Amuq (F: Braidwood and Braidwood 1960), and finer wheelmade wares sometimes exhibiting burnish. Shapes 149 include holemouth jars with globular or ovoid bodies (Grê Dimsê: Karg 1999, 284), globular pots with simple rims, jars with short necks and straight or slightly everted rims (Hirbemerdon Tepe: Laneri et al. 2006), burnished pots with no necks and everted rims, and bowls with exaggeratedly inverted rims (Kavuşan Höyük: Kozbe et al. 2004, 500). More unique shapes include buff–colored fruit stands and pedestal bowls, spouted vases, buff and beige colored biconical vases with string–cut holes, metallic ware cups and fine ring base bowls with greenish cream colored fabrics that often carry incised decorations (Aşağı Salat: Şenyurt 2004; Müslüman Tepe: Ay 2004). These incised wares are similar to Ninevite V forms at Hassek Höyük (Behm–Blancke 1988) and north Syrian sites. Though the Upper Tigris region is directly connected via river travel to the rich and ancient copper mines of Ergani Madden, there is little direct evidence for metallurgy or the processing of raw metal materials during the Late Chalcolithic in this region. However small copper and bronze finished products such as pins do occur in both domestic and funerary contexts (see below). Chert is readily accessible in this area and evidence for chipped stone technologies and the use of stone tools is prevalent. Settlers in the Upper Tigris seemed to have also benefited from close proximity to local obsidian sources at Nemrut Dağ/Bingöl. Burial practices in the Upper Tigris during this period are varied, ranging from simple pit inhumations to brick lined intramural graves (as at Kenan Tepe; see Hopwood 2008; Parker et al. 2008, 2009 and below) and extramural cemeteries. The best example is a very early third millennium cemetery from Aşağı Salat that extended over a maximum 50 square meter area and contained cist graves and graves with a stone enclosure and cover. All the graves contained pebble floors and were capped with 150 limestone slabs (Şenyurt 2002a, 694). Due to a high salt content in the soil, the skeletal material in many cases was too deteriorated to determine the positions of the interred individuals.8 However a single intact grave (M–14), allowed excavators to note a hocker position oriented east–west with the head on the east end facing north (Şenyurt 2004, 665). Signs of robbery are evident as the east end of all the cover stones were found broken and the ceramics and other grave goods broken and scattered. Among the grave goods remaining were bronze pins, beaded necklaces made from mountain crystal, white frit and black stone, and a bone “idol” in the form of a stylized human figure. Similar stone cist graves with pebble floors and limestone capstones were also found at Müslüman Tepe (Ay 2004). Evidence for the Uruk Phenomenon in the Upper Tigris is slight, but notable. Beveled–rim bowls have been excavated at two sites (Aşağı Salat and Giricano) and collected on numerous surveys (Algaze 1989b; Algaze et al. 1991). Globular vessels with crosshatched painted designs were also uncovered at Giricano though they are only remotely similar to the squatter four–lugged jars with crosshatch and chevron designs from other Uruk sites such as Habuba Kabira–Süd (Strommenger 1980, fig. 52). A baked clay wall mosaic cone was unearthed at Aşağı Salat near the two–room building and raised stone platform discussed previously (Şenyurt 2004, 661). Finally the bulla from Giricano impressed with a stamp seal appears to be a local hatched design and based on other examples from southeast Turkey and northern Iraq, fits securely within a pre–Uruk contact sphere of local administrative technologies. 8 A similar problem was observed in the Early Bronze Age cemetery at Berecik on the Euphrates (Sertok and Ergeç 1999, 90). 151 Much of the data for Late Chalcolithic settlement in the Upper Tigris discussed previously is derived from site survey, surface scrape, small exploratory soundings or narrow step trenches, all of which severely limit our understanding of the nature of these occupations especially in terms of households and domestic economy. One site however, Kenan Tepe, does contain extensive horizontal exposures of Late Chalcolithic occupations whose superimposed remains span the latter half of the fourth millennium or the LC 3 through 5. Kenan Tepe thus serves as exceptional case study in which to examine the changing nature of households and domestic production during the entire span of the Uruk Phenomenon. Kenan Tepe: A Brief Settlement History Introduction Kenan Tepe is a 4.5 hectare multi–period mound located 20 kilometers west of the Tigris–Batman confluence and 10 kilometers east of the modern town of Bismil in the Diyarbakır province of southeast Turkey (figure 4.4). The site commands a prominent position from atop a natural limestone outcropping of Upper Miocene date (Tolun 1962) bordering the north bank of the Tigris River, as it winds its way down from the Taurus foothills and into the upper Tigris River valley. The site is composed of a tall central mound and a lower town that extends east toward the river measuring approximately 350 meters on its long axis (southwest to northeast) and over 200 meters on its short axis (southeast to northwest; figure 4.5).9 Cultural deposits overlay a natural sedimentary outcropping of interbedded conglomerates and siltstones including sterile clay with 9 The main datum, located on top of the high mound, is 37 49 50.11634 N by 40 47.59917 E and is 603.724 meters above the World Geodetic datum (Parker et al. 2004, 582). 152 calcium carbonate inclusions (Creekmore 2007, 77; Parker et al., forthcoming). Since these deposits are densest on the easternmost edge of the mound it is likely that settlement continued further east but was eroded way by the changing course of the river. Figure 4.5. Kenan Tepe facing northeast with Tigris River in foreground (UTARP Digital Archive). Kenan Tepe was initially identified in reconnaissance surveys carried out by Guillermo Algaze and his team (Algaze 1989b; Algaze et al. 1991, fig. 2b #42 and #43). A total of eight seasons of fieldwork between 2000 and 2008 were carried out under the auspices of the Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP), a multi–year archaeological excavation and survey project founded and directed by Bradley Parker of the University of Utah and co–directed by Lynn Dodd of the University of Southern California.10 Between 2000 and 2005, excavations at Kenan Tepe carried out by UTARP team members revealed over 2.5 meters of accumulated Late Chalcolithic occupational 10 Preliminary reports: Creekmore 2007; Dodd et al. 2005; Parker et al. 2002a, 2002b, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2008, forthcoming. 153 Figure 4.6. Topographic map of Kenan Tepe (UTARP Digital Archive, prepared by Andrew Creekmore). debris in the lower town (Areas F and G) and in several soundings on the high mound (Areas A, D, and E; figure 4.6). Carbon analysis of these remains shows that the site was occupied between the late LC 3/early LC 4 period (ca. 3600–3500 BCE) and the LC 5 period (ca. 3100 BCE; table 4.1). Four more carbon dates from fortification/retaining walls on the high mound discussed below show that occupation continued through the Late Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age transition (ca. 3000 BCE). Because remains in the 154 outer town area are not covered by later material, that is Middle Bronze or Iron Age occupation, Kenan Tepe seems to have reached its largest extent of approximately 4.5 hectares during this period. Area Trench Sample # 2–Sigma Cal. BC A 2 A2.2139.2 3350—3010 LC 5 A 2 A2.2131.15 2880—2580 EB I A 8 A8.33.6 3100—2900 LC 5 – EB I A 8 A8.30.3 3080—3060 3040—2890 EB I A 9 A9.37.2 3100—2900 LC 5 – EB I Occupational surface F 2 F2.2065.10 3360—3020 LC 5 – EB I Occupational surface F 4 F4.4004.4061 3350—2910 LC 5 – EB I Fill above large oven F 4 F4.4023.4157 3360—3030 LC 5 – EB I Large oven F 4 F4.4023.4229 F 4 F4.4023.4253 3630—3570 3540—3360 3660—3620 3600—3520 LC 3 – LC 4 LC 4 LC 3 LC 3 F 7 F7.7094.28 3360—3020 LC 4 – EB I Pit F 19 F19.14.6 3020—2890 EB I Occupational surface F 19 F19.14.16 3370—3080 LC 4 – EB I Occupational surface Chronology Context Retaining wall foundation Debris above retaining wall Retaining wall foundation Retaining wall superstructure Large oven Large oven Table 4.1. Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze calibrated carbon dates from Kenan Tepe. Areas A, C, D, E and G On the high mound, evidence for Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age occupations comes from Areas A, C, D and E (figure 4.6, table 4.2). The most substantial 155 constructions are two parallel fortification or retaining walls that likely circumvented the high mound, as sections of these walls were uncovered in a step trench in Area A (trenches 2 and 8),11 a sounding in Area C (trench 5),12 and possibly in Area E (trench 2; see below). Both walls were constructed of stone foundations over 1.5 meters wide with a mud brick superstructure that included a damp reed course every 10 to 12 courses (figure 4.7). The superstructures were also built of at least four different kinds of mud brick, each having a slightly different color that was likely pronounced in antiquity. While these colors could be explained by aesthetic preference, they also signal the use of multiple clay sources by different labor gangs or tribute payments from various factions for the construction of these large walls (Parker et al. 2005, 76). Several carbon dates taken from the wall foundations, a reed course in the mud brick wall matrix, and fill above the walls anchor the construction and use of these walls during the very end of the fourth millennium (table 4.1). Area Date (BCE) Major Architectural Features LC 5: 3350—2890* Parallel fortification walls with stone foundations and mud brick superstructure; likely circumvented mound D Late Chalcolithic Large ovens cut into natural mound E Late Chalcolithic Two phases of superimposed structures; pebble streets; Possible southeast portion of fortification wall G LC5–EBA: 3350—2900* Domestic architecture with open–pit fireplaces; tandır oven; pithos child burials A/C *Derived from calibrated carbon dates (see table 4.1) Table 4.2. Summary of Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age architectural features in Areas A, C, D, E and G at Kenan Tepe. 11 12 Trench A2: loci 2125, 2126, 2129, 2131, 2132, 2139, 2140, 2144; Trench A8: locus 33. Trench C5: loci 10, 12, 13, 16, 17, 43, 46, 49. 156 A B Figure 4.7. Fortification or retaining wall from Area A: A, cobblestone foundation; B, mud brick superstructure (UTARP Digital Archive). A pair of pyrotechnic facilities was uncovered in Area D and is attributed to the Late Chalcolithic period based on its associated ceramic assemblage. In trenches D5 and D9, two ovens (D5: L5126/5138; D9: L7/8/10/20/22)13 were cut into Ubaid period architecture and the natural slope of the mound creating a flat–bottomed niche that was guarded from the prevailing winds that, at least in modern times, blow from the southwest (figure 4.8).14 One of these ovens (D5 L5126/5138)15 had a wall of mud bricks constructed to shore up the vertical section. Both ovoid–shaped ovens averaged 1.5 meters in diameter and in the case of trench D9, were preserved to a height of 80 centimeters. They were composed of beehive–shaped clay dome cores placed over a layer 13 The Kenan Tepe project uses the locus system in which each distinguishable context, stratum, or entity in an excavated area is given a locus number. Within each locus are multiple categories of object types separated by material (e.g., pottery, stone, bone) that are represented by sequential “KT numbers.” KT numbers are the equivalent of “basket numbers” on other excavation projects. In this dissertation, locus numbers will be preceded by an “L” and KT numbers preceded by “KT.” The area and trench number will be a combined prefix before locus numbers to prevent confusion, thus Area F trench 7 = F7. 14 These installations have been designated as ovens for the use in cooking and baking due in part to the absence of wasters or slag that would indicate their use as kilns for ceramic production or metallurgy (Parker et al. 2006, 75). 15 The mud brick walls of this oven are loci 5126 and 5138. The interior fill for the oven is represented by loci 5111, 5120, 5121, 5123, 5124 and 5127. 157 A B Figure 4.8. Late Chalcolithic ovens from Area D: A, trench D5; B, trench D9 (UTARP Digital Archive). of mud bricks that probably elevated the fuel and allowed for air circulation. More mud bricks were packed around this core and the entire oven was covered with a layer of mud pisé. Because no side openings for access were present, it is likely these ovens were top– loading like tandır ovens common in southeast Turkey today (Parker et al. 2006, 78; Parker and Uzel 2007). The ashy debris found inside these ovens included ceramics common to the Late Chalcolithic assemblage at Kenan,16 jar stoppers (D9 L20 KT4 and 11), and a pot stand fragment (D9 L20 KT12). Finally at least three phases of superimposed architecture dating to the Late Chalcolithic were uncovered in Area E trench 2 on the southeast side of the high mound. The first two phases of architecture are similarly orientated and are represented by parallel walls (mud brick [L37/43, L70] and stone [L53, L70]) from two neighboring structures with a wide street or passageway in between them (L50, L56, L78). Compacted mud surfaces (L51, L60) on the opposite sides of these walls possibly represent interior 16 This includes chaffy cook pots, flaring and simple straight rim bowls, carinated or hemispherical cups with a beaded rim, and hammerhead–rim bowls. See Parker and Foster, forthcoming; Parker et al. 2006, fig. 11. 158 spaces (figure 4.9 A). In the final phase a 1.4–meter–thick wall (L35/42) was constructed on the north end of existing wall L37/43 with an additional smaller mud brick wall (L38) also added to form at least two large spaces or rooms (figure 4.9 B). This massive construction can be interpreted as either the southeastern extension of the fortification/retaining wall uncovered in Areas A and C or a monumental building hitherto unattested for the Late Chalcolithic period on the high mound. The artifacts associated with this construction—ceramics, animal bone, chipped stone, beads—seem to represent a domestic assemblage. A B Figure 4.9. Late Chalcolithic architecture from Area E trench 2: A, whole vessels in situ adjacent to mud brick wall; B, large wall dissecting trench (UTARP Digital Archive). Outside of the main mound, Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age material was uncovered in Area G with several phases of simple structures, surfaces and burials that spanned multiple trenches. Most of these structures averaged a minimum of 12 square meters in size and were composed of mud brick on cobblestone foundations (G7: L46, L52, L9/21, L23, L27; G10: L15, L19, L21/27). Interior spaces were marked by mud plastered flooring (G10 L29) and pyrotechnic facilities that ranged from simple open–pit 159 fireplaces (G10 L16, L24, L28) to a tandır oven (G9 L7) 0.6 meters in diameter with a stoking hole at the base (figure 4.10). Extensive pebble surfaces between buildings most likely represent streets or alleyways (G7: L14/15, L50). The most spectacular find in this area was a bead cache (G9 L19) inside of a ceramic vessel that was, unfortunately, not connected to any architectural features.17 A total of six burials were found associated with this architecture, four of which were pithos (pot) burials of young children.18 Figure 4.10. Top view of tandır oven from Area G trench 9 (UTARP Digital Archive). Area F The most extensive and diachronic evidence for Late Chalcolithic occupation at Kenan Tepe derives from Area F, located on a flat terrace approximately 23 meters above the Tigris River on the northeast side of the main mound (figure 4.6). In total, seven stratigraphic levels have been identified and distinguished (table 4.3). Due to spatial 17 For a complete description of the beads, see section by Marie Hopwood in Parker et al. 2008, 144–145. For a complete osteological report of these burials, see section by David Hopwood in Parker et al. 2008, 122–125. 18 160 constraints and a lack of minute carbon dating, these levels cannot, with certainty, be reconciled with Late Chalcolithic occupational evidence from areas A, C, D, E, and G discussed previously. In terms of material culture however, there are many similarities that lead me to consider the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze corpus of materials at Kenan Tepe as a coherent whole. The earliest evidence for occupation in Area F, Levels 7 and 6, is a large mud brick oven (F4 L4009, L4027) built into sterile clay (figures 4.11, 4.12). Carbon dates Figure 4.11. Levels 6 and 7 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 3). 161 Figure 4.12. Late Chalcolithic oven from Levels 6 and 7; “House Lot 1” (UTARP Digital Archive). Figure 4.13. Architecture from Level 7 in trench F1 (UTARP Digital Archive). Level Area F Trenches Major Architectural Features 1 1, 5, 7, 14, Pit burials 2 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 20, 22 Cobblestone surfaces (pavement?); tandır ovens; pot stands and pits 3 1, 7, 8, 13 Shallow pits, Oven windbreak or animal pen (F7) Destruction Layer 4 1, 2, 7, 8, 9, 19, 20, 22 Building with interior platform (F2); Magazine–style store room (?) with adjacent deep pit, brick–lined burial (F7); Large multi–room building (F1,19,20,22) 5 1, 9 Domestic architecture with earthen floors and interior oven; compacted pebble alleyways; possible barn 6/7 1, 4 Large oven; small ephemeral structure; several superimposed pebble surfaces Table 4.3. Summary of Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age architectural features in Area F at Kenan Tepe. 162 from the basal levels of the oven date this feature to between 3600 and 3500 BCE (table 4.1). Adjacent to this oven was a small ephemeral structure (F1 L1123) and several superimposed surfaces (F1 L1116, L1117) of tightly packed pebbles and crushed pottery (figure 4.13). Stone grinders, pestles, obsidian debitage, worked stone needles, loom weights, tiny shell beads and a large amount of teeth and jaw bones were found on and embedded within the surfaces. These data suggest this was an outdoor working area such as a courtyard with an oven or an alleyway between houses where domestic debris was dumped and subsequently trampled. These data will be discussed in more detail below under “House Lot 1.” This working area remained in use during the subsequent Level 5 when two phases (A and B) of superimposed earthen and cobblestone surfaces19 were added and demarcated, presumably into outdoor and indoor areas, by additional mud brick walls20 (figures 4.14, 4.15). A circular pit (F1 L1090, L1091) in the northwest corner of the interior space was likely an oven, as it was filled with ash and the surrounding outer edge showed signs of burning. A modest building of packed mud pisé construction (L9052) lay nearby in trench F9 (figure 4.16). An entrance on the southern end was marked by a door pivot (L9046 KT7) and raised earthen threshold. The inside of the structure had a packed mud surface (L9049) covered with a white pseudomorph layer mostly likely the remains of straw or matting. This surface sealed an earlier 1–meter–deep refuse pit (L9055). When compared with ethnographic data (Kramer 1982, 106–107), this structure has many of the characteristics of a barn or stable area with trampled fodder on the floors and, if it 19 20 F1 L1086, L1057/1097, L1089, L1098, L1100, L1101. F1 L1069, L1076, L1080, L1096. 163 can be identified as such, a packed mud trough. It is possible that this stable serviced the nearby domestic area in trench F1. Figure 4.14. Level 5 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 3). 164 A B Figure 4.15. Architecture from Level 5 in trench F1: A, phase A; B, phase B (UTARP Digital Archive). Figure 4.16. Packed mud pisé building in trench F9 (UTARP Digital Archive). 165 These more ephemeral constructions of Level 5 gave way to significant architecture with several subphases of construction and reconstruction in Level 4 (figure 4.17).21 The earliest of these was a large mud brick structure from trench F2 (phase B) with plastered mud brick walls half a meter thick, a plastered platform, and a mud plastered floor into which a complete string–cut base bowl was set (figure 4.18; “House Lot 2” discussed below). The floor has been carbon dated between 3360 and 3020 BCE (table 4.1). This structure was not reused during the later occupation phase A. Instead, an L–shaped mud brick wall (L2034) with an adjacent mud brick platform (L2033) and pebble surface (L2035) was constructed in this area that either served as a poorly preserved building or retaining/separation wall (figure 4.19). In neighboring trench F7 five separate building phases of Level 4 were distinguished though they likely post–date the structure discussed above in trench F2. The F7 phases were characterized by a series of small overlapping walls, pebble surfaces, and plaster floors cut by later pits and burials. The earliest phase E had a central sunken hearth or fire pit inside a mud brick wall structure (figure 4.20). This was followed by a 3 by 0.5 meter mud brick wall (L7209) that was a combination of two walls joined at a corner during Phase D (figure 4.21). To the north of this wall was a compacted clay surface with flat–lying ceramic fragments and rounded river pebbles (L7208) that overlapped the mud plaster surface (L7213) from Phase E. It is possible that this compacted pebble surface is actually debris from when the mud plaster surface went out of use. 21 Due to space constraints, only select construction phases for Level 4 are depicted in figure 4.18. This does not imply that the phases shown are contemporary, but are meant to display the variety of architectural features from this level. 166 Figure 4.17. Level 4 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 2). 167 Figure 4.18. Mud brick structure from Level 4 phase B in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). Figure 4.19. Mud brick constructions from Level 4 phase A in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). 168 Figure 4.20. Sunken hearth or fire pit from Level 4 phase E in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). Figure 4.21. Mud brick wall from Level 4 phase D in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). 169 This architecture does not continue into the following phase C. Instead, disjointed features like wall stubs (L7202, L7201), a large pit (L7199; figure 4.22 A) and an adjacent adolescent burial were constructed (L7200; figure 4.22 B). The burial was inside a mud brick–lined pit with no associated grave goods. It is possible that this inhumation A B Figure 4.22. Brick-lined burial and pit from Level 4 phase C in trench F7: A, before excavation; B, detail of burial (UTARP Digital Archive). was not associated with this phase, but the following Phase B, in which a multi–roomed structure opened onto a courtyard area under which the adolescent was buried. This structure (L7178) was composed of multiple connecting walls forming two magazine– type rooms roughly 1 meter wide and 2.5 meters long (figure 4.23). Flimsy construction, lack of floor, and minimal debris suggest this building may have been used for keeping animals or as temporary agricultural storage. Perhaps an adjacent structure (L7163, L7154), only the corner of which falls within F7, served as the primary living space. These data will be discussed in more detail below under “House Lot 3.” The latest phase A consisted of a single–room structure, which only a portion of the walls (L7160, L7158) and compacted pebble floor (L7169) with door socket (L7152 KT4) were found 170 Figure 4.23. Magazine structure from Level 4 phase B in trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). Figure 4.24. Structure from Level 4 phase A in trench F7, facing southwest (UTARP Digital Archive). preserved directly above the Phase B structure (figure 4.24). Adjacent to the Phase B magazine building was a burial construction made from three courses of burnt and unburned mud brick that contained an adult female in a flexed position on her left side (figure 4.25). It is unclear whether this was a pit that was lined with bricks as was 171 discovered in the adolescent burial nearby or a freestanding structure comparable to Late Chalcolithic burials at Tepe Gawra (Rothman 2002; Tobler 1950) and Tomb J at Korucutepe (van Loon 1975).22 Figure 4.25. Brick-lined burial of an adult female adjacent to Phase B magazine building in Trench F7 (UTARP Digital Archive). In trench F8, Level 4 contained a single–course mud brick wall (L8034) with a possible doorway. This wall did not continue into trench F2 to connect with L–shaped wall L2034, but their orientation is similar, suggesting perhaps different building phases of the same structure or contiguous features. Level 4 in trench F9 yielded a one–course mud brick wall (L9035) and a small rectangular pebble surface (L9036), in whose suprasurface fill a bronze needle or pin was uncovered. Whether these features are contiguous with an adjacent deep pit (L9045), extending from the north baulk is unclear. The northern half of this pit was uncovered in trench F7 (L7146). A heavily disturbed 22 For a complete report on this burial see Parker et al. 2008, 113, 125–128. 172 burial (L9042) from the southwest corner of F9 was partially obscured by the baulk and may be associated with this level or a later addition. The latest architectural construction from Level 4 was a relatively large building that spanned trenches F1, F19, F20, and F22 that will be discussed in detail below under “House Lot 4.” Level 4 occupations came to a violent end, as heavy burning and burnt mud brick slump throughout Area F contexts attest to a large conflagration. Following this destruction, Level 3 was composed of ephemeral occupation throughout Area F with shallow, debris–filled pits (F8 L8023, L8022; F13 L14), ash lenses, mud brick slump, and a mud brick structure measuring approximately 2 by 4 meters in trench F7 (figures 4.26, 4.27). Composed of three 0.4–meter–thick single course walls (F7 7033/7053), the structure lacked an eastern wall, which is perhaps due to later disturbances by Level 1 burials (F7 L7028, L7094) and Level 2 cobblestone surfaces (F7 L7005). A pivot stone or door socket was uncovered on the eastern end of the southern wall (F7 L7077 KT 22) marking some kind of entrance on this side of the structure. Earthen surfaces cut by later pits (L7042, L7043) were found both inside (F7 L7075) and surrounding this structure (F7 L7074) and were strewn with ceramic and bone debris. Strangely, baked brick oven material was found inside the building but there was no other evidence for burning or a permanent pyrotechnic installation. This structure perhaps functioned as a windbreak for an oven or shelter for animals (Creekmore 2007, 83). 173 Figure 4.26. Level 3 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 2). Figure 4.27. Mud brick structure in trench F7, Level 3 (UTARP Digital Archive). 174 These Level 3 contexts were sealed by an extensive layer of cobblestone surfaces that are the distinctive feature of Level 2 (figure 4.28).23 Most of these surfaces were composed of two layers: a bottom foundation of smaller stones and pebbles and a top layer of larger cobbles (figure 4.29). While the cobblestone surfaces in the northern trenches of Area F contained a scattering of pottery and animal bone fragments, the surfaces from trenches in the south (F1, F19, F20, F22) were mostly devoid of cultural material, save for a large animal bone embedded within the cobbles of F19. Three small Figure 4.28. Levels 1 and 2 in Area F (adapted from Creekmore 2007, fig. 1). Note: two burials from trench F6 not pictured. 23 Trench F1 L1006, L1009; trench F2 L2003, L2008; trench F7 L7005, L7029; trench F8 L8010; trench F14 L3, L19; trench F15 L6–12; trench F19 L2; trench F20 L2; trench F22 L2. 175 Figure 4.29. Detail of Level 2 cobblestone surface and oven in trench F2 (UTARP Digital Archive). A B Figure 4.30. Tandır ovens from Area F Level 2: A, trench F2 L2002; B, trench F8 L8002 (UTARP Digital Archive). tandır ovens with similar diameters ranging from 50 to 70 centimeters were associated with these surfaces (figure 4.30 A and B). Three circular cobblestone, rock and ceramic fragments installations were also uncovered in trench F8 that most likely represent pot stands (F8 L8005, L8006, L8009), and several debris pits containing burnt pottery, 176 animal bones, chert and obsidian (F20 L4; F22 L4). Based on the domestic debris and lack of substantial architectural features, these cobblestone surfaces and ovens seem to represent an outdoor work area or disposal site that covered the majority of Area F. These surfaces were then later cut by Level 1 intrusive pit burials whose exact date is unknown, but could range anywhere between the Early Bronze Age and Islamic Period (figure 4.28). A total of thirteen burials were scattered across the entirety of Area F.24 Due to poor preservation, excavators have been unable to determine the sex or age of the interred individuals. Most seem to be adults in extended or flexed positions with the head oriented to the west and the rest of the body to the east (figure 4.31). Grave goods were minimal and included a spindle whorl, a miniature vessel, a small juglet, and a bronze pin. A B Figure 4.31. Level 1 pit burials from Area F: A, trench F5 L5000/5005; B, trench F7 L7006 (UTARP Digital Archive). 24 Trench F1 L1004, L1008A, L1008B, L1011/1021A, L1011/1021B, L1017/1022; trench F5 L5000/5005; trench F6 L6004, L6011; trench F7 L7006, L7028/7054, L7084; trench F14 L7. See also Creekmore 2007, 79-81, 106 table 1. 177 Late Chalcolithic House Lots As discussed in chapter 2, my investigation of households is limited to the primary locus of activities: the house and its immediate surroundings, collectively identified as house lots. Traditionally defined house lots often, but not always, contain a large area, often bounded, comprised of a primary dwelling unit (the house), adjacent uncovered patio or open courtyard area, and garden zone. To this I would add a mobility zone adjacent to the house lot composed of walkways or alleyways and a refuse zone where secondary deposition of objects take place. It is also possible that these two zones, mobility and refuse, coexist spatially, that is refuse can pile up along streets and alleyways between house lots. Four house lots are described below that make up chronologically distinct bounded units at Kenan Tepe that I will be using for the study of the DMPC (table 4.4). These particular house lots were chosen primarily because they stand as the best preserved examples of domestic architectural units for the Late Chalcolithic at Kenan Tepe. They are also located in the same area of the site allowing for a spatial and diachronic study of the domestic economy. House Lot Trench(es) Calibrated 14C (BCE) Chronology 1 F1, F4 3523 to 3335* LC 4 2 F2 3360 to 3020 LC 4/5 3 F7 3360 to 3020 LC 4/5 4 F1, F19, F20, F22 3020 to 2890 LC 5 *Range is averaged from six carbon dates. See table 4.1. Table 4.4. Late Chalcolithic house lots with their corresponding trenches and dates from Area F. 178 House Lot 1 Located in Trenches 1 and 4 in Area F in the outer town east of Kenan Tepe’s main mound, this house lot represents multiple continuous building episodes that span Levels 7 through 5. The earliest phase (Level 6–7) is an outdoor work area built into virgin clay consisting of a large mud brick oven or kiln adjacent to a small structure (figure 4.32a). The oven or kiln (F4 L4009, L4027) is approximately 2 meters in diameter and was constructed of bricks measuring 15 by 7 centimeters that were laid lengthwise in two rows. Twelve courses of bricks were preserved allowing excavators to note a slight incurving of the walls that perhaps signify a domed roof much in the tradition of other later ovens at Kenan Tepe (see Level 2 contexts in Area F [table 4.3] and trench G9 L7) and tandırs in modern Turkish villages (Parker and Uzel 2007). A deposition of black, gray and white ash (F4 L4007, L4012, L4023) nearly half a meter thick filled with animal bones, ceramics and other debris was uncovered curving up the inside of the oven. Adjacent to this kiln or oven is a small street or alleyway bordering a small structure of which only an ephemeral wall remains from the earliest construction (figure 4.13). This wall (F1 L1123) is composed of mud bricks measuring 30 by 50 centimeters bonded by a mud plaster mortar with only a single course preserved. This wall runs approximately north–south for 3 meters with the rest of the wall and structure hidden in the trench’s north and east baulk. The street or outdoor surface (F1 L1117) stretches for 4 meters between the structure and the oven/kiln sloping at a 35 to 45 degree angle on its eastern visible edge most likely due to an earlier pit (F1 L1130) that lay below. The surface is composed of compacted pebbles less than 5 centimeters in size in a coarse clay matrix into which various categories of debris had been embedded. These included 179 Figure 4.32a. House Lot 1, phase 1. crushed ceramic fragments, animal bones, and lithics. As mentioned previously, an earlier pit (F1 L1130) was sealed by this alleyway. Roughly circular in shape, this pit was 50 centimeters in depth and filled with heavy amounts of carbon and ash with subdivisions composed of alternating strong brown and black ash layers perhaps indicating multiple dumping episodes. 180 In a second phase of building (Level 5 phase 2; figure 4.32b), the oven in trench F4 went out of use and was instead utilized as a locus of trash disposal along with a pair of adjacent pits (F4 L4024/L4033 and F4 L4034/L4043). The original wall (F1 L1123) was rebuilt (F1 L1096) with the same north–south orientation though smaller in dimension (1.75 meter long by 40 centimeters wide). A second wall (F1 L1069) Figure 4.32b. House Lot 1, phases 2 and 3. 181 measuring 0.94 meters by 0.36 meters wide was added running perpendicular east–west. These two walls served to demarcate two areas of cobblestone surfaces (F1 L1100, L1101) and an earthen surface (F1 L1098) into which a flared–rim cooking pot (F1 L1103 KT5) had been sunk so that the lip of the vessel was flush with the surface.25 Later additional walls were added in Level 5 phase 3 (figure 4.32b). One (F1 L1076) runs north–south perpendicular to wall L1069 and measures 28 by 20 centimeters. Only two bricks were visible and only a single course was preserved to a height of 10 centimeters. The other wall (F1 L1080), measuring 2.7 meters long by 0.5 meters wide, runs east–west and encloses a second earthen surface (F1 L1089) between it and wall L1096 to the east. This second surface covered the earlier sunken cooking pot but was itself cut by what was probably a brick oven (L1090, L1091) that is unfortunately obscured by the northern baulk of trench F1. Measuring 80 centimeters in length and 45 centimeters in width, this roughly circular pit was quite shallow with only the basal levels preserving a thin layer of ash in the center encircled by a thin residual layer of burned and hardened clay, which represents the last vestiges of the oven or fire pit wall. Presumably outside of this interior space, additional cobblestone surfaces (F1 L1086, L1057/1097) were built/accumulated atop earlier surfaces of the same type in Phase 2 forming an alleyway east of wall L1096 and continuing south between walls L1080, L1069 and L1076. The largest of these surfaces (F1 L1086) measures 4.15 meters long by 0.7 meters wide and is composed of debris and cobbles up to 5 centimeters in size. 25 A similar context was excavated at Tell Brak where bowls had been inset with their mouths level with the floor (Emberling and McDonald 2003, fig. 3: 8–9). This is a common feature throughout the Late Chalcolithic period at Kenan Tepe (see especially House Lot 2 discussed below). 182 House Lot 2 This house lot, located in trench 2 of Area F, consists of a partially excavated single room building measuring approximately 4.5 by 3.5 meters and composed of plastered mud brick walls whose individual bricks measure 25 by 50 centimeters (L2050, L2064; figure 4.33). The floor consists of superimposed surfaces including a pseudomorph layer (L2056) that most likely represents grass matting above a prepared mud plaster floor (L2065). The building contained only two permanent fixtures: a 1.8 by 0.5 meter plastered platform (L2051) in the southeast corner and a 1.15 by 0.55 meter pisé/mud brick feature (L2064) on the western end. Figure 4.33. House Lot 2. 183 This latter installation most likely served as a room divider or screen for an adjacent circular indentation (L2067) that measures 82 centimeters in diameter and less than 50 centimeters deep. It was covered by a compact black ashy surface (L2069) at the center of which was a simple rim bowl with string–cut base (L2070) that had been positioned so that the rim was flush with the ashy surface (figure 4.34). This entire feature connected smoothly with the larger building floor suggesting that the two are contemporaneous. The function of this sunken bowl feature is unclear, as no artifacts were recovered inside or adjacent to it. Ashy remains adhering to the interior surface of the bowl suggest the presence of fire or burning at some point around this feature; however, this most likely derived from the destruction of the entire building. Figure 4.34. Sunken bowl feature in House Lot 2 (UTARP Digital Archive). Two later pits cut into the interior surface. One measuring 35 centimeters in diameter (L2066) was filled with small pieces of coarse potsherds, plaster fragments, and a heavily damaged ceramic animal figurine (KT6). The other (L2042) measures 1.55 by 184 1.1 meters and cut both the mud surface and the plastered platform. This pit contained mud brick debris, pottery fragments, and a cylinder seal (KT7; discussed below and also chapter 5). Part of a child inhumation was partially excavated at the base of this pit, but it is unclear whether the burial was truly within the pit or part of the layers that the pit disturbed. A compacted pebble surface with crushed ceramic fragments and other debris was located outside this building on the eastern (F2 L2049) and southern side (F2 no locus). These most likely correspond to alleyways or streets that were used for trash disposal. House Lot 3 This house lot is located in trench 7 of Area F (figure 4.35). The largest feature is a 2.8 by 3.3 meter structure (L7178) composed of mud bricks averaging 25 by 35 by 8 centimeters in dimension. Internally the structure is divided into two narrow rooms or magazines roughly 0.75 meters wide and 2 meters long. There is no indication for floors, even compacted earth, or distinct and permanent doorways marked by pivot stones. Instead these rooms open onto an undeveloped area devoid of architecture or other discernable features. North of the building is a large circular pit (L7181) 2 meters in diameter that was only partially excavated, but still reached 0.80 meters deep (figure 4.36 A and B). It was filled with ash and other debris that had been partially covered or sealed by 1–centimeter–thick compacted mud layer and lined by a single row of mud bricks averaging 25 by 40 centimeters. A shallow 1 by 1.3 meter ovoid–shaped bin (L7186) adjacent to this pit was also lined with mud plaster and flanked on the east by a 25 centimeter wide mud brick wall (L7187). 185 Figure 4.35. House Lot 3. A B Figure 4.36. Large plastered pit in House Lot 3: A, before excavation; B, after excavation (UTARP Digital Archive). 186 To the northwest stands a heavily burned and damaged structure composed of at least two spaces or cells that were able to be only partially excavated. The two remaining walls (F7 L7154, L7163) are composed of reddish brown (2.5YR 6/4) and white, possibly plastered mud bricks with pebble inclusions that average 20 by 40 centimeters (figure 4.37). Between these walls and to the west of wall L7163 are several phases of smoothed mud plastered surfaces,26 all of which are bonded with the walls and thus are contemporary with them. With such a relatively small amount of this presumably larger structure excavated, it is not surprising that no permanent installations or features were uncovered in this space. The preservation of the surfaces was, however, quite good allowing for numerous superimposed microsamples to be taken and later compared (see below). Figure 4.37. Top view of heavily damaged structure from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive). 26 In order of deposition: Cell 1: L7174, L7168; Cell 2: L7194, L7189, L7185, L7182, L7170. See figure 4.35. 187 This structure was wholly destroyed by a large conflagration and destruction level that essentially sealed these contexts. They were later damaged by a large pit (F7 L7162) measuring 1.8 meters in diameter and approximately 1 meter deep. This pit cut into the southern portion of the Cell 2 surfaces and wall 7154 and most likely completely destroyed the cross wall that effectively closed off this space on the southern end. An adult male skeleton (F7 L7148) was also excavated at the southern extension of surfaces from Cell 1 (figure 4.38). This individual was resting on a black ashy surface that likely corresponds to the surfaces from Cell 1, notably L7174, suggesting this individual was perhaps a victim of the fire and subsequent collapse of this building. That there is no evidence for a specifically cut pit in which to intern the individual for a burial further supports this assertion. Figure 4.38. Partially preserved male individual south of Cell 1 in House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 188 House Lot 4 This large structure stretches across four trenches in Area F (1, 19, 20, and 21) but spans only a single construction phase (figure 4.39).27 The excavated portion of this structure measures approximately 7 by 9 meters though it is unclear whether this represents a single large interior space or two separate rooms. The walls28 are composed of mud bricks averaging 25 by 46 by 10 centimeters in size laid lengthwise as stretchers atop a cobblestone foundation.29 The southern walls (F22 L11 and L17; L16 and L21) adjoin to form a double wall, signaling either structural reinforcement on the south side of the building or a second abutting structure. There is evidence for slight modifications to the building in the form of blocked doors or passageways, one separating the main structure from the abutting building (F22 L22) and one possibly separating two rooms inside of the main structure (southern end of wall F19 L5/21). The foundation for wall L11 in trench F22 is also deeper such that the cobble foundations of walls L17 and L20 abut the northern face of wall L11 indicating that L11 was built prior to the main structure. A number of possibilities could account for this including different builders, expansion of the house due to an enlarging family unit (i.e., new marriage, etc.). A mud plaster surface (F1 L1055/1060; F19 L15; F20 L14; F22 L19) was uncovered in Rooms 1 and 2. In the center of Room 1 is a large brick oven (L1045) measuring 1.5 meters in diameter with only a single 10 centimeter high course of bricks preserved (figure 4.40). Inside the oven is a rectangular mud brick pedestal or stand 27 That we know of. Trenches F19, 20, and 22 were not excavated below this structure. Future excavations in this area may reveal additional constructions or visual modifications to the existent structure. 28 Trench F20: L11; trench F19: L5/21, 18, 20; trench F22: L11, 16, 17, 21, 22. 29 Because this structure was not completely excavated, the cobblestone foundation was only visible below two walls: F19 L10/19 and F22 L17. 189 Figure 4.39. House Lot 4. Figure 4.40. Brick oven from House Lot 4 (UTARP Digital Archive). 190 (L1045 KT1246) with smoothed sides measuring 64 by 30 by 9 centimeters sitting atop a hardened clay floor bright orange in color due to firing. In Room 2, a 1–meter–diameter shallow pit (L16) was sunk into the mud plastered floor. Though no obvious brick superstructure was recovered, the contents of this pit—ash, slag (KT 3), and a hardened red bottom—suggest it was used for pyrotechnic activities. This house lot was destroyed by a large conflagration as well. The mud brick walls and earthen interior surface were lightly baked suggesting the structure burned before collapse. The floor was also covered with a thin layer of ash (F1 L1047) that either derived from the central oven or the fire that destroyed the building. Household Level Production and Consumption With the loci of inquiry established on the regional and site level, I now turn to the archaeological evidence for the DMPC at Kenan Tepe for the four house lots introduced previously. While some interpretation of this evidence is necessary for a complete understanding of the primary data, my full interpretations as to how this evidence can be applied to the interpretation of diachronic changes to the DMPC in terms of morphology and scale between house lots will be discussed in chapter 5. Agriculture This category of production includes the cultivation of crops on arable land and the pastoral herding of domesticate animals or livestock. The former necessarily requires open space or terracing and good soil. While further geomorphological work remains to be carried out around Kenan Tepe (see Parker et al., forthcoming), as discussed 191 previously during the Chalcolithic the Tigris was much wider and flowed deeper than current conditions, most likely the result of higher annual precipitation levels, lower evaporation rates, and possibly increased flow of water from the river source. Cultivation most likely took place in fields to the north and west, as these would have been the only areas not engulfed by the river and with adequate precipitation levels for dry farming. Animal husbandry requires pasture land for sheep, goat and cow, for example, along with appropriate housing units, most likely inside of the settlement and close to the house lot. These pens do not need to be permanent mud brick installations, but could also have been pisé and/or reed constructions suitable for containing small herds. Pigs would also require pens of this nature, though as will be discussed in the following chapter, they are not always necessary. Admittedly plant cultivation is difficult to detect in house lots since most of the activities that make up this type of production—growing, harvesting, and threshing—take place beyond living spaces. However the processing, use and storage of cultivated plants, especially cereals, are evident for some house lots. The richest of these is House Lot 1 where the oven in trench F4 contained large amounts of two–rowed hulled barley (Hordeum distichum) along with einkorn (Triticum monococcum), emmer (Triticum dicoccoum), and probably spelt (T. spelta) wheat (tables 4.5 and 4.6: samples 1 through 11). These grains were accompanied by glume bases, spikelets and rachis fragments that provide evidence for processing, storage or transportation of these cereals in their “raw” form (Parker et al. 2003, 122). 192 Sample 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Tr. F1 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F4 F7 F7 Loc. 1130 4004 4004 4007 4009 4012 4012 4012 4012 4013 4034 7162 7181 KT# 2 4053 4057 4079 4023 4109 4303 4304 4308 4314 4197 23 17 Chronology LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 3/4 LC 4/5 LC 4/5 Context type Pit associated with F4 oven Inside F4 oven Inside F4 oven Inside F4 oven Inside F4 oven F4 oven wall Base of F4 oven Base of F4 oven Base of F4 oven Base of F4 oven Pit Pit Pit Table 4.5. Contextual information for botanical sample data presented in table 4.6. 193 X = few (1-5) XX = common (6-25) XXX = many (>25) Table 4.6. Botanical sample data across Late Chalcolithic house lots based on relative abundance. 194 Storage vessels in the form of ledge rim collared jars, necked jars with slightly everted rims, and large handled jars or pithoi (figure 4.41 I–L), make up only 6% of the ceramic assemblage (N=298).30 This, compared with the over 85% of the vessels being open bowls and other serving–related vessels that will be discussed below, provide minimal evidence for long–term storage of these agricultural products in ceramic vessels or permanent installations such as stone or plaster–lined silos. It is likely then that foodstuffs were either stored in locations outside the house lot for community consumption or only temporarily in perishable containers such as baskets or wood bins. Wild seeds were also identified in the oven and pit assemblages that consist primarily of field species, riparian species, or species usually associated with animal food. These include various Cyperaceae (sedges and reeds), wild grasses (Galium, Scirpus, Gramineae) Rumex sp., Malva sp., and wild legumes (table 4.6). This type and abundance of grass and field weeds supports an assemblage used in the foddering of domesticate animals, as opposed to seed rain deposition for example (Minnis 1981). According to the faunal assemblage (N=176, table 4.7), these animals included primarily sheep and goat (29%) and to a lesser extent pig (14%) and cow (11%). Based on mandibular specimens, most of these animals were culled at prime–age (2–3 years) for meat consumption and utilized to a lesser extent for secondary products such as milk, wool or traction. This was the case for the faunal assemblage across all house lots, therefore their role as food products will be discussed in the following section (“Food and Eating”). 30 Diagnostic sherds that could be typologically categorized based on function represent 18% of the ceramics analyzed for this house lot, based on sherd weights available. The percentage of functional types is based on count. 195 Figure 4.41. Descriptions of Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 1 A F4 L4007 KT4077 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/4). Light reddish brown interior surface (5YR 6/6). Light brown fabric (7.5YR 6/4). Fine grit. B F1 L1115 KT1 #1: Brown exterior surface (7.5 YR 4/3). Pale brown interior surface (10 YR 6/3). Very dark gray fabric (7.5YR 3/1). Medium micaceous sand. Vertically burnished. C F4 L4020 KT4021 #3: Pink exterior surface (7.5YR 7/4). Pink interior surface (7.5YR 7/3). Light brown fabric (7.5YR 6/3) grading to a dark gray core (10YR 4/1). Medium chaff. D F4 L4007 KT4086 #2: Reddish yellow exterior surface (10YR 7/4). Very pale brown interior surface (5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 7/6). Abrupt transition to a red core (2.5YR 5/6). Medium grit. E F1 L1106 KT12 #2: Pink exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 7/4). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 7/6) grading to a dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Medium to fine chaff and fine grit. Smoothed interior. Chaff facing. F F1 L1116 KT7 #1: Reddish yellow exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 6/6). Abrupt transition to a dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Medium micaceous grit and low levels of fine chaff. G F1 L1117 KT7 #6: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/6). Light red interior surface (2.5YR 7/6). Strong brown fabric (7.5YR 5/6). Abrupt transition to a dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Very fine grit with low levels of fine chaff. H F1 L1116 KT7 #9: Yellowish brown exterior surface (10YR 5/4). Brown interior surface (7.5YR 5/4). Strong brown fabric (7.5YR 5/6). Abrupt transition to a brown core (7.5YR 4/3). Fine chaff and grit. I F1 L1121 KT1 #1: Reddish yellow exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/6). Abrupt transition to a pale brown core (10YR 6/3). Coarse to medium chaff. Burnished exterior. J F4 L4033 KT4191 #2: Pale brown exterior surface (10YR 4/2). Dark grayish brown interior surface (10YR 6/3). Olive brown fabric (2.5YR 4/3). Abrupt transition to a dark grayish brown core (2.5YR 4/2). Fine chaff and grit. K F4 L4016 KT4004 #2: Pink exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 8/3). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/6). Medium to fine chaff. Burnished exterior and interior. L F1 L1117 KT7 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow interior surface (5YR 6/8). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/8). Abrupt transition to a greenish black core (10Y 2.5/1). Large to fine grit and fine chaff. Horizontally burnished on interior surface. 196 Figure 4.41. Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 1. 197 While the botanical remains discussed above do not represent primary refuse inside this oven, they most likely represent the domestic plant assemblage from the neighboring structure during a later phase of this house lot where this large oven would have been a readily accessible refuse area. Various levels of fill within this oven (F4 L4004, L4007, L4009) were sampled separately in order to make a comparison and possibly identify multiple depositional episodes. Based on the botanical data, there are no marked differences between the samples except for a larger amount of barley in the very basal levels of the oven (F4 L4009; K. Meegan, pers.comm.). The neighboring pits (L4012, L4013, L4034) did contain a relatively larger number of Cyperaceae, especially Scirpus maritimus–type, wild grasses, wild legumes, and small unidentifiable wild seeds than inside the oven that is likely due to different depositional histories and less intensive burning inside the pits resulting in greater survival of botanicals. This trend is echoed on the microlevel where samples from pit L1130 had the greatest number of seed remains in the microdebris compared with the other house lots (figure 4.42). This same rich assemblage of botanical remains is unfortunately not echoed in House Lot 2. All surface and pit features sampled (25 samples in total) were essentially sterile. The absence of botanical data in the archaeological record for this house lot could be due to several factors including poor preservation conditions, the existence of prepared floors that minimize the potential for charred material to become embedded in the sediment, or rigorous floor cleaning by the household living and working in this space (Parker et al., forthcoming). Another alternative reason is perhaps this was a very specialized household or physical space that was not utilized for the essential “day–to– 198 day” activities of living that would normally have included agricultural production and consumption, as it does for most village–level community groups today (Kramer 1982). Seed Count Density (All House Lots) 3 2.5 Count / Volume (L) 2 1.5 1 0.5 House Lot 1 House Lot 2 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F7.7181.9.1 F7.7181.19.1 F7.7181.13.1 F7.7168.1.1 House Lot 3 F7.7162.18.1 F7.7174.2.1 F7.7170.5.1 F7.7170.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7194.1.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F1.1130.2.1 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1117.5.4 0 House Lot 4 Figure 4.42. Seed count density compared across all house lots. Without botanical data it is then difficult to interpret the faunal assemblage for this house lot, consisting primarily of sheep/goat and pig, in terms of herding and rearing of these animals. While pigs do not require foddering per se, sheep and goat do need food storage for the winter months when grazing is less predictable. The absence of permanent storage facilities or receptacles in the form of bins, pits, or silos could provide evidence that this house lot was occupied on a seasonal basis. This hypothesis is supported by the ceramic assemblage where only a miniscule 5% of the vessels are identified as storage– related vessels. Because the total ceramic assemblage is quite small (N=19), this 199 percentage may not be significant. However the low level of ceramics used by this household in–and–of–itself could be an indication for seasonal encampment. In House Lot 3, two pits (F7 L7162 and L7181) provided the best preserved botanical remains and, as with House Lot 1, likely represent oven rake–out deposits. The assemblage consists largely of cereals like barley (Hordeum sp.), emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccoum) and other wheat species (Triticum sp.; tables 4.5 and 4.6: samples 12 and 13). These grains were again accompanied by cereal internodes, glume bases, spikelets and rachis fragments that attest to processing of these cereals within the house lot after local cultivation and harvesting. Unlike House Lot 1, storage vessels utilized by this household make up a larger percentage of the vessels in the assemblage (11%; N=75). Vessel forms range from necked jars with slightly everted rims to pithoi and large necked jars (figure 4.43 A–C). The presence of grass peas (Lathyrus sp.), wild seeds (Adonis sp., Teucrium sp., and small legumes such as Medicago radiata and Astragalus sp.) and domestic sheep and goat dung and intact pellets in at least one of the samples (F7.7162.23) not only provide possible evidence for the foddering of domestic animals, but also the use of dung cakes as a source of fuel (see below and Parker et al., forthcoming). Further evidence is provided by the faunal assemblage that shows a level distribution of domestic pig (25%), cow (21%), sheep and goat (27%) out of a total NISP of 56 (table 4.7). Based on available mandible specimens, most of these animals were killed by the prime age of 2 to 3 years, again a pattern consistent with meat production and consumption. Unfortunately all sixty samples collected for archaeobotanical analysis for House Lot 4 were essentially sterile. Likewise the microdata evidence, derived from surfaces 200 Figure 4.43. Descriptions of Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 3 A F7 L7178 KT3 #3: Pink exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 7/4). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/6) grading to a dark gray core (5YR 4/1). Chaff and grit. Chaff facing on interior surface. B F7 L7180 KT10 #2: Brown exterior surface (7.5YR 4/2). Dark grayish brown (10YR 4/2). Red fabric (2.5YR 4/6) grading to dark brown core (7.5YR 3/2). Fine chaff and medium white grit. Burnished exterior and interior. C F7 L7180 KT10 #3: Reddish yellow exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 6/6) grading to a black core (7.5YR 2.5/1). Medium to fine chaff and grit. Burnish on exterior. D F7 L7194 KT2 #1: Dark gray exterior surface (5YR 4/1). Black interior surface (5YR (2.5/1). Black fabric (5YR (2.5/1). Abundant chaff and fine white grit. E F7 L7163 KT1 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/8). Reddish yellow interior surface (7.5YR 7/6). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/6). Abrupt transition to a yellowish red core (5YR 5/6). Dense fabric with large to medium calcareous grit and fine mica. Parallel incised lines. F F7 L7162 KT20 #2: Light brown exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 6/3). Brown fabric (7.5YR 5/3). Abrupt transition to a very dark gray core (7.5YR 3/1). Very fine grit and fine chaff. Some fine micaceous grit. Burnished interior and exterior. G F7 L7162 KT5 #1: Light reddish brown on exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 6/4). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 7/6). Simple ware with fine grit and chaff in a dense fabric. Horizontal burnish on exterior. H F7 L7162 KT20 #1: Light reddish brown exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 6/4). Yellowish red fabric (5YR 5/6). Medium chaff and very fine grit. I F7 L7181 KT13 #6: Yellowish red exterior surface (5YR 5/6). Light red interior surface (2.5YR 8/6). Pinkish red fabric (5YR 6/2) grading to light red core (7.5YR 6/8). Fine grit. Burnish on exterior. J F7 L7182 KT2 #1: Very pale brown exterior surface (10YR 7/3). Light gray interior surface (10YR 7/2). Very pale brown fabric (10YR 7/3). Medium to fine chaff. Smoothed interior and exterior. K F7 L7162 KT20 #5: Very pale brown exterior and interior surfaces (10YR 7/3). Light brown fabric (7.5YR 6/4). Very fine chaff. Four incised lines at shoulder. L F7 L7180 KT10 #1: Light brown exterior and interior surface (7.5YR 6/4). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 6/6). Light exterior horizontal burnish. Small to medium fine grit temper. M F7 L7181 KT13 #1: Brown exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 5/4). Strong brown fabric (7.5YR 5/6). Medium and some coarse grit and fine chaff. 201 N F7 L7163 KT1 #2: Pink exterior surface (7.5YR 7/4). Pink interior surface (7.5YR 8/4). Pink fabric (7.5YR 7/4) grading to a light reddish brown core (5YR 6/4). Grit and chaff facing. O F7 L7181 KT13 #3: Strong brown exterior surface (7.5YR 4/6). Reddish brown interior surface (2.5YR 5/4). Yellowish brown fabric (10YR 5/4) grading to a grayish brown core (2.5YR 5/2). Very fine grit. Burnished interior and exterior. 202 Figure 4.43. Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 3. 203 and suprasurface debris inside the house lot, is miniscule consisting of a single charred seed (figure 4.42). This makes House Lots 2 and 4 stand out as lacking any remains of botanical evidence. As mentioned previously, the absence of these data could be due to several factors including poor preservation, non–porous surfaces, rigorous cleaning or a specialized household group. As with House Lot 2, it is difficult to discuss foddering of domestic animals without the botanical evidence though this does not undermine the possibility that these animals were kept elsewhere. Certainly sheep/goat and cow were utilized by this household, as will be discussed below, however a sharp increase in the consumption of pig may account for the relative absence of botanical remains as well (see below and chapter 5). Storage vessels were recovered from this context, though they make up a minimal percentage (12%) of the entire ceramic assemblage (N=92) as with the other house lots. Food and Eating By its very nature, recovering evidence for the production and consumption of food requires a multidisciplinary approach. This includes floral and faunal data, ceramic assemblages, and tools such as grinding stones, fishing weights, and andirons used to acquire and transform raw material into food. As discussed previously, House Lot 1 contained the best preserved evidence for domesticate cereals like hulled barley and wheat that were likely used in the production of breads. The sheer size of the earliest oven (2 meters in diameter) utilized by this household speaks to either baking and bread production that exceeds the level of need for a single household unit or the simultaneous use of this oven by multiple households. Certainly the high level of basalt grinding 204 querns (F1.1115.4, F4.4023.4126), mullers (F1.1109.4), pestles (F1.1116.20) and large pounders (F1.1112.3, F1.1116.14, F1.1082.3) found incorporated into the cobbled streets as refuse and on household surfaces attest to high levels of cereal processing into flour, though these tools could have been used to grind nuts as well (see below). This high level of production however does not seem to have lasted, as the F4 oven went out of use and a new, smaller oven was used inside of the domestic space. Apart from cereals, the botanical assemblage includes large and small legumes (Leguminosae), peas (Pisum sativum), nuts and grapes (Vitis sp.; table 4.6). Both the nuts and grapes could have derived from household gardens or small orchards, though no other orchard–type plants are present. An abundance of wood charcoal throughout the samples likely corresponds to this resource being used in cooking fires. Apart from bread and stews, meat was also a common staple for this household with sheep and goat House Lot Sheep & Goat Lg–MM Md–MM Sm–MM Bird Fox Hare Pig Cow Gazelle Fish Crab Red Deer Unident Total NISP comprising the majority of the assemblage (29%; table 4.7). Pig (14%), cow (11%), and 1 29 10 20 2 2 0 1 14 11 0 3 2 0.6 9 178 2 22 6 6 6 0 6 0 17 11 6 0 0 0 22 18 3 27 9 9 2 0 0 0 25 21 4 2 0 2 0 56 4 12 0 4 4 0 0 0 60 16 0 0 0 4 0 25 Lg–MM = large mammal Md–MM = medium mammal Sm–MM = small mammal Unident = unidentified Table 4.7. Percentages of species across Late Chalcolithic Period house lots at Kenan Tepe based on NISP of identified bones. 205 other medium mammals (20%) were also consumed along with wild species like bird (2%), hare (1%), fish (3%), freshwater crab (2%), and red deer (0.6%). While some adult pig specimens were present in the assemblage, most of these animals were culled at young ages (2–3 years) based on available sheep/goat and pig mandible specimens that show a trend toward meat production and consumption, with a lesser focus on the use of secondary products like milk, wool and/or traction. The bones exhibit evidence for cutting, specifically crushing, slicing, breaking on the distal ends and long deep chopping, all indicative of butchering practices. That all parts of the carcass are present in many examples, and not simply choice cuts of meat, provides evidence for the local raising, butchering and consumption of these animals as opposed to gifts of meat for example. Furthermore the lack of evidence for gnawing on the bones from dogs or other scavengers that would result in disturbance of the spatial patterning of the faunal remains shows this assemblage was primarily consumed and discarded in this household locus. These animals and plants were likely cooked in small globular–shaped cook pots (figure 4.41 B) elevated above open wood fires as indicated by the botanical assemblage, the lack of spit marks on the bones that would indicate cooking over an open flame, and the presence of several andirons (F4.4023.4315/4320; F4.4023.4225) inside the F4 oven and in household debris (figure 4.44). The location of the cooking fire(s) is not apparent for the excavated portion of this house lot, unless the interior oven from the later building phases was not in fact used as a bread (tandır) oven but as an open fire pit encircled by mud bricks. The low amount of cooking vessels and utensils like lids in the ceramic assemblage (9% of N=298) perhaps reinforces the fact that the actual cooking of food took place in other locations. In this way, the cooking vessel sunk into the floor of the 206 Figure 4.44. Example of andiron from House Lot 1 (F4.4023.4225; UTARP Digital Archive). house near the southern doorway in Phase 2 (F1.1103.5) should be seen as a secondary reuse of this ceramic type, likely functioning as some sort of drain or small receptacle.31 Instead of cooking, the majority of the ceramic assemblage (85%) is vessels typically used for serving and eating. These range from open platters (figure 4.41 D), casseroles (figure 4.41 C) and large hammerhead rim bowls (figure 4.41 E, G, H)32 to beaded rim cups (figure 4.41 F), string–cut flat base bowls, carinated fine ware cups and bowls with horizontal grooves (figure 4.41 A), and open bowls/platters with pedestal bases. 31 At fourth millennium Tell Brak, ceramic vessels were also found sunk into floors where their rims/lips were flush with the surface. These were sunken storage jars however and not cooking pot types (Emberling and McDonald 2003). 32 I have included hammerhead rim bowls within the category of “serving–type vessel” based on the lack of evidence that this ceramic type was used in cooking procedures. While admittedly much of the evidence for hammerhead rim bowls at Kenan Tepe lack the entire vessel, the base being the most important, none of the extant sherds I have analyzed contain any traces of charring or burning, even in minute levels, that would indicate coming into contact with fire. This is in contrast to the assemblage at Hacınebi for example, where these bowl types were used for both cooking and serving (Pearce 2000). 207 House Lot 1: Microartifact Count Density by Material Type 120 100 Count / Volume (L) 80 60 40 20 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell Bone Seed Grindstone F1.1117.5.4 50.18181818 0.909090909 2.727272727 F1.1130.5.1 77.33333333 0.666666667 0.666666667 61.27272727 0 0.181818182 27 5.666666667 F1.1130.2.1 106.8571429 1.428571429 2.285714286 3.333333333 38.28571429 2.857142857 3.142857143 House Lot 1: Microartifact Weight Density by Material Type 1.8 1.6 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell Bone Seed Grindstone F1.1117.5.4 1.077454545 0.001636364 0.002 0.441636364 0 0.036545455 F1.1130.5.1 0.587 0.001666667 0.006666667 0.166666667 0.005333333 0.015333333 F1.1130.2.1 1.567714286 0.008857143 0.004857143 0.317428571 0.005142857 0.018571429 Figure 4.45. Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by material type. 208 In terms of the microassemblage, only three HAP samples are available for analysis and were collected from the cobblestone street (F1.11175.4) and ash pit (F1.1130.2 and 5) of Phase 1 (figure 4.45). A somewhat low density of microbasalt is present representing pieces of grinding stone that flaked off during the use of querns and mullers and reinforce the assertions made previously that grinding of cereals and most likely nuts and other foodstuffs were being carried out in this household. Overall though the highest levels of microdebris is ceramic and animal bone. When examined in detail (figure 4.46), these assemblages are comprised of a relatively even count density of medium and coarse fabric ceramics that equate to both serving/eating and cooking vessels respectively, a trend that is not echoed in the macroassemblage where medium ware serving vessels dominate. Also in contrast to the macroassemblage, fine ware ceramics are not present in these microsamples. This may be due in part to the fact that microsamples are currently only available for the earliest building phase of this house lot and that the trend toward finer ware presentation vessels took place in Phases 2 and 3. Finally the occurrence of microbone, especially burnt specimens, are especially telling in terms of animal butchering, cooking and eating. While I acknowledge that there are a number of ways in which bone can become embedded in archaeological contexts,33 I contend that a large portion of the bone found in the soil matrices of floors and other domestic features represent the residue of meat processing or consumption, especially since tiny fragments of larger mammals or fish, for example, are not likely to have been deposited in domestic contexts without human agency. The count and weight densities for microbone show, not unexpectedly, a large portion of unidentifiable mammal bone 33 For a detailed discussion of this issue, see the “Microarchaeological Analysis” section in Parker et al., forthcoming. 209 House Lot 1: Microceramic Count Density by Fabric Type 100% 90% 80% Count / Volume (L) 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% F1.1117.5.4 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1130.2.1 0 0 0 Medium 30.72727273 45 58.57142857 Coarse 19.45454545 32.33333333 48.28571429 Fine House Lot 1: Microceramic Weight Density by Fabric Type 100% 90% Weight (g) / Volume (L) 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% F1.1117.5.4 Fine Medium Coarse F1.1130.5.1 F1.1130.2.1 0 0 0 0.364 0.304333333 0.278857143 0.713454545 0.282666667 1.288857143 Figure 4.46. Percentage of microceramic based on count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by fabric type. 210 House Lot 1: Microbone Count Density by Species 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% F1.1117.5.4 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1130.2.1 0.545454545 0.333333333 0 Bird 0 0.333333333 0 Fish 0 0 0 Rodent Burnt 5.454545455 5 8.571428571 Mammal 55.27272727 21.33333333 29.71428571 Figure 4.47. Percentage of microbone based on count and weight densities for House Lot 1 by species. along with burnt bone in all three samples (figure 4.47). Minute levels of rodent and bird are also distinguishable and mirror examples in the macroassemblage. Evidence for the production and consumption of food in House Lot 2 is exceedingly difficult to assess due in part to the relative absence of botanical data as mentioned above. This fact alone causes difficulty in interpreting the occurrence of grinding stones (F2.2044.4, F2.2062.15, F2.2062.21) and a single stone pounder (F2.2063.2) inside of this house as either primary or secondary refuse. In this case it is perhaps the microbasalt grinding stone debris throughout the house lot HAP samples, albeit in low densities, that provide evidence for grinding activities (see below). This situation is further exacerbated by the low numbers of faunal data available for this house 211 lot compared with the others. In fact House Lot 2 has the overall lowest NISP of all house lots (table 4.7). While this alone may be enough to skew the percentages, the fact that 22% of the total assemblage (one of the highest) is unidentifiable fragments makes assessing the exact types of food consumption even more difficult. If we set aside the category of unidentifiable bones, sheep/goat (22%) and pig (17%) make up the majority of the assemblage with cattle trailing shortly behind (11%). Fox and gazelle (6% each) provided supplementary meat for the diet of this household group. The majority of the faunal material derives from a large pit (L2042) that cut into the interior of the eastern wall of the structure, seemingly after the house went out of use. The remaining faunal data derive from the compacted pebble street outside of the house and from the northeast corner of the interior of the house. None of the bones from this small assemblage exhibit cut or butcher marks, though the animals do appear to have been raised and butchered locally due to the representation of all parts of the carcass in the assemblage and not just specific “cuts” of meat. One small to medium–sized mammal bone however did show signs of punctures or gnawing from the teeth of a carnivore, most likely dog. Based on mandibular specimens available for sheep/goat and pigs, these animals were culled at prime–age (2–3 years) for meat consumption. Part of the assemblage was also charred suggesting contact with an elevated heat though there is no direct evidence, in the form of spit marks, for the use of open fires. Nor is there any evidence for andirons or other stands for supporting cook pots. In fact the ceramic assemblage derived from the various surfaces and pits from this house lot shows an overwhelming dominance of serving–type vessels (84%) as opposed to 212 Figure 4.48. Descriptions of Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 2 A F2 L2070 KT1 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/6). Coarse chaff-grit fabric. B F2 L2049 KT1 #4: Pale brown exterior and interior surfaces (10YR 6/3). Yellowish brown fabric (10YR 5/4). Fine grit and medium chaff. C F2 L2049 KT1 #2: Light yellowish brown exterior surface (10YR 6/4). Light brown interior surface (7.5YR 6/4). Yellowish red fabric (5YR 5/6). Sandy with medium chaff. D F2 L2066 KT1 #3: Reddish yellow exterior surface (7.5YR 7/6). Reddish yellow interior surface (7.5YR 6/6). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 6/6) grading to a dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Medium chaff and fine to medium white grit. E F2 L2049 KT1 #3: Light brown exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 6/4). Strong brown fabric (7.5YR 5/6). Very fine grit. F F2 L2049 KT1 #1: Pale brown exterior and interior surfaces (10YR 6/3). Brown interior surface (10YR 5/3). Yellowish brown fabric (10YR 5/4). Abrupt transition to Dark gray fabric core (10YR 4/1). Fine grit and medium chaff temper. G F2 L2066 KT1 #1: Brown exterior surface (7.5YR 5/3). Pale brown interior surface (10YR 6/3). Brown fabric (10YR 5/3). Dense fabric with fine grit temper. Four parallel incised lines on exterior. H F2 L2056 KT4 #1: Light reddish brown exterior and interior surface (5YR 6/4). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/6). Burnished exterior surface. Large calcareous grit temper. I F2 L2042 KT1 #7: Reddish yellow exterior surface (7.5YR 7/6). Pink interior surface (7.5YR 7/4). Very pale brown fabric (10YR 7/4) grading to reddish yellow core (5YR 6/6). J F2 L2066 KT1 #2: Light yellowish brown exterior and interior surface (10YR 6/4). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 7/6). Smoothed exterior and mica visible on exterior surface. Fine to large grit temper. K F2 L2042 KT1 #6: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 6/6). Light reddish brown interior surface (5YR 6/4). Reddish gray core (5YR 5/2). Medium density fabric with few, fine grit temper. Burnish on exterior. L F2 L2042 KT1 #4: Light brown exterior and interior surface (7.5YR 6/3). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 6/6). Abrupt transition to dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Large, coarse chaff and white angular grit temper. Coarse ware with smoothed exterior. 213 Figure 4.48. Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 2. 214 storage or cooking wares. While this calculation could, like the faunal assemblage, be skewed based on a low counts (N=19) the relative abundance of simple–rim cups and bowls (figure 4.48 A–C, E), fine ware cups (figure 4.48 G), pedestal bowls and/platters, and open hammer–head rim bowls (figure 4.48 F, H, I, K) reflect activities involved with food serving and consumption. The microdata in many ways support the depositional patterns inherent in the macroassemblages of ceramics and bone. A total of four HAP samples were collected from several contexts in and around this house lot including a surface covered with a pseudomorph layer (F2.2056.5.1), the large mud plastered floor on the interior (F2.2065.1.1, F2.2065.3.1), and the street, alleyway or compacted midden located to the southeast (F2.2049.2.1). The densest material categories for these samples are ceramic and bone, a pairing that correlates well with food–related serving and consumption (figure 4.49). The occurrence of medium ware ceramic types indicative of most serving vessels at Kenan Tepe dominates this microceramic assemblage both in terms of count and weight density, though there are smaller numbers of heavier coarse ware cook pot sherds in the street context (F2.2049.2.1; figure 4.50). Looking closer at the densities of the microassemblages between the indoor and outdoor areas of this house lot, one can see the great difference between these two sectors. By examining the three most common microartifact types—ceramic, lithic, and animal bone—for the house lot microsamples in figure 4.49 there emerges a distinct pattern. One sample (F2.2049.2.1) stands out as the highest count and weight density for two of three microartifact categories despite being the smallest in sample volume at 1.5 liters. Rainville (2005, 49–54) has argued that there are correlations between specific 215 House Lot 2: Microartifact Count Density by Material Type 180 160 Count / Volume (L) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell F2.2049.2.1 109.3333333 0.666666667 6 F2.2056.5.1 0 2 2.666666667 F2.2065.1.1 38.95238095 0.19047619 2.095238095 F2.2065.3.1 82.66666667 0.666666667 4.666666667 Bone Seed Grindstone 164 0 1.333333333 40.66666667 0 0 29.14285714 0 1.142857143 33 0 3.666666667 House Lot 2: Microartifact Weight Density by Material Type 2 1.8 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell Bone Seed Grindstone 0.02 F2.2049.2.1 1.760666667 0.001333333 0.136666667 1.680666667 0 F2.2056.5.1 0 0.010666667 0.004666667 0.359333333 0 0 F2.2065.1.1 0.24352381 0.000285714 0.00447619 0.117142857 0 0.008761905 F2.2065.3.1 0.725 0.003333333 0.018333333 0.202666667 0 0.019 Figure 4.49. Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 2 by material type. 216 House Lot 2: Percentage of Microartifacts Based on Count Density 100% 90% 80% 70% Medium ware 60% Coarse ware Chert 50% Obsidian Fish 40% Rodent 30% Unidentified mammal 20% 10% Ceramic Lithic F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 0% Bone House Lot 2: Percentage of Microartifacts Based on Weight Density 100% 90% 80% 70% Medium ware 60% Coarse ware Chert 50% Obsidian Fish 40% Rodent 30% Unidentified mammal 20% 10% Ceramic Lithic F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 0% Bone Figure 4.50. Percentage of microartifact types for House Lot 2 based on count and weight densities. 217 contexts or loci and microartifact signatures such that outdoor spaces like streets, exterior surpra–floors and surfaces contain the highest density of microceramics, bone and lithic.34 This very dense accumulation of microdebris in sample F2.2049.2.1 supports this correlation made by Rainville that, when combined with the dense accumulation of macroartifacts in this same space, identifies this context as a midden or street. The other samples (F2.2056.5.1, F2.2065.1.1, F2.2065.3.1) share roughly the same densities but exhibit significantly fewer microartifacts than the outdoor space, especially for microceramics and microbones. While this trend could be due to diminished use of this space in general for production or consumption–based activities, I instead theorize that the low density of microartifacts is due to habitual cleaning of inside work surfaces as documented by numerous ethnoarchaeological observations and other microarchaeological studies (Özbal et al. 2004; Rainville 2005). Returning to the outdoor midden or street, one interesting note is the lack of variety in microartifact subtypes that one would expect to find in a general–use refuse area. While this does not lessen my appropriation of sample F2.2049.2.1 as an outdoor midden or street, it instead highlights who actually used the space, i.e. deposited trash there. As diagramed in figure 4.50, the ratio of coarse to medium ware microceramics are relatively proportionate between the midden sample and those from inside the structure. The same is true for the percentage of specific faunal types like fish, rodent, and unidentified mammal. There is however a divergence when we consider chert and obsidian densities. One hundred percent of the lithic material recovered from the exterior midden is chert, while both chert and obsidian are found within the interior floors. This 34 This notion has been challenged by Cessford (2003) who argues that increased microartifact density could also reflect surfaces or areas with longer occupation. 218 occurrence is rendered insignificant however when we reconsider the extremely low density of microlithics overall in this context (figure 4.49). Thus the trend in the percentage of microartifact subtypes between indoor and outdoor samples suggests that the waste or byproducts from certain activities carried out within this structure were deposited directly outside in the street. As discussed previously, House Lot 3 contained evidence for barley and wheat, but also large and small legumes (Leguminosae) and bitter vetch (Vicia sp. and ervilia). Basalt grinding stone fragments from querns (F7.7179.10, F7.7181.24) and mullers (F7.7162.7) used in the processing of the cereal grains derive both from refuse pits and occupational debris inside the magazine structure. These grinders exhibit evidence of heavy use, especially one example (F7.7181.24) that was completely smoothed. It is likely these grinding implements were used to transform the cereals into flour for bread baking or stews. While there is no oven associated directly with this house lot, unexcavated areas to the north, especially within the burnt building of which we only have the small southern portion, could have contained these cooking facilities either for community or single household use. House Lot 3 has the second highest NISP of the house lots (table 4.7) with a relatively even distribution of pig (25%), cattle (21%), and sheep/goat (27%). At least 14% of pig remains are from wild, not domesticate, species. The small percentage of wild species such as red deer (2%), gazelle (4%), and fish (2%) along with a fishnet weight (F7.7162.21; figure 4.51) highlight the fact that hunting and trapping of wild game was practiced, albeit on low levels overall. The mortality rate for this group of animals, domesticates in particular, show once again a kill–off pattern of 2 to 3 years based on 219 mandibular specimens. Marks of chopping and slicing from skinning and disarticulation of the animal are consistent with on–site butchering. There is at least one example of crushing/chopping of a cow cranium and charring of a goat cranium, perhaps due to consumption of the brain (S. W. Kansa, pers.comm.). However none of the assemblage exhibited evidence for gnawing by dogs or other animals that would have likely disturbed the spatial distribution of the assemblage (see Kent 1984). Figure 4.51. Fish net weight from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive, original drawing by Marie Hopwood). The lack of spit marks, low levels of charring overall, and evidence for heavy fracturing of the bones for possible pot sizing suggests that animals (and plants) were most likely stewed in semi–closed vessels elevated above open wood or dung–burning 220 fires as suggested by the botanical data. Several andirons (F7.7155.7, F7.7173.14, F7.7176.4) recovered from the burnt building and near the magazine structure provide further evidence for this type of cooking. One in particular (F7.7155.7) was pierced horizontally through the upper part of the body to allow for even cooking (figure 4.52).35 Figure 4.52. Pierced andiron from House Lot 3 (F7.7155.7; UTARP Digital Archive). While the majority (57% of N=75) of the ceramic assemblage is serving–related vessels like open bowls and platters (figure 4.43 I, G, N, O), carinated cups and simple rim bowls (figure 4.43 K), globular cooking pots (figure 4.43 A, M); coarse ware lids and lug handles helpful in lifting hot pots off the fire (figure 4.43 D, M) are present in relatively large numbers (27% of the assemblage). It is likely that this ceramic evidence, recovered primarily from secondary contexts like pits and other loci of trash disposal, were originally used in the burnt building to the north. In fact this hypothesis is substantiated by the microassemblage. A total of twelve HAP samples were collected and 35 For a more detailed description of this andiron, see the “Small Finds” section in Parker et al. 2008: 142. 221 House Lot 3: Microartifact Count Density by Material Type 200 Count / Volume (L) 150 100 50 0 F7.7194.1.1 Ceramic Lithic 1 1 Shell Bone 2.666666667 18.66666667 Seed Grindstone 0 0.166666667 F7.7189.1.1 28.82352941 0.117647059 4.588235294 33.29411765 0.117647059 0.588235294 F7.7185.1.1 1.777777778 0.222222222 1.888888889 16.22222222 0 0 F7.7185.2.1 4 0.5 9 54.5 0 0 F7.7170.1.1 29.25 0.25 2.75 22.75 0.25 30 F7.7170.5.1 9 6.5 6.5 103.5 0 0 4 0 0 22 0 8 F7.7174.2.1 9.333333333 0.333333333 0.333333333 F7.7168.1.1 12 0.285714286 1.714285714 F7.7162.18.1 212.5 1.5 F7.7181.13.1 1 0.5 2 34 0.833333333 20.66666667 1.833333333 19.83333333 0 0 F7.7181.19.1 15.33333333 17.66666667 13.33333333 72.66666667 0 0.333333333 1.666666667 0.166666667 3.666666667 31.33333333 0 0 F7.7181.9.1 Figure 4.53a. Microartifact count density for House Lot 3 by material type. 222 House Lot 3: Microartifact Weight Density by Material Type 3 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Ceramic Lithic F7.7194.1.1 0.216 0.0055 F7.7189.1.1 0.368 F7.7185.1.1 Shell Bone 0.00516667 0.10366667 0.00011765 0.00517647 0.19411765 0.16777778 0.02766667 0.00311111 0.14211111 Seed Grindstone 0 0.01216667 0.002 0.00517647 0 0 F7.7185.2.1 0.1655 1.027 0.014 0.9825 0 0 F7.7170.1.1 0.15325 0.001 0.0065 0.1325 0.00075 0.07725 F7.7170.5.1 0.122 0.02 0.0095 0.672 0 0 F7.7174.2.1 0.286 0.00033333 0.001 0.01333333 0 0 0.07485714 0.00028571 0.00057143 0.25485714 0 0.02314286 F7.7168.1.1 F7.7162.18.1 3.00166667 0.0075 0.07616667 0.31366667 0.00066667 F7.7181.13.1 0.18116667 0.00416667 0.00516667 0.20983333 F7.7181.19.1 F7.7181.9.1 0.0955 0 0 0.86266667 0 0.08433333 0.47983333 0.00033333 0.00766667 0.16316667 0 0 0.153 0.22833333 0.035 Figure 4.53b. Microartifact weight density for House Lot 3 by material type. 223 available for analysis, eight of which derived from superimposed mud plastered floors in Cells 1 and 2 of the burnt building and the remaining four from pits (figures 4.53a, 4.53b). If we look specifically at microceramics by ware type (figure 4.54a), medium wares representing serving vessels dominate a large proportion of the microassemblage from Cell 2, while coarse cooking wares are proportionately higher in Cell 1. In total these ceramic types are densest in the burnt house except for one pit sample (F7.7162.18.1) that contains the highest count and weight density for microceramics overall. Meticulous microsampling can also offer a diachronic view of food production and consumption for the burnt structure. Figure 4.55 displays the densities of microceramics, lithic and bone based on count and weight to volume ratios for the six samples collected from Cell 2. These are listed in chronological order of deposition from left to right. The level of microceramics, which include fine, medium, and coarse wares, is relatively steady throughout the use–life of this space save for two notable exceptions. One sample (F7.7189.1.1) reflects a general trend based on both count and weight densities for more intensive use of ceramics during this phase. The other sample (F7.7170.1.1) shows a dramatic increase that is visible only in count density, meaning there are a higher number of lightweight pieces. This trend most likely represents more intense fracturing of the microceramics as opposed to a general higher density. This fracturing could derive from excessive trampling if this space served as a walkway or busy kitchen area or if the ceramics used in this space were especially friable (such as cooking pots) or frequently used (such as “everyday tableware” like serving vessels and cups). 224 House Lot 3: Microceramic Count Density by Fabric Type 100% 90% 80% Count / Volume (L) 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% F7.7194. F7.7189. F7.7185. F7.7185. F7.7170. F7.7170. F7.7174. F7.7168. F7.7162. F7.7181. F7.7181. F7.7181. 1.1 1.1 1.1 2.1 1.1 5.1 2.1 1.1 18.1 13.1 19.1 9.1 Fine 0 0.235294 0.444444 0 0 2.5 Medium 1 15.05882 0.222222 2.5 24.75 4.5 Coarse 0 13.52941 1.111111 1.5 4.5 2 0 0 2.166667 0 0.666667 0.333333 1.333333 2.857143 166.3333 0.666667 13.66667 0.166667 8 9.142857 44 0.333333 1 1.166667 House Lot 3: Microceramic Weight Density by Fabric Type 100% Weight (g) / Volume (L) 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% F7.7194. F7.7189. F7.7185. F7.7185. F7.7170. F7.7170. F7.7174. F7.7168. F7.7162. F7.7181. F7.7181. F7.7181. 1.1 1.1 1.1 2.1 1.1 5.1 2.1 1.1 18.1 13.1 19.1 9.1 Fine Medium Coarse 0 0.216 0 0.001412 0.029 0.203294 0.035444 0 0 0.014 0 0.05 0.062 0.0745 0.02 0.049714 1.096333 0.09125 0.0335 0.266 0.025143 1.787667 0.007167 0.035667 0.218333 0.163294 0.103333 0.1155 0 0.117667 0 0.054667 0.021667 0.174 0.062667 0.239833 Figure 4.54a. Percentage of microceramic based on count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by fabric type. 225 House Lot 3: Microceramic Count Density by Fabric Type 220 200 180 160 Count / Volume (L) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 F7.7194. F7.7189. F7.7185. F7.7185. F7.7170. F7.7170. F7.7174. F7.7168. F7.7162. F7.7181. F7.7181. F7.7181. 1.1 1.1 1.1 2.1 1.1 5.1 2.1 1.1 18.1 13.1 19.1 9.1 Fine 0 0.235294 0.444444 0 0 2.5 Medium 1 15.05882 0.222222 2.5 24.75 4.5 Coarse 0 13.52941 1.111111 1.5 4.5 2 0 0 2.166667 0 0.666667 0.333333 1.333333 2.857143 166.3333 0.666667 13.66667 0.166667 8 9.142857 44 0.333333 1 1.166667 House Lot 3: Microceramic Weight Density by Fabric Type 3.5 3 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 F7.7194. F7.7189. F7.7185. F7.7185. F7.7170. F7.7170. F7.7174. F7.7168. F7.7162. F7.7181. F7.7181. F7.7181. 1.1 1.1 1.1 2.1 1.1 5.1 2.1 1.1 18.1 13.1 19.1 9.1 Fine Medium Coarse 0 0.216 0 0.001412 0.029 0.203294 0.035444 0 0 0.014 0 0.05 0.062 0.0745 0.02 0.049714 1.096333 0.09125 0.0335 0.266 0.025143 1.787667 0.007167 0.035667 0.218333 0.163294 0.103333 0.1155 0 0.117667 0 0.054667 0.021667 0.174 0.062667 0.239833 Figure 4.54b. Microceramic count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by fabric type. 226 House Lot 3: Microartifact Density Through Time Based on Count Ratios 110 100 90 Count to volume (liters) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 F7.7194.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7170.1.1 Ceramic 1 28.82352941 Lithic 1 0.117647059 Bone 18.66666667 33.29411765 F7.7170.5.1 1.777777778 4 29.25 9 0.222222222 0.5 0.25 6.5 16.22222222 54.5 22.75 103.5 House Lot 3: Microartifact Density Through Time Based on Weight Ratios 1.2 Weight to volume (grams/liters) 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 F7.7194.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7170.1.1 F7.7170.5.1 Ceramic 0.216 0.368 0.167777778 0.1655 0.15325 0.122 Lithic 0.0055 0.000117647 0.027666667 1.027 0.001 0.02 Bone 0.103666667 0.194117647 0.142111111 0.9825 0.1325 0.672 Figure 4.55. Microartifact densities through time based on count and weight densities for House Lot 3 by type. 227 To explore the space functionality further, let us return to figure 4.54a and the break down of microceramic densities for each sample by fabric type. For sample F7.7170.1.1, only medium and coarse ware microceramics are present. In the macroceramic assemblage, these types are represented by serving and storage vessels (e.g., open platters, bowls, storage jars) and cooking pots respectively (Creekmore 2007; Parker and Foster, forthcoming). By nature, cooking pots and serving vessels are more prone to chipping and breakage because of their portability and daily use compared with storage vessels that are often large and immobile. Based then on the high fragmentation rate discussed above, the medium ware microceramics most likely represent serving and eating vessels. As figure 4.54b shows, there are a large number of medium wares that weigh less than the smaller amount of coarse cook pot wares that are larger in size and weight. This trend in smaller, lighter, more fragmented medium wares suggests a higher use of serving–type vessels during this phase. If we also take a diachronic look at the microassemblage from the burnt structure, we can see the density of microbone remained relatively constant through time,36 but then there is a dramatic increase in the latest sample (F7.7170.5.1) suggesting a higher level of bone processing (to extract marrow, for example) or consumption of meat during this phase (figure 4.55). Reflecting once again on the microceramic data in figure 4.54a and 4.54b, the level of coarse cook pot wares are at their lowest in this sample, while at the same time there is a roughly even amount of fine and medium wares in use. Coupled with the microbone data, we can then hypothesize that serving and the possible consumption of meals in this space increased at the final phase of the building perhaps due to the 36 Except for sample F7.7185.2.1. This dramatic increase in all micromaterial subtypes is likely the result of sample size. This sample was twice the volume (9 liters) of all other samples in this house lot. 228 increased availability or use of fine ware ceramics that are traditionally reserved for eating and/or feasting occasions. In summary, the microdebris shows how the majority of cooking and eating took place in the burnt structure partially preserved in the northern area of the house lot and that cooking, consumption or disposal of animal–related food or products was consistent throughout the use–life of the structure. A significant increase in the density of bone during the final phase of habitation coincides with a shift in ceramic types whereby there is a large percentage of medium and fine ware serving vessels compared to coarse cooking wares. These data suggest that there was a significant increase in serving of meat foodstuffs perhaps instigated by more communal–style eating or feasting (Pearce 2000) as evidenced by the significant inclusion of fine ware ceramics in the microdebris that most likely included cups, bowls, and raised plates based on the macroceramic assemblage (Creekmore 2007; Parker et al. 2008; Parker and Foster, forthcoming). As already mentioned, cereals and other botanical foodstuffs are either absent or have gone undetected for House Lot 4. This fact again makes interpretation of the ground stone evidence difficult. At least two grinder fragments (F20.8.5, F19.13.4) were reused in a wall foundation and discarded in a refuse pit, however two more were uncovered in debris above the primary interior surface (F19.14.8) and in occupation debris outside (F22.10.4). In all cases, the grinders are in an extremely fragmented state from what appears to be active use with one quern fragment in particular (F20.8.5) quite smooth from wear. The microdata for grindstone however provides evidence that grinding likely took place elsewhere as there is an overall low density of grindstone fragments in all samples (figure 4.56). 229 House Lot 4: Microartifact Count Density by Material Type 50 45 40 Count / Volume (L) 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell Bone Seed Grindstone F19.14.1.1 45 0 1 16.8 0 0.4 F19.14.2.1 25.27272727 0.181818182 1.090909091 37.45454545 0.181818182 0 F19.15.2.1 45.55555556 0.222222222 3.111111111 25.55555556 0 0.888888889 F19.15.1.1 6.888888889 5.333333333 10.44444444 28.44444444 0 0.444444444 F19.15.5.1 46.88888889 0.444444444 3.777777778 45.77777778 0 0 House Lot 4: Microartifact Weight Density by Material Type 1.4 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Ceramic Lithic Shell Bone Seed Grindstone 0.0016 F19.14.1.1 1.2246 0 0.002 0.1128 0 F19.14.2.1 0.385818182 0.000181818 0.000363636 0.352545455 0.000181818 0 F19.15.2.1 0.622444444 0.000222222 0.004222222 0.118666667 0 0.009111111 F19.15.1.1 0.221111111 0.066444444 0.082 0.280888889 0 0.011555556 F19.15.5.1 0.660888889 0.000444444 0.010444444 0.292666667 0 0 Figure 4.56. Microartifact count and weight densities for House Lot 4 by material type. 230 If not plants, then meat consumption appears to be dominant within this household with the overall faunal data reflecting a bias for domestic pig at 60% of the total assemblage (table 4.7; NISP=25). This is followed by cow (16%) and sheep/goat (12%) with only a minimal number of red deer (4%) comprising the only wild species consumed. While there is no evidence for cutting or butchering marks, the bones represented in the assemblage are once again consistent with on–site butchering such that many parts of the entire carcass are present. There is also no evidence for gnawing by dogs or other animals that would have disturbed the spatial patterning of the assemblage. Most of the bones derived from a refuse pit (F20 L8) west of the house lot structure and from occupational debris inside (F19 L14, L15, L19). Evidence for the actual cooking of this meat is low as only 16% of the total ceramic assemblage (N=92) are cooking vessels and utensils in the form of flat lids, globular pots with slightly everted rims and fingernail–impressed jars (figure 4.57 I). This is compared to the over 66% of the identifiable ceramics that are serving and eating related. These vessels include holemouth jars (figure 4.57 A), simple bowls and casseroles (figure 4.57 J, K, P, R), string cut–base and hammerhead rim bowls (figure 4.57 H, Q, S), fine ware bowls and cups (figure 4.57 C), and pedestalled bowls or platters. This precedent of medium serving wares is supported by the microdata, derived from five HAP samples collected from the interior surface and suprasurface debris of this structure. Once again there is a high density of ceramic and bone, specifically medium wares representative of serving vessels and unidentified mammal bone, rodent and fish, which was notably not visible in the macroassemblage (figure 4.58). There is a high 231 Figure 4.57. Descriptions of Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 4 A F1 L1026 KT1141 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5 YR 6/6). Reddish yellow interior surface (7.5YR 8/6). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/8). Fine grit and chaff temper. B F19 L14 KT10 #3: Pinkish gray exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 6/2). Black fabric/core (5 YR 2.5/1). Medium to large chaff and fine to medium white grit. C F19 L12 KT2 #5: Pale yellow exterior and interior surface (2.5YR 7/3). Light yellowish brown fabric (2.5YR 6/4). Three parallel incised lines on exterior. Very fine grit temper. D F19 L9 KT8 #2: Pinkish gray exterior surface (7.5YR 6/2). Black interior surface and fabric (10YR 2/1). Decorated with parallel vertical and horizontal incised lines. Fine white grit and large chaff temper. E F19 L12 KT2 #3: Very dark gray exterior surface (10YR 3/1). Grayish brown interior surface (10YR 5/2). Black fabric (2.5YR 2.5/1). Gray (2.5YR 5/1) painted (?) decoration beneath rim. Fine micaceous grit temper. Burnished exterior and interior surfaces. F F19 L12 KT2 #4: Very pale brown exterior and interior surfaces (10YR 7/4). Yellowish brown fabric (10YR 5/4). Fine chaff and grit. G F19 L12 KT2 #7: Brown exterior surface (10YR 5/3). Reddish brown interior surface (5YR 5/6). Brown fabric (7.5YR 4/2). Grit and chaff temper. H F19 L13 KT5 #2: Gray exterior and interior surfaces (10YR 6/1). Light brownish gray fabric (10YR 6/2). Very dense with very little micaceous grit and chaff. I F19 L12 KT2 #2: Brown exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 5/2). Brown fabric (7.5YR 5/4) grading to a dark gray core (7.5YR 4/1). Very fine grit and fine chaff. J F19 L12 KT2 #1: Light brown exterior surfaces (7.5YR 6/3). Pale brown interior surfaces (10YR 6/3). Brown fabric (10YR 5/3) grading to a dark gray core (10YR 4/1). Fine grit and chaff. Wash on exterior. K F22 L14 KT1 #2: Reddish yellow exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 7/6). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/8). Fine white grit. Burnished on exterior. L F19 L13 KT5 #1: Reddish yellow exterior and interior surfaces (5YR 7/6). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 7/6) grading to a light brown core (5YR 6/4). Chaffy medium fabric. Burnished and smoothed on exterior. M F1 L1026 KT1141 #2: Reddish yellow exterior surface (7.5YR 7/4). Pink interior surface (7.5YR 7/6). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 7/6). Abrupt transition to a very dark gray core (7.5YR 3/1). Fine grit and chaff. N F19 L14 KT10 #2: Gray exterior surface (5YR 5/1). Light reddish brown (5YR 6/3). Light olive brown fabric (2.5YR 5/3). Medium chaff and fine grit. 232 O F1 L1037 KT1197 #1: Reddish yellow exterior surface (5YR 7/8). Reddish yellow interior surface (5YR 6/8). Reddish yellow fabric (7.5YR 7/8). Abrupt transition to a gray core (7.5YR 5/1). Medium grit and chaff. Outcurve rim of slip on the exterior side. Cream slip on orange clay. P F1 L1036 KT1189 #2: Light brown exterior surface (10YR 7/3). Very pale brown interior surface (7.5YR 6/4). Very pale brown fabric (10YR 7/4). Abrupt transition to a dark gray core (2.5YR 4/1). Medium grit and chaff. Burnished exterior. Q F22 L14 KT1 #1: Brown exterior surface (7.5YR 4/2). Dark gray interior surface (7.5YR 4/1). Brown fabric (10YR 4/3). Large to fine chaff and medium grit with some mica. R F19 L14 KT10 #4: Light reddish brown exterior and interior surface (5YR 6/4). Reddish yellow fabric (5YR 6/8). Dense fabric with fine chaff and grit temper. Chaff facing with visible wheel striations. S F19 L9 KT8 #1: Light brown exterior and interior surfaces (7.5YR 6/4). Light brown fabric (7.5YR 6/4). Medium to fine chaff and very minimal grit. Burnished and smoothed on exterior. T F19 L12 KT2 #6: Pale brown exterior surface (10YR 6/3). Strong brown interior surface (7.5YR 5/6). Brownish yellow fabric (10YR 6/6). No visible temper. 233 Figure 4.57. Late Chalcolithic ceramic assemblage from House Lot 4. 234 House Lot 4: Percentage of Microartifacts Based on Count Density 100% 80% Fine ware Medium ware 60% Coarse ware Chert Obsidian 40% Fish Rodent Unid mammal 20% Ceramic Lithic F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 0% Bone House Lot 4: Percentage of Microartifacts Based on Weight Density 100% 80% Fine ware Medium ware 60% Coarse ware Chert Obsidian 40% Fish Rodent Unid mammal 20% Ceramic Lithic F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 0% Bone Figure 4.58. Percentage of microartifact types for House Lot 4 based on count and weight densities. 235 proportion of burned bone however, when compared with the other house lot HAP samples. This seems strange as the density of microcharcoal in these same samples that would indicate cooking and fire pit/oven rake–out is the lowest of all the house lots (figure 4.59). This does not diminish the fact that pyrotechnic activities were taking place here, as indicated by the large central oven/fire pit; however, it speaks to the cleaning patterns of the household members. Ash and other debris seem to have been deposited well outside of the excavated house lot space, leaving the microbone and ceramic as the only remaining evidence for cooking activities. Weight Density of Microcharcoal 0.3 Weight (g) / Volume (L) 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 House Lot 1 House Lot 2 House Lot 3 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F7.7181.9.1 F7.7181.19.1 F7.7181.13.1 F7.7162.18.1 F7.7168.1.1 F7.7174.2.1 F7.7170.5.1 F7.7170.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7194.1.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F1.1130.2.1 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1117.5.4 0 House Lot 4 Figure 4.59. Weight density of microcharcoal across all house lots. 236 Stone Tools This category of production and consumption primarily involves chipped stone technologies of specifically chert and obsidian. Gray and beige–gray chert is a locally available resource in the Upper Tigris with most large rounded cobbles deriving from the river gravel and terraces. Conversely the black and green obsidian utilized by the inhabitants of Kenan Tepe had to be brought in from mountainous locations 150 kilometers to the north. The most likely sources for this obsidian are Nemrut Dağ/Bingöl or Meydan Dağ, although this hypothesis waits to be confirmed through geochemical House Lot Cores Struck Lumps Flakes Blades Indet Frag Piercer Scraper Glossed Retouch Total analysis (Healey in Parker et al., forthcoming). 1 4 2 68 3 9 2 0 3 5 96 2 0 0 9 0 7 0 0 2 1 19 3 3 0 69 1 4 0 0 1 1 79 4 1 1 28 1 13 0 1 2 3 52 Table 4.8. Composition of chert assemblage by house lot based on absolute counts. The production and consumption of chipped stone tools is evident in the House Lot 1 assemblage, which is dominated by chert that comprises 71% of a total 135 pieces (table 4.8). Flakes make up the majority of the chert artifacts (71%) and are evenly distributed across the entire house lot both spatially and throughout all building phases. Four cores were identified, one of which derived from a surface in the second phase of the house lot (Level 5B: F1.1098.3) and the other three from the large oven in trench F4 237 (F4.4013.4101; F4.4023.4175; F4.4023.4209). In terms of spatial patterning, there appears to not be any spatial or numerical (density) correspondence between the flakes and cores that would suggest in situ knapping activities (E. Healey, pers.comm.). This situation could also be the result of thorough cleaning of work areas as is so often evident for reductive technologies like knapping that produces large amounts of dangerous (sharp) waste. The consumption of final products takes the form of two tripartite chert blades (F1.1117.1, F1.1117.2) that were embedded within the compacted pebble walkway adjacent to the F4 oven in Phase 1 (figure 4.60). Two more chert blades (F1.1083.21 and 22) were found in occupational fill associated with Phase 2. Other tools included two piercers, three glossed pieces, and five more examples with edge retouch. Figure 4.60. Pair of tripartite chert blades embedded within a compacted pebble walkway in House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). Green obsidian comprises 29% of the total assemblage for House Lot 1 with blade fragments and flakes being the most common type present (table 4.9). Of these, four have evidence for edge retouch and one contained a small notch (though this may have been caused by damage). Two obsidian blades (F4.4023.4235, F1.1071.6) were recovered from debris inside the F4 oven and occupational fill respectively, signalling the 238 House Lot Cores Flakes Blades Indet Frag Ecaille Retouch Other Total 1 0 23 7 2 3 3 1 39 2 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 3 0 11 3 0 1 1 4 20 4 0 6 5 0 1 0 0 12 Table 4.9. Composition of obsidian assemblage by house lot based on absolute counts. use/consumption of these final products. The distribution of obsidian shows a relatively even distribution across surfaces and inside ovens, pits and occupational fill. The density of microlithic debris for House Lot 1 is exceptionally low when compared to the other microartifact material categories (figure 4.45). When we compare the count and weight densities of microliths by material subtype (figure 4.61), there is a range between the samples such that obsidian is densest in the cobbled alleyway adjacent to the F4 oven (F1.1117.5.4) and evenly distributed with chert in a neighbouring pit (F1.1130.2.1 and F1.1130.5.1). While the low density could be a result of sampling bias, the results do not support intensive production activities for stone tools in this area. This microlithic assemblage stands at odds with the macroassemblage where this house lot contained the highest amount of obsidian chert cores, struck lumps, flakes and blades of all the house lots. This situation could be explained as the result of thorough cleaning of work areas as noted above for chert. The microlithics in the cobblestone alleyway could also be the result of displaced debris; that is, individuals walking through a lithic work area and tracking the microlithics into this house lot area. In this case, the microlithic 239 House Lot 1 House Lot 2 House Lot 3 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 House Lot 3 F19.14.1.1 F7.7181.9.1 F7.7181.19.1 F7.7181.13.1 F7.7162.18.1 F7.7168.1.1 F7.7174.2.1 F7.7170.5.1 House Lot 2 F7.7170.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7194.1.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 House Lot 1 F2.2049.2.1 F1.1130.2.1 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1117.5.4 F19.15.5.1 F19.15.1.1 F19.15.2.1 F19.14.2.1 F19.14.1.1 F7.7181.9.1 F7.7181.19.1 F7.7181.13.1 F7.7162.18.1 F7.7168.1.1 F7.7174.2.1 F7.7170.5.1 F7.7170.1.1 F7.7185.2.1 F7.7185.1.1 F7.7189.1.1 F7.7194.1.1 F2.2065.3.1 F2.2065.1.1 F2.2056.5.1 F2.2049.2.1 F1.1130.2.1 F1.1130.5.1 F1.1117.5.4 100% Percentage of Microlithic Based on Count Density 80% 60% 40% Chert Obsidian 20% 0% House Lot 4 Percentage of Microlithic Based on Weight Density 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% Chert 40% Obsidian 30% 20% 10% 0% House Lot 4 Figure 4.61. Percentage of microlithic based on count and weight densities across all house lots. 240 debris inside the adjacent pit is most likely the result of inadvertent chipping of other macrolithic debris that was deposited inside. The number of pieces representing the lithic assemblage for House Lot 2 is quite low at 22 total (86% chert, 14% obsidian; tables 4.8 and 4.9). There are no cores or blades and the assemblage is largely comprised of flakes and flake fragments. Of the chert, there are two glossed pieces (F2.2049.4; F2.2066.3) and one example with evidence for edge retouch (F2.2059.2). Among the obsidian there is a single flake (F2.2049.4) and two splintered pieces of primarily green obsidian (F2.2042.10; F2.2059.2). The highest number of pieces derived from the alleyway or compacted midden on the southeast side of the house lot. The distribution of obsidian seems even across the entire house lot, despite the low numbers. This even distribution, however, is not paralleled in the microdata where one hundred percent of the microlithic material recovered from the exterior midden was chert (F2.2049), while both chert and obsidian are found within the interior floors (F2.2056 and F2.2065; figure 4.61). Despite this distribution, the overall density of lithic material reflected in both the macro and microassemblages is exceedingly low. These data, along with the absence of cores and blades, supports the assertion that chipped stone tools were not being produced within this house lot, though evidently consumed to a minimal degree as evidenced by flakes and an example of retouching. For House Lot 3 the chipped stone assemblage is represented by 99 pieces, 80% of which are chert (table 4.8). Evidence for lithic production comes from the 87% of this chert subassemblage that are flakes derived from all stages of core reduction. This includes some large early stage flakes with cortex on their dorsal surfaces and some 241 resulting from a change in core orientation, perhaps representing core maintenance pieces (E. Healey, pers.comm.). Three actual flake cores (F7. 7180.14 (x2) and F7.7181.15) of changed orientation were recovered as well. Overall most of the raw chert appears to have been struck from the same nodule.37 A retouched blade fragment with slight gloss, a diffuse bulb of percussion and regular scarring pattern on the back (KT F7.7162.13) was also found as part of this assemblage though it appears to have been produced using a different technology from the flakes. Green and black obsidian was also worked but comprises much less of the overall lithic assemblage at 20% (table 4.9). The majority are flakes, though three blades with evidence for retouch are present (F7.7162.2; F7.7179.3; F7.7180.14). Other types include a small splintered piece and a side blow blade flake which has been truncated at both ends (E. Healey, pers.comm.). The level of retouch on blade pieces and the general character of the assemblage suggest production by non–specialists, though some weathered and damaged pieces could be residual, and therefore not evidence for production. The majority of the macroassemblage derived from fill levels inside of the two long magazine rooms (F7 L7179–7180) and the large pit to the north of this building (F7 L7181). Little to no evidence for lithic production or disposal was found associated with the surfaces or fill in the destroyed building on the north end of the house lot. This pattern is reflected in the microassemblage where the signature for microlithic debitage for this house lot is extremely weak for the majority of microsamples collected. As shown in Figures 4.53a and 4.53b, the low level of microlithics occur mostly in samples derived from surfaces while the largest sample, locus 7181, is from the pit located between the 37 This has yet to be confirmed by refitting. 242 two structures where a large portion of the macrolithic flakes and cores were uncovered. This pattern suggests that the actual production of lithic tools most likely occurred away from living quarters, perhaps in the adjacent courtyard area and the manufacturing debris was deposited in a centralized and easily accessible pit and inside the magazine structure, most likely as secondary refuse. Chert flakes with evidence for retouching dominate the lithic assemblage for House Lot 4 comprised of 64 pieces total (tables 4.8). Flakes comprise 54% of the chert assemblage. A single core was also recovered (F19.14.13) along with a blade (F1.1033.1192), scraper (F1.1060.1), and several chipped fragments. Of the retouched material, there are three pieces with edge retouch (one of which is serrated) and two artifacts with gloss on their edges (F1. 1037.1181; F1.1060.20). All these data are collectively indicative of local production and modification, once again by non– specialists. The distribution of chert artifacts, especially the flakes, is even across the entire interior house lot space and densest in fill directly above the floors. Green and black obsidian flakes and blades are also evenly distributed, though this material comprises only 20% of the total assemblage (table 4.9). While there is one splintered piece (F1.1060.24) there are no other modified artifacts such as cores or evidence for retouching. The overall density of microlithics is once again low for both count and weight ratios (figure 4.56), but unlike the previous house lot whose densest sample derived from a pit, the densest sample here derives from the floor in the far eastern area of the house lot (F19 L15). This confirms the production or use of chipped stone implements within the interior household space as evident in the macrolithic assemblage. 243 Industry This category of production and consumption encompasses the wide breadth of industries that can be performed on the household level by both specialists and non– specialists alike. These include spinning and weaving as part of textile production and consumption, beadwork and other adornment, metallurgy, ceramics and the management of these industries. A: F4.4023.1 B: F1.1092.10 C: F1.1109.5 D: F1.1083.23 E: F4.4023.4159 (x1) F: F4.4007.1 G: F4.4007.4095 H: F4.4024.4159 (x2) I: F4.4023.4159 (x3) J: F4.4025.4182 K: F4.4007.4089 L: F4.4007.4092 M: F4.4025.4181 Figure 4.62. Selection of spindle whorls from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 244 While the evidence for actual textile production is minimal in House Lot 1 (see below), there is ample evidence for the spinning of fibers into usable threads. Several spindle whorls in the form of pierced ceramic disks were disposed of inside the large oven from the earliest phase of this house lot that most likely reverted to a refuse bin for neighboring structures at the end of its use–life. A total of ten spindle whorls38 were recovered from inside this oven, while six more39 were discovered within the later phases (Level 5A and B) of the house lot itself (figure 4.62). A possible ceramic spool (F1.1130.8.1) was also broken and deposited in a pit from Phase 1 and is similar in shape to a spool from contemporary Arslantepe (Andersson, forthcoming, fig. 10). The whorls were fashioned from re–used ceramic sherds of mainly light brown (7.5YR 6/4) to reddish yellow (5YR 6/6) fabric with coarse to medium chaff and sometimes grit inclusions. Beyond one example of burnish, none of the whorls are decorated with paint or incised designs. Where measurements were available, the whorls range from 13 to 96 grams in weight with an average of 30 grams (figure 4.63). Their internal diameters ranged from 5 to 15 millimeters with an average of 6 millimeters. The majority cluster between 10 and 20 grams and between 5 to 10 millimeters in diameter. Even the heavy outliers remain within this diameter range. 38 F4.4007.1, F4.4007.4089, F4.4007.4092, F4.4007.4095, F4.4023.1, F4.4023.4159, F4.4023.4161, F4.4023.4162, F4.4025.4181, F4.4025.4182. 39 F1.1069.10, F1.1071.21, F1.1083.23, F1.1092.10, F1.1098.10, F1.1109.5. 245 Spindle Whorls from House Lot 1 100 90 80 70 Weight (g) 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Diameter (mm) Figure 4.63. Weights and diameters of whorls from House Lot 1. According to Barber (1991, 53), a relatively small diameter, as we have in this house lot, equates to a fast spin and therefore, a tighter thread.40 The whorl dimensions reveal that these medium to light weighted spindle whorls were most suitable for spinning short, fine wool and possibly long flax fibers if multiple whorls were used on the same spindle (Barber 1991, 52).41 It is likely that both materials were being utilized, though admittedly there is minimal evidence to support this. As the faunal data discussed above shows, the kill–off pattern for the majority of both sheep and goat in House Lot 1 is at prime–age (1–2 years) suggesting that these animals were only utilized for their meat and not their wool or hair. These data could be skewed due to small sample size since it 40 For a complete and informative description on the function and use of spindle whorls and the process of thread production for both plant and animal fibers, see: Barber 1991; Forbes 1956; Keith 1998; McCorriston 1997; Raheel 1994. 41 McCorriston (1997, 522) notes, however, that spindle whorls alone are unlikely to be informative about type of fiber because flax, wool and other hairs (e.g., goat) use similar equipment. 246 stands to reason that at least some of the caprine herd would be reserved for wool production. Likewise for plant fibers, the archaeobotanical record for this house lot is lacking any evidence for flax (domesticate: Linum usitatissimun; wild: Linum bienne). However this does not necessarily negate the use of flax in spinning since the best bast fiber (eg. stem) of the flax plant is harvested before the seed develops (Barber 1991, 12). A: F4.4026.4194 B: F4.4023.4212 Figure 4.64. Pierced stones from House Lot 1 as possible loom weights (UTARP Digital Archive). 247 As mentioned above, there is little actual evidence for textile production at this or any of the house lots (see below). Two pierced stones (F4.4023.4212 and F4.4026.4194; figure 4.64) were uncovered from House Lot 1 that could have served as weights for a vertical/warp–weighted loom or a spindle whorl, though all whorls uncovered in the house lots have been of re–used ceramic sherds.42 This does not mean that textile production was not taking place however. The horizontal ground loom requires no weights since the warp threads are tied to stakes that are hammered into the ground to provide tension. It is most likely this same type of loom pictured on a late fourth millennium cylinder seal from Susa (level C) showing a top view of two weavers on either side of a large loom and a third individual warping thread (figure 4.65). All parts of this type of loom would most likely be made from wood and thus not preserve in the archaeological record. The use of a horizontal ground loom would also explain the relative lack of loom weights from this and other house lots. Figure 4.65. Cylinder seal impression depicting a ground loom and weavers (from Le Breton 1957, fig. 20 #20. No scale in original). 42 They could equally have been used as fishnet weights (see “Food and Eating” this chapter). One should also be reminded that objects need not be monofunctional. A pierced stone could have served a multitude of functions simultaneously over its use–life. 248 Various bone needles and/or pins have also been uncovered in association with this house lot as debris on top of a cobblestone surface neighboring the large oven and as later debris inside the oven.43 I hesitate to call these artifacts “needles” because the critical tip with the eyehole has been unfortunately broken off all three of these objects (figure 4.66). Only one fully preserved awl (F4.4023.4174; figure 4.66 D) was recovered in this context which might suggest, by association, that the other pins were indeed awls as well used for various breaking, boring, cutting and polishing activities (Moorey 1994, 107). While unlikely that these pins were used in clothing production as sewing needles, they either helped fasten lengths of cloth about the body or were tools in the creation of spindle whorls or beads. A: F1.1116.22 B: F1.1116.25 C: F1.1116.10 D: F4.4023.4171 Figure 4.66. Bone pins or needles from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 43 F1.1116.10, F1.1116.22, F1.1116.25. 249 In fact, a number of beads derive from House Lot 1, the majority being made of shell with one stone exception (figure 4.67).44 The diameter of these beads ranged from 2 to 3.5 millimeters with an average of 3 millimeters. They are incredibly small; with the shell beads averaging 1.24 millimeters in thickness while the single stone bead measure 6 by 8 millimeters (figure 4.67 D). A micro stone bead was also recovered from pit L1130. The shell beads were found both above and within the matrix of a pebble floor of the initial phase of House Lot 1 while the stone bead came from inside the latest phase of the building. While the stone bead could easily have been suspended from a necklace, the tiny shell beads most likely decorated clothing as seen on the scarves of modern village women in Turkey today. Unfortunately whether these beads were produced in this house lot, and not purely consumed, is unclear. The maximum diameters for at least two of the A: F1.1116.23 B: F1.1115.3 C: F1.1116.5 D: F4.4025.4180 (two views) Figure 4.67. Selection of shell and stone beads from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). 44 Shell: F1.1115.3, F1.1115.8, F1.1116.13, F1.1116.23, F1.1116.5. Stone: F1.1074.4. 250 pins from these contexts (2 to 3 millimeters) falls within the diameter of all the shell beads so they could have been used in the threading or sewing of these beads onto necklaces or clothing or as tools (awls) in the drilling of the beads themselves (Moorey 1994, 107). The microshell data shows an overall low count and weight density of shell for this house lot, roughly under three pieces total (figure 4.45), supporting this hypothesis that production of these shell beads (or any other shell production for that matter) did not occur in this household. But a possible micro bead from a pit sample (F1.1130.2.1) does attest to their use in this space. What this household–level industry has to do with a cylinder seal found with this house lot is unclear. The ceramic seal (F4.4026.4132, figure 4.68) bears a geometric intaglio design with shallow drill holes and a vegetal motif paralleled at Tell Brak (Mallowan 1947, pl. XXI fig. 18), Norşuntepe (Hauptmann 2000, Abb. 2:1), and Early Bronze I levels at Hassek Höyük (Behm–Blancke et al. 1981, Taf. 11 #6) and, more Figure 4.68. Ceramic cylinder seal from House Lot 1, multiple views (UTARP Digital Archive, drawing by Marie Hopwood). 251 more locally, Ziyaret Tepe (Matney and Rainville 2005, 57).45 There is no evidence for burnishing around the puncture holes that would result from twine or cord rubbing against this area, suggesting that the seal was barely or not wore at all. Based on the medium and rudimentary construction (e.g., off–center perforation, sloppy execution), this seal is most likely a local imitation of stone seals characteristic of southern Mesopotamia. Of metal artifacts, only a single bronze pin was recovered (F4.4025.4160; figure 4.69). Measuring 55 millimeters long, the pin features a fiddlehead scroll terminal formed by the looping around of the metal during the pliable stage. Other than this final product, there is no other evidence for the production or consumption of metal artifacts. Figure 4.69. Bronze pin from House Lot 1 (UTARP Digital Archive). Only a single spindle whorl (F.2.2061.23; figure 4.70 C) was uncovered from the interior debris from House Lot 2. It too was made from a re–used ceramic sherd of medium ware with fine chaff and micaceous grit tempering light brown in color (7.5YR 6/4). The diameter (5 millimeters) and weight (15.95 grams) of this whorl suggest that, like the whorls from House Lot 1, it was used to produce fine, tight thread from light 45 For a detailed description of this cylinder seal, see “Kenan Tepe 2001: Small Finds Analysis” by Eleanor Moseman in Parker et al. 2003, 137, fig. 15A. 252 wool or plant fibers. A small, but unique, stone bead (F2.2065.5; figure 4.70 B) was uncovered on this floor of this house lot. This polished rectangular–shaped bead had six perforations averaging only 1 millimeter in diameter. A ceramic cylinder seal (F2.2042.7; figure 4.70 A) was also uncovered in this house lot also carved with a vegetal motif of possibly clustering leaves or reeds similar to the seal design from House Lot 1.46 A, Cylinder seal (F2.2042.7); B, stone bead (F2.2065.5); C, spindle whorl (F.2.2061.23) Figure 4.70. Various small finds from House Lot 2 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Marie Hopwood). 46 For a detailed description of this cylinder seal, see “Small Finds” by Marie Hopwood and Melissa Eppihimer in Parker et al. 2008, 152–153, fig. 28C. 253 In terms of craft production, the evidence from House Lot 3 is severely lacking. No spindle whorls, loom weights, needles, pins or awls were uncovered. A single shell bead (F7.7181.4) with a diameter of 3 millimeters and a maximum thickness of 1 millimeter was recovered from the plastered pit north of the magazine–style building. A whole microbead 4 millimeters in size and a possible pendant fragment also derived from this pit (F7.7181.9; figure 4.71). Figure 4.71. Microbead from House Lot 3. Only a single partially preserved bone needle or pin (F1.1057.7) was uncovered from the interior surface of House Lot 4 (figure 4.72 A). This 3.5 centimeter pin has a diameter of 3 millimeters and is highly polished. A ceramic token (F20.3.4) made from a wheelmade potsherd of fine texture and burnish decoration was deposited in the occupational fill west of the primary building (figure 4.72 B). The disk measures 1.7 centimeters in diameter and 0.45 centimeters in thickness. With a weight of only 1.4 grams, this unpierced disk was perhaps a token or gaming piece. There is minimal evidence to suggest that the central oven was in fact a kiln, as only a single over fired sherd (F1.1030.1153) and possible kiln stand (F1.1061.7) were found in association with this entire house lot. It is entirely possible that the stand is 254 A, Bone point (F1.1057.7) B, Ceramic token (F20.3.4) Figure 4.72. Various small finds from House Lot 4 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawing by Marie Hopwood). actually an andiron used in the supporting of cooking vessels over the flame. However it is also possible that the permanent mud brick located within the oven served as a ledge onto which new ceramic vessels were placed and then fired. However without further evidence for the use of this pyrotechnic installation as a kiln, the designation of this feature as a large oven for the cooking of bread and other foodstuff will remain. Finally there is some, albeit low, evidence for the possible smelting of copper ores. The shallow, irregular pit (F19 L16) in the eastern room of the building had a hard, reddish compacted bottom that contained pieces of slag, as noted by the excavator. The surface surrounding this pit also contained tiny pieces of microslag (figure 4.73) grayish– green in color and vitrified and bubbly in shape. Based on XRF testing, the microslag certainly derived from some aspect of intentional copper or copper based mineral processing. What this entailed exactly can vary from copper, cuprite, or malachite smelting, working or as a colorant in pottery decoration (though painted/decorated 255 ceramics from these house lots are extremely rare). Such small pieces that make up the microslag could even have been transferred off of hammer stones or other tools thus negating copper smelting activities (M. Abraham, pers.comm.). Figure 4.73. Microslag from House Lot 4. Symbolism This category of production and consumption includes symbolic systems of the household that are often thought of in terms of religion, magic, or fetish. The most common material manifestation of this is ceramic figurines, followed by miniature vessels. As discussed in the following chapter, both categories of artifacts can, and most likely did, encompass multiple meanings and functions for their creators and users. Because the resources needed for ceramic figurine production, namely clay and water, are readily available there is no reason to assume that they were anything other than locally–made (Moorey 2003). Their relatively even distribution across the majority of the house lots supports the notion that each household was producing their own figurines. However it is difficult to detect primary evidence for production since no 256 specialist tools are necessary to create these hand–molded objects. Thus the evidence available can only trace the use/consumption and discard of the final products: namely the figurines themselves. House Lot 1 contained only a single zoomorphic figurine (F1.1131.4) measuring 3.2 by 2.1 centimeters in dimension (figure 4.74 A).47 It was badly burned, most likely from final deposition in an ash pit in the earliest occupation level. The head and two front legs had also been snapped off at the joins with the body. From what remains, namely the torso, rump and back legs, one can assess the animal represented was most likely a caprid with a stubby tail. The majority of the body was impressed with irregularly shaped punctuations that could represent wooly hair or pigment spots on the animal’s coat. In House Lot 2, two zoomorphic figurines were recovered, one from a pit and the other from the interior house debris.48 The first (F2.2066.6; figure 4.74 B) represents a quadruped that was unfortunately very badly damaged; all four legs and head are missing. The remaining torso measured 2.6 by 1.9 centimeters in dimension. The other (F2.2061.25; figure 4.74 C) is a relatively complete horned quadruped animal measuring 4.2 by 1.6 centimeters and 2.8 centimeters in height at the head. Damage was incurred to the front of the face and torso and the tips of the horns and the two front legs are missing. House Lot 3 also contained two zoomorphic figurines (F7.7162.4 and F7.7162.6), both deposited together in a large pit along with a miniature bowl or token (see below).49 The first (F7.7162.4; figure 4.74 E) is a mostly complete recumbent quadruped with 47 For a full description see “Small Finds” section by Marie Hopwood and Melissa Eppihimer in Parker et al. 2008, 146. 48 For a full description of both these figurines, see “Small Finds” section by Marie Hopwood and Melissa Eppihimer in Parker et al. 2008, 147. 49 For a full description see “Small Finds” section by Marie Hopwood and Melissa Eppihimer in Parker et al. 2008, 146–147. 257 horns, representing either a caprid or a small equid like a donkey. The figurine measures 4.9 by 2.9 centimeters and incurred damaged only to the tip of the right horn, which is broken. The second (F7.7162.6; figure 4.74 D) is entirely too damaged to propose what it represented. Of what is preserved—a partial torso (?) measuring 4.4 by 1.5 centimeters— six breaks indicate protruding elements such as legs, a head and tail. A, Wooly caprid (F1.1131.4); B, quadruped (F2.2066.6); C, horned quadruped (F2.2061.25); D, badly damaged caprid? (F7.7162.6); E, horned caprid or equid (F7.7162.4) Figure 4.74. Zoomorphic figurines from all house lots (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Marie Hopwood and Jennifer Henecke). Apart from the largest assemblage of figurines, House Lot 3 was also the only house lot to contain miniature ceramic vessels. One of these (F7.7162.25; figure 4.75 A) 258 was found in the same pit as the recumbent quadruped figurine with horns (F7.7162.4) discussed above. This vessel is a miniature ceramic bowl in the form of a hemisphere with a shallow depression. The total dimensions are 1.6 centimeters in height and 2.5 centimeters in diameter. A second miniature ceramic vessel (F7.7155.8; figure 4.75 B) represents a footed bowl or jar and was deposited in occupational fill from the courtyard area south of the heavily burnt building and west of the magazine structure. The globular body of the bowl has an everted rim and sits a top a short thin neck and a splayed foot that is concave, not flat, on the underside. This tiny vessel measures 5.1 by 3.6 centimeters with a broken rim diameter of 1.8 centimeters. A final miniature ceramic vessel (F7.7173.4; figure 4.75 C) from this house lot was also recovered from occupational fill in the open (courtyard?) area. The object resembles a small cup with straight sides and a flat base. In total the cup measures 2.2 centimeters in height and 1.9 centimeters in interior diameter. A small straight hole 0.1 centimeters in diameter punctuates the center of the base, thus rendering the vessel unsuitable for holding liquids but instead could have been used for suspension (see chapter 5). In a marked change from the other house lots, no evidence for figurines or miniature ceramic vessels was recovered from House Lot 4. The production and consumption of these types of objects as part of a symbolic system does not seem to have been taking place, however this does not mean that the beliefs and spiritual practices of the household members did not manifest itself in other, less–material ways. 259 Figure 4.75. Miniature ceramic vessels from House Lot 3 (UTARP Digital Archive, drawings by Jennifer Henecke and Diana Backus). Conclusion In this chapter I have presented the unsynthesized archaeological evidence for the DMPC for four Late Chalcolithic house lots at Kenan Tepe spanning the LC 3 to LC 5 that includes multiple strands of evidence ranging from environmental conditions to architectural styles and finally the primary household data itself. I have attempted to include as many datasets as possible, such as faunal, floral, ceramic and lithic, to bring a more holistic picture of household production and consumption that is often not possible with disparate specialist reports and publications that often, but not always, examine material datasets in isolation. While my full interpretations are reserved for the following chapter, I believe a word or two in summation is necessary here. The household members that occupied and worked within House Lot 1 practiced agriculture, specifically the cultivation of two–rowed barley and various wheat species that were then ground into flour, baked and consumed, seemingly within a short period of 260 time as there is no substantial evidence for long–term storage in jars, bins or plaster–lined pits. They also ate legumes, peas, nuts and grapes from either a cultivated orchard, household garden or the local wooded area. Herds of domestic sheep and goat were foddered and tended and then butchered locally by the age of two in order to utilize their meat. Pig and cattle were utilized as well, but to a much lesser extent as were a diverse array of wild species from bird and hare to red deer, fish and crab. Food was stewed in semi–open containers elevated above an open flame by use of ceramic andirons. And while the actual cooking of food seems to have taken place in areas outside of the limits of this house lot, there is ample evidence for the serving and eating of these foods and disposal of food waste. These household members also engaged in the production and consumption of chipped stone tools like flakes, blades and piercers of mainly chert but obsidian as well. Spinning and possibly weaving and bead production were also performed, likely on “cottage industrial” levels such that a portion of the final products were distributed outside of the household. Symbolic systems were also at play within this household as attested by zoomorphic figurines. The household members of House Lot 2 did not seem to partake in the cultivation or consumption of domesticate plants like cereals. Likewise with no botanical remains, it is unclear whether the animals used by this household were raised locally or brought in “on the hoof” to be butchered. Either way sheep, goat and pig were the primary animals raised for meat and consumed. Wild resources like hare and gazelle were equally exploited though on low levels and likely reflect opportunistic hunting. These meats were likely cooked on spits over open flames and later served and consumed on the many serving vessels found. Chipped stone tools were not being produced, but certainly 261 consumed by residents who likely utilized small chert and obsidian flakes for simple cutting and scraping tasks. Again zoomorphic figurines attest to symbolic systems at work. The proportion of debris between inside and outside spaces is clearly demarcated on both the micro and macrolevels, reflecting the fastidious cleaning habits of this household group. Specifically the relatively low densities of all major microartifact categories from samples inside the house are reflective of habitual cleaning activities. When comparing the percentages of microartifact subtypes between the interior and exterior spaces, a uniform pattern is apparent and supports the hypothesis that debris derived from activities within the structure was disposed of in the convenient street or midden behind the building. The household of House Lot 3 participated in all stages of barley and wheat processing from storage in ceramic containers to grinding, baking and consumption. It is likely that the dough created from this flour was baked into bread in a shared oven located in an alleyway or other house lot not excavated. Apart from these cereal products, legumes and peas were also consumed. Both dung and wood were used in the cooking of breads, stews and meat from domestic flocks that reflect a diversified diet of pig, cow, sheep and goat along with red deer, gazelle, and fish caught through the use of nets. These animals were butchered locally by the household and likely stewed in semi–closed pots above open fires elevated by the use of ceramic andirons. The microdebris shows how the majority of cooking and eating took place in the burnt structure partially preserved in the northern area of the house lot and that cooking, consumption or disposal of animal–related food or products was consistent throughout 262 the use–life of the structure. A significant increase in the density of microbone during the final phase of habitation coincides with a shift in ceramic types signaling a shift from individual to more communal–style eating. Stone tools like flakes and blades made from locally available chert and imported obsidian were likely knapped in the open courtyard space between buildings that afforded adequate light and work space. And the symbolic system at work within this household included not only zoomorphic representation in clay, but also miniature vessels that mimic “normal size” vessels. Finally the householders of House Lot 4 seem to not have engaged in the processing or consumption of cultivated plants or at least the practice was not common. They did consume the meat of domestic animals including sheep, goat and cow, but primarily relied upon pig while at the same time utilizing less wild species. These foods were likely cooked inside the large central oven/fire pit that was habitually cleaned by the household residents. Apart from food, they also produced and utilized chert and obsidian tools like flakes, blades and scrapers. Production and modification seems to have taken place throughout the house lot, which might be more of an indication of relaxed cleaning habits than actual manufacturing distribution. However increased production does seem to have centered on the eastern (back) room of the house. Together these households help paint a generalized picture of what the DMPC “looks like” for Late Chalcolithic Kenan Tepe. It consistently involves, not surprisingly, food and food–related activities like cooking, serving and eating. Though not consistent, chipped stone technologies are certainly common with locally available chert as the material of choice and heightened use. The incorporation of symbolic systems materialized through physical objects like figurines and miniature vessels are also a 263 common presence. And while the consumption and utilization of cultivated plants are surprisingly not consistent for these households, as stated earlier in the chapter, perhaps this is a reflection of the fact that the majority of this type of production occurs outside the physically bounded space of house lots. Still, the shifts in this and other specific types of production and consumption, such as herding and weaving, are notable and can offer an avenue by which to explore the mechanisms and motivations behind changes to the DMPC. 264 CHAPTER 5: DOMESTIC ECONOMY AND REGIONAL RELATIONS With the domestic modes of production and consumption now established for four household groups at Late Chalcolithic Kenan Tepe, in this chapter I will delve deeper into specific aspects of the domestic economy—their characteristics, mechanisms, and diachronic shifts—that have larger bearing on topics of regional trends. I argue that while there are common themes to the various components that comprise the DMPC for households at Kenan that are consistent through time, there are also prominent changes and specific elements that are notably absent from the domestic economy. The elements that change are particular and significant, especially when examined from a broader regional perspective. In fact I contend that shifts in plant cultivation practices, textile manufacture and animal husbandry coincide with marked changes on the household level that are directly reflective of local, regional and supraregional sociocultural trends embodied within the Uruk Phenomenon. In short, they are a result of economic fluctuations and household reactions to controlled economic provisioning. Stability and Change on the Household Level Thematic Elements The DMPC for Kenan Tepe in the late fourth millennium has several stable elements or household activities that involve aspects of production and consumption that remained constant throughout this period and thus stand as foundations for the generation of a general domestic economy. For example, all Late Chalcolithic households at Kenan engaged in chipped stone tool production and consumption to some degree and at roughly 265 equal levels of intensity. One exception is the household from House Lot 2 that seems to have consumed/used chipped stone tools like small chert and obsidian flakes for simple cutting and scraping tasks, but did not produce these tools in or near the house lot space. The ratio of materials, specifically chert to obsidian, remained consistent across households as well. Gray and beige–gray chert, a locally available resource and seemingly easy to acquire, was the preferred stone used by all household groups at a steady ratio of approximately four to one. Obsidian, on the other hand, was much less used most likely due to the scarcity of this stone and the fact that it had to be collected by individual households or imported to the village from over 150 kilometers away. The fact that obsidian remained in use, albeit in small numbers, throughout the Late Chalcolithic at Kenan speaks to continuous access to this non–local resource through a presumed regional trade in obsidian that likely incorporated all sites within the upper Tigris River valley. This assertion must remain in the realm of speculation until further detailed excavations and publication of the lithic data from other neighboring Late Chalcolithic sites in the area are carried out. All microsamples from house lots exhibit very low densities in lithic materials like microflakes that would signal primary use contexts for knapping and tool production. However, in light of the macroassemblage that provides clear evidence for all stages of core reduction and final products, the low density of microlithic might be a product of differential sampling as opposed to less intense knapping activity. As already noted in chapter 4, this type of production likely occurred in open courtyards and/or alleyways, as with House Lot 3, where microsampling was admittedly less intense for this study. 266 This household–based production and use of chipped stone tools is similar to other Late Chalcolithic/Uruk sites like Abu Salabikh (Pope 1994) and Tell Brak (Conolly 1997)1 where chert and obsidian knapping was practiced by local, non–specialists across household groups and for immediate household consumption. For example, there are no lithic specialist workshops evident for this early period.2 The data suggest therefore that chipped stone technologies were not socially controlled or centralized.3 Naturally the DMPC of household groups at Late Chalcolithic Kenan also included ceramics, specifically the consumption/use of ceramic vessels for all manner of activities from cooking and serving to eating, storage, and containing a variety of products like beads, spun thread, and tools, to name but a few. While a detailed discussion of the ceramic typology for Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze I transitional assemblage appears elsewhere (Creekmore 2007; Parker and Foster, forthcoming), in general the wares and shapes retain signature elements of a local ceramic tradition that is paralleled at other sites throughout southeast Anatolia and north Syria. In terms of gross categorization, the percentage of cooking versus serving/eating versus storage vessels remains relatively consistent across all household groups despite variation in the size of the house lot assemblages and diagnostic constituents. One exception is House Lot 2 where the percentage of cooking and storage vessels is equal (5%), but the entire number of diagnostics is the lowest of all household assemblages 1 At Brak however there is a decrease in the use of obsidian between the Middle Uruk and Ninevite 5 periods that is not paralleled at Kenan. 2 According to Edens (1999), this was not the case at Hacınebi where flake technologies were a part of domestic production while blades came from specialist workshops based on the irregular distribution of “blade workshop debris.” However Edens does not take into account that this distribution could also be an artifact of systemic contexts such that, at the time of abandonment, each household was likely engaged in differential processes or stages of lithic production that could vary between procurement, production, (re)use, and discard reflected in the distribution of chipped stone artifacts (see Schiffer 1972). 3 This is perhaps the case even at Arslantepe where lithic production was apparent in both “administrative” and “domestic” contexts at the site (Caneva 1993). 267 (N=19).4 That ceramics were not produced by all households is notable and discussed below. Diachronic Shifts in the Domestic Economy Along with the consistent attributes of the domestic economy outlined above, there are also pockets of productive elements and diachronic shifts in the DMPC. One of these pockets is the cultivation of domesticate plants, notably cereals such as barley and wheat, that was not consistent across the households examined at Kenan. In particular the households of House Lot 1 and 3 were the only ones with evidence for the processing and consumption of these domesticate cereals. As noted several times previously, this pattern could be due to multiple factors. Pyrotechnic histories can alter preservation such that botanicals that are not charred often do not preserve in the Near East unless under specific circumstances. It is clear however that House Lots 2 and 4 were each thoroughly destroyed by fires that would have fully charred any botanical remains present within the house lots whether in pits, storage bins or embedded within the house floors themselves. Sampling bias, as with all datasets in archaeology, could also account for the differential levels of botanical remains between households. While flotation and HAP samples were taken from multiple contexts like floors, pits, and suprasurface fill within each of the house lots, the majority of samples for House Lot 4 derive from surfaces, which are traditionally poor in botanical data especially if they are hard packed and nonporous. However the same cannot be said for House Lot 2 where multiple pits along with outdoor middens and interior surfaces were sampled. In this case the absence of 4 Though based on weight, diagnostic pieces account for 25% of the ceramics analyzed for this house lot compared with 18% for House Lot 1 and 16% for House Lot 4. Diagnostics from House Lot 3 also comprised 25% of the ceramic assemblage based on weight. 268 botanical data follows an overall trend of low debris density for all data subsets in this location. Finally, the lack of botanical data for these two households could also be due to the fact that the major procedures associated with plant cultivation—sowing, harvesting, threshing—take place well beyond the limits of house lot spaces in agricultural fields and specialized areas (Kramer 1982, 33). However this does not account for the absence of garden and/or orchard type crops like herbs, nuts and fruits that were a part of other household diets that are usually cultivated within the vicinity of the domestic structure unless centrally managed or maintained. Likewise the grinding of grains and nuts as a necessary process for the creation of flour for bread making is apparent for these botanically sterile households in the form of mullers, pounders and microfragments of basalt grinding stones.5 While the botanicals available for House Lots 1 and 3 are paralleled at both Hacınebi and Korucutepe (Parker et al. 2003, 124), the assemblage reflects a low diversity and small relative percentage of cultigens. This may indicate a trend toward monocropping or an increased reliance on pastoralism (K. Meegan, pers.comm.). Comparing the relative abundance of these cultigens between the households, there does not appear to be divergent trends in the types of plants grown and their levels of consumption or use by the two groups. 5 Another factor affecting the preservation of botanical remains suggested to me by David Frankel may be that domestic pig was the primary animal raised and utilized by the householders of House Lot 4 (to be discussed below). Pigs, of course, are prolific eaters able to consume any means of household waste including plant parts, fruits, nuts, and general refuse. However this suggestion assumes that pigs were able to roam freely within the inhabited living and working spaces of the house; a situation that is not impossible but highly improbable. 269 A major diachronic shift in the DMPC at Kenan revolves around spinning, weaving, clothing and adornment. House Lot 1 contained the most primary evidence for this type of production and consumption. In particular, the clustering of spindle whorls within a single oven locus offers three possibilities for interpretation: 1) the use of this (nonfunctional) oven by multiple household groups for trash disposal in Phases 2 and 3, 2) multiple dumping episodes over the use–life of the entire house lot, or 3) a small household–based industry of spinners. The first interpretation is possible, though there is currently no evidence available for other house lots in the immediate area. According to spatial data, there are two distinct groupings of whorls separated by no more than 20 centimeters of debris inside of the oven and within the occupational debris from the neighboring structure that discounts multiple episodes of deposition over an extended period of time. That is of course unless the episodes were consecutive with little break in between them. Certainly the archaeobotanical record from the F4 oven shows no marked differences between sampled deposits (chapter 4). A cottage textile industry is supported not only by the density of spindle whorls and other tools within this single household but also the nature of one of the primary raw materials being spun, namely flax. The procedures by which flax fibers are prepared for spinning are both complex and time consuming requiring certain expertise or knowledge and the use of specialized tools.6 Flax is thus unlikely to have been a minor or occasional spinning product (Keith 1998, 510). However I would stress that I do not believe this household industry was intense enough for participation in regional systems of trade and exchange, but instead focused on an intra–settlement market or the pooling of resources (e.g., raw materials, tools, time) between multiple household groups. Also the currently 6 For detailed discussions of these procedures, see Barber 1991 and Forbes 1956. 270 available evidence can only confirm one half of this type of production: spinning and the production of thread. Unless ground looms were used, there is no evidence in the form of weights to support the actual weaving process. This pattern of spinning and possibly textile production is either not as visible in the following households or else no longer an industry practiced at the household level, although it should be noted that ceramic spindle whorls need not be used to spin thread.7 This could also suggest a centralization of textile production such that not every household is producing thread and weaving in later periods at Kenan. Another hypothesis is that textiles were increasingly imported to the site from other polities in the upper Tigris or beyond. Either scenario speaks of a non–self–sustaining household structure in terms of this type of production after 3300 BCE. Diachronic shifts in diet are also evident for each of the Kenan households such that there is a changing preference for pig as part of the animal husbandry strategies. I say “preference” as opposed to intensification because there does not appear to be an increased amount in pig so much as an increased ratio of pig to cow, sheep and goat. For example there are very subtle changes in the household reliance on sheep and goat from House Lots 1 to 3 such that ovicaprines shift from being the dominant animal (House Lot 1) to only a single element in a larger diversified diet (House Lots 2 and 3). At the very end of the fourth millennium however there is a more drastic change represented by the faunal assemblage of House Lot 4 where pig comprises well over the majority. 7 Methods such as hand spinning or hooked stick require no spindle and perishable materials like wood (Crowfoot 1931). Spindle whorls can also be made out of a variety of materials including wood, gourds, wax or fruits (Liu 1978). Bone whorls were also found at Late Chalcolithic Mersin (Garstang 1953, 156) and in ‘Ubaid Period contexts at Kenan Tepe (Parker et al. 2008, 174 fig. 26B). 271 This shift could be the result of several factors. Environmental change could have diminished natural resources over time or make suitable pasture or agricultural plots unavailable for adequate grazing and foddering. Individual household decision making based on specific socioeconomic circumstances could also have played a role (see below). However diet and the way that food is prepared is a sensitive indicator of ethnic, cultural and economic categories especially because food practices tend to be quite conservative. While other material categories such as ceramics and chipped stone give no evidence for radical alterations in manufacturing techniques or styles that might indicate shifts in the ethnic or cultural makeup at Kenan, the switch to a wholly meat–based diet dominated by pigs most likely reflect: 1) increased sedentarization by a semi–pastoral household group, 2) economic changes or 3) a reaction to shifts in larger socioeconomic systems in the region. As will be discussed below, options 2) and 3) seem the most likely. Another unstable element of the DMPC at Kenan is a pattern of symbolism manifest in the physical form of ceramic zoomorphic figurines and miniature vessels. As discussed in chapter 4, three of the four household groups produced and used figurines at a relatively even distribution of one to two figurines per household. The majority of these figurines were disposed of in pits with one exception (F2.2061.25) that derived from the occupational debris inside House Lot 2. I say “disposed of” because along with the figurines, these pits contained broken ceramic vessels, animal bone, and lithic debris, all elements that are normally acquainted with trash assemblages. One deposit stands out however, in that two figurines were deposited along with a miniature vessel in House Lot 3. One of these figurines (F7.7162.4) was also the most complete of all house lot 272 assemblages where normally there is a consistent breakage pattern involving the head, front legs or all four legs. Interpretation of these miniature vessels has relied primarily on context and the nature of their deposition such that they have variably been identified as cultic vessels, tokens (Nilhamn 2002; Schmandt–Besserat 1992) and toys (Bahrani 1989).8 They have been found in a variety of contexts from tombs and burials (Early Bronze Age Jericho; Acemhöyük [Özgüç 1993]; Gre Virike [Ökse 2002]) to potter’s workshops (Middle Bronze Age Hazor), houses (Sabi Abyad [Spoor and Collet 1996]; Girikihaciyan [Watson and LeBlanc 1990), and refuse pits (Early Dynastic period Abu Salabikh [Green 1993; Postgate and Moon 1982]). At Abu Salabikh miniature vessels were accompanied by sealings, tokens, figurines, and pot disks much like the deposits at Kenan. Thus in this particular case study,9 miniature vessels seem to embody some kind of relationship to figurines and the symbolic systems to which they belong for the household. This is reinforced by the fact that almost all of the miniature vessels from house lots at Kenan resemble regular ceramic forms like simple or tapered rim bowls and pedestalled jars or platters (figure 4.41 D, 4.43 G). The psychological effects of miniaturization and three–dimensionality in the form of figurines has been discussed by Bailey (2005), who stresses that the creators of miniatures do not seek accuracy in representation. Thus figurines need not be precise or exact replicas of humans, animals or other forms observable in the cultural/natural world. However, because the reducing of size inevitably reduces the ability to construct details, 8 Interesting work has also been done with fingerprints on miniature vessels that provide evidence in particular cases for production of these ceramics by children (Kamp 2001; Králík and Hložek 2007). 9 This contextual information is for the Late Chalcolithic house lots examined in this dissertation specifically. Miniature vessels appear in other contexts, notably burials, from later Early Bronze levels in Area F at Kenan (F1.1021.1087 and F1.1021.1118). 273 the features and traits represented in figurines are highly selective and most likely represent the focal point of the creator’s intent. As Bailey (2005, 32) eloquently states, “miniaturism concentrates and distils what is normal in peoples' routine day–to–day activities and thoughts and then produces a denser expression of a part of that reality.” Thus the inclusion of hair or pigment spots on the animal’s coat for the caprid figure from House Lot 1 likely reflects the importance of wool or hair in terms of the household economy or the marking of the animal to signal ownership much in the way sheep coats are dotted with distinctive colors in southeast Turkey today. Figurines could also have been subject to forms of distortion on the basis of social and aesthetic preference (Wengrow 2003, 149). For example, the enlarged horns of the caprid figurine from House Lot 3 signal to the creator and the viewer the importance placed upon horns or matured males in the household flocks. How these figurines functioned within their specific household contexts can only be hypothesized and likely fluctuated between roles as representations of supernatural beings or ancestors, vehicles of magic, teaching aids, and toys (see Ucko 1968; Voigt 1983). Creating and interacting with miniature figures in many ways transforms the human actors such that they have complete control over the object. As a small three– dimensional object, the spectator has the ability and power to view all sides of the figurine and from all angles. This complete comprehension gives the viewer, the human actor, a sense of control over that thing and what it represents, whether fertility of the herd or a mythical story, thus offering security and also pleasure (Bailey 2005, 33). At Late Chalcolithic Kenan Tepe the zoomorphic figurines, when identifiable, almost exclusively take the form of ovicaprines. These figurines are also commonly used 274 by all the household groups except one, House Lot 4, which had no figurines or other identifiable physical manifestations of symbolic systems or representation. While this may simply be a product of archaeological sampling, preservation or ancient patterns of disposal, the fact that figurines in the form of ovicaprines (sheep/goat) are discontinued at a point in which pigs become a primary staple in the diet of this particular household is intriguing. If figurines truly represent the means of achieving authority over the animate or inanimate subjects modeled (Lévi–Strauss 1966) or gaining a feeling of control over the hazards of daily living (Moorey 2003, 19), it seems they were no longer necessary when a low risk pattern of swine consumption was in place (discussed below). This change is echoed in the gradual decline in household–based spinning and weaving production of animal hairs and plant fibers that likely correspond with a lessening reliance and/or preference on sheep and goat. Conspicuous Absence A final category of the DMPC at Kenan is absence or the particular elements of production and consumption that were not visible for the four households under investigation. Absence does not mean that these activities were not practiced at Late Chalcolithic Kenan, but instead signal that they were not carried out at the household level, that only certain households participated (specialists), that production was centralized, or that products were imported. In many respects the absence of certain activities is more telling and informative than those that are apparent. For example, 275 metals and metal working were not a component for any of the households examined.10 This is despite the relative close proximity of Kenan Tepe to Ergani Madden and Siirt, two copper mines adjacent to the Tigris River still exploited today. There are also numerous copper ore deposits to the north of Kenan within the foothills of the Taurus Mountains, but none within the Tigris River valley itself (see Palmieri et al. 1993, 579 fig. 3). Metals such as copper and tin are supposedly one of the main resources sought by southern Mesopotamian Uruk traders since the southern alluvium lacks any known metal deposits (Moorey 1994) and indeed there is evidence for metal working at sites like Hacınebi, Brak, and Sheikh Hassan. Copper ingots were also found at Jebel Aruda (van Driel 2002), one of the definitive Uruk colonial sites. Perhaps the greatest example comes from neighboring Arslantepe where numerous objects like silver rings, arsenical copper sword blades, and spearheads were uncovered (Palmieri et al. 1993). Two–piece molds for on–site casting provide evidence for production. Similarly at Norşuntepe metal spirals, rings, awls and over 2 kilograms of copper ore and slag were found adjacent to a smelting furnace (Hauptmann 1976). This apparent lack of metal working technologies at Kenan is perhaps one of the underlying reasons there is no evidence for direct contacts with a larger Uruk network. Because metallurgy requires a specialized knowledge and access to raw materials (Yener 2000) it would make sense that southern Mesopotamian entrepreneurs would enter into trading partnerships with those who already had a long tradition of this specific type of production. 10 One exception is perhaps the central pit in the eastern room of House Lot 4 that reportedly contained small pieces of slag, but certainly not enough to indicate full smelting. It is possible that these “slag bits” derived instead from the breakdown of ceramic pieces or even mud brick from a wall collapse caused by the intense fire that brought about the destruction of this building. 276 While ceramics were obviously used by the households at Kenan, there is no evidence for the production of these vessels on the household level. Of all the pyrotechnic installations that have been uncovered in the house lots, most were relatively clean and left no concrete evidence for their use as kilns for firing ceramics. This low visibility of ceramic production on the household level is perhaps due to the specialization of production during the Late Chalcolithic occupation such that workshops were established in certain areas of the village that have yet to be excavated. An alternative is that ceramic vessels were traded in from neighboring settlements within the river valley, perhaps in exchange for textiles manufactured by a household industry of weaving at House Lot 1. This situation at Kenan stands in contrast to several Late Chalcolithic sites throughout the region and beyond. For example at Hacınebi and Hassek, kiln wasters and a study of fabric types indicate that local and “Uruk” ceramics were produced onsite (Helwing 1999; Stein 2002b). Arslantepe had overwhelming evidence for mass–produced conical bowls, some of which were found unbaked, suggesting onsite production (Frangipane and Balossi 2004). Further afield at Abu Salabikh, pottery wasters were uncovered across the site suggesting small–scale or household level production of ceramics (Pollock et al. 1990a, 87). Some of these wasters included nested groups of beveled–rim bowls that had been fused together during the firing process (Pollock 1987, 137). While it is true that cylinder seals of local manufacture and style were evidently used by household groups from House Lots 1 and 2, because of a lack in sealings we cannot be sure if the seals were actually used for an economic function or were instead 277 apotropaic or decorative. Similarly a ceramic token discovered in House Lot 4 has parallels at contemporary Adaba, Brak, and Habuba–Süd however its function remains unclear. These types of tokens or jetons could have been used as external symbolic storage units (Costello 2000), counting devices (Jasim and Oates 1986; Schmandt– Besserat 1992), or gaming pieces. With this range of possibility and functional debate (see especially Zimansky 1993), it seems premature to equate a single token from this household context to a larger complex economic system better represented at Brak, Habuba–Süd and elsewhere. What I will say as a general observation only is that there seems to have been a continued use of this class of object in the form of cylinder seals and tokens throughout the Late Chalcolithic at Kenan reflecting interaction with a wider cultural system where these items were produced and consumed. However the evidence from these house lots clearly shows that these domestic entities did not practice higher– level accounting or centralized storage or distribution. Nor did they not engage in forms of long distance trade and interaction that would manifest through raw materials like bitumen (Schwartz et al. 1999) and lapis or even sealings in terms of the clays used and iconography (as demonstrated for Hacınebi [Blackman 1999; Pittman 1999]). Mechanisms for Change Why did specific aspects of the DMPC at Kenan change over time? In this section I will explore and answer this question by focusing on the three major elements of change: 1) differentiation in plant cultivation between households, 2) shift in textile manufacturing and 3) change in animal husbandry practices and, in particular, diet with a preference for pig. I do not wish to oversimplify by asserting that all of these diachronic 278 shifts are the result of a single interpretive explanation. On the contrary, as I have already argued in chapter 2, households and domestic economies are much more nuanced systems of production, consumption and sociocultural interaction. By their very nature households embody multifaceted relationships both externally with larger community and regional relations as well as internally between their own individual members. Thus while various avenues of explanation can be explored for each of these elements of the DMPC, the mechanisms behind the shifting nature of production and consumption are not necessarily tied to singular events. Sedentarization and Seasonality Increased sedentarization or seasonality are possible avenues of explanation for the diachronic shifts in the DMPC at Kenan that saw changes in textile production, inconsistent cultivation of domesticate cereals and other plants, and preference for swine as the major component of a primarily meat–based diet. Indeed it has already been recognized that segments of society, households in particular, can move between lifestyles of semi–pastoralism and agriculture or practice them in tandem (Pollock 1992). As exemplified at Sos Höyük and Büyüktepe Höyük (Howell–Meurs 2001), temporary and more permanent architecture, just as we have for Kenan, may be found together within a single settlement as the result of gradual sedentarization of a nomadic population. And because there is no evidence for radical environmental changes in southeast Anatolia for this time, it seems that any alterations in terms of household mobility would be contingent upon group–based decisions, no doubt affected by various cultural, economic and political considerations and situations. 279 However it has been exceedingly difficult to detect seasonality for households at Kenan due to a fragmentary archaeobotanical assemblage and a generally small faunal assemblage for each household. Evidence for migratory bird species or wear stage scores for teeth that could indicate the particular time of year animals were culled are unfortunately not available (S.W. Kansa, pers.comm.).11 Of the faunal data that is available and has been analyzed, the diversity of domestic taxa between all household groups supports a primarily sedentary population that was well established throughout the Late Chalcolithic. This fact does not necessarily rule out seasonality, specifically the minimal movement of groups between sedentary occupation sites usually in the summer and winter months. This non–year round settlement at Kenan may account for why the botanical assemblage from the house lots, when present, have a narrow variety of cultigens whereas with a permanent sedentary community, one would expect a wider range of plant types derived from both large agricultural lands and household garden plots. Yet the presence of pigs in all the household assemblages is the strongest case against seasonality primarily because of their high water needs, sensitivity to heat and inherent difficult attitude make them poorly suited for mobile pastoralism or for even biannual migratory journeys (Grigson 2007; Horwitz 1989). Economic Degradation The primary elements of change in the DMPC are one of specialization (weaving) and staple production (animal husbandry), both of which could have been affected by 11 This specific type of information was possible to examine at Tell Brak, where the absence of individuals showing wear stage scores of 4 to 6 and 11 to 16 suggest that animals were killed at particular times of the year (Dobney et al. 2003). 280 economic realities. For example, flax cultivation requires suitable agricultural land and high labor inputs with frequent watering, weeding, and lengthy processing after harvest (McCorriston 1997, 522). A change in the ecological setting or household structure could account for the absence of flax spinning technologies for the later Kenan households. Yet, as discussed at the beginning of chapter 4, the climatic conditions for the upper Tigris and indeed the eastern Mediterranean do not support drastic changes in the annual precipitation levels. Nor do we have adequate resolutions in which to examine changing water output levels for the Tigris River that would have altered available agricultural plots. Perhaps in this case an economic downturn is to blame such that the time and energy required to maintain domesticate flax exceeded the capabilities of individual domestic economies. In such a case the harvesting of wild flax (Linum bienne) growing along the marshy edges of the riverbed could provide alternative raw materials, although its collection would have to be strictly monitored to not deplete supply. Likewise if there was instead a shift, and not an overall decline, in textile production such that wool and not flax was the primary material, one would expect to see an intensification of caprines in the faunal assemblages of later house lots, which as discussed previously, is not the case at Kenan. In terms of animal husbandry, a shift in diet reflected in an increased preference for pig could also have much to do with economic conditions. Pigs can play a large role in risk management and abatement strategies for small household groups, especially ones that have minimal access (or control; see below) to other food resources. Pigs require minimal labor input and can consume a variety of products from fruits and nuts to garden clippings and food scraps (i.e., basic household rubbish). They then convert 35% of the 281 energy they receive from their feed into meat, while sheep only convert 13% and cattle even less (Harris 2007). Piglets gain more meat faster and with less feed than your average sheep, goat or cow and the payout for breeding pigs is much greater: one pig will birth eight or more piglets that can reach four hundred pounds within six months. From an economic standpoint, pig rearing is cheaper, more reliable and easily manageable by smaller, independent household groups. Thus a preference, even reliance, on pig coupled with low to no plant cultivation and the absence of certain essential activities of production like weaving, ceramic making and even storage are evidence for a relatively underdeveloped infrastructure during the Late Chalcolithic at Kenan. That this infrastructure possibly underwent an economic downturn at the end of the fourth millennium is perhaps best reflected in a more specialized diet that was easier to maintain. Along side economic degradation could also be devolving environmental conditions resulting from human practices. For instance an increase in domestic pig use can be linked to over–hunting and habitat degradation to compensate for the loss of meat from wild animals (Zeder 1998, 62). While it is currently impossible to see Kenan as the type site for the region, this unspecialized, purely household–based economic system may account for why the general impact of the Uruk Phenomenon was less intense in the upper Tigris, despite it being a resource–rich zone in antiquity provided with timber, metals, and water transportation. Over the last twenty years research in the periphery zones of greater Mesopotamia have revealed local developments of complex economic systems through which the Uruk settlers came into contact (see chapter 1, appendix). These entrenched and matured systems might have been the draw for attention from the south since, from a 282 purely economic standpoint, it is easier to do business within and between already developed systems of production, consumption and distribution as it is to create and implement your own.12 Along the same lines this shift in diet, and to pigs in particular, reflects how isolated and self–sufficient the householders at Kenan truly were by the end of the fourth millennium such that they were not integrated into any transregional economy.13 Yet there might be more dynamic explanations at play that underlie a more active, agent–centered domestic economy. Regional Considerations As discussed in chapter 2, households and domestic economic systems are very much determined, organized and transformed by certain conditions that are inherent to the household itself (e.g., group structure, life cycles, organization of the DMPC) and external to it such as the larger community, settlement or region. It is with this mindset that I now look to regional considerations for shifts in the DMPC at Kenan, focusing on the two major diachronic trends: a sharp decrease (cessation?) in textile manufacturing and increased preference for swine. The shift in textile production from one of intense household production, most likely for intra–settlement exchange, to specialized production was not the trend seen at contemporary Hacınebi where Kathryn Keith was able to perform both a diachronic study of spindle whorl weights and diameters and a spatial analysis of their distribution across 12 This was exactly the case with sites like Arslantepe, Hacınebi, and Tell Brak (see appendix) who had already well established economic and administrative systems in place, not to mention strong local traditions for ceramics, food, and metallurgy. The new founded settlements like Habuba–Süd and Jebel Aruda are the obvious exceptions. 13 A similar trend is noted at Bronze Age Tel Halif where fluctuations between isolated and integrated economic patterns coincided with high and low levels of pig consumption on the nonelite household level (Zeder 1998). 283 the site.14 At Hacınebi, as at Kenan, undecorated sherd disks are the dominant material for spindle whorls (chapter 4; Keith 1998, 512; Stein et al. 1997). Keith found no evidence for centralized control of spinning products, though she is not clear exactly what this evidence would be. The data was consistent with household production for local use that was steady between the pre– and post–Uruk contact phases at the site (LC2–LC4; 4150–3350 BCE). Similarly at Arslantepe, there is no dramatic or noticeable shift in the weight, diameters or density of spinning and weaving tools between Levels VII (LC4; 3500–3350 BCE) through V (Jemdat Nasr/Early Dynatic; 2800 BCE) that would indicate changes in the degree and type of production that was consistent across the site in both household and palatial contexts (Andersson, forthcoming). What this evidence shows is that despite supposed Uruk colonial incursions in the north, the local household production of thread and textiles remained locally managed by domestic groups, and there does not seem to be a shift in production that would indicate increased demand for these products (contra Frangipane and Palmieri 1987, 299, J. Oates and D. Oates 2004, 185). The consistency in the textile data however does mask any shifts there might have been in the types of raw materials being used. Therefore a move away from linen toward the production and consumption of more wool garments and textiles would not be visible unless faunal datasets and specific culling patterns were taken into consideration. How then can we interpret the absence of spinning and weaving by later households at Kenan? Compared with contemporary southern Mesopotamian whorls that 14 Two studies that I am, unfortunately, unable to perform due to the low occurrence of spindle whorls in House Lots 2 through 4. 284 are predominantly stone or clay and ovoid or hemispherical in shape,15 the ceramic sherd whorls at Kenan reinforce the presence of an indigenous population using local spinning traditions. Based on the minimal evidence for the herding of domestic ovicaprines for wool or hair, flax seems to have been the primary material used by one of the earliest Late Chalcolithic households at Kenan for the creation of linen textiles. Early household–based textile production and consumption based on linen fits well within the pre–urbanized Near Eastern landscape where flax was the earliest of materials to be domesticated and used for weaving, even before the creation of ceramics (van Zeist and Bakker–Heeres 1975). While the seeds of flax plants are also harvested and processed for their oil, it seems the fibrous stalk of the plant was readily sought as well. This is most visually attested in Late Uruk images, most notably from the Warka Vase (Crawford 1985, 74). However the gradual shift from linen to wool production specifically in southern Mesopotamia at the end of the fourth millennium was significant for fiber extensification and the development of class–based (as opposed to kin–based) societies (McCorriston 1997). The culmination of this process can be found in the centrally administered textile industries composed of workshops with specialist (female) laborers that were a major aspect of the southern Mesopotamian economic system demonstrated by textual documents of the third millennium BCE (Szarzynska 1988). For some, the foundations of this industry lay in the fourth millennium with textile exportation as a mechanism for 15 These data admittedly derive from incredibly small samples sizes at Tepe Farukhabad (Wright 1981), Susa Acropolis (LeBrun 1978) and a slightly later Jemdat Nasr period trash pit at the Uruk mound at Abu Salabikh (Pollock 1990b). 285 trade and exchange within the wider Uruk network (Algaze 1993, 74).16 This is supported by depictions of weaving and spinning on cylinder seals common for this period reflecting the importance of this activity for communities throughout the region. For example a seal from Choga Mish in Khuzistan depicts a spinner seated on a platform or cushion (figure 4.71 A). Another seal from Susa shows an aerial view of a ground loom used by two weavers (figure 4.71 B) offers a side view of a warping frame (figure 4.71 C).17 The greater amount of pasture required to produce wool (as opposed to agricultural land for growing flax) may have fueled northward expansion by southern Mesopotamian groups (McCorriston 1997, 534). Yet it does not seem that Uruk incursion into southeast Anatolia at least had any effect on household–based production and consumption of textiles that would reinforce this shift to wool and the centralization of manufacturing. At Kenan there is indeed a shift in textile production, however it is not one of raw materials (as expressed, if anything, in the decrease of ovicaprines and a steady prime–age culling pattern) but instead of who is carrying out the production. If textiles were indeed a major product of trade, then the reduction of household–based production at Kenan during the primary phases of the Uruk Phenomenon between 3300 and 3000 BCE (House Lots 2 through 4) is notable and is perhaps a result of this trend. The issues of increased wool production and pasturage are, not surprisingly, intimately tied to animal husbandry and pastoral lifeways. Thus it has been stated 16 Although later third millennium textual documentation records that high quality textiles produced by workshops in the southern Mesopotamian heartland were locally consumed and not exported over long distances (Waetzoldt 1972, 72). 17 For more depictions of textiles and weaving, see J. Oates and D. Oates 2004 fig. 15.6. I would note here that these depictions are not necessarily of large–scale “factory” production of textiles as accounted in the third millennium textual corpus, but could just as easily show household cottage industry. 286 elsewhere that the cultural influence of a Late Uruk organized state, with new approaches and new demands, had very powerful repercussions on the economic and social fabric of the communities in Upper Mesopotamia, specifically influencing animal husbandry strategies that saw a sharp increase “everywhere” in the numbers of sheep and goat (Siracusano 2002, 194). I contend this is only partially true in that the web of interaction dominant during the Uruk Phenomenon did not affect the husbandry strategies at all sites or in all sectors of the population of those sites. For example, the proportion of pigs and cattle in the general faunal assemblage at Hacınebi steadily decreased (50% to 26%) while the level of sheep and goat increased (45% to 72%) between the pre–Uruk contact (Phase A) and Uruk contact (Phase B1 and B2) phases (Bigelow 1999). But when viewed in terms of ethnic distinctions, the indigenous Anatolian population maintained a well diversified diet of sheep and goat (45%), pig (32%) and cattle (20%) that was seemingly unchanged by the embedded Uruk colony at the site. This Uruk colony, on the other hand, predominantly consumed sheep and goat, which comprised 83% of the total assemblage. Still the age at which ovicaprines were culled remained approximately less than two years for both the pre– and Uruk contact phases showing that herding did not shift toward specialization in wool production. This trend correlates with the evidence for spinning and weaving at Hacınebi discussed earlier that exhibited no change in levels of production that might have been spawned by the introduction of wool as a raw material used in the extensification of textile manufacturing. Clearly at Hacınebi and echoed at Kenan, there does not seem to be a drastic shift in the indigenous assemblage toward ovicaprines that would reflect heightened levels of 287 production, especially specialized production of wool for textiles, on the household level. As discussed previously there is an intensification of textile production on the household level at Kenan that pre–dates the height of the Uruk Phenomenon into this area of southeast Anatolia and that likely ceased before any incursions into the river valley at sites like Giricano were accomplished. What is distinctive for our latest household at Kenan is the overwhelming preference for pig, a dramatic change from the diversified diets of the previous households that included relatively equally proportions of pig, cow, sheep and goat, along with some wild resources. The primary questions to address now are why pigs and why now, at the transition between the fourth and third millennia BCE when this household was living at Kenan? The answer may be shifts in cultural or even ethnic elements. At contemporary Anatolian sites like Arslantepe and Hacınebi, a dramatic increase in the ovicaprines with a simultaneous reduction in pigs and cow populations during Uruk contact phases has been used as supporting evidence for the influx of either foreign peoples (or simply influence) with diets and cultural traditions reminiscent of those in southern Mesopotamia. Between the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze I levels at Arslantepe there is an increase in the number of sheep with a simultaneous decrease in pigs (from 16.8% to 0.6%) that, for the excavators, signal the advent of a centrally governed economy (Frangipane 1997a, 54–55; Frangipane and Palmieri 1987, 299). The same is true of Hacınebi as discussed previously where the influx of ovicaprines reinforced an Uruk enclave at the site (Bigelow 1999). The return to “normal” husbandry patterns that evidentially focused on cattle (along with sheep and goat) in areas north of the Taurus and pigs south of the mountains further confirms the intrusion of Uruk influence as 288 populations supposedly returned to traditional lifeways at the collapse of this regional interaction system around 3000 BCE (Siracusano 2002). In essence this theory relies on a correlation between pigs/cattle and indigenous populations as a cultural or even ethnic marker. Looking briefly at the faunal assemblages of colonial and outpost sites of the Uruk Phenomenon this may be true. Uruk–Warka Levels III and IV, Jebel Aruda, Habuba–Süd and Godin Tepe all contain an overwhelmingly low density of pig at 1% of the entire population throughout the fourth millennium (Boessneck and Steger 1984; Grigson 2007; van den Driesch 1993).18 El Kowm 2 Caracol and Farukhabad contain even less (0%; Redding 1981; Vila 1998) while local sites like Kurban and Korucutepe each retained normative levels in both the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze I between 7% and 14% (Boessneck and von den Driesch 1975; Wattenmaker and Stein 1986). An exceptional example is Tell Brak where the fauna throughout the fourth millennium is consistently focused on sheep and goat (90% of the assemblage), but pig are increasing present in the Ninevite 5 period (10.8%; Dobney et al. 2003; Emberling and McDonald 2003). Two significant outliers to this trend are Hassek Höyük (see appendix) and the households under investigation at Kenan where pig remained one of the major staple commodities largely for meat throughout the LC 5 to Early Bronze I transition. In fact at Hassek between the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze I, pig jumped dramatically from 37.6% to 50% of the total assemblage (Boessneck 1992). This greater reliance or preference for pig at the height of Uruk influence at Hassek has been explained as a program of specialized breeding possibly based on the external exchange of elements of 18 Admittedly the NISP for some of these sites is relatively low: Uruk NISP equals 75 for example and Godin is 161. For Habuba-Süd and Jebel Aruda however the numbers are much higher (NISP = 2219 and 1014 respectively) and more statistically significant. 289 primary production (Frangipane and Palmieri 1987, 300). While this seems like a viable explanation for our Kenan household, especially if textiles are truly being imported (see previous), there is not enough evidence to support a domestic industry of pig rearing for House Lot 4 such that exportation of meat and other secondary products like lard and hide, even within the settlement, was being practiced. The preference by Hassek’s residents for pig might also be an outcome of its size such that small villages were less involved in the major changes that took place at larger sites like Arslantepe and Brak during the period of the Uruk Phenomenon (Siracusano 2002, 194). This image of Hassek as an example of resilient animal husbandry practices in rural villages is downplayed however when we consider the site was heavily influenced by this regional Uruk network evident in ceramics, sealings and major architectural features (see appendix: Turkey/Atatürk Dam). While a heavy reliance on pig at Kenan households would indeed underscore an indigenous population at the site, if an intensification of ovicaprines is truly an indication for Uruk influence this does not account for a dramatic increase or preference for swine. This is especially true when we consider that the shift to pigs as a reaction against outside cultural and/or ethnic influences could not be possible since there was never an intensification of ovicaprines during the height of Uruk Phenomenon at Kenan to indicate influence.19 An alternative and the explanation I argue fits best for the unique situation at Kenan is that the preference for pig consumption is a reaction to controlled economic provisioning that is one of the hallmarks of the Uruk administrative system and likely goes hand–in–hand with an economic downturn discussed previously. Certainly in later 19 This is substantiated by the overwhelmingly local character of the entire Late Chalcolithic Kenan assemblage from southeast Anatolian ceramic wares to architecture to chipped stone technologies (chapter 4). 290 periods, but most likely beginning at the end of the LC 5, centrally managed flocks of both sheep and goat developed as a primary way to feed the textile industrial machine in the south. The very nature of these animals as well—their portability and relative ease with which large herds can be kept and managed—lent themselves well to large–scale redistributive economies present at places like Brak and Arslantepe. The same cannot be said of the pig. Despite the economic advantages discussed previously, raising pigs requires some amount of effort and specific environmental conditions. Pigs require high amounts of both water and shade since their bodies cannot tolerate temperatures above 35 ºC (Grigson 2007, 98). They cannot be herded in the traditional way of sheep and goats, nor can they be migrated long distances to take advantage of fresh pasture, for example. In village and agricultural settings pigs will also trample and uproot cereal grains, thus they cannot be allowed to roam free and must remain closely monitored or penned (Zeder 1991, 30–31, 1998, 108). Yet as mentioned before, pigs are a sustainable meat source and ideal for risk abatement strategies for a domestic economy. Thus it would seem that pigs are more suitable for rural family and/or small–scale sty management, especially in arid and semiarid environments. Pigs as an indicator of domestic–level economy, and likely nonelite as well, is supported by the almost total lack of pigs and pig herding entries in the archaic administrative texts of the late fourth and early third millennia that record in great detail the care, management and distribution of sheep, goats, cattle and donkey. One exception is a Late Uruk lexical text of pigs and pig products (W 12139).20 However this text likely 20 Textual sources provide evidence that swine herding apparently did become centrally managed in the later third millennium (Dahl 2006). One example is an Ur III administrative text (W 23948) that records the distribution of animals from a large herd of ninety–five pigs into one group of juveniles and two additional groups of adults assigned to temple units in Uruk (Englund 1995). 291 refers to wild pigs, as opposed to their domestic counterparts, who are often depicted in cylinder seal iconography of this period being hunted (often by the aid of dogs) in the reed thickets of the southern marshes.21 Also reinforcing their nonelite status are later third millennium urban examples like Tell Leilan, where pigs make up 50% of the assemblage in the lower town areas supposedly inhabited by poorer residents (Zeder 1998, 118). Thus the role pigs most likely played in the nonelite domestic diet was as a supplemental food source to balance out resources acquired through other means, most likely from centralized redistribution. In this sense an increase or heavier reliance on pig could be seen as either a disruption in the redistributive channels (through economic crisis, war, etc.) or as intentional undercutting of the centralized administration through strategic household decision–making. The existence of this centralized administration at Kenan is not overt but if we look closely at the major elements not present in the DMPC of the later households—ceramics, plant cultivation, weaving—it is likely that some kind of centralizing productive agent was present in the form of specialized households or centralized elites. This might also account for the lessen of ovicaprines in the later house faunal assemblages if sheep and goat became centrally managed. It is also telling that during the occupation of House Lot 4 at the turn of the third millennium at Kenan a major change took place at the site in the form of a monumental wall 1.5 meters thick that was constructed encircling the upper mound (chapter 4). Its role remains elusive, acting as either a defensive mechanism, a physical boundary between the upper and lower portions of the village or a massive foundation and/or shoring device for a monumental construction above. Because the relevant occupational levels inside the 21 See Englund 1995, 122 fig. 1 for an assortment of examples from Uruk–Warka, Susa and Habuba–Süd. 292 wall are buried deep within the mound, more information about what is inside the perimeter or who exactly occupied this space is presently unavailable. However whoever built or financed this construction certainly had adequate control of resources and labor to carry out such a project. That the mud bricks for the superstructure derived from four different clay sources (distinguished by their colors) and likely represent multiple labor gangs or tribute payments from various factions reinforce the extent to which this control stretched. There is no evidence to support Uruk colonists fortifying the upper mound, however my point here is that while resources are being applied to massive construction projects on one side of town, individual households are reinforcing and adapting their food production and consumption strategies to underscore their self–sufficiency on the other side of town most likely as a reaction to changing economic and political situations. Conclusion In many respects, this analysis of the domestic economy of households at Kenan has carried out two separate yet equally worthwhile goals. One was to elucidate the nature of the DMPC at a village site of the upper Tigris. The other was to examine closely the effects the Uruk Phenomenon had, or did not have, on household–level economies in this region in particular and what that might mean in the broader scope. The results, it seems, are a little of both. The core elements of the DMPC that remained constant—chipped stone technologies and ceramics—substantiate the current understanding we have (but still question!) about the mechanisms for the Uruk Phenomenon that did not involve unspecialized lithic tools or implements and southeast Anatolian ceramic traditions. 293 Fluctuations in other elements, most notably plant cultivation, are perhaps best explained by more local conditions such as seasonality and issues of preservation. And the absence or low visibility of significant elements like metallurgy, ceramic production, trade items, and administration and distribution of products in the households examined best highlight Kenan’s role as either an independent indigenous village or levels of specialization in production (and consumption) that lay outside the households under consideration. The conspicuous absence of these elements could also point to economic degradation, a supposition that is further supported by the discontinuation of linen textile manufacturing after 3300 BCE, most likely based on the high labor inputs involved. That this critical shift in the DMPC coincides with heightened interaction with southern Mesopotamian peoples or influences in southeast Anatolia, whose supposed items of exchange included textiles, is perhaps not a coincidence. A dietary shift to primarily pig consumption can also be seen as a signal of economic downturn, especially since pigs play a large role in conservative domestic economies and risk abatement strategies for food supplies. If increasing centralization of resources in terms of production and labor are indeed occurring region–wide, whether instigated by Uruk colonists themselves or as a byproduct of newly developing interactions, then a pig–based consumption pattern can also be seen as a vehicle of subversion. Pigs can supplement any domestic diet that has become increasingly reliant on the centralized administration of other products and resources like sheep, goat and agriculture. In this way, households can remain relatively independent of a centralizing authority in terms of the most important element of the DMPC: food. 294 CONCLUSION. KENAN TEPE HOUSEHOLDS AND THE URUK PHENOMENON In the Near East, the late fourth millennium BCE was a period of fundamental social change that witnessed the rise of the earliest known states at sites like Uruk–Warka in the southern alluvium of Iraq. Part of the culmination of this development was the proliferation of interregional connections across the Mesopotamian landscape manifest by the distribution of distinctive categories of material culture. These included architectural styles, ceramics, accounting practices, artistic conventions, and the earliest writing and pre–literary forms. The mechanisms, motivations, and meaning behind this patterning of material cultural and what it represents in terms of sociocultural and economic interactions remains contested in part by the limitations inherent from one of the primary type sites of the period, Uruk–Warka, and the frameworks by which scholars have traditionally studied this Uruk Phenomenon. Both suffer from a lack of multiscalar approaches that bring to bear all levels and social groups including nonelite households and domestic economies. Uruk–Warka has remained the centerpiece of these archaic states for several reasons. It is one of the earliest ancient sites to be excavated in the Near East. Extensive surveys highlight Uruk–Warka as a central polity adversely affecting settlement of the immediate hinterland. And the material culture remains from the Eanna and Anu precincts represent an unprecedented level of sociocultural advancement in terms of craftsmanship, architecture, organization and control of resources. Yet the archaeological evidence from Uruk–Warka also presents a host of problems in seeking to understand the whole of Uruk society. Only the elite and centralized elements of social life at the city are 295 currently known from various temple and public buildings and the wealth of finds that were deposited inside of each to prepare them for the next rebuilding. Further surveys and excavations in the hinterlands of Uruk–Warka have also highlighted the heterogeneous patterns of settlement and movements of populations across the region that reinforce a multifaceted network in which Uruk–Warka is perhaps a unique case. Finally the incomplete ceramic assemblage and chronological issues in many ways make Uruk– Warka a poor type site in which to examine the whole of fourth millennium Mesopotamian society. The same holds true for several sites excavated beyond the Uruk heartland. Only limited exposures at a handful of settlements in southern Mesopotamia have been excavated that unfortunately offer evidence for primarily the elite sectors of Uruk society. While further north at places like Nineveh and Habuba Kabira–Süd there is more complete evidence for ceramic sequences or domestic architecture, no examinations have been carried out of the larger contexts from which both “local” and “Uruk” ceramics derived or the activities of production, consumption, or distribution that comprise a domestic economy and its relationship to more centralized systems. This body of evidence, along with others from sites like Susa, Arslantepe, Hacınebi, and Tell Brak, has become the framework by which models about the Uruk Phenomenon have been created, developed and contested. Scholars have made significant advances toward understanding the mechanisms and motivations by which systems of interaction and exchange developed and functioned during the Late Chalcolithic period, whether through an Uruk world system, trading diasporas, or political fallout. Yet these models all share common weaknesses: the reinforcement of top–down approaches to 296 economic histories, focus on the elite segments of society, and exclusion of smaller indigenous village communities. Most important is the underestimation of the domestic economy and the role that household groups play in shaping their social and economic destinies. Household archaeology as an important subdiscipline has developed over the last forty years as a productive and evocative means by which scholars can access these Late Chalcolithic domestic groups through the examination of architecture and domestic artifact patterning. Very specific methodological approaches like microdebris analysis, micromorphology and soil chemistry grant scholars the finest resolution by which to uncover household activities. Households, defined as activity groups that engage in spheres of activities that overlap in space and time, are the level at which individuals engage with society at–large. As the basic unit of societies, households are sensitive indicators of political, economic, or cultural change. They also offer a window through which to view the nuanced and shifting relationships between people, families, working groups and communities. In this way houses and households should not be viewed as static entities or as representing whole social groups and classes. Indeed households occupy an integral place for conceptualizing larger social developments that cannot be fully understood by examinations of elite and overarching processes alone. Domestic modes of production and consumption are especially insightful avenues of approach to the social, and in terms of the Uruk Phenomenon economic, developments during the late fourth millennium specifically because household economies are affected by and effect change themselves in these arenas. Examples drawn from the Inka Empire and third millennium states in upper Mesopotamia exhibited the shifts in domestic 297 production and the organization of labor to accommodate evolving political demands and the ways in which households can determine the market and flow of craft production and specialist goods. These examples have bearing on the Uruk Phenomenon because it has been traditionally understood as motivated by resource procurement strategies and subjugation of the periphery through a colonial system. Such a radical change in the socioeconomic climate, therefore, should be visible in the domestic economy or the daily production and consumption activities of households. At Kenan Tepe, a small village site in the upper Tigris River valley of southeast Turkey, this type of change was evident in the domestic modes of production and consumption (DMPC) in four household groups chronologically spanning the late fourth millennium or the over three hundred year course of the Uruk Phenomenon. Consistencies, prominent shifts and conspicuous absence of distinct elements of the DMPC were distinguished by examining the microarchaeological evidence in tandem with macroassemblages of ceramics, bone, lithics, ground stone, botanicals and architecture. The results show the core elements of the DMPC—chipped stone technologies and ceramics—remained at consistent levels across all house lots or the physical space that households inhabit. Fluctuations in plant cultivation are best explained by seasonality, local environmental conditions and/or issues of preservation. The lower visibility or absence of metallurgy, ceramic production, and trade items underscores the likely centralization of these craft activities at specialist households outside the scope of the groups under investigation or increased economic degradation. Devolving conditions likely played a role as well in the shifting levels of textile 298 production as linen became an economic burden and the spinning and weaving of wool likely transitioned to either specialist households or the final products were imported. Yet it is the shifts in diet of these nonelite households that are most telling for the impact of the Uruk Phenomenon at Kenan Tepe and the wider region. The gradual transition from the consumption of predominantly ovicaprines to a balance of domesticates to a greater reliance on pigs by the turn of the millennium suggests both economic and social changes. Pigs play a large role in more conservative domestic economies especially in terms of risk abatement strategies where economic conditions for food production are threatened or in flux. In a time of increased centralization of resources in greater Mesopotamia evident at sites like Brak and Arslantepe, it seems the householders of Kenan were reorganizing their production and consumption patterns to accommodate and even subvert changing times. This reflects the continued sense of independence, at least economically, that households were actively seeking to maintain. As a case study, it is my hope that Kenan Tepe serves as a point of departure by which scholars can begin to reconceptualize the Uruk Phenomenon by incorporating household–level approaches when examining the development of social, economic, political and ideological life in the fourth millennium. While it has been neither my intention to discount the theoretical approaches to the Uruk Phenomenon discussed in chapter 1, nor to choose a theory that fits Kenan Tepe best, I believe these types of examinations could benefit from the incorporation of household data if only to distinguish the variety of sociocultural systems at play during the Late Chalcolithic. To this end, my study has also highlighted the applicability of household archaeology to move beyond investigations of domestic architecture, economy, religion and family life 299 to help answer broader questions about the social and cultural movements of the ancient world over the longue durée. In the case of Late Chalcolithic Mesopotamia, this includes the development of archaic states, urbanization, bureaucracies and social class distinctions. The current study would in the future benefit from other examinations of households and domestic economies at sites within the upper Tigris River valley, most notably Giricano, to serve as a comparative dataset and to more securely place the Late Chalcolithic DMPC at Kenan within a regional context. This will only be possible however through more horizontal exposures of architecture and domestic spaces and timely publication of these results. A further step would be the comparison of domestic economies from smaller villages like that of Kenan and Hacınebi with larger polities like Brak, Hamoukar and Arslantepe to examine the interaction between elites and household groups in order to elucidate further the nature of the Uruk Phenomenon. As the preliminary reports suggest, much work has already been done concerning the individual components of production and consumption at Hacınebi and it is my hope that the final reports will offer an inclusive view of the domestic economy at that site. The same holds true for Arslantepe and Tell Brak where we have a unique opportunity to examine the dynamic relationship between these highly complex and, for the latter, urban settings and their rural counterparts. Finally an avenue of approach that remains to be further explored comprises elements of gender, class, and age that are inherent to household groups and crosscut aspects of the domestic economy. These categories in many ways are the determining 300 factors in how labor and production is organized and carried out and who is doing the producing and consuming. From this, aspects of power and familial roles are negotiated on a domestic stage that will transfer to the types and nature of relationships between individuals in the wider community. For the Uruk Phenomenon this will be important for differentiating domestic economies between households that were likely affected by increased regional interactions in different ways. This type of nuanced analysis would also be helpful in distinguishing the types of groups participating in this interaction: rich male entrepreneurs or poor refugee families of men, women, children and elderly? 301 APPENDIX. LATE CHALCOLITHIC/LATE URUK SITES, SETTLEMENT HISTORIES AND MATERIAL CULTURE This appendix summarizes the primary archaeological datasets used by scholars examining the Uruk Phenomenon and acts as a complement to the larger approaches and issues about interregional interactions discussed in the dissertation. These datasets include excavation background, settlement histories and the material culture of a number of fourth millennium sites scattered across greater Mesopotamia. The evidence is presented by modern country and then, if applicable, by region. Iraq As the site of Uruk–Warka has already been discussed in detail in chapter 1, this section will focus on the material culture of neighboring settlements that share architectural and ceramic similarities. The best example is Eridu (modern Tell Abu Shahrein), located 24 kilometers southwest of Ur and 40 kilometers southwest of the modern city of Nasiriyah. The site is actually composed of eight separate mounds whose collective occupations span the sixth to the first millennia BCE. The site was initially investigated in the mid–nineteenth century CE by J.E. Taylor (1855) and then later by R. Campbell Thompson and H. R. Hall. More extensive excavations were carried out over three seasons between 1946 and 1949 by Sayyid Fuad Safar (field director), Sayyid Mohammed Ali Mustafa (surveyor, architect), and Seton Lloyd (technical adviser). Architectural remains dating to the Uruk period from the excavated areas of Eridu are limited to the main mound and are sparse in number due to ancient tunneling and the construction of the massive ziggurat of Ur–Nammu during the Ur III period. What does 302 remain are mostly foundations and massive stepped platforms of Riemchen bricks from two protoliterate temples (I and II)—most of which lay buried beneath the Ur III ziggurat—a small portico, a 1–meter–thick walled building of white gypsum bricks, and extensions of the ‘Ubaid Temple VI platform assigned by excavators to the Early Uruk period. A large plastered building east of the ziggurat within the outer retaining wall of the citadel area is better preserved. This structure is composed of multiple rooms grouped around a central hall. Intact door lintels, two of which are parabolic archways 1.7 meters in height, attest to the striking preservation of this structure. The interior debris consists of ceramics, like beveled–rim and conical bowls and straight–spouted jars, identified by the excavators as “votive vessels” (Safar et al. 1981, 72). Other ceramic types found on these levels are characteristic for southern Mesopotamia and include red wares, gray wares, lugged pots, and jars with twisted strap handles. Though data from Eridu is limited, it is clear the site remained occupied beyond the ‘Ubaid period. The initial labor and resources that were placed on the construction of a long–lived temple sequence seems to have continued with the construction of two more massive platforms during the Uruk period on which presumably temples or other public buildings were placed.1 It is unclear whether the other relatively large constructions opposite the temple platforms served a religious function (as assigned by the excavators) or domestic function (as the material remains suggest). The nature of the architectural and ceramic evidence places Eridu well within the sphere of southern Mesopotamian material culture with little evidence for trade outside of Mesopotamia.2 1 In digging these temple platforms, excavators uncovered decorated stone and clay cones similar to those recovered at Uruk–Warka (Safar et al. 1981, figure 118). 2 A kiln was excavated adjacent to the multi–roomed building on the eastern edge of the citadel that was lined with bitumen, presumably derived from Hit in the north (Safar et al. 1981, 76). 303 This picture changes upriver at sites like Abu Salabikh and Tepe Gawra where evidence for complex economic systems involving regional trade are continually developing throughout deep occupational sequences. Tell Abu Salabikh, most likely ancient Eresh, lies at the heart of the southern alluvial plain between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers 16 kilometers northwest of the ancient site of Nippur. The site is composed of six low–lying mounds, none higher than 5 meters, scattered across a total area of 1 by 2 kilometers and intersected by a wide modern drainage ditch and several canals. Most of the remains that have been excavated date to the Uruk and Early Dynastic periods (ca. 3900–2200 BCE). The site was first explored in 1963 and 1965 by Vaughn E. Crawford, Donald Hansen, and Robert Biggs on behalf of the University of Chicago. In 1973 a contour survey was carried out and excavations were resumed in 1975 by J.N. Postgate on behalf of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq (Postgate 1977, 1978, 1980, 1983, 1990; Postgate and Moorey 1976; Postgate and Moon 1982). The Uruk mound is roughly 10 hectares in size and located southwest of the Early Dynastic main mound and due south of the West Mound. Crawford and Biggs began initial investigations here in 1963 that consisted of soundings and small–scale surface scrapings. More substantial work on the Uruk mound was conducted later by Susan Pollock over the course of three seasons (Pollock 1987, 1990a; Pollock et al. 1991, 1996). Pollock employed a combination of surface survey, large–scale scrapping3 and excavation to reveal more coherent architectural features, compare the density of artifacts from surface survey with those from the subsurface scrape, and determine the distribution of production and consumption activities across the entire site. Surface scraping revealed 3 Removal of 10 to 15 centimeters of sediment from the surface of the mound. Pollock and her team used a grid system over the entire Uruk mound in order to complete a systematic scrape. 304 that the Late Uruk town was surrounded by a 20–meter–wide wall with buttresses on the outer edge that most likely served as both a symbolic and defensive function (Pollock et al. 1991, 64). The most substantial architecture recovered on the Uruk mound was two superimposed buildings dating to the Middle Uruk period (ca. 3550 BCE). The walls of these structure were one and a half meter thick, composed of square sectioned Riemchen bricks, and both later cut by a pair of Jemdet Nasr period refuse pits (Pollock 1990b). These buildings were associated with fire installations and a large mud brick platform. A similar platform was found in the northern area of the tell adjacent to two unattached rooms containing fire installations. These were most likely pottery kilns as one contained wasters and beveled–rim bowl fragments (Pollock et al. 1991). A 1.5–meter–deep sounding excavated at the edge of the tell revealed an entire Early to Middle Uruk period sequence of occupation including part of a pisé structure with straw–covered floor and sheets of raw bitumen (Pollock 1990a). An infant burial later cut this pisé structure and contained a beveled–rim bowl placed upside down on top of the skull. Overall the excavators were surprised at the sheer amount of open space within the Uruk settlement as compared to the dense construction of houses and other buildings on the Early Dynastic mound.4 The ceramic assemblage from the Uruk mound contains a wide range of forms including mass–produced vessels like beveled–rim bowls, “flower pots,” and conical bowls with string–cut bases.5 Other forms include open bowls with various diagnostic rims, rounded and flat–rimmed jars, and spouted jars in straight, conical and droop spout 4 This may also be due in part to their limited excavation areas and the fact that the surface scrape only penetrates a maximum of 15 centimeters below the surface. 5 For a full description of the ceramic assemblage including plates, see Pollock 1987. 305 styles. Ceramic production seems to have been non–centralized as evident by pottery wasters found across the site that attest to small–scale or household production. Despite this, only one of the fire installations excavated contained pottery wasters, unlike similar Uruk period installations uncovered on the West Mound (Postgate and Moon 1982). Specifically beveled–rim bowls appear to have been made on site and apparently in batches (Pollock 1987, 137). Other clay objects recovered by the excavators include spoons, wall cone fragments, and sickles that were produced on–site (Benco 1992). There is also widespread and overlapping distribution of manufacturing refuse from lithic production across all surveyed areas. The presence of cores and debitage, specifically core rejuvenation flakes, further support the idea of local production of chert tools. Even though high soil salinization has severely affected the preservation of floral and faunal remains at the site, excavators could still determine that sheep and goat comprise the majority of the animals being exploited while wheat and barley were the staple crops. The presence of grinders and grinding stones, along with clay and stone sickle blades, reflect the local agricultural base for the Uruk period communities at Abu Salabikh. Overall these data suggest a small–scale farming and herding community whose production and consumption patterns were based on the household level and not controlled or organized by a centralized authority, as is traditionally argued for the structure of southern Mesopotamian Uruk economies (Johnson 1973; Nissen 1988; Wright and Johnson 1975). Pollock does not rule out the possibility for larger households with highly specialized workforces, as documented in Mesopotamian texts (Nissen 1988, 80–83), however these must be seen as only one of a variety of production units within any one community, town, or region (Pollock et al. 1996, 697). 306 Moving north outside of the traditional heartland of southern Uruk–Warka, a lengthy Middle Uruk occupation is also attested at Tepe Gawra, a small 1 hectare tell located east of the Tigris River on a tributary of the Khosr River in close proximity to the ancient site of Nineveh. This area is a piedmont zone where both rain–fed and irrigation agriculture is possible. Gawra likewise lies at the mouth of a natural pass through the Jebel Maqlub on its way to the hills of the northern Zagros. Thus the site lies at a crossroads for communications and trade with the eastern mountainous zone as well as north–south riverine traffic along with Tigris. Tepe Gawra was first excavated by Ephraim Speiser in 1927 who also carried out two six week seasons in 1931 and 1932. Charles Bache then took over as field director between 1933 and 1936. During the sixth campaign (1936/1937) Speiser returned as director while the final seventh season (1937) was led by Bache once again. The incomplete and often inaccurate final publications by Ephraim Speiser (1935) and Arthur Tobler (1950) led Mitchell S. Rothman (1988, 2002) to provide a subsequent reanalysis of the Tepe Gawra material for Levels XII–VIII that date to LC 1–3. Though the end of occupation at Gawra marks the beginning stages of the Uruk Phenomenon during the LC 3, it nonetheless stands as an important site. The evidence from Tepe Gawra suggests a highly integrated and complex level of social organization that was actively engaged with neighboring polities via an economic relationship (at least, that is what is visible archaeologically). Gawra thus stands as one of several examples that higher level administration, trading networks, and social complexity were already established in periphery areas outside of southern Mesopotamia before the onset of the Uruk Phenomenon. 307 During the early fourth millennium at the height of settlement, Gawra was relatively small (1 hectare) when compared with neighboring Nineveh (discussed below). However there remain some five hundred years of continuous occupation spanning six phases at Gawra that encompass the LC 1 to LC 3 periods, predating the Uruk Phenomenon. The earliest occupations (Levels XII–XIA; LC 1) are dominated by extended families occupying houses with large central rooms, exterior kitchens and individual storage rooms. Larger tripartite structures, such as the so–called White Room building (Level XII), are ritual spaces and the loci for specialized production of goods like cloth making, woodworking, knapping, and seal cutting.6 Other later monumental structures like the Round House fortress and gateway complex (Level XIA) attest to communal labor and/or high levels of social organization. Gawrans seemed to have been active in a long distance trading network attested by non–local items of gold, lapis, shell, alabaster, obsidian and worked copper. Seals and sealings of both local and non–local Gawran clays are further evidence for the importation of foreign goods.7 In the following occupations (Levels XI–IX; LC 2) these widespread specialty workshops for weaving, spinning, woodworking and ceramic production, continue though eventually disappear in favor of more centralized production. This took place within, or adjacent to, a formal temple built on the southeast edge of the mound, a large public building and depot. The types of production shift as well with more luxury items like beads and bone inlay being created as opposed to staple products. Seals and sealings are limited to the temple, public building and workshop area reflecting centralized control 6 Though the contents found inside the White Room—spindle whorls, a spatula, obsidian core, and four small celts—reflect domestic use for the building’s final phase of occupation. 7 Interestingly, none of the non–local sealings came from Nineveh, suggesting that in fact, Gawra was not dependent upon the regional center (Rothman and Blackman 1990). 308 of goods. Extended family dwellings from previous levels give way to smaller cramped units with only one to two rooms and an attached kitchen. The final occupation at Gawra (Level VIII–VIIIA; early LC 3) is characterized by the main temple and public building seen previously, along with a central warehouse containing seals and sealings of both local and non–local clays. The ceramic evidence for all levels at Gawra is very poor (Rothman 2002, 52); however, of the assemblage that has been analyzed, the ceramics reflect a local Late Chalcolithic, non–“Uruk” character consisting of wheel and handmade vessels with various levels of grit and chaff temper. Gawra’s large neighbor to the south is Nineveh, a regional center on the east bank of the Tigris River just north of the confluence of the Tigris and Khosr Rivers. The site is roughly 2 kilometers wide and 5 kilometers long and encompasses an area of approximately 1,750 acres (700 hectares) having an estimated population of 250,000 people at the height of settlement in the seventh century BCE. The site is encircled by a roughly rectangular city wall and defined by two primary mounds: Kuyunjik and Nebi Yunus. Nineveh is best known as the capital of the Neo–Assyrian empire under Sennacherib (704–681 BCE) and Ashurbanipal (668–627 BCE); however, occupation on the main mound (Kuyunjik) extends back into the fifth millennium BCE. The earliest excavations at Nineveh began in the mid–nineteenth century (1842) under Paul–Émile Botta. Austen Henry Layard, on behalf of the British Museum, continued this work from 1846 to 1851 by unearthing a large part of the Southwest Palace of Sennacherib. In 1852 Layard’s assistant, Hormuzd Rassam, took over directorial duties, subsequently excavating the North Palace of Ashurbanipal. Fifty years later, R. Campbell Thompson 309 carried out a number of expeditions at the site between 1904 and 1905, and 1927 to 1932 (Campbell Thompson 1934; Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1929). Excavations on Kuyunjik east of the third millennium BCE Temple to Ishtar platform revealed a massive building made of unburned mud brick identified by the excavators as vaulted tombs (Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1931, 81; Campbell Thompson and Hamilton 1932, 78). The building was quite large (50 by 60 feet and maximum 15 feet high) with thirty courses of dark gray libn bricks preserved. Thick piers support a system of parallel vaults and archways that encircled a central courtyard.8 Their designation as tombs is misleading as no human remains were ever found within the structure. The excavators however suggest these tombs had been plundered in antiquity, to which they attribute the wide scattering of beads (ten thousand in total) across areas neighboring the vaulted building and other pits found inside (Beck 1931; Campbell Thompson and Hamilton 1932, 79–80). Mainly ceramics were uncovered from inside the building under and near the frontage and well inside the building at floor level. The assemblage is composed of mostly beveled–rim bowls though other shapes such as conical cups, large jars with tubular spouts, and four–lugged squat jars with shorts necks are also present. The beveled–rim bowls in particular were often found stacked in groups of two to six and turned upside down above caches of animal bones and accompanied by black ash and/or 8 According to Algaze (1986b, 129) in his reassessment of protoliterate Nineveh, this type of vaulted architecture seems to be the forerunner of a larger tradition in northern Mesopotamia. However the example of Gawra VIIIA that is given by Algaze and dated to the Ninevite 5 period based on the initial report by Tobler (1950) has now been shown to be incorrect based on the subsequent reappraisal of the Gawra excavation data by Rothman (2002). It is now universally accepted that Gawra VIII (the final phase of occupation at the site) dates to LC 3 (see “Tepe Gawra” section this chapter). 310 bitumen.9 Beveled–rim bowls were also found in Areas G and H on the slopes between the Ishtar and Nabu Temple platforms on the floor of a large building (24 by 80 feet) and on the northeast edge of the mound at a depth of 22 feet from surface (Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1931, 81 no. 2) suggesting that a large portion of Kuyunjik may have been occupied during the latter half of the fourth millennium BCE.10 A cylinder seal was also found adjacent to this building along with a bulla bearing a cylinder seal impression depicting two bulls standing back to back in southern Mesopotamian Uruk style.11 This same impression was encountered on a numerical notation tablet from the Deep Sounding on Kuyunjik, but unfortunately the context is uncertain (Algaze 1986b; Collon and Reade 1983). The other area in which material culture datable to the Uruk period was recovered was a deep sondage abutting the northwest side of the Temple of Ishtar platform. Excavated by Max Mallowan for a total of two months during the 1931–32 season, this 50 by 65 foot pit reached a total depth of 90 feet (Campbell Thompson and Mallowan 1933). The various levels in the pit were later divided into five strata based primarily on ceramic assemblages. These strata (Ninevite 1–5)12 cover the span of some three millennia, with 12 meters of occupation representing the Uruk period (Ninevite 3–4) alone. Briefly, Ninevite 3 is characterized by lightly burnished grey ware and plain undecorated ceramics, many of which are handmade but others show the tell–tale signs of 9 This consistent arrangement of the beveled–rim bowls upturned above animal bones reinforced the excavator’s theory, “that they were votive offerings, perhaps to the dead” (Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1931, 104 no. 3). 10 This ceramic assemblage, specifically the beveled–rim bowls, is the primary means by which the vaulted building has been traditionally dated. Renate Gut (1995, 2002) however believes the building to not be prehistoric, but instead built into earlier levels at a later date. 11 Collon and Reade (1983) and Algaze (1986b) claim it depicts a lion attacking two bulls standing dos à dos. In my opinion the lion is not entirely clear in the original publication (Campbell Thompson and Hutchinson 1931, 82; Pl. XXII, no. 10). 12 Also seen written as Ninevite I–V. 311 fast wheel manufacture. Shapes include heavy squat–bellied bowls, shallow bowls with incurved rims (related to the Coba bowls of north Syria and Anatolia)13, pots with club– head sections, and burnished holemouth jars found also at neighboring Tepe Gawra (XI– IX). The earliest beveled–rim bowls also appear in small numbers.14 Cylinder and stamp seals are continuously found in this stratum along with baked clay sickles, bone awls, a copper pin, a clay cone believed to be a gaming piece, sun–dried clay sling bolts, and anthropomorphic figurines. Ninevite 4 (roughly equivalent in date to LC 5) is characterized by classic Late Uruk period forms and wares: reserved slip, drooping spouted vessels, flat dishes, beveled–rim bowls en masse and turned upside down, incised wares, and “Erech red slip ware” with perforated lug handles. The following Ninevite 5 phase (Early Bronze Age) exhibits a complete shift in the ceramic repertoire to elaborate painted and incised wares of round bottom bowls with beaded or straight rims, stemmed bowls, and large stemmed jars with ovoid bodies. Small finds from the Ninevite 5 level include a long tanged copper arrow or spear head, flanged bronze arrowhead, clay dog figurines along with anthropomorphic figurines, a granite bowl, and a reddish limestone macehead. The seals and seal impressions from this stratum and earlier Ninevite 4 mirror similar motifs such as trees, plants and animals found at Kish, Jemdet Nasr, Ur, Susa and Uruk–Warka. Items that were common throughout the entire Ninevite sequence include flint and obsidian implements (i.e., blades, cores, scrapers), ax heads made of serpentine or diorite, carding combs, and baked clay spindle whorls. The limited faunal remains suggest that domestic 13 Gut 2002, 19. The beveled–rim bowls are given a votive function by Mallowan citing, “third rate quality of the ware leave little hardly a doubt that they must be dedicatory” (Campbell Thompson and Mallowan 1933, 168). 14 312 pig, sheep, goat and cow were common throughout with the interjection of the occasion wild species such as ass and deer. Though evidence at Nineveh is limited to the Deep Sounding, the vaulted building and smaller excavations upslope from the Temple of Ishtar platform, Nineveh seems to have been a significant site during the Late Uruk as its long depositional history suggests. The presence of beveled–rim bowls, higher level accounting implements, and cylinder seals/sealings with motifs attested in neighboring sites to the south suggest Nineveh was within the sphere of southern Mesopotamian influence or cultural milieu. If the vaulted building does in fact date to the LC 4 or 5, this would perhaps substantiate Algaze’s (1986, 130; 1993, 37) claim that Nineveh served as a major protoliterate outpost on the Upper Tigris with monumental buildings and access to key trade routes.15 Iran Susiana / Khuzistan The heartland for much of Elamite history is Khuzistan in western Iran, also called Susiana after the city of Susa located at the region’s center. This high alluvial plain is bordered on the northwest by the Deh Luran plain, on the southeast by the plains of Ram Hormuz, and on the east by the Zagros foothills. Five principal rivers traverse this well–irrigated landscape (Kirkby 1977). Topographically Khuzistan can be seen as the eastern extension of the southern Mesopotamia alluvial plain. Some researchers (Algaze 1993; Johnson 1973; Wright 1972) also view the region as a cultural extension as well in the protoliterate period since assemblages between the two are largely analogous. 15 For an alternative hypothesis, see Stronach 1994. 313 Whether this indicates simultaneous development or asymmetrical influence remains largely debated concerning the Uruk Phenomenon. Susa is the primary site regarding cultural developments during the latter half of the fourth millennium in this region. The 550 hectare mound is located on the western edge of the Khuzistan plain on the left bank of the Shaur River. After initial soundings by W. K. Loftus (1857), a total of five areas were excavated under the leadership of several directors: Jacques de Morgan beginning in 1897, Roland de Mecquenem (beginning 1908), Roman Ghirsham (1946–1967) and Jean Perrot (1968–1979).16 The most important data concerning the prehistoric levels at Susa come from a deep sounding in the Acropole on the west side of the mound and the Apadana Mound, an area on the north side later occupied by an Achaemenid palace. The earliest phase, Susa I or A (dated LC 1–3), occupations both these areas totaling 7 hectares and was encircled by a 6–meter–wide pisé wall. On the Apadana is a monumental multi–roomed building (Bâtiment de Suse I) with 2–meter–thick pisé walls coated with prepared plaster. On the Acropole (I, levels 27–23; II levels 11–7) is a large, low mud brick platform (massif funéraire) measuring between 8 and 14 meters containing the buried remains of approximately two thousand individuals in primary and secondary internments. This structure has been variously interpreted as a graveyard for the inhabitants of Susa, a centralized cemetery for use by surrounding settlements (Vértesalji 1989), and a mass grave site (Hole 1990). Later in this phase, a second mud brick platform (haute terrasse) is constructed atop this funerary structure and accumulated residential debris. This 10–meter–high stepped structure is decorated with inlaid ceramic cones, clay models of goat horns and plaque mosaics (Canal 1978; Pollock 16 An extensive bibliography for excavations at Susa can be found in Carter and Stolper 1984. 314 1989). Apart from these more monumental architectural features, Susa I was also characterized by stamp seals bearing glyptic styles paralleled in southwestern Iran, various copper implements such as chisels, pins and flat axes, and beautiful painted ceramics, most notably tall slender black and white beakers with stylized animals and geometric motifs (Le Breton 1957). In the following phase, Susa II or B, the Bâtiment de Suse I and haute terrasse are destroyed by fire, the latter seemingly abandoned for some time while the former was filled in with occupational debris datable to LC3. This suggests occupation continued at least on the Apadana Mound area, initially shrinking Susa’s overall size to 5 hectares at the beginning of this phase. Further excavation showed however that the settlement did expand to encompass both the Apadana and Acropole (levels 22–17), plus a lower town area—a total of 25 hectares by the end of the LC 4 but then constricted again to 9 hectares by LC 5 (Johnson 1973). While the material cultural assemblage of Susa I is completely local to the Khuzistan plain, Susa II exhibits a total break. Evidence has derived mostly from the Acropole sounding levels 17 and 18 (LC 5) where well–built private houses were uncovered. The ceramic assemblage shows similarities with southern Mesopotamia: beveled–rim bowls, four–lugged jars with crosshatch decoration, drooping spouted bottles, reserved slip wares, jars with twisted strap handles and pouring–lip bowls. Sealed bullae with tokens are common inside these houses along with stamp seals and numerical tablets with cylinder seal impressions similar to tablets at Uruk–Warka IVa, Habuba Kabira-Süd, Jebel Aruda, Tell Brak, Godin Tepe and Chogha Mish. Of the thirteen notation systems in use at Uruk–Warka, three have been identified at Susa II 315 leading some to believe unequivocally in the Urukean origin of these counting systems (Potts 1999, 61).17 However no protocuneiform texts dealing with economic and lexical subject matter have been found at Susa or anywhere outside of Uruk–Warka. The glyptic on the cylinder sealings is executed in both “baggy style”18 and the smooth iconic “true Uruk style” depicting scenes of hunting, animal attacks, warfare, and occupational activities like weaving. There are direct parallels for this imagery at Uruk–Warka and Chogha Mish, most importantly that of the so–called “priest–king” figure who is depicted bare–chested and wearing a skirt with his long hair tied back into a tight bun at the nape of the neck. He is often shown in the presence of bound captives wielding a spear or, as in one example from Susa, a composite bow with which he slays his enemies before an ornately decorated building. A drastic contraction in settlement size and change in ceramics signal a cultural break for excavators between Susa II and the following Susa III or C, represented only on the Acropole levels 16–14b (LeBrun 1978). The Acropole is abandoned but reoccupied after a short duration. One of the major changes are in glyptic and writing where over fifteen hundred “Proto–Elamite A” or “Susa III” texts were excavated in the Acropole I level 16. While the numerical systems employed at Susa III have been shown to exactly parallel, or be derived from, systems in protocuneiform texts from Uruk–Warka III (Damerow and Englund 1989), the signs employed by the Susan scribes, along with the cylinder seal imagery on the Susa III tablets, are decidedly different from those in use in Mesopotamia. For many, this is seen as the critical juncture in which the cultural 17 However the arrangement of the signs and the shape of the tablets themselves from Susa are completely unlike those from Uruk–Warka (see M.W. Green 1981; as cited in Potts 1999, 63). 18 First introduced by Amiet (1961) to describe seal designs that have been cut with a ball drill whereby the drill marks have been left obvious and incorporated into the design. 316 developments in Susiana and southern Mesopotamia, once seemingly intertwined, diverge as Susa looks to the north and east. Chogha Mish is the sister–city to Susa in terms of cultural development in the region. The site is located in the eastern edge of the Susiana plain between the outlets of the Dez and Kuran Rivers and is composed of a high mound towering 27 meters above the surrounding plain and a long terrace. Chogha Mish was first identified and surveyed by Austin Henry Layard (1846) and Robert McCorrmick Adams (1962), and later excavated by Pierre Delougaz and Helene Kantor between 1961 and 1978 (Delougaz and Kantor 1996). Evidence for Protoliterate period occupation, specifically LC 4 through early LC 5, was found across the entire 18 hectare site with notable architectural elements coming from the high mound, terrace, and east/west areas. Monumental architecture in the form of a 2.5 by 4.5 meter building with 3–meter–thick walls was uncovered on the high mound along with brick–lined cesspits filled with beveled–rim bowls, terra cotta drains, ceramic mosaic cones from debris pits similar to those from Uruk–Warka, and a possible city wall on the backside of the mound (Delougaz and Kantor 1996, 27). The terrace and east areas contained large sections of stratified, densely packed domestic architecture intersected by alleyways and streets that contained open channels and covered drains. These houses were relatively poorly preserved due to their ephemeral nature and cutting by later refuse pits. The pits however, were an abundant source of finds including ceramics, baked bricks, jar stoppers, door sealings, and unbaked fragments of animal figurines. Kilns within the vicinity of these houses also show evidence for ceramic production, specifically of beveled–rim bowls. Finally in the west area, a 350 square meter polygonal platform composed of hard brickwork attests to 317 perhaps another monumental structure on this side of the site. Overall the architectural character at Chogha Mish suggests an urban environment with a population living within a confined space and perhaps surrounded by a city wall. The ceramics that this population used seem to have been a coherent assemblage with parallels at Susa 17/18, Uruk–Warka VII–IV, and Habuba Kabira-Süd. These include “flower pots,” drooping spouted jars, beveled–rim bowls, and squat four–lugged jars. One unique double spouted vessel has appliqués of a snake biting the neck of a goat at the base of each spout, parallels for which have been found at Habuba Kabira-Süd (Sürenhagen 1974/5, pl. 9–11). Another unique four–lugged vase exhibits an incised pictorial design of a man holding a fish in either hand. Similar imagery has been found at Uruk–Warka (Lenzen 1960, pl. 26, 31) and Susa (Amiet 1972, pl. 14, 78). Evidence for sealing and accounting practices are prevalent at Chogha Mish ranging from tallying slabs to tokens, hollow clay balls, bullae, and numerical tablets with cylinder seal impressions whose motifs are paralleled at Susa, Eanna V/IVb at Uruk–Warka,19 and Habuba Kabira–Süd. These include both animal and human imagery, the former of which includes scorpions, birds, snakes and turtles. Human figures are depicted as “master of animals” between pairs of snakes, battlefield scenes, archers, processions of pig–tailed figures, and “priest–king” imagery. The development in style and manufacture of these seals, from “baggy–style” to more smoothed lines, is evident at Chogha Mish though the designs never reach the full extent of classic Late Uruk style seals prevalent in southern Mesopotamia (Pittman 2001, 426–431). The apparent abandonment of Chogha Mish near the end of the LC 5 coincides with drastic changes in settlement patterns and glyptic traditions within the Susiana plain 19 Though not for Eanna IV or III dated to the LC5 and EBI (see Pittman 2001, 430). 318 (Johnson 1973, 143; Pittman 2001, 436). Evidence from surface surveys show that after a rapid increase in the number of settlements and expansion of occupied areas during Susa I and the beginning of Susa II, settlement numbers greatly decreased by the end of Susa II or the LC 5 (Wright and Johnson 1975, 1985). During this time a wide spatial separation developed between the two centers in the plain—Susa and Chogha Mish—such that no villages were occupied between them. This “buffer zone” reflects growing hostilities between the two settlements (Johnson 1973, 145). Though conflict is not particularly visible in the assemblages from either of these sites in terms of destructions or weaponry (Chogha Mish was abandoned, not destroyed), the glyptic evidence from sealings discussed above certainly portray mythical, if not actual, wartime events or themes. This political insecurity coupled with a major population decrease lays the evidentiary foundation for Johnson’s theory that the Uruk Phenomenon is the movement of political refugees forced out of Khuzistan by their elite rivals (see chapter 1).20 Luristan A final site of significance to the Uruk Phenomenon lies outside of the Susiana/Khuzistan heartland in the central western highlands of Iran, specifically in the area of Luristan. This site, Godin Tepe, is located in the Kangavar Valley nestled within the Zagros Mountain range and lays astride the major east–west “High Road”21 between the alluvium of central Mesopotamia and the Iranian plateau. The site, which is composed of a citadel mound and outer town to the west, was first identified on survey 20 Though Johnson does acknowledge the possibility that populations agglomerated inside the cities (an increase in settlement size at Chogha Mish during the LC 5 could account for this) or instead formed small dispersed villages whose ephemeral nature made them unrecognizable during surface survey (Johnson 1973, 154). 21 Also called the “Royal” or “Great Khorassan” Road. 319 and later excavated by T. Cuyler Young between 1967 and 1973 under the auspices of the University of Toronto and the Royal Ontario Museum. A total of eleven cultural phases were uncovered in three areas of the site,22 two of which (Periods V and VI) span the LC 3 to LC 5 periods with a total occupational size of 15 hectares. The earlier period (VI; LC 3 in date) is composed of several phases of multi–room domestic architecture in the outer town and a continuous sequence of purely local ceramic forms and wares (Young 1969; Young and Levine 1974). At the end of this phase however are the earliest beveled–rim bowls and other forms that have parallels at Middle Uruk period Nippur and Tepe Farukhabad (Badler 2002, 81). Also dated to the end of Period VI are a triangular geometric token and metal implements showing the beginnings of higher level accounting practices and longer distance trade (Young 1969). There is a noticeable change in the cultural material assemblage of the following period (V) dated to the LC 4/5, ca. 3500–3200 BCE. While a continuation of domestic architecture was evident in the outer town, there is a dramatic increase in the use of distinctive Uruk ceramic forms like coarse conical cups and beveled–rim bowls, alongside local wares. The most significant evidence was uncovered in the Deep Sounding on top of the citadel mound where over 500 square meters of excavation exposed an oval enclosure (Weiss and Young 1975, fig. 2). Inside the oval is a complex of structures that went through three distinct building phases, the latest of which (Level V:1) being the most extensive and well preserved. This consists of a set of buildings and rooms placed around a central open courtyard, all of which are surrounded by a 1.5– meter–thick oval enclosure wall. In total, the enclosure covers an area of 33 by 21 meters. 22 The Deep Sounding on the citadel mound, the Brick Kiln Cut (BKC) to the west of the citadel mound, and Operation B to the east. 320 The complex was accessed from the south through a gateway that is flanked by storerooms and a possible kitchen. Directly across the courtyard from the gateway is what seems to be the architectural focus of the entire complex: a large, multi–room structure with an elaborate fireplace and two windows (Weiss and Young 1975, 5). The ceramics inside this room—horizontally pierced four–lugged pots and beveled–rim bowls—have parallels at Susa 17 and Eanna IV at Uruk–Warka. In one of the storerooms excavators uncovered a large cache of unbaked tablets and tablet fragments, one of which displayed pictographic signs (Weiss and Young 1975, 8). At least thirteen tablets contain cylinder seal impressions with various motifs of sitting lions, squatting archers, running goats and files of bulls, lions, and humans paralleled at Susa (Amiet 1972).23 These data, along with jar stoppers, cylinder seals, and metal implements all solely contained within the oval structure, suggest this was the center of administrative activities within the settlement.24 These most likely included trade with neighboring regions though what product(s) were involved remains enigmatic.25 However, recent analysis of storage jar residues and special stone basins within the oval enclosure suggest wine and beer were being produced at Godin and possibly traded to Susa, Uruk–Warka and Telloh (Badler 1996, 2000; McGovern et al. 1996). In terms of the Uruk Phenomenon, this seemingly drastic appearance of material culture characteristic of Khuzistan and southern Mesopotamia represented in the oval enclosure suggests to the excavators an arrival of foreign peoples, most likely from Susa, 23 Weiss and Young (1975, 13) point out the use of drill centered circles and radial star motifs as space fillers within seal design as a regional style common to Susa, the Diyala and the Amuq. This design occurs on four of thirteen sealed tablets and both cylinder seals recovered from the Period V oval at Godin. 24 Though Badler (2000) has suggested the oval functioned as a fort with the inhabitants distributing food rations and weaponry like sling stones. 25 Weiss and Young (1975, 14–15) contend that Godin served as an outpost along the Khorasan Road for trade in lapis lazuli. This idea remains tenuous at best since no caches of raw lapis or finished products using this stone were uncovered in any areas at Godin. 321 who established themselves within the local population. This seems to have been a peaceful undertaking that most likely developed over several generations as there is no evidence for destructions or warfare and lengthy rebuilding sequences of structures within the oval. Likewise the abandonment of the oval enclosure was not violent, but most likely harkened by the interruption of trade routes at the beginning of Period IV (ca. 3100–2650 BCE) with the arrival of peoples utilizing Early Transcaucasian cultural material (Weiss and Young 1975; Young 1972). Syria Tabqa Dam The most well known of sites in this region and most influential for spawning the idea of an Uruk Phenomenon is Habuba Kabira. Located 100 kilometers east of Aleppo and approximately 15 kilometers north of Meskene, Habuba Kabira was composed of two ancient settlements now flooded by the waters of the Tabqa Dam reservoir: Tell Habuba Kabira and Habuba Kabira–South (Süd). The latter site was approximately 900 meters long and contained the smaller mound of Tell Kannâs/Qannas. Habuba Kabira was noticed in early surveys by Abdel Kader Rihaoui and Maurits N. van Loon in 1963 and 1964 (van Loon 1967). Habuba Kabira South (hereafter “Habuba–Süd”) was subsequently excavated by Ernst Heinrich and Eva Strommenger between 1969 and 1975 on behalf of the Deutsche Orient–Gesellschaft (Strommenger 1980). Tell Kannâs was excavated by André Finet on behalf of the Belgian mission (Finet 1973, 1975, 1977, 1982). 322 Habuba–Süd contained a long rectangular town with a 3–meter–thick city wall made of Riemchen bricks on three sides and the Euphrates River acting as a barrier on the fourth. In total, the town is estimated to have been 18 hectares in size. Three building levels were distinguished by excavators who estimated a total occupation of six to eight thousand people over a span of one hundred fifty years all carbon dated to the LC 5 (Strommenger 1985, 86). Some level of town planning is evident in the street system where compacted pebble paving runs below the primary building level for the surrounding houses signifying that they were built afterward. A main street runs north– south through the heart of the town with two additional streets running perpendicular. A town–wide drainage system comprised of fitted terra cotta pipes also speak to civic planning. The densely built houses average 300 square meters in size and are composed solely of Riemchen bricks. Most floor plans consist of a central courtyard surrounded by rooms, prompting the excavators to call these Mittelsaal–type houses (Strommenger 1980, 36). The citadel area of Tell Kannâs on the southern end of the inner town is considered to be the administrative and religious center for the town. A grouping of public buildings were excavated here, the so–called North and South Temples, with tripartite floor plans, interior decorative niches, and basins (Finet 1975, 1977, 88–90). A third large building was uncovered in the central sector that is also tripartite in plan with an attached magazine filled with storage jars. Inside these structures a wealth of objects were recovered from cylinder seal–impressed jar stoppers to traces of bitumen, and alabaster vases that resemble Uruk forms of four–lugged jars. 323 Along with architectural elements, the material culture assemblage at Habuba– Süd and Kannâs is completely foreign to the local Syrian assemblages seen at Tell Brak (discussed below), instead exhibiting characteristics that are wholly common to southern Mesopotamia. The ceramics include the full corpus of southern Mesopotamian wares and forms from beveled–rim bowls to four–lugged jars, drooping spouts, and conical cups. Higher level accounting in the form of numerical tablets, clay balls with tokens, and clay bullae was practiced by the residents in domestic houses and near the southern gateway. Most of these had been impressed with cylinder seals whose glyptic style matches those from sites in Iran (e.g., Godin, Susa, Chogha Mish) and Uruk–Warka. The actual products of trade were also uncovered including Canaanean flint blades, fan scrappers, alabaster vessels, and semiprecious stones. A wavy ledge handle fragment from a ceramic vessel betrays connections with the Levant, while an anthracite–colored bowl was likely imported from Nagada IIc period Egypt (see below). Though there is evidence for chipped stone recycling, ceramic production and metal working, storage facilities or tools for agricultural production are notably rare (Strommenger 1980, 55).26 There is evidence the inhabitants fished and hunted the wild resources, but local chaff–faced ware ceramics paralleled at Amuq F with remains of grain and dried–out oil show that agricultural products were provided by people from the countryside (Sürenhagen 1986, 21). These data suggest that Habuba–Süd was a relatively short–lived settlement that was founded by a group or groups from a non–local population. They seem to have been reliant on their neighbors for agricultural products, but were heavily involved in interregional trade and exchange that necessitated the use of 26 Specifically Strommenger states, “Die Bewohner von Habuba Kabira–Süd erzeugten nur einen geringen Teil ihrer Nahrungsmittel selbst” (1980, 55). 324 higher level accounting practices that the tablets and tokens represent. At the end of the LC 5, the site was abandoned for reasons that are not entirely clear. Many see this as a result of the collapsing interregional Uruk trading network, but political instability, environmental degradation or crop failures could also account for the abandonment of a settlement, especially one that is not agriculturally self–sufficient. Though there is no evidence for warfare at Habuba–Süd, the perceived threat of violence could also have exacerbated the situation.27 Another site that shares a strong cultural affiliation with southern Mesopotamia is Jebel Aruda, located approximately 8 kilometers upstream from Habuba–Süd. Aruda is an isolated settlement that lies 60 meters above the Euphrates flood plain nestled into a steep ridge. The site was excavated by Govert van Driel and C. van Driel–Murray from 1974 to 1982 (van Driel 1979, 1983, 2002; van Driel and van Driel–Murray 1979, 1983). The LC 5 period site is contemporary with Habuba–Süd and post–dates Tell Sheikh Hassan (discussed below). Jebel Aruda lacks any direct access to water sources, whether from wells or the river itself, and also bears no access to agricultural production or other foods. Thus the occupants at the site were required to bring water and food up the mountainside themselves, or else have someone else bring it for them. The settlement is composed of three sectors: a central open air temple precinct and two residential quarters. The multi–phase precinct included a large tripartite temple constructed of reddish Riemchen bricks (the so–called “Red Temple”), with a raised central platform flanked by steps and recess decoration along the exterior of the 27 This is best exemplified in the city wall at Habuba–Süd. Late Uruk houses were excavated below the wall, signaling that it was not built until after the community had been settled (Sürenhagen 1986). 325 building.28 A second tripartite temple built of grayish–blue Riemchen bricks (the so– called “Gray Temple”) was constructed alongside the Red Temple during a later phase and mirrors the floor plan and external decorations of the earlier temple. Both temples open onto a large rectangular courtyard that is surrounded by a tall enclosure wall. Two gatehouses, one of which has exterior niching, allow access to the precinct through the outer temenos. While the area west of the temple complex seems to have been left unoccupied, to the north a large multiphase broad room–style building (“First Lower Building” and “Second Lower Building”) was constructed that contains a large oven and attached enclosed courtyard. Major terracing projects, along with the construction of these monumental buildings, suggest that this central precinct was the focus of activities at the site. The northern and southern residential areas are separated from the temple complex by an open area. Both are characterized by a blend of well–proportioned tripartite houses and smaller residential structures that are squeezed in to available spaces or terraced into the steep slope of the ridge as settlement expanded. Multiple building phases are reflected by blocked doorways, wall additions/demolitions, and converted passageways that attest to changing form and function of the residential spaces. Inside, excavators recovered ceramics, spindle whorls, saddle querns, chert tools, tablets and stone vessels (Hanbury Tenison 1983). The general ceramic assemblage contained simple sand–tempered wares that when mapped across the settlement, show clustering of particular types, such as torpedo–shaped vessels and “rolly–bins,” within particular structures that perhaps reflects preferences based on specialized household–level labor 28 In fact, this recessing and niching (along with the raised platform) are the sole criteria by which the excavators designate this building as a temple (van Driel and van Driel–Murray 1979, 3). 326 (van Driel 2002, 194). Other types, specifically goblets and spouted bottles, were frequently found together and most likely represent ceramic sets. Specialized and/or centralized production is also evident by the presence of a large storeroom that housed lumps of unworked lapis lazuli and large bread ovens in separate, special areas. During the final phase of occupation at the site, the temple complex is systematically filled in with stones and the upper courses of the building walls. Most of the contents from the structures had been removed save for a cache of twenty to thirty clay sealings whose iconography is reminiscent of designs from Habuba–Süd and the occasional smashed beveled–rim bowl fragment (van Driel 1983). All areas including the northern and southern residential districts were subsequently consumed by a huge conflagration. The function of the settlement at Jebel Aruda remains obscure. The fact that there is no water source or a defensive system in place discredits the idea that the settlement could be a defensive stronghold of some kind. It is possible that this area was a citadel to a settlement on the margins of the Euphrates River valley, as fragments of ‘Ubaid and Uruk pottery in the mud bricks from the buildings at Aruda whose material derived from the floodplain below, attest to a lengthy occupation in the valley. Van Driel (2002) suggests the settlement acted as a service area for something on top of the jebel, though the idea of this being a seasonal camp for semi–nomadic populations or even a pilgrimage site cannot be overlooked. Certainly Jebel Aruda does not represent a typical settlement of the Late Chalcolithic period in Syria. Next to Habuba–Süd, Tell Sheikh Hassan stands as the type–site for southern Mesopotamian cultural interaction in this area of the Euphrates basin. The 21 hectare 327 mound is located 45 kilometers north of Raqqa and 40 kilometers south of the modern Turkish border in an area now flooded by the Tabqa Dam reservoir, though Hassan remains accessible to excavators. The site was excavated by Johannes Boese between 1987 and 1990, and again from 1992 to 1994 (Boese 1986/7, 1987/8, 1995). These excavations focused on the prehistoric and protoliterate periods (Uruk) while also revealing ceramic evidence for an earlier ‘Ubaid settlement and a later Iron Age palace that is similar in floor plan to the bit hilani structure at contemporary Zincirli (Boese 1987/8, 160). Since 2000, the Syrian Antiquities Service has excavated the tell under the direction of Murhaf al–Khalaf focusing on the later Hellenistic and Islamic Period occupations. In total there are twenty “Uruk levels” at Sheikh Hassan (levels 4–22) that cover just over 1 hectare in area. This lengthy occupation sequence spans the entire latter half of the fourth millennium (LC 4/5, 3600–3100 BCE). The settlement is characterized by a significant and long–lived mud brick city wall (levels 6–13) that contains niches and towers/projections nearly 2 meters wide. Within this wall is a succession of buildings with a variety of floor plans and functions. The earliest Uruk levels (10–12) seem to have been composed of relatively simple structures with mud floors, ovens, fireplaces, simple ceramics and animal bones. One of these buildings (level 10) had been burned, sealing within the debris pan–shaped ovens, a four–lugged jar filled with grain, hollow balls or bullae, and stamp and cylinder seal impressions whose motifs are similar to those found at Habuba–Süd and Jebel Aruda (Boese 1986/7). These sealings are among the earliest well–stratified examples of cylinder seals in the Near East (Akkerman and Schwartz 2003, 196). 328 In later levels (4–9), larger buildings are constructed abutting and adjacent to the city wall that used Riemchen–style mud bricks and typical southern Mesopotamian floor plans such as a Mittelsaal–style house in levels 8 and 9 (see Boese 1995, Abb. 5 from the 1989 season). Levels 6 and 7 contain a clustering of buildings in the southwest corner of the mound next to the city wall that include a thick–walled and enigmatic Kammergebaude or chamber building with unique grill plan, Nischengebaude or niched building, a single–roomed house, and single–celled temple (Boese 1995, Abb. 5 from the 1993 season). This temple contains elaborate internal niching with a raised platform on the northern end opposite a central pan–shaped fireplace. A wealth of small finds was recovered from these contexts that included, apart from those mentioned above, stamp seals, clay cones, a ceramic ladle or spoon similar to those recovered at Qraya (see below), a sickle made out of retouched flint blades in a bitumen holder, zoomorphic vessels, stone and copper weapons, stone vessels, alabaster sculpture, and other implements made of clay, bitumen, bone and metal. The ceramic repertoire includes beveled–rim bowls, reserved slip jars, four–lugged vessels with crosshatched design, miniature vessels, sealed jar stoppers, drooping spouted jars, and conical bowls with a pouring spout. The material culture present at Tell Sheikh Hassan is overwhelmingly southern Mesopotamian/Uruk in character especially in terms of architecture and ceramics though some local north Syrian elements are present, most notably “eye idols” similar to those from Tell Brak (see below). In general, Sheikh Hassan seems culturally associated with other nearby sites like Habuba–Süd and Jebel Aruda while at the same time representing the very earliest occurrence of this southern Mesopotamian–style material culture in the 329 Tabqa Dam region. Furthermore the lengthy Uruk period occupation at Sheikh Hassan attests to a longer duration of contact or colonization with/from the south than previously suggested by data from Habuba–Süd or Aruda, whose settlements are relatively short– lived and established at the very end of the fourth millennium (LC 5, 3350–3100 BCE). Tishrin Dam This region is located north of the Tabqa Dam area along the Euphrates River due south of the site of Carchemish and the present Turkish border. A dam was completed here in 1999 creating a reservoir 60 kilometers in length that subsequently flooded eighteen archaeological sites that had been excavated as salvage projects during the 1990s (del Olmo Lete and Montero Fenollos 1999). Less is known about Late Chalcolithic occupations in this region as compared with Tabqa, however a number of sites exhibit ties with the larger cultural interactions occurring during this time. While evidence at sites like Carchemish (Woolley 1952) and Kosak Shamali (Nishiaki 1999; Nishiaki et al. 2000) are limited to only ceramics during this period, other sites such as ‘Abr and Jerablus Tahtani exhibit a rich history of occupation that spanned the latter half of the fourth millennium. The site of Tell al–‘Abr is located on the east bank of the upper Euphrates River, 15 kilometers south of Jerablus and 3 kilometers northwest of Tell Ahmar (Til Barsip). The site was excavated for five seasons between 1989 and 1995 by Hamido Hammade and Yayoi Yamazaki of Aleppo University (Hammade 1989; Hammade and Koike 1992; Hammade and Yamazaki 1993, 1995, 2006; Yamazaki 1999). Approximately 8 meters of occupational debris were uncovered and a total of seven archaeological phases, the latest 330 of which (Level 1–A, 1–B, and 1–C) being Middle, Late, and terminal or post–Uruk in date.29 These Uruk levels seal a long, continuous sequence of dense ‘Ubaid occupation. Contextual data for the Late Uruk occupation is, unfortunately, limited to the eastern section of the excavated area on the main tell. The lowermost level of Uruk occupation is Level 1–C (Middle Uruk), represented by an ash lens probably derived from erosional wash.30 Though no architectural features could be discerned, classic Uruk ceramic forms such as fragments of beveled–rim bowls, red–slip ware, and conical cups were recovered. The following Level 1–B (Late Uruk) is represented by three partially preserved buildings, constructed of Riemchen mud bricks and situated around a pebble– and sherd–paved courtyard. At least one of the buildings (B1–1) had two distinct phases with two rooms connected by a doorway, a circular fireplace, an oblong or oval horseshoe–shaped hearth, and beveled–rim bowl found in situ. Necked jars with reserve slip are now the dominate ceramic type along with conical cups, beveled–rim bowls, drooping spouts and low nose–lugs characteristic of Late Uruk southern Mesopotamian types. The final Uruk level (Level 1–A “Terminal” or “Post– Uruk”) is restricted to an extremely small area of the upper mound and yielded very little in the way of ceramics or architectural elements. The ceramics show a break from the preceding Level 1–B including open bowls with beaded rims similar to those from Hassek Höyük (datable to the EBI), fragments of a coarse "flower pot" with string–cut base, a conical bowl with beveled–rim bowl fabric, and fragments of vessels with true reserved–slip. 29 This dating was determined by ceramic data only and not through carbon dating. Radiocarbon dates were only acquired from Levels 5–7 (Hammade and Yamazaki 2006, 431). 30 See chapter by T. Oguchi and C.T. Oguchi in Hammade and Yamazaki 2006 regarding sedimentological analyses of deposits from ‘Abr and Hammade and Yamazaki 2006, 40. 331 The nature of these occupational phases loosely dated to the end of the fourth millennium is unclear. Very little material culture was recovered from any of the Level 1–B buildings apart from small amounts of flint in the form of Canaanean blades, various baked clay objects (e.g., scraper, pipe, “bobbin–shaped object”), a straight bone needle, and a cylindrical–shaped pestle. According to the excavators, there is a clear gap between the Uruk and ‘Ubaid periods recognized both stratigraphically and in the ceramic sequence (Hammade and Yamazaki 2006, 91). The Uruk pottery at ‘Abr corresponds to that from Sheikh Hassan and Habuba–Süd with no evidence for local Late Chalcolithic ceramics. All fabrics are mineral tempered, well levigated and wheel–made, except for the coarse beveled–rim bowls. Bearing in mind that very little data has been recovered, the known architectural and ceramic data from Tell al–‘Abr reflects southern Mesopotamian Uruk characteristics in terms of material culture. The same can be said of Jerablus Tahtani, an oval steep–sided mound 180 by 200 meters in size and 16 meters tall that was located 5 kilometers south of Carchemish along the west (right) bank of a branch of the Euphrates River. This multi–period site with occupation levels stretching from the mid–fourth millennium BCE through the Islamic period, was excavated over seven seasons by a team from the University of Edinburgh under the auspices of the Syrian General Directorate of Antiquities and Museums' Tishreen International Rescue Programme (Peltenburg 1999; Peltenburg et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, 2000; Stephen and Peltenburg 2002). Early soundings on the eastern side of the mound revealed only limited amounts of Late Uruk material including some mud brick, tauf and stone walls forming small rooms with hearths, pits and an earthen oven. Later investigations uncovered a sequence of six occupational episodes. The earliest, 332 dating to the Middle Uruk or LC 3 period, is characterized by post holes and an adjacent platform of irregularly laid mud bricks into which a sub–rectangular hearth was cut (Peltenburg et al. 2000). The pottery is completely local with an assemblage of chaff– faced wares that is common to southeast Turkey and north Syria for the mid–fourth millennium: hammerhead rim bowls, conical cups with pouring lip spout, plain–rimmed shallow bowls with thick walls, and jars with everted plain and flange rims. Following the fiery destruction of the LC 3 settlement, the subsequent occupation is markedly different in architectural style, ceramic sequence, and general material culture. Excavators uncovered several buildings, one of which is a two–phase rectangular mud brick structure composed of bun–shaped, unfired Riemchen bricks in various colors (Peltenburg et al. 2000, 58). Finds from these buildings include ceramic scrapers, spindle whorls, conical stoppers, and a sealing of unbaked clay. An alabaster jar with cross– hatched band, polished stone bowls with beaded rim, and a flattened oval white stone bead, also found in relation to these buildings have parallels at Tell Sheikh Hassan and Hacınebi (see below). The ceramic sequence for this phase is exclusively Uruk in form and fabric with reserved–slip jars and locally made beveled–rim bowls containing bitumen residues (Peltenburg 1999, 100; Peltenburg 2000, fig. 6; Stephen and Peltenburg 2002, 178). The floral record corresponds to a local agricultural system with fields neighboring the settlement. The occurrence of Canaanean blades substantiates this premise while a pure sample of barley found in a sealed context is consistent with cleaned crop storage within the settlement. 333 Unfortunately the full extent of the Late Uruk period settlement at Jerablus Tahtani will never be known because of heavy flooding in antiquity, the depth of these levels below Early Bronze Age fortifications, and mostly because the site has now been flooded by the waters behind the Tishrin Dam. From the available evidence, it appears that the site was first settled in the mid–fourth millennium BCE by people who used local chaff–faced pottery and lived in ephemeral housing, perhaps as part of a semi–nomadic population. Sometime during the end of the LC 3/beginning of the LC 4 there was a destruction episode and the area was re–inhabited by peoples with a completely different material culture: rectangular buildings with polychrome Riemchen mud bricks, mass– produced pottery, bitumen processing capabilities, and high status goods that have direct connections with sites further south in the Tabqa Dam area. Khabur The Jezira is an open expanse of steppe and high alluvial plains positioned between the Euphrates River and “Syrian Saddle” on the west, the Tigris River and Tur Abdin mountain range on the east, and the Jebel Sinjar range to the south. The plain is cut by the Khabur and Balikh Rivers, the two main tributaries of the Euphrates. In the most northern reaches of the Khabur, the “Upper Khabur” or “Khabur Triangle,” the river branches into an alluvial watershed that is especially fertile for agriculture and home to a number of ancient sites relevant to discussions of the Uruk Phenomenon. For example, sites such as Tell Leilan (Schwartz 1988a; Stein and Wattenmaker 1990; Weiss 1983), Bderi (Pfälzner 1990), Tell Ziyadeh (Buccellati et al. 1991), Tell Umm Qseir (Tsuneki and Miyake 1998) and Fadgami (Röllig and Kühne 1977–78, 126) exhibit both local 334 north Syrian and southern Mesopotamian elements of material culture, though this evidence is limited to ceramics only. The largest and most extensively excavated site in the Upper Khabur area is Tell Brak. Located near the Wadi Jaghjagh in the southern reaches of the Khabur Triangle, Tell Brak is strategically positioned at the southern entrance to the Khabur plains controlling entry to both the Sinjar mountainous area to the north and southern Mesopotamia via the Euphrates River. The site was first scientifically excavated by Max Mallowan between 1937 and 1938 under the auspices of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq (Mallowan 1947). Excavations resumed in 1976 under the directorship of David and Joan Oates from the Institute of Archaeology at University College of London. In total, they conducted fourteen seasons at Brak between 1976 and 1993 (D. Oates 1977, 1982a, 1982b, 1985, 1987; D. Oates and J. Oates 1989, 1991, 1993a, 1993b, 1994; D. Oates et al. 1997, 2001).31 Roger Matthews continued excavations as field director from 1994 to 1996 with the support of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq and the McDonald Institute of the University of Cambridge (R. Matthews 1995, 1996, 2003a, 2003b; Matthews et al. 1994). He has since been followed by Geoff Emberling and Helen McDonald (Emberling and McDonald 2001, 2003; Emberling et al. 1999), Augusta McMahon, and H.T. Wright as field directors of the current ongoing excavations. Brak contains 10 meters of Uruk period occupation divided into twenty–two levels that span the mid–fourth millennium (TW Levels 19–20: “Northern Early Uruk”) to the early third millennium (TW Level 1: early Ninevite 5, ca. 2800 BCE). The average occupational size of Brak is estimated to have been 65 hectares, with the largest total area 31 A complete bibliography of Tell Brak preliminary reports can be found in D. Oates and J. Oates 1994. 335 of settlement dating to the LC 3 period (“Northern Middle Uruk” ca. 3500 BCE) at over 100 hectares (J. Oates 2002, 113).32 The earliest levels of occupation are represented by a massive perimeter wall up to 2 meters thick and a monumental gateway with a huge basalt threshold dated to the LC 2 (ca. 3800 BCE, TW Levels 19–20; Matthews 1996; J. Oates 2002, 199). A probable temple with niched façade and building with two small mud columns also dated to this period were recovered in Area CH (Oates and Oates 1994; D. Oates 1987). The following “Northern Middle Uruk” or NMU phase (levels 14–18, ca. 3500 cal BCE) represents a completely indigenous settlement at Brak (J. Oates 2002). Well– built houses made of square bricks, some with high status goods, characterize the NMU levels. One large building for example (level 16), contains finely made ground stone tools, ivory objects, carnelian and gold beads, clay pipes, and two “eye idols”—the only ones to be found in situ at Brak (Oates and Oates 1993a, 178; J. Oates 2002, 116). A slightly later (level 18) tripartite public building with niched decorations and a well– preserved domed mud brick oven also contains storage jars, stone mace heads, an alabaster bear statuette (Pittman 2002), and a bone eye idol fragment (Trench TW B; Emberling et al. 1999; Emberling and McDonald 2003; Oates and Oates 1997). Detailed accounting practices are evident by the presence of clay and stone geometric tokens, a numerical tablet resembling those found in the Anu Ziggurat deposits at Uruk–Warka (Reade 1992), and over eighty vessels with distinct incised markings made post–firing on the shoulder. Much of the ceramics from these levels are completely indigenous to the north Syrian/upper Khabur area with heavy chaff–tempered fabric with dark cores, 32 Based on excavation of occupation phases (Felli 2003; R. Matthews 1995, 1996, 2003a, 2003b; Matthews et al. 1994) and ceramic remains from small soundings and surface surveys (Emberling et al. 1999; J. Oates 1985, 1986, 2002; Oates and Oates 1993a). 336 though there are some examples of fine cream, pink and green eggshell wares in mostly hemispherical bowl forms. Following the NMU phase of occupation, there begins to be an infiltration of ceramic and architectural styles reminiscent of those from southern Mesopotamia. Specifically, later levels are characterized by a series of superimposed structures ranging from large Mittelsaal houses built of Riemchen bricks with a series of small rooms and frying pan–shaped hearths across an open courtyard similar to those at Habuba–Süd, Jebel Aruda and Sheikh Hassan (TW Level 11; Emberling and McDonald 2003; Oates and Oates 1993a; J. Oates 2002).33 Grill plan structures made of Riemchen bricks possibly for grain storage (TW Levels 8–10), a large circular building also made of Riemchen bricks (TW Level 6; Oates and Oates 1991, 138), and an Early Dynastic I structure (TW Level 1) are also present. Inside the hastily abandoned Level 11 structure, excavators recovered large flint and obsidian cores for use in Canaanean blade production, hammer stones, a bone awl, spindle whorls, unbaked clay balls, sling bullets, and a large number of perforated baked clay cylinders that were most likely spools for thread. A capped drain over 25 meters long similar to ceramic pipes found at Habuba– Süd (Strommenger 1980, 46) was also found below a courtyard surface in this area (Emberling and McDonald 2003, 8). Deep pits (Level 12) sealed by this building contain massive amounts of lithic debitage, pierced tokens, and seal impressions resembling styles from Habuba–Süd and Jebel Aruda (Emberling et al. 1999; J. Oates 2002). Perhaps the most well known structure from Tell Brak datable to these later phases of occupation is the Eye Temple, so named because of the thousands of eye 33 Note this building was originally attributed to Level 12 (Oates and Oates 1993a, fig. 23), but has subsequently been moved to Level 11 (J. Oates 2002, 115). 337 images and eye idols discovered inside the precinct and buried within the temple platform (Mallowan 1947). This temple is, in fact, just one of a number of superimposed structures located on the southern edge of the ancient mound whose accumulated ruins reach 6 meters in depth and date to as early as the LC 3–4 (ca. 3500 BCE; Oates and Oates 1997, 291). The architecture of the earlier temples was not well preserved; however, the infilling of these buildings contain stone sculptures, stone amulets, alabaster eye–idols, spectacle–topped idols and thousands of beads made of faience and black steatite.34 The latest and best preserved temple was built atop a platform created by the infilling of these previous temples. This Eye Temple is 25 by 30 meters and roughly tripartite in plan with an elongated cella or sanctuary flanked by chambers of rooms on either side. These two wings however differ in character. While to the west there are three large chambers accessible only through a small corridor off the cella, the east has a series of self– contained courtyards and service chambers with direct access to the central sanctuary. The external walls of the building are buttressed with black basalt and white gypsum blocks that had been plastered over with mud. The sanctuary has only one permanent fixture: an altar or raised podium against the northern wall. Three sides of this podium are decorated with a frieze composed of fretted bands of white limestone and grey shale encased by two strips of gold. These golden strips are attached to a wooden backing by silver nails with golden heads. The interior walls of the cella are decorated with eight–petalled stone rosettes and copper paneling stamped with an eye design. A life–sized stone eye socket was also discovered 34 So many beads were recovered that the excavator remarked, “the foundations of [this] earlier “Eye Temple” had literally been sown with beads and even the mud–bricks themselves contained beads within them” (Mallowan 1947, 33). 338 on the floor adjacent to podium. The outer façade of the north wall was also decorated with stone rosettes and a mosaic of clay cones with red–colored tips. The ceramic assemblage from these levels contain a mix of indigenous Late Chalcolithic types and Late Uruk/EBI–type wares including tall–footed chalices (J. Oates 1986, fig. 4 no. 59), horseshoe–lug–handled cooking vessels (J. Oates 1986, fig. 4 nos. 61–63), grooved bowls (J. Oates 1986, fig. 4 nos. 54 and 55), button and fine ware ring bases, spouted teapots, and reserve slip sherds identical with types from Uruk–Warka and Nippur. Wheel–made, cut–rim and beveled–rim conical bowls are also prevalent (D. Oates 1982a, pl. IX a, c) along with drooping spouted jars, red–slipped nose–lug jars, large storage jars, coarse “casseroles,” fine plain bowls or beakers with beaded rims (J. Oates 1986, fig. 5 no. 87 and 90) and Gawra XI–A to X pottery (D. Oates 1985; Oates and Oates 1994). In summary, fourth millennium Tell Brak is an urban settlement with fortification or perimeter walls, monumental architecture and elite goods that occupied an area of some 45 hectares in its earliest phases and expanded to at least 100 hectares by the LC 3. This appears to be a completely indigenous development, though evidence for early contact with southern Mesopotamia comes primarily in the form of ceramic types. The presence not only of large–scale construction projects but also mass–produced pottery, numerical tablets and tokens, lithic production, and monitoring of commodities through incised pot marks shows a level of socioeconomic complexity predating the period of supposed Uruk contact in the region. As the excavators rightly state, “whether or not Late Uruk Brak was a colony in the Habuba sense remains to be established, but it is clear that a long indigenous tradition is previously and subsequently represented at the site, and that 339 this tradition reflects a highly developed administrative and economic system, perhaps owing relatively little to its southern neighbours and occasional settlers” (Oates and Oates 1993a, 184).35 The neighboring site of Hamoukar is equally developed in its level of complex economic administration derived from a seemingly indigenous development. Hamoukar is located in the northeast corner of the Upper Khabur basin along strategic trade routes between Nineveh and Aleppo. This multi–period site that has, thus far, been excavated for four seasons under the direction of McGuire Gibson (1999–2001; Gibson 2000, Gibson et al. 2002a, 2002b), and later by Clemens Reichel and Salam al–Quntar (2004). The mound has ceramic evidence attesting to occupation as early as the Halaf and ‘Ubaid periods, and actual excavated contexts from the Northern Middle Uruk phase, Late Uruk period, third millennium Akkadian and post–Akkadian phase, a seventh century village, Seleucid settlement and an Early Islamic village. Based on a regional surface survey that encompassed not only the mound, but also a 5 kilometer radius around the site (Ur 2002a, 2002b), the mid–fourth millennium BCE seems to be the period when the settlement reached its maximum occupation at 100 hectares, rivaling neighboring Tell Brak in size and socioeconomic complexity. The LC 3 period site is characterized by a large city wall 4 meters thick with four possible gateways. Within the settlement there is a monumental building complex comprised of two large buildings of the Mittelsaal–type and an adjacent production area (Gibson et al. 2002a, 33). Both buildings were heavily burned and collapsed, sealing thousands of in situ artifacts inside including carbonized grain, a bone facsimile of a 35 This view of a completely indigenous development paralleled by the implantation of a small–scale trading enclave is challenged by later excavators at the site who see Brak as the victim of conquest by the Uruk–controlled south (Emberling 2002). 340 dagger in a scabbard, whole ceramic vessels, stamp seals and impressed sealings, unbaked solid clay balls and over twelve hundred oval–shaped clay bullets that attest to the violent destruction of the buildings. One of the structures also contained a large kitchen with a series of grinding stones embedded in clay benches and a massive baking oven, suggesting that food production occurred here beyond the needs of a single household. A rectangular pit or grave nearby contained thousands of bone beads, dozens of faience and stone beads and ninety stamp seals in a variety of animal forms (Gibson et al. 2002a, 17). The motifs used on these seals ranged from hatching or cross–hatching to files of horned animals, animals under trees or animals attacking other animals. These same motifs are found in Late Chalcolithic period contexts at Tell Brak, Hacınebi, Arslantepe and sites in Susiana.36 Stamp and cylinder seals, bitumen residues, and stone and bone eye idols similar to those from Tell Brak and Hacınebi were also recovered from the interior debris of the buildings in this area. Following the destruction of these buildings, a number of deep pits containing southern Mesopotamian Late Uruk ceramic types, such as beveled–rim bowls, strap handle cups, and four–lugged vessels, were dug into the destruction debris and along the city wall. It is possible that an incursion by peoples utilizing these pottery styles launched the attack against the settlement at Hamoukar sometime at the end of the fourth millennium BCE or at least seemed to have benefited from the destruction of this well– established, economically complex city. The importance of Hamoukar in relation to the Uruk Phenomenon is its developed economic system that predates contact from the south 36 Specifically Susa and Choga Mish; see Reichel 2002 for a detailed description of motifs from seals and sealings at Hamoukar 1999–2001. 341 (mirrored also at Tell Brak, Hacınebi, and Arslantepe) and its evidence for early warfare at the moment of supposed Uruk colonization in northern Syria at sites like Habuba Kabira–Süd and Jebel Aruda. Hamoukar stands as a violent example of arising conflicts during an age of interregional interaction. Similarly the site of Mashnaqa, located approximately 20 kilometers south of Hasseke in the Middle Khabur valley, shows occupational disruption. Though this multi– period mound is mostly known for its extensive ‘Ubaid period remains (Monchambert 1985, 1987; Thuesen 1991), above these is a long sequence of local Late Chalcolithic material that spans from the post–‘Ubaid to the Northern Early and Middle Uruk periods (LC 1–3). In general these levels are characterized by multiple phases of domestic buildings, the most substantial of which being a tripartite plan structure from the post– ‘Ubaid level with partially preserved windows (Beyer 1998a, 140). Both phases of the Northern Middle Uruk levels are dominated by circular cooking ovens with attached rectangular fournils or bakeries, the largest being 2 meters in diameter (Beyer 1993, 1995, 1997). Ceramic evidence from these contexts are contemporary with Hammam et– Turkman (V B), Tell Brak (TW 16) and Tell Leilan (V). North of these installations at the base of the tell another large tripartite building was also uncovered that, based on ceramic evidence, dates to the Northern Middle Uruk period or LC 3. The mud brick building features two small internal niches and a possible stairway (Beyer 1998a, 1998b). Directly above this Middle Uruk phase is a completely different and perhaps intrusive occupation utilizing southern–Mesopotamian pottery types. A large circular fort is built on the south slope of the mound measuring 20 meters in diameter with walls 3.5 meters thick. A massive bastion eroding off the slope juts out from the northwest side 342 (Beyer 1998a, 144). The function of this enormous construction is unknown though a defensive purpose is most likely. Excavators also uncovered several phases of large domestic structures with tandır–style ovens and alleyways between houses. Mashnaqa is often cited as an example of dramatic intrusion of peoples from the south because of the radical shift in material culture that occurs at the site between the Middle and Late Uruk phases. Algaze (1993) signals this as the implantation of a colonial trade unit; however, the sudden fortification at the site could also signal growing unrest or violence (whether from intruding southerners or local rivals) that is physically represented at Hamoukar. Balikh Valley and Beyond The Balikh is a tributary of the Euphrates River that cuts across the western side of the el–Jezira plain in northern Syria. One of the largest sites in this region is Tell Hammam et–Turkman, located 80 kilometers north of Raqqa. The tell is roughly 500 meters in diameter and over 40 meters in height and holds a dominate position on the edge of a low terrace on the left bank of the Balikh River 4 meters below. The site was excavated over nine seasons between 1981 and 2001 by Maurits N. van Loon and Diederik J.W. Meijer with a team of researchers from the University of Amsterdam and Leiden University.37 This multi–period mound features seven phases stretching from the end of the fifth millennium (Phase IV, ‘Ubaid) to the Roman/Parthian period (Phase X).38 Phase V A and V B represent the Late Chalcolithic occupation (3600–3200 BCE) uncovered in a step trench on the eastern slope of the mound that lay atop over 10 meters of accumulated 37 Preliminary and final reports: Akkermans 1988a, 1988b, 1988c; van Loon 1982, 1983, 1985, 1988; van Loon and Meijer 1982; van Loon et al. 1986/1987; Meijer 1988, 1989, 1996. 38 For a detailed chronological chart, see Akkermans 1988c, 131 343 occupational debris from the ‘Ubaid period (4400–3600 BCE; Phases IV 2–IV 14). Phase V A occupation consists of multiroom and multiphase structures with plastered floors and niches and benches or sleeping platforms.39 Inside these buildings are massive amounts of pottery along with antler fragments, a jar stopper, grinding slabs, sling stones, spindle whorls, a stamp seal, house model, and a possible model of a temple (Meijer 1988, 74).40 After a devastating fire and hiatus, the site is reoccupied in the following Phase V B where a monumental plastered building and attached courtyard are built (Meijer 1988, 75). This is eventually leveled to make way for a massive mud brick terrace on which stood another monumental building with lime plaster recesses, buttressing and triple niches at regular intervals. Five carbon dates derived from wooden roof beams found on the floor of the central hall date this building between 3400 and 3200 BCE (Akkermans 1988c, 130), slightly predating similar niched buildings from Jebel Aruda (van Driel and van Driel–Murray 1983), Tell Kannâs (Finet 1977) and Uruk–Warka IVa.41 The function of this building is enigmatic despite the amount of small finds that were recovered from the floors after the fiery destruction including grinding slabs, jars, large storage vessels, and clay pipes (Meijer 1988, 77). The ceramic sequence is purely indigenous in character, showing numerous affinities with the Late Chalcolithic ceramic tradition of north Iraq, Syria and southeast Turkey. Large plain–rim bowls, such as Coba bowls, dominate the assemblage along with gray or black holemouth pots, large wide bowls, and corrugated bowls that mirror Chaff– 39 One of these partially excavated buildings was designated as tripartite in plan based on the presence of a central hall flanked on one side by three smaller rooms (Meijer 1988). Naturally this is only an assumption that three rooms would be mirrored on the other side of the central hall. 40 A complete report of the small finds from these contexts can be found in van Loon 1988, volume II: chapters 13–21. 41 However unlike these sites with dominant southern Mesopotamian material culture, Hamman et– Turkman, “appears to be set against a background of local north Syrian material culture” (Meijer 1988, 78). 344 Faced Simple Ware of the Amuq F sequence (Akkermans 1988a, pl. 92; Braidwood and Braidwood 1960, 232). The assemblage at Hammam et–Turkman contains no ceramics reminiscent of the southern Mesopotamian Uruk style such as beveled–rim bowls, drooping spouted jars or reserved slip wares. In fact, a gap in occupation at the end of Hammam V B coincides with the introduction of true Uruk wares at Brak (CH 12–9), Leilan (IV), Kurban (VIA) and Hassek (I). Thus Hammam et–Turkman occupies an interesting place in this discussion of the Uruk Phenomenon, as the material culture is completely local in nature but monumental buttressed buildings similar to those at Uruk sites are also present, whether through influence or actual contact from the south. This monumental architecture however, was constructed before the onset of Uruk contact in the region that is traditionally reserved to the very end of the fourth millennium (LC 5). Beyond the Balikh Valley, specifically to the southern areas of the Syrian desert, a pair of sites stand as anomalies but also reflect on the extent to which interregional contact was prevalent, even within remote locations. The first of these sites, El Kowm 2– Caracol, lies within the El Kowm basin, 100 kilometers northeast of Palmyra. The site was excavated for five seasons by a French team led by J. and M.–C. Cauvin (Cauvin 1981; Cauvin et al. 1979; Cauvin and Stordeur 1985; Stordeur et al. 1982). Though better known for its large sixth millennium Neolithic occupation, El Kowm 2–Caracol does exhibit some ephemeral evidence for a Late Uruk presence. This is mostly in the form of small mud bricks structures poorly preserved and stratigraphically confusing, dense refuse middens, deep pits, and hearths that were up to a meter in diameter. Within these secondary contexts, mixed with ash and charcoal, excavators recovered a large amount of animal bones (mostly bovine) and ceramic fragments characteristic of a southern 345 Mesopotamian Late Uruk assemblage. This includes four–lugged jars with incised decoration, beveled–rim bowls, and deep bowls with a pouring spout (Cauvin and Stordeur 1985, fig. 5–6). Scrappers and chisels dominate the lithic assemblage and small finds include an anthropomorphic bone figurine and interestingly, a stone eye idol figurine identical to those recovered at Tell Brak (Mallowan 1947, pl. 51). The recovered evidence seems to suggest a very limited occupation, perhaps as a seasonal hunting camp utilized by a semi–nomadic population. The other site of mention is Qraya, a low oval shaped mound 2 hectares in size located approximately 16 kilometers downstream from the confluence of the Euphrates and Khabur Rivers and 5 kilometers upstream from Tell al ‘Asharah (ancient Terqa) in the Middle Euphrates floodplain. The site was first mentioned by J.–R. Kupper (1950, 112) and then acknowledged later during the regional survey of Tell al ‘Asharah and its vicinity carried out by Wachtang Djobadze and Olivier Rouault in 1977 and 1978. The following year, William R. Shelby directed the excavation of a small sounding at the site. Kay Simpson continued these soundings for an additional two years (Simpson 1988). In 1981, Daniel Shimabuku carried out a six–week excavation at the site followed by Stephen Reimer who excavated for an additional two seasons (Reimer 1989). As most of the mound is covered by modern house compounds, excavators were only able to open a limited number of areas for investigation. However these areas yielded a total of three building phases with thirteen associated surfaces within a total accumulation of 4 meters of occupation dating to the LC 5. Forty fire installations including bread ovens and kilns are present in all of the building phases, the most elaborate having sunken fire chambers with permanent clay grills that were possibly used 346 in salt processing (Buccellati 1990; Reimer 1989). The cultural assemblage reflects that of southern Mesopotamia with beveled–rim bowls in large concentrations and other ceramic types typical at Habuba–Süd, Susa and Uruk–Warka, two dozen seal impressions on door seals, jar stoppers, clay bullae, ladles, and clay sickles. Qraya seems to have been a specialty production center or trading outlet based on the cultural assemblage and its relative isolation from other Late Chalcolithic sites. Other Syrian sites such as Hama on the Orontes River (Thuesen 1988 and discussed below), Ramadi in the Middle Euphrates valley near Mari (Beyer 1991–92), Tell Hajib in the western Jazirah (Einwag 1993) and late Amuq F/early Amuq G period (Braidwood and Braidwood 1960) are attested in the Uruk Phenomenon debate only by the occurrence of southern Mesopotamian Uruk–style ceramics that derived from soundings or survey data.42 Apart from this, all other facets of material culture at these sites, including architecture and the majority of the ceramic assemblage, are familiar local Syrian styles. Turkey Birecik and Carchemish Dams These reservoir basins are located along the southern border of Turkey, with the Carchemish dam just upstream from the ancient site of the same name and the Birecik dam approximately seven kilometers upstream from the modern town of Birecik. At their completion in 1999 and 2000 respectively, the reservoirs that formed behind the dams inundated some 85 square kilometers of land that had been previously surveyed (Algaze 42 A summary of more “Uruk–related sites” found throughout Syria can be found in Schwartz 2001, 251– 254 and Akkerman and Schwartz 2003, 190–203. 347 1989b; Algaze et al. 1991, 1994). Those surveys identified 22 sites with local Late Chalcolithic and Uruk remains including Tıladir, Şadı Tepe, Kum Ocağı, Hacınebi, and the Acropolis at Carchemish itself (Woolley 1952). Of these sites, only Hacınebi has been systematically excavated allowing us to closely examine the remains within the broader context of the Uruk Phenomenon. Located in the Euphrates River valley approximately 5 kilometers north of Birecik in Şanlıurfa Province, Hacınebi is a triangular–shaped mound measuring 3.3 hectares in size that sits atop a bluff overlooking the river. The site was excavated by a team from Northwestern University for six seasons between 1992 and 1997 under the direction of Gil Stein (Stein et al. 1996a, 1996b, 1997, 1998). In that time eighteen trenches were opened for a total exposure of fourteen hundred square meters. Over 9 meters of cultural deposits are recorded at the site that date to the LC 2–4 (ca. 4100–3300 BCE), Early Bronze I (ca. 3100–2800 BCE), and Achaemenid/Hellenistic periods (ca. 500–100 BCE). Based on ceramic chronology and carbon dating, the fourth millennium occupations at Hacınebi span three distinct phases, two of which (A and B1) are culturally “Local Late Chalcolithic” (LLC) in nature and a third (B2) that is a mixture of local and southern Mesopotamian Uruk cultural traits. The earlier indigenous phases are characterized architecturally by a monumental terrace and platform complex, two adjacent storage buildings, a 3–meter–wide enclosure wall with buttressing and a massive mud brick raised platform. Apart from these public structures, domestic architecture was also uncovered with child inhumations beneath the floors.43 The ceramic assemblage is 43 One of these burials contained an infant with one copper and two silver rings, some of the earliest silver to be recovered in Anatolia (Stein 2002b, 150). 348 dominated by handmade chaff–tempered wares like flint–scraped hammerhead bowls and “casseroles” with parallels at Kurban, Leilan, Brak and Kenan Tepe (Pearce 2000; Stein et al. 1998, 160–164). Wheelmade grit–tempered wares do occur but in smaller numbers and in completely local forms. Early metallurgy, specifically copper production, is evident throughout this early settlement. All stages of production were recovered including special smelting pit furnaces, crucible fragments, open–faced casting moulds, and final products like copper chisels and pins.44 That Hacınebi was involved in long–distance exchange during these early phases is evident by the occurrence of non–local raw copper, chlorite pendants derived from sources over 300 kilometers away (Stein et al. 1996a, 212), and record keeping technologies. These included engraved stamp seals, seal blanks and impressions whose iconography is paralleled across the piedmont zone from Değirmentepe to Gawra to the Khuzistan plain (Pittman 1999, 45). The following contact phase (B2) shows evidence for the continuation and evolution of the local indigenous settlement along with the sudden emergence of southern Mesopotamian material culture. While architectural evidence is severely lacking—baked clay wall cones are the only indicator for supposed public or religious buildings45—the full range of other material categories attest to an intrusive presence. These include metrological devices (cruciform grooved stone weights similar to ones at Habuba–Süd and Sheikh Hassan), agricultural implements (baked clay sickles), bitumen imported from 44 For more information concerning the metallurgical finds from Hacınebi, see Özbal et al. 1999 and Stein et al. 1998, 167–170. 45 These same types of clay wall cones were also found in surface surveys of private homes (Adams and Nissen 1972, 211) and villages (Johnson 1973, 105), suggesting that they were used as decorative elements in both public and private contexts. This undermines Stein’s (2002b, 151) assumption that at Hacınebi, the cones necessarily represent temples or elite public buildings. 349 Hit and the Deh Luran area (Schwartz et al. 1999) and specific accounting practices. While the use of stamp seals and seal iconography from Phase B1 continues and expands,46 new intrusive elements emerge: hollow clay balls with clay tokens inside, jar stoppers, jar rim sealings, and prepared clay slabs all impressed with cylinder seals whose iconography is echoed at Susa and Uruk–Warka (Pittman 1999; Stein et al. 1996a, 231). While chemical characterization has shown that a good portion of the sealings with Anatolian and some Uruk motifs were made with clays local to the environs of Hacınebi, other Uruk–style sealings (and their associated portable products) were imported, most likely from the Khuzistan plain around Susa (Blackman 1999). Southern Mesopotamian ceramic wares and forms also become prevalent during this Phase B1 including wheelmade mineral–tempered conical cups and nose–lug jars as well as chaff–tempered trays, ceramic ladles, and beveled–rim bowls (Pollock and Coursey 1995; Stein et al. 1996a, 233–239). Though ceramics from both the local and southern Mesopotamian assemblages were found together in many contexts, the majority of Uruk–related materials are restricted to the northern area of the settlement while local Late Chalcolithic materials remain mostly in the south. This arrangement is paralleled with the accounting practices discussed above with the use of stamp seals only in the southern area and cylinder seals only in the northern area. These distribution patterns, when coupled with specialist analyses of faunal and chipped stone assemblages that reflect distinctively different modes of production and consumption between the two 46 For example, over one hundred clay sealings uncovered in a single pit context on the northeast part of the site represents approximately thirty different distinct stamp motifs (see Pittman section in Stein et al. 1996a, 232). 350 areas,47 point to a segregated community of Uruk colonists embedded within a local and well–established Late Chalcolithic settlement (Stein 1999a). Thus the evidence from Hacınebi not only reflects an economically complex indigenous community that predates intrusions from the south, but also the continuation of a seemingly peaceful settlement with the arrival of foreign populations. This picture is vastly different from the circumstances we see in northern Syria where at Hamoukar for example, evidence for warfare precludes contact from Uruk southern Mesopotamia. Atatürk Dam The Mustafa Kemal Atatürk Dam, initially named the Karababa, lies 60 kilometers north of Birecik on the Euphrates River bordering between the Adıyaman and Şanlıurfa provinces. The reservoir created by the dam flooded over 800 square kilometers of land that included over 300 historic and prehistoric sites that were extensively surveyed (Blaylock et al. 1990, 1998; Özdoğan 1977; Serdaroğlu 1977). Of these sites, the largest and most well–excavated is Kurban Höyük, located at the southern edge of the dam reservoir in the upper Euphrates Valley of southeast Turkey and 60 kilometers north of the modern city of Şanlıurfa. The 6 hectare site is composed of two mounds connected by a saddle whose maximum height is 10 meters above the surrounding flood plain. Kurban was excavated for five seasons (1980–1984) by the Chicago Euphrates Archaeological Project of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago under the direction of Leon Marfoe (Algaze 1990; Marfoe et al. 1986). A regional settlement and land use survey was undertaken simultaneously by Tony Wilkinson (1990a). 47 For faunal see: Bigelow 1999; Stein et al. 1996a, 257–260. For chipped stone see: Edens 1999; Stein et al. 1996a, 239–247, 1996b, 100–104, 1997, 124–127, 1998, 155–160. 351 Occupation datable to the Late Chalcolithic period (Kurban Period VIA–B) is limited to a step trench (Area A) and two soundings (Areas C01 and F) whose excavations revealed nearly 2 meters of deposits spanning five phases in Area A. Only ephemeral structures with stone foundations were uncovered along with a mixture of prepared plaster floors, pebble–paved courtyards, and beaten earth surfaces. Among the assemblage of ceramics, chipped stone, and animal bones from these contexts, small finds include spindle whorls, spools, copper/bronze pins and other implements, worked bone and shell, beads, stone vessels, a macehead and a rectangular uninscribed “tablet– like” object (Algaze 1990, 397–418). Settlement seems to have shifted from the south mound during the earlier Period VIB to encompass the south and north mound as well as the saddle in between during Period VIA where a natural spring provided water for the inhabitants. There is also an economic and agricultural shift between these two subperiods as the earliest evidence for grape cultivation derives from Period VIA (Marfoe et al. 1986, 85–89) along with copper implements and imported finished flint blades of the Canaanean–type that most likely derived from neighboring Hassek Höyük (see below and Behm–Blancke et al. 1984). This shift is also visible in the ceramic assemblage, which consequently serves as the sole evidence by which the periodization of the two Late Chalcolithic phases at Kurban are distinguished (Algaze 1990, 261). The earlier Period VIB exhibits a majority of chaff– tempered wares paralleled in the Amuq (phase F) while during Period VIA grit–tempered plain simple wares become dominant in number. Southern Mesopotamian shapes become increasingly frequent during this latter phase including beveled–rim bowls, conical cups with pouring rims, four–lugged jars, and drooping spouted jars (Algaze 1990, 264). 352 It is unclear whether or not there was a sudden abandonment of the site at the end of Period VIA or whether the settlement area was slowly contracting throughout this phase concluding in the establishment of an Early Bronze community (Period V) restricted to the north mound. Based solely on ceramic evidence, the excavators see parallels in the expansion of the Late Chalcolithic settlement at Kurban, with its increasing frequency of grit–tempered wares and southern Mesopotamian vessel types, and the wider sociopolitical developments occurring across the region during this time. Small exposures limit my ability to determine exactly how Kurban fit within these regional developments. However, a shift in the ceramic sequence is evident, though whether this change derived from Late Uruk intrusions into the north remains debatable. Upriver there is a similar situation at the large mound of Samsat. Now flooded by the waters of the Atatürk Dam reservoir, the large mound of Samsat once towered 40 meters above the west bank of the Euphrates River measuring 500 by 350 meters at its base for a total area of 17.5 hectares. The site was first excavated by T. Goell in 1964 and 1967 and later surveyed by various teams (Blaylock et al. 1990, 1998; Özdoğan 1977; Serdaroğlu 1977). Salvage excavations were conducted by Middle East Technical University under the direction of Nimet Özgüç between 1978 and 1989 as part of the Lower Euphrates Project (Özgüç 1987, 1988, 1992). Much of the architectural remains dated to the Late Chalcolithic are limited to a 16 by 20 meter area on the eastern slope of the mound and were largely destroyed by latter occupants. Extensive pebble surfaces and fireplaces were preserved, along with a drain pipe (Level XX; Özgüç 1992, 152), a possible fortification wall (Level XXIV; Mellink 1989, 114) and numerous child inhumations below the house floors. The ceramic 353 assemblage is represented by both local and Uruk styles with primary examples being chaffy “casseroles” and straight–spouted jars along with reserve slip jars, beveled–rim bowls, stone goblets, and red polished lug jars (Özten 1984). Small finds include a terracotta cylinder seal, stone stamp seals with tête–bêche animals, and stone and obsidian beads. This mix of local and non–local cultural elements is echoed at Hassek Höyük, located 40 kilometers north of Samsat in the Elaziğ province. The site was excavated by Manfred R. Behm–Blancke between 1978 and 1986 on behalf of the Deutschen Archäologischen Instituts (Behm–Blancke 1986; Behm–Blancke et al. 1981, 1984). The earliest settlement at Hassek dates to the Late Uruk (LC 5; Hassek level 5 A–C).48 A complex of buildings surrounded by a thick enclosure wall were excavated on the high point of the mound (Hügelplateau). These consisted of a large tripartite building with attached anterooms (Haus 1), a single–room structure with three lateral doorways (Haus 3) and two smaller workshop and storage buildings (Haus 2 and 4). Haus 1 is most reminiscent of Mittelsaal houses at Habuba–Süd with frying pan–shaped fireplaces in the central hall. Together Uruk and local ceramics are associated with these buildings including beveled–rim bowls, nose–lugged jars, drooping spouts, burnished cook pots, hammer– head and carinated bowls (Helwing 1999, 2002; Hoh 1981, 1984). Other finds include a spectacle–topped idol paralleled at Brak, cylinder seals with geometric and figural design, clay tokens, and a copper pin along with evidence for Canaanean blade production (Behm–Blancke et al. 1981, pl. 11–14). This Late Chalcolithic phase is 48 Most recent ceramic analysis suggests that only levels 5 A–B are Late Uruk in date and that level 5 C is much earlier (Helwing 1999, 94). 354 burned in a violent destruction and later rebuilt but with a completely different configuration. Uruk–style pottery continues to be used, however the Mittelsaal style house vanishes. The identification of Hassek as a “station” within the larger Uruk trading network has been accepted by many scholars, including the excavators (see chapter 1 and Behm– Blancke et al. 1984, 40). However, as Helwing (1999) has pointed out, much of the material culture assemblage at Hassek reflects more local trends. This includes Canaanean blade production and seal designs common to north Syria and southeast Anatolia. The relatively simple enclosure wall more closely resembles the fortifications found at later Early Bronze I levels at Tarsus (Goldman 1956) than the elaborate bastions at Habuba–Süd. Even much of the Uruk pottery found at Hassek, traditionally heavy in grit temper, surprisingly are mostly chaff suggesting that indigenous inhabitants and not Uruk colonists were copying southern Mesopotamia forms (Helwing 1999, 96). Unfortunately very little has been excavated around the walled enclosure to place this building complex in context. Keban Dam and Beyond The Keban Dam, one of the northernmost dams on the Euphrates in Turkey, was also one of the first to be completed in 1974. Located just below the junction of the Euphrates and Murat Rivers in Elazığ province, the dam produced a long narrow lake that covers a huge area of 680 square kilometers. This reservoir covers hundreds of historic and prehistoric sites as far east as the Altınova, a broad alluvial plain due east of Elazığ, which were surveyed and recorded by Charles Burney (1958) and Robert Whallon 355 (1979). The Middle East Technical University (METU) Keban Dam Area Salvage Project was also responsible for a series of publications documenting the survey and excavation of a number of archaeological sites within the dam reservoir area.49 A major site occupying the Altınova valley figures prominently within the Uruk Phenomenon debate: Tepecik. This multi–period mound is located 30 kilometers east of the modern city of Elazığ. The site, flooded by the waters behind the Keban Dam, stood 17 meters in height and was approximately 200 meters in diameter. Tepecik was first identified by Charles Burney (1958) in his survey of the region and later by Robert Whallon and Sonmez Kantman (1970). The site was geophysically surveyed and excavated between 1968 and 1974 under the directorship of Ufuk Esin (1970, 1971, 1972a, 1972b, 1975, 1976, 1979, 1982). Evidence from the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age I transitional settlements are limited to a deep sounding on the northeast side of the mound and a single structure on the southwest slope. The sounding produced no architecture, but instead a hearth, stone and sherd pavement, lumps of copper, and a large amount of animal bones and beads perhaps as part of a midden (Esin 1972a). Wheel and handmade ceramics of chaff–faced simple wares paralleled with Amuq F were recovered along with a handful of reserved slip fragments. The single structure was composed of stone foundations with a mud brick superstructure divided into several rectangular rooms and a courtyard. Three building episodes are evident by the slight modification of walls and doorways and the reapplication of reed and plaster flooring. Inside this structure a wealth of artifacts were uncovered including grinding stones, copper awls, fine bone pins, a terracotta idol head, 49 Middle East Technical University Keban Project Publications, 1968–1974 Activities. 356 and flint Canaanean–type blades and obsidian implements inside a coarse handmade jar (Esin 1979, 110). The ceramic assemblage is composed of both southern Mesopotamian styles from the end of the LC 5 and EBI forms that are paralleled at sites further west. The Uruk types include beveled–rim bowls, spouted jars, short–necked jars with perforated ledge handles, and reserved slip pithoi (Esin 1976, 115). Adjacent to this structure, large pits up to two meters in diameter and furnaces were found containing evidence for metal working such as slag and arsenical copper ores (Çukur and Kunç 1989). Such little evidence from Tepecik is difficult to interpret; however, the occurrence of southern Mesopotamian ceramic types shows how the Uruk Phenomenon touched the Altınova region, though seemingly in a small degree. Other evidence, such as copper production and chaff–tempered ceramic wares, places the settlement at Tepecik firmly within a local Anatolian cultural sphere. Interestingly southern Mesopotamian material culture does not seem to have penetrated other sites in the region. Norşuntepe for example, located 30 kilometers southeast of Elazığ, had architecture and ceramics reminiscent of local and Amuq styles. The large multi–period tell was excavated by Harald Hauptmann on behalf of the German Archaeological Institute between 1968 and 1974 when the site was submerged below the waters behind the Keban Dam.50 All Late Chalcolithic exposures spanning the entire fourth millennium BCE derived from a deep sounding on the western slope of the mound where numerous superimposed buildings and a mud brick fortification wall were uncovered. The former were single–room houses with round interior hearths and 50 Annual reports authored by Hauptmann can be found in the Keban Project Activities volumes, 1968– 1974. 357 associated child burials, many in pots (Hauptmann 1976, pl. 42, 1979, pl. 41). One of these houses had two interior niches with a frescoed wall painting in between that depicted a stylized horned animal in black outline with red fill (Level 8; Hauptmann 1976, pl. 42). The ceramics recovered inside many of these buildings reflect an Early to Middle Chalcolithic date (LC 2–3) whose painted wares seem to draw from the preceding ‘Ubaid levels at the site. Later Amuq F parallels are present supporting occupation through at least LC 4. The assemblage is characterized by chaff–faced simple wares and decoration ranging from painted to stamped and incised patterns paralleled at Gawra XI–IX (LC 2– 3; see Gülçur 2000). Copper processing seems to have taken place within the settlement as attested by the presence of copper slag. A stamp seal and clay bulla with the impressed image of an ibex reveal at least a low level of administrative control, perhaps in association with metallurgy. Overall the cultural assemblage at Norşuntepe is indigenous to southeast Anatolia and the Amuq. Similarly Korucutepe, another Altınova site, has no evidence for the use of southern Mesopotamian material culture, specifically ceramics. Now flooded by the waters of the Keban Dam, Korucutepe was a 16–meter–high mound located northeast of Norşuntepe and approximately 30 kilometers east of the modern city of Elazığ. The site was first surveyed by Burney (1958) and Whallon and Kantman (1970) and then excavated over three seasons, from 1968 to 1970, by teams from the University of Chicago, UCLA, and the University of Amsterdam directed by Mauritis N. van Loon, Giorgio Buccellati and Philo Houwink ten Cate (van Loon 1971, 1973, 1975; van Loon and Buccellati 1970; van Loon and Güterbock 1972). 358 The excavated data for the Late Chalcolithic period (Phase B: Strata XXX– XXXIII 3500–3000 BCE), though limited in scope, reflects a completely local cultural assemblage. Over 1.5 meters of accumulated deposit held multiple superimposed domestic structures with central hearths, evidence for reed matting, and crushed sherd/pebble pavements. The ceramic assemblage is comparable to other Altınova sites with mostly handmade chaff–tempered wares, though grit does occur, and heavy chaff– facing. The forms are all local Anatolian styles with no evidence for southern Mesopotamian Uruk influences (Brandt 1978a). A small cemetery was unearthed on the northwest corner of the mound that held two rectangular tombs made of mud bricks with wooden roofs. These tombs contained numerous grave goods including a mace head, silver band with spirals, belts, metal and stone beads, silver rings and a stamp seal whose design is comparable to Gawra IX (Brandt 1978b, 62). West of these important Altınova sites on the Euphrates River, outside of any flood zone, is perhaps the most well preserved and significant site for the discussion of local cultural development and complexity both pre– and post–Uruk contact. That site is Arslantepe, a 5 hectare mound located 15 kilometers west of the Euphrates River and 6 kilometers northeast of the modern city of Malatya. Excavated by the Italian Archaeological Expedition of the University of Rome “La Sapienza” under the direction of Salvatore M. Puglisi (1975–1982), Alba Palmieri (1983–1990), and Marcella Frangipane (1990–current), Arslantepe contains a deep chronological sequence of settlements that span the fourth and early third millennium BCE. The earliest Late Chalcolithic level (Period VII; LC 3 ca. 3500 BCE)51 is characterized by both domestic structures and monumental architecture, in particular a large tripartite mud brick structure 51 Based on carbon dates in Alessio et al. 1983, 578–579. 359 with painted walls and mud columns (Building XXIX; Frangipane 1993; Frangipane and Balossi 2004). Within the structure, mass–produced conical and flint–scrapped bowls were uncovered along with a collection of unimpressed clay balls, presumably unused sealings. Period VIA (LC 4/5, ca. 3500–3000 BCE),52 though distinguished by the minimal inclusion of characteristically southern Mesopotamian elements, retains an overwhelming local Anatolian character. The greatest example is the “palace–temple” complex built on top of the preceding Period VII structures. The complex is composed of a conglomerate of four terraced buildings (Building I, II, III, and IV) that were most likely two–storied and connected by several passages. Two of these structures (I and II) were designated as temples (A and B) based on the occurrence of circular offering tables with adjacent fireplaces, rectangular mud brick basins, internal niches, and elaborate paintings and plastic decorations on the walls (Frangipane and Palmieri 1983; Frangipane 1997b). These temples are composed of a single cella with side storage rooms filled with local style ceramics including pithoi, chaffy cook pots, wheel–made high–stemmed bowls, and mass–produced conical bowls. In fact the only real evidence for southern Mesopotamian materials at Arslantepe comes from inside these temple storerooms where a drooping spouted jar, high shouldered red–slipped jar, beveled–rim bowl fragments and two elongated vessels identical to ones found at Susa, Uruk–Warka, Habuba–Süd, Brak and Hassek were recovered. Other items include Canaanean flint blades, copper pins, andirons, and mat impressions (Palmieri 1977). 52 Though the published stratigraphy from Arslantepe refers to Period VII as “Late Chalcolithic” and Periods VIA and VIB as “Early Bronze I A and B” respectively, I retain the designation Late Chalcolithic or LC here to avoid confusion. The carbon dates however from Period VIA do show a transition into the early part of the third millennium BCE. 360 A great deal of administrative and redistribution activities were centered inside the many storerooms throughout the complex as evidenced by thousands of stamp and cylinder sealed impressed bullae and clay fragments discovered in stockpiles. In one room (A206), over five thousand clay–sealing fragments were uncovered representing 124 different designs with sealings of similar design being grouped together. These designs, while in some cases exhibiting thematic elements mirrored at Uruk–Warka IV, Susa and Chogha Mish,53 retain a local Anatolian glyptic style. There was also evidence for arsenic bronze manufacture and finished products like a cache of bronze swords, spearheads, and a quadruple spiral plaque found within Building III (Caneva and Palmieri 1983; Palmieri 1981). The succeeding occupation (Period VIB) saw a complete shift in the nature of settlement and material culture at the site, though some evidence of these new cultural trends were already becoming evident in the preceding period.54 The “palace–temple” complex is burned and hastily abandoned, only to be resettled by local nomadic groups using wattle–and–daub construction techniques and later, rectangular mud brick architecture (Hopkins 1996). Handmade Red–Black Burnished ware now dominates the ceramic assemblage along with some Ninevite V and ETC ware types (Palmieri 1977). A large rectangular cist grave lined with stone slabs was also found on the western edge of the former Period VIA complex area that contained a presumed elite individual, four 53 The best examples of this are a cylinder seal impression of an intertwined snake and another impression from room A206, Building IV depicting a person (or statue?) within a canopied sledge being carted by an ox with a driver (for image and discussion, see Frangipane and Palmieri 1983, 419, 1). Motifs of intertwined snakes are found at Uruk–Warka (Heinrich 1938, pl. 30 i), Susa (Amiet 1972, pl. 6, 63, 64) and Chogha Mish (Delougaz and Kantor 1996, pl. 36 H). 54 For example, arsenic bronze production and techniques for the manufacture of “Red Black Burnished Ware” ceramics characteristic of the Early Transcaucasian Culture (ETC) were already evident in Period VIA (Frangipane 1997b, 69). 361 adolescents, and a wealth of grave goods including ceramics and a wide selection of metal objects (Frangipane et al. 2001). The downfall of the “palace–temple” complex at Arslantepe seems to be a reflection of the larger sociocultural changes evident throughout the region at the close of the fourth millennium, though the excavators, perhaps rightly, contend that internal political strife underlies the upheaval that ended the settlement (Frangipane 1997b). In terms of the Uruk Phenomenon, Arslantepe stands as an example of a well–established community that was active in local networks of production, exchange and redistribution that was either outside the sphere of southern Mesopotamian interaction or unable to be affected by it. Upper Tigris As discussed in chapter 4, the Upper Tigris region of southeast Turkey occupies a river valley between the modern city of Diyarbakır and the Tigris–Batman River confluence approximately 60 kilometers to the east. Within this region there are a number of sites that have been surveyed and partially excavated, though none equaling the breadth and depth of exposures at Kenan Tepe. The westernmost of these sites in the valley is Kavuşan Höyük, located 10 kilometers southeast of Bismil and south of where the Seyhan Çayi meets the Tigris River. The site is composed of a higher northern end that rises 8 meters and a lower southern area 2 meters in height. The mound is almost 200 meters in length east to west and 75 meters in width north to south, occupying a total of 1.3 hectares. Since 2000, intensive survey and excavations have been undertaken by Gülriz Kozbe, Kemalettin Köroğlu and Haluk Sağlamtemir under the auspices of the 362 Diyarbakır Museum (Kozbe et al. 2003, 2004). The Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age occupy the earliest levels at the site (Building level V in Trench No. III) and consist of 2 meter diameter pits with mud plastered floors containing handmade pottery and well–fired thin metallic wares along with animal bones, zoomorphic figurines, and flint tools (Kozbe et al. 2004, 499). The Late Chalcolithic pottery consists of burnished pots with no necks and everted rims and bowls with exaggeratedly inverted rims, all with coarse fabrics of large grit and dense chaff temper (Kozbe et al. 2004, 500). Across the river from Kavuşan is the site of Giricano, located 11 kilometers southeast of Bismil on a strategic crossing of the Tigris and was excavated between 2000 and 2003 under the direction of Dr. Andreas Schachner with financial support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Schachner 2003, 2004; Schachner et al. 2002). The site measures 170 by 120 meters and was founded on top of a low natural hill overlooking the Tigris flood plain. On the southern side of the site only a single test trench produced well preserved architectural remains of a large (6 meters long) and regularly planned building whose associated painted ceramics and stamp seal impressed clay bulla date it relatively to the middle of the fourth millennium (Level 06). Beveled– rim bowls from this context also attest to connections with a wider network of interaction that extend beyond the Upper Tigris valley. Continuing further east past Kenan Tepe (see chapters 4 and 5) is Salat Tepe, a site that lies atop a 6–meter–thick alluvial terrace overlooking the Salat Çay, a tributary of the Tigris River, approximately 14 kilometers east of Bismil and 35 kilometers west of Batman. The site is composed of a single mound 30 meters in height and 115 by 110 meters in length and width (Ökse 1999, 345). There is a 45 by 30 meter flat area on the 363 summit and a northwest terrace measuring 100 by 65 (Ökse et al. 2001, 620). The site was first identified by Algaze in his 1988 survey (Algaze et al. 1991, 213) and, based on ceramic analysis, found to be occupied from the fifth millennium BCE to the Byzantine Period. From surface surveys, Ökse and her team have recovered Late Chalcolithic chaff temper, coarse handmade pottery, Early Bronze Age hand–made burnished wares, wheel–made monochrome, and metallic wares. Excavations, which began in 2000, have uncovered early Islamic burials and the remains of a Neo–Assyrian settlement. Architectural remains of the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age have yet to be uncovered (Ökse 2004; Ökse and Alp 2002). Neighboring Salat is Aşağı Salat, a low–lying mound topped by the village of Aşağı Salat located 20 kilometers east of Bismil and 2 kilometers east of where the Tigris is joined by the Salat Çayı (Ay 2001, 717; Şenyurt 2002b). The site measures 150 by 100 meters though there is evidence of heavy flood damage in the present, and probably the past as well, since the mound itself lies only 5 meters above the river (Şenyurt 2002a, 689). The primary context here is an Early Bronze Age cemetery extending over a 50 square meter area at the most and containing cist graves and graves with a stone enclosure and cover. All the graves exhibit pebble floors and are capped with limestone slabs (Şenyurt 2002a, 694). Due to a high salt content in the soil, the skeletal material in many of the graves were too deteriorated to determine the positions of the individuals. A similar problem was observed in the Early Bronze Age cemetery at Birecik (Sertok and Ergeç 1999, 90). However a single intact grave (M–14), allowed the excavators at Aşaği Salat to note a Hocker position oriented east–west with the head on the east facing north (Şenyurt 2004, 665). Signs of robbery are evident as the east end of all the cover stones 364 were found broken and the ceramics and other grave goods broken and scattered. Among the grave goods recovered were bronze pins, beaded necklaces made from mountain crystal, white frit and black stone, and a bone “idol” in the form of a stylized human figurine. Of the ceramics recovered from these graves, most common are buff–colored fruit stands and pedestal bowls, spouted vases, buff and beige colored biconical vases with string–cut holes, and ring base bowls with greenish cream colored fabrics similar to Ninevite V forms at Hassek Höyük (Behm–Blancke 1988). According to the excavator, this Early Bronze Age ceramic assemblage shows a continuation of the Late Uruk pottery tradition uncovered through surveys at the site (Ay 2001, 697). Finally within the stratigraphic sounding at the southeast part of the mound, a two–roomed building with a three course stone foundation was uncovered, along with a square platform composed of stone posts, grinding stones, and cobbles. A baked clay wall mosaic and several beveled rim bowls characteristic of the Late Chalcolithic/Late Uruk period were found associated with this stone platform (Şenyurt 2004, 661). Continuing further east in the valley is Grê Dimsê, a medium–sized mound 30 meters high with steep sides and a flat circular top 60 meters across (Karg 1999, 283). It is located at the junction of the Batman Su and the Tigris, roughly 15 kilometers southwest of Batman and just over 1 kilometer north of the village of Köprüköy (Karg 2001, 671). A surface collection and scrape survey was carried out in 1998 with excavations commencing in 1999. Primarily Hellenistic–Roman and “Imperial” to “Post– Assyrian” architectural levels have been uncovered, with the only Late Chalcolithic 365 remains being chaff–tempered pottery and whole mouth jars with globular to ovoid bodies recovered from survey (Karg 1999, 284). The final site in the eastern most extension of the river valley is Hirbemerdon Tepe, an approximately 10 hectare mound located 30 kilometers east of Bismil at the confluence of the Batman Su and Tigris Rivers (Laneri 2005; Laneri et al. 2006). The site is composed of a “high mound” (4 hectares), “lower town” (3 hectares) and “outer town” (3 hectares). Middle to Late Chalcolithic material, dating specifically to the first half of the fourth millennium, has been uncovered in a two meter square sounding in the outer town (Laneri et al. 2006, 158). A yellowish sandy layer uncovered in this sounding shows ancient flooding by the Tigris occurred sometime between the Late Chalcolithic and the end of the third millennium. Very little in the way of architecture has been uncovered, apart from a portion of a surface and a shallow pit. The pottery assemblage is dominated by local, cream–brown chaff faced wares in the forms of globular pots with simple rims, jars with short necks and straight or slightly everted rims. Charring on the outside of most of the sherds indicates presence of a fire that probably destroyed the settlement. Egypt and the Levant The impact of the Uruk Phenomenon in the Levant, specifically along the eastern Mediterranean littoral from Lebanon south through Israel/Palestine, seems to have been minimal. Evidence for connections with southern Mesopotamia via north Syria are limited to ceramics at a handful of sites. In the ‘Amuq area of inland west Syria, chaff– tempered bowls and jars dominate the local assemblage but a small number of beveled– rim bowls and drooping spouted bottles were recovered from Tell al–Judeideh and some 366 reserved slip examples from the ‘Amuq F sequence equating to LC5 (Braidwood and Braidwood 1960, 232). Along the Orontes River valley, Phase K at Hama revealed more beveled–rim bowl fragments and a possible terra cotta eye idol in its characteristically indigenous assemblage (Thuesen 1988). 55 South of Hama however, there is no documentation of southern Mesopotamian Uruk ceramics until one reaches the Nile Delta (see below). The glyptic evidence for interaction is slightly wider spread, but in no terms serving as a direct linkage to Uruk–Warka itself. Instead the evidence suggests inland west and north Syrian sites participated in the Syro–Anatolian tradition (W.F. Collins 2005; Philip 2002, 218). Stamp seals with zoomorphic decoration are attested at ‘Amuq F–H and Hama. A cylinder seal from Ras Shamra (Level IIIB) that most likely dates to the end of the fourth millennium (Amiet 1992) depicts a procession of horned animals exceedingly similar in design to those from Habuba–Süd. In Egypt, there is much more substantial evidence than in the Levant for interactions with north Syria and southern Mesopotamia between the Naqada IIc–d (ca. 3400 BCE) and Naqada IIIb (ca. 3100 BCE; see Joffe 2000), more generally known as the Predynastic period. This evidence is limited to glyptic and ceramics as no architecture or accounting practices (e.g., bullae, tablets, tokens) have been found do date that are reflective of Mesopotamian or north Syrian styles (Moorey 1987). 56 During the Predynastic period, a few large settlements in Upper Egypt like Abydos, Hierakonpolis and Naqada itself most likely served as regional centers. The latter two sites had royal cemeteries with elaborate mud brick–lined tombs, one of which (Tomb 100 at 55 This eye idol is also argued to be a tool used for the spinning of thread and not an idol (Breniquet 1996, as cited in Philip 2002, 215). 56 However Wilkinson (2002, 244) postulates that “small, cone–shaped objects of fired clay” excavated in Predynastic mortuary contexts could likely be tokens. See also Schmandt–Besserat 1992 for a discussion of counting tokens mistakenly identified by archaeologists as gaming pieces or amulets. 367 Hierakonpolis) was plastered and painted with a “master of animals” scene—imagery that is well–known and most likely derived from Mesopotamia (Adams 1996; Case and Payne 1962). Other glyptic parallels are found on ivory knife handles, most of which are unfortunately unprovenanced.57 These include the Gebel el–Arak and Gebel el–Tarif handles that display scenes of hand–to–hand combat, animal attacks, boats, hunting and the “priest–king” figure flanked by two lions.58 Ceramic evidence for interaction is much smaller with only a few examples of imported four–lugged jars and drooping spout vessels along with locally–made imitations deriving from burial contexts in Middle Egypt (Wilkinson 2002, 239). Likewise cylinders seals are rare but do occur as imports and local imitations. The imagery used on seals from Naqada—geometric patterns and lentoid shapes representing fish—are known from Susa, Gawra and Brak. Much debate has surrounded the route of transmission for these ceramic and glyptic styles into the Levant and Egypt. For the former, the route seems obvious that communications must have traveled west from the Euphrates bend (Habuba–Süd, Tell Sheikh Hassan, Jebel Aruda) or from the northern Amuq valley. Connections with Egypt, however, are a bit more tenuous. While early researchers argued this influence derived from Elam and/or Uruk–Warka via a sea route around the Arabian Peninsula and into the Red Sea (Frankfort 1951; Kantor 1952), a Mediterranean coastal route that linked the major port cities of the time with the Nile Delta and further south into Middle and Upper Egypt seems the most likely (Joffe 2000; Moorey 1987; Teissier 1987). For example, 57 One flint knife with handle was in fact excavated from a secure archaeological context in the cemetery at Abu Zaidan (Needler 1984). 58 According to Holly Pittman (1996, 27–28), this is not so much a borrowing of visual ideas from greater Mesopotamia as it is an adoption of artistic formulas whereby the particular meaning behind these images differed by sociocultural context. For example these Mesopotamian images do not necessarily represent the same ideas for Egyptians. 368 despite a direct ceramic link with Mesopotamia, Ras Shamra exhibits a primarily coastal ceramic assemblage linking it with Byblos and further south implying maritime communication that could have aided the transmission of Uruk glyptic to Egypt (Philip 2002, 216). More recent evidence for Amuq F plain wares, locally made clay cones, and the use of niched mud brick decoration at the Delta site of Buto (von der Way 1992, 5; Köhler 1992, 20–21) and the presence at Habuba–Süd of an anthracite–colored bowl with white incrusted punctuation decoration known from Nagada II (Sürenhagen 1986) further reflect on the relationship between Egypt, west Syria and the Levant during this period.59 59 Though one should note that this influence was decidedly one–sided: no Predynastic “Egyptian” artifacts have ever been found in southern Mesopotamia or Elam. 369 ABBREVIATIONS AA American Antiquity AC Artefacts of Complexity: Tracking the Uruk in the Near East. Edited by J. N. Postgate AUWE Ausgrabungen in Uruk–Warka, Endberichte CA Current Anthropology JNES Journal of Near Eastern Studies METU Middle East Technical University Keban Project TAÇDAM Salvage Project of the Archaeological Heritage of the Ilısu and Carchemish Dam Reservoirs UA Ausgrabungen der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft in Uruk–Warka UMN Uruk Mesopotamia and its Neighbors: Cross–Cultural Interactions in the Era of State Formation. Edited by M. Rothman UVB vorläufiger Bericht über die von dem Deutschen Archäologischen Institut und der Deutschen Orient–Gesellschaft aus Mitteln der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft unternommenen Ausgrabungen in Uruk–Warka ZA Zeitschrift für Assyriologie und Vorderasiatische Archäologie REFERENCES Abbott, R. T. 1989. Compendium of Landshells. Melbourne: American Malacologists. Abbott, R. T., and S. P. Dance. 1998. Compendium of Seashells. El Cajon: Odyssey. Adams, B. 1996. “Eite Graves at Hierakonpolis,” in Aspects of Early Egypt. Edited by J. Spencer, pp. 1–15. London: British Museum Press. Adams, R. M. 1962. Agriculture and Urban Life in Early Southwestern Iran. Science 136:109–122. Adams, R. M. 1981. Heartland of Cities: Surveys of Ancient Settlement and Land Use on the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Adams, R. M., and H. J. Nissen. 1972. The Uruk Countryside: The Natural Setting of Urban Societies. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. 370 Akkermans, P. M. M. G. 1988a. “The Period IV Pottery,” in Hammam et–Turkman. Report on the University of Amsterdam's 1981–84 Excavations in Syria, Vol. I. Edited by M. N. van Loon, pp. 181–285. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch– Archeologisch Instituut. Akkermans, P. M. M. G. 1988b. “The Period V Pottery,” in Hammam et–Turkman. Report on the University of Amsterdam's 1981–84 Excavations in Syria, vol. I. Edited by M. N. van Loon, pp. 287–349. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch– Archeologisch Instituut. Akkermans, P. M. M. G. 1988c. An Updated Chronology for the Northern Ubaid and Late Chalcolithic Periods in Syria: New Evidence from Tell Hammam et– Turkman. Iraq 50:109–145. Akkermans, P. M. M. G., and G. M. Schwartz. 2003. The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter–Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (ca. 16,000–300 BC). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Albert, R. M., R. Shahack–Gross, D. Cabanes, A. Gilboa, S. Lev–Yadun, M. Portillo, I. Sharon, E. Boaretto, and S. Weiner. 2008. Phytolith–Rich Layers from the Late Bronze and Iron Ages at Tel Dor (Israel): Mode of Formation and Archaeological Significance. Journal of Archaeological Science 35:57–75. Albright, W. F. 1949. The Archaeology of Palestine: A Survey of the Ancient Peoples and Cultures of the Holy Land. Harmondsworth: Penguin Books. Alden, J. R. 1982. Trade and Politics in Proto–Elamite Iran. CA 23:613–640. Alessio, M., L. Allegri, C. Azzi, F. Bella, G. Calderoni, C. Cortesi, S. Improta, and V. Petrone. 1983. 14C Dating of Arslantepe. Origini 12:575–580. Alexander, R. T. 1999. “Mesoamerican House Lots and Archaeological Site Structure: Problems of Inference in Yaxcaba, Yucatan, Mexico, 1750–1847,” in The Archaeology of Household Activities. Edited by P. M. Allison, pp. 78–100. London: Routledge. Algaze, G. 1986a. Mesopotamian Expansion and Its Consequences: Informal Empire in the Late Fourth Millennium B.C. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Chicago. Algaze, G. 1986b. Habuba on the Tigris: Archaic Nineveh Reconsidered. JNES 45:125– 137. Algaze, G. 1989a. The Uruk Expansion: Cross–Cultural Exchange in Early Mesopotamian Civilization. CA 30:571–608. 371 Algaze, G. 1989b. A New Frontier: First Results of the Tigris–Euphrates Archaeological Research Project, 1988. JNES 48:241–281. Algaze, G. Editor. 1990. Town and Country in Southeastern Anatolia: The Stratigraphic Sequence at Kurban Hoyuk. Vol. 2–3. Chicago: Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. Algaze, G. 1993. The Uruk World System: The Dynamics of Expansion of Early Mesopotamian Civilization. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Algaze, G. 2001a. Initial Social Complexity in Southwestern Asia: The Mesopotamian Advantage. CA 42:199–234. Algaze, G. 2001b. “The Prehistory of Imperialism: The Case of Uruk Period Mesopotamia,” in UMN, pp. 27–83. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Algaze, G., R. Breuninger, C. Lightfoot, and M. Rosenberg. 1991. The Tigris–Euphrates Archaeological Reconnaissance Project, 1989–90. Anatolica 17:175–240. Algaze, G., R. Breuninger, and J. Knudstad. 1994. The Tigris–Euphrates Archaeological Reconnaissance Project: Final Report of the Birecik and Carchemish Dam Survey Areas. Anatolica 20:1–96. Algaze, G., G. Dinckan, B. Hartenberger, T. Matney, J. Pournelle, L. Rainville, S. Rosen, E. Rupley, D. Schlee, and R. Vallet. 2001. Research at Titris Höyük in Southeastern Turkey: The 1999 Season. Anatolica 27:23–106. Allison, P. M. 1999. The Archaeology of Household Activities. New York: Routledge. Amiet, P. 1961. La Glyptique Mesopotamienne Archaïque. Paris: Editions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. Amiet, P. 1972. Glyptique Susienne des Origines à l'Époque des Perses Achéménides: Cachets, Sceaux–Cylindres et Empreintes Antiques Découverts à Suse de 1913 à 1967. Paris: Paul Geuthner. Amiet, P. 1986. L'Âge des Échanges Inter–Iraniens, 3500–1700 Avant J–C. Paris: Éditions de la Réunion des Musées Nationaux. Amiet, P. 1992. Corpus des Cylindres des Ras Shamra–Ougarit II Sceax–Cylindres en Hématite et Pierres Diverses. Ras–Shamra–Ougarit IX. Paris: Éditions Recherche sur les Civilisations. 372 Andersson, E. Forthcoming. “Textile Tools from Arslantepe, Turkey,” in Tools, Textiles, and Contexts. Edited by E. Andersson and M.–L. Nosch. The Danish National Research Foundation’s Centre for Textile Research University of Copenhagen. Oxford: Oxbow Books. Andrefsky Jr., W. 1998. Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis. Cambridge Manuals in Archaeology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Ascher, R. 1968. "Time's Arrow and the Archaeology of Contemporary Community," in Settlement Archaeology. Edited by K. C. Chang, pp. 43–52. Palo Alto: National Press. Ashmore, W., and R. R. Wilk. 1988. “Household and Community in the Mesoamerican Past,” in Household and Community in the Mesoamerican Past. Edited by R. R. Wilk and W. Ashmore, pp. 1–27. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Aurenche, O. 1981. La Maison Orientale. L'Architecture du Proche–Orient Ancien des Origines au Milieu du Quatrième Millénaire. Paris: Librairie Orientaliste Paul Genthner. Ay, E. 2001. “Upper Tigris Valley Survey: 1999 Season,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 1999. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 715–753. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Ay, E. 2004. “Müslümantepe Excavations 2001,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Greenhalg, and J. Velibeyoglu, pp. 383–407. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Badler, V. R. 1996. “The Archaeological Evidence for Winemaking, Distribution and Consumption at Proto–Historic Godin Tepe, Iran,” in The Origins and Ancient History of Wine. Edited by P. E. McGovern, S. J. Fleming, and S. H. Katz, pp. 45–56. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. Badler, V. R. 2000. The Dregs of Civilization: 5000 Year–Old Wine and Beer: Residues from Godin Tepe, Iran. Bulletin of the Canadian Society for Mesopotamian Studies 35:48–56. Badler, V. R. 2002. “A Chronology of Uruk Artifacts from Godin Tepe in Central Western Iran and Implications for the Interrelationships between the Local and Foreign Cultures,” in AC, pp. 79–110. Cambridge: University of Cambridge. Bahrani, Zainab. 1989. The Administrative Building at Tell Al Hiba, Lagash. Doctoral Dissertation, New York University. 373 Bailey, D. W. 1990. “The Living House: Signifying Continuity,” in The Social Archaeology of Houses. Edited by R. Samson, pp. 19–48. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. Bailey, D. W. 2005. Prehistoric Figurines: Representation and Corporeality in the Neolithic. London: Routledge. Baker, C. M. 1978. The Size Effect: An Explanation of Variability in Surface Artifact Assemblage Content. AA 43:288–293. Banning, E. B. 2003. Housing Neolithic Farmers. Near Eastern Archaeology 66: 4–21. Banning, E. B., and B. F. Byrd. 1981. Houses and the Changing Residential Unit: Domestic Architecture at PPNB 'Ain Ghazal. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 53:309–325. Barber, E. J. W. 1991. Prehistoric Textiles: The Development of Cloth in the Neolithic and Bronze Ages with Special Reference to the Aegean. Princeton: Princeton University Press. Basso, K. H. 1996. Wisdom Sits in Places: Landscape and Language Among the Western Apache. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Beale, T. W. 1978. Bevelled Rim Bowls and Their Implications for Change and Economic Organization in the Later Fourth Millennium BC. JNES 37:289–313. Beck, H. C. 1931. Beads from Nineveh. Antiquity 5:427–437. Becker, H., and J. W. E. Fassbinder. 2001. “Uruk– City of Gilgamesh (Iraq): First Tests in 2001 for Magnetic Prospecting,” in Magnetic Prospecting in Archeological Sites, vol. VI, International Council on Monuments and Sites. Edited by H. Becker and J. W. E. Fassbinder, pp. 93–97. Behm–Blancke, M. R. 1986. Die Ausgrabungen auf dem Hassek Hoyuk im Jahre 1985. Kazi Sonuclar Toplantisi 8:139–147. Behm–Blancke, M. R. 1988. Periphere Ninive 5–Keramik am Oberen Euphrat. Mitteilungen der Deutsche Orient–Gesellschaft zu Berlin 120:159–172. Behm–Blancke, M. R., H. Becker, J. Boessneck, A. von der Driesch, M. Hoh, and G. Wiegand. 1981. Hassek Höyük: Vorlaufiger Bericht Uber die Ausgrabungen der Jahre 1978–1980. Istanbuler Mitteilungen 31:11–93. Behm–Blancke, M. R., M. Hoh, N. Karg, L. Masch, F. Parsche, K. L. Weiner, A. von Wickede, and G. Ziegelmayer. 1984. Hassek Hoyuk. Vorlaufiger Bericht uber die Grabungen in den Jahre 1981–1983. Istanbuler Mitteilungen 34:31–150. 374 Belck, W. 1899. Aus den Berichten über die Armenische Expedition. Zeitschrift für Ethnologie XXXI: 236–275. Benco, N. L. 1992. Manufacture and Use of Clay Sickles from the Uruk Mound, Abu Salabikh, Iraq. Paléorient 18:119–134. Bender, D. 1967. A Refinement of the Concept of Household: Families, Co–Residence, and Domestic Functions. American Anthropologist 69:493–504. Benedict, P. 1980. “Survey Work in Southeast Anatolia,” in Prehistoric Research in Southeastern Anatolia. Edited by R. J. Braidwood and H. Çambel, pp. 207–238. Istanbul: Edebiyat Fakültesi Basimevi. Bermann, M. 1994. Lukurmata: Household Archaeology in Prehispanic Bolivia. Princeton: Princeton University Press. Bernbeck, R., and S. Pollock. 2002. “Reflections on the Historiography of 4th Millennium Mesopotamia,” in Material Culture and Mental Spheres: Rezeption archäologischer Denkrichtungen in der Vorderasiatischen Altertumskunde. Internationales Symposium für Hans J. Nissen, Berlin, 23.–24. Juni 2000, Alter Orient und Altes Testament, Band 293. Edited by A. Hausleiter, S. Kerner, and B. Müller–Neuhof, pp. 171–205. Münster: Ugarit–Verlag. Beyer, D. 1991–92. Le Campagne 1991 de Tell Ramadi (Syrie). Orient Express 1991– 92:16. Beyer, D. 1993. Mashnaqa 1993: Rapport Sommaire sur les Travaux de la Mission Archéologique Française. Orient Express 1993/2:7–8. Beyer, D. 1995. Mashnaqa (Syrie) 1994: Rapport Sommaire sur les Travaux de la Mission Archéologique Française. Orient Express 1995/2:43–46. Beyer, D. 1997. Tell Mashnaqa (Syrie): Travaux de La Mission Archéologique Française 1996 (Mission De L'ifapo Damas). Orient Express 1997/1:3–5. Beyer, D. 1998a. “Évolution de l'Espace Bâti sur un Site de la Vallée du Khabur au IVe Millénaire: les Fouilles Françaises de Mashnaqa,” in Espace Naturel, Espace Habité en Syrie du Nord (10e – 2e millénaires av. J–C.). Edited by M. Fortin and O. Aurenche, pp. 139–148. Lyon and Québec: Maison de l'Orient Méditerranéen and Canadian Society for Mesopotamian Studies. Beyer, D. 1998b. Mashnaqa 1997: travaux de la mission archéologique française. Orient Express 1:8–11. 375 Bigelow, L. 1999. Zooarchaeological Investigations of Economic Organization and Ethnicity at Late Chalcolithic Hacınebi: A Preliminary Report. Paléorient 25:83– 89. Binford, L. R. 1973. “Interassemblage Variability – The Mousterian and “The Functional” Argument,” in The Explanation of Culture Change: Models in Prehistory. Edited by C. Renfrew, pp. 227–54. London: Duckworth. Binford, L. R. 1978. Dimensional Analysis of Behavior and Site Structure: Learning from an Eskimo Hunting Stand. AA 43:330–361. Blackman, M. J. 1999. Chemical Characterization of Local Anatolian and Uruk Style Sealing Clays from Hacınebi. Paléorient 25:51–56. Blaylock, S. R., D. H. French, and G. D. Summers. 1990. The Adiyaman Survey: An Interim Report. Anatolian Studies XL:81–135. Blaylock, S. R., G. D. Summers, and C. A. I. French. 1998. “Adiyaman Survey 1985– 1991,” in Ancient Anatolia: Fifty Years' Work by the British Institute of Archaeology at Ankara. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 101–110. London: British Institute of Archaeology at Ankara. Boehmer, R. M. 1990. Zur Funktion des Steinstifttempels in Uruk. Nach Befunden der Kampagne 39. Baghdader Mitteilungen 21: 49–66. Boehmer, R. M. 1991. Uruk 1980–1990: A Progress Report. Antiquity 65:465–478. Boese, J. 1986/7. Excavations at Tell Sheikh Hassan: Preliminary Report on the 1987 Campaign in the Euphrates Valley. Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 36/7:67–100. Boese, J. 1987/8. Excavations at Tell Sheikh Hassan: Preliminary Report on the 1988 Campaign in the Euphrates Valley. Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 37/8:158–189. Boese, J. 1995. Ausgrabungen in Tell Sheikh Hassan I: Vorläufige Berichte über die Grabungskampagnen 1984–1990 und 1992–1994. Saarbrücken: Saarbrücker Druckerei und Verlag. Boessneck, J. 1992. Besprechung Der Tirknochen– Und Molluskenreste von Hassek Höyük. Naturwissenschaftliche Untersuchungen und lithische Industrie 38:58–74. 376 Boessneck, J., and U. Steger. 1984. Tierknochenfunde Des Ausgrabungen Der Deutchen Archäologischen Instituts Baghdad in Uruk–Warka, Iraq. Baghdader Mitteilungen 15:149–189.Boessneck, J., and A. von den Driesch. 1975. “Tierknochenfunde com Korucutepe bei Elazig in Ostanatolien,” in Korucutepe I: Studies in Ancient Civilisation. Edited by M. N. van Loon, pp. 3–220. Amsterdam: North Holland. Bourdieu, P. 1977. Outline of a Theory of Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Bourdieu, P. 1990. The Logic of Practice. Stanford: Stanford University Press. Braemer, F. 1982. L'Architecture Domestique du Levant a l'Age du Fer. Paris: Editions Recherche sur les Civilisations. Braidwood, R. J. 1974. “The Iraq Jarmo Project,” in Archaeological Researches in Retrospect. Edited by G. R. Willey, pp. 61–83. Cambridge: Winthrop. Braidwood, R. J., and L. S. Braidwood. 1960. Excavations in the Plain of Antioch I: The Earlier Assemblages, Phases A–J. Chicago: Oriental Institution Publications 61. Braidwood, R. J., and L. S. Braidwood. 1982. Prehistoric Village Archaeology in South– Eastern Turkey: The Eighth Millennium B.C. Site at Çayönü: Its Chipped and Ground Stone Industries and Faunal Remains. Oxford: BAR. Braidwood, R. J., and H. Çambel. 1980. Prehistoric Research in Southeastern Anatolia. Vol. I. Istanbul: Edebiyat Fakültesi Basımevi. Braidwood, R. J., H. Çambel, and W. Schirmer. 1981. Beginnings of Village–Farming Communities in Southeastern Turkey: Cayönü Tepesi, 1978 and 1979. Journal of Field Archaeology 8:249–258. Brandt, R. W. 1978a. “The Chalcolithic Pottery,” in Korucutepe: Final Report on the Excavations of the Universities of Chicago, California (Los Angeles) and Amsterdam in the Keban Reservoir, Eastern Anatolia 1968–1970, Volume 2. Edited by M. van Loon, pp. 57–61. Amsterdam: North–Holland Publishing Company. Brandt, R. W. 1978b. “The Other Chalcolithic Finds,” in Korucutepe: Final Report on the Excavations of the Universities of Chicago, California (Los Angeles) and Amsterdam in the Keban Reservoir, Eastern Anatolia 1968–1970, Volume 2. Edited by M. van Loon, pp. 61–63. Amsterdam: North–Holland Publishing Company. 377 Breniquet, C. 1996. “Du Fil a Retordre: Réflexions sur les "Idoles aux Yeux" et les Fileuses de l'Époque d'Uruk," in Collectanea Orientalia Histoire, Arts de l'Espace et Industrie de la Terre. Etudes Offerts en Hommage à Agnès Spycket. Edited by H. Gasche and B. Hrouda, pp. 31–53. Neuchatel: Recherches et Publications. Brumfiel, E. M. 1991. “Weaving and Cooking in Aztec Mexico,” in Engendering Archaeology: Women and Prehistory. Edited by J. M. Gero and M. H. Conkey, pp. 224–254. Cambridge: Basil Blackwell. Buccellati, G. 1990. “Salt at the Dawn of History: The Case of the Bevelled–Rim Bowls,” in Resurrecting the Past: A Joint Tribute to Adnan Bounni. Edited by P. Matthiae, M. van Loon, and H. Weiss, pp. 17–40. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archaeologisch Instituut. Buccellati, G., D. Buia, and S. Reimer. 1991. Tell Ziyada: The First Three Seasons of Excavation (1988–90). Bulletin of the Canadian Society for Mesopotamian Studies 21:31–61. Bullard, R. G. 1970. Geological Studies in Field Archaeology. Biblical Archaeologist 33:98–132. Bullock, P., N. Fedoroff, A. Jongerius, G. Stoops, and T. Tursina. 1985. Handbook for Soil Thin Section Description. Wolverhampton: Waine Research. Bulmer, R. N. H. 1960. Leadership and Social Structure among the Kyaka People of the Western Highlands District of New Guinea. Ph.D. thesis, Australian National University. Burney, C. A. 1958. Eastern Anatolia in the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age. Anatolian Studies 8:157–209. Butterlin, P. 2003. Les Temps Proto–Urbain de Mésopotamie: Contacts et Acculturation à l'Époque d'Uruk au Moyen–Orient. Paris: CNRS Éditions. Butzer, K. W. 1982. Archaeology as Human Ecology: Method and Theory for a Contextual Approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Butzer, K. W. 1995. “Environmental Change in the Near East and Human Impact on the Land,” in Civilizations of the Ancient Near East. Vol. I. Edited by J. M. Sasson, J. Baines, G. Beckman, and K. S. Rubinson, pp. 123–153. Peabody: Hendrickson Publishers. Campbell Thompson, R. 1934. The Buildings on Quyunjiq, The Larger Mound of Nineveh. Iraq 1:95–104. 378 Campbell Thompson, R., and R. W. Hamilton. 1932. The British Museum Excavations on the Temple of Ishtar at Nineveh, 1930–1931. Liverpool Annals of Archaeology and Anthropology 19:55–116. Campbell Thompson, R., and R. W. Hutchinson. 1929. A Century of Exploration at Nineveh. London: Luzac and Co. Campbell Thompson, R., and R. W. Hutchinson. 1931. The Site of the Palace of Ashurnasirpal at Nineveh, Excavated in 1929–1930 on Behalf of the British Museum. Liverpool Annals of Archaeology and Anthropology 18:79–112. Campbell Thompson, R., and M. E. L. Mallowan. 1933. The British Museum Excavations at Nineveh, 1931–32. Liverpool Annals of Archaeology and Anthropology 20:71–186. Canal, D. 1978. La Haute Terrasse de l'Acropole de Suse. Paléorient 4:169–176. Caneva, I. 1993. “From Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age III at Arslantepe: A Lithic Perspective,” in Between the Rivers and Over the Mountains: Archaeologica Anatolica Et Mesopotamica Alba Palmieri Dedicata. Edited by M. Frangipane, H. Hauptmann, M. Liverani, P. Matthiae, and M. Mellink, pp. 319–339. Rome: Dipartimento di Scienze Storiche Archaeologiche e Antropologiche dell'Antichità, Università di Roma, “La Sapienza.” Caneva, C., and A. Palmieri. 1983. Metalwork at Arslantepe in Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze I: The Evidence from Metal Analysis. Origini 12:637–654. Carsten, J., and S. Hugh–Jones. Editors. 1995. About the House: Lévi–Strauss and Beyond. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Carter, E., and M. W. Stolper. 1984. Elam: Surveys of Political History and Archaeology. Berkeley: University of California Press. Case, H., and J. C. Payne. 1962. Tomb 100: The Decorated Tomb at Hierakonpolis. The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 48:5–18. Cauvin, J. 1981. “L'Occupation Néolithique de la Région d'El Kowm: Resultats 1978– 1979,” in Préhistoire du Levant. Edited by J. Cauvin and P. Salanville, pp. 471– 483. Paris: CNRS. Cauvin, J., and D. Stordeur. 1985. Une Occupation d'Époque Uruk en Palmyrène: Le Niveau Supérieur d'El Kowm 2 – Caracol. Cahiers de l'Euphrate 4:191–205. Cauvin, J., M.–C. Cauvin, and D. Stordeur. 1979. Recherches Préhistoriques à El Kowm (Syrie). Cahiers de l'Euphrate 2:80–118. 379 Cessford, C. 2003. “Microartifactual Floor Patterning: The Case at Çatalhöyük," in Assemblage, Issue 7. Last Accessed: 21 January 2008. <http://www.assemblage.group.shef.ac.uk/issue7/cessford.html> Cessford, C. 2005. “Heavy–Residue Analysis,” in Changing Materialities at Çatalhöyük: Reports from the 1995–99 Seasons. Edited by I. Hodder, pp. 45–64. Cambridge and London: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and the British Institute at Ankara. Chase–Dunn, C., and T. Hall. 1997. Rise and Demise: Comparing World–Systems. Boulder: Westview. Chayanov, A. V. 1966. The Theory of Peasant Economy. Homewood: Richard D. Irwin. Cohen, A. 1971. “Cultural Strategies in the Organization of Trading Diasporas,” in The Development of Indigenous Trade and Market in West Africa. Edited by C. Meillassoux, pp. 266–281. London: Oxford University Press. Cohen, M. N. 1985. “Prehistoric Hunter–Gatherers: The Meaning of Social Complexity,” in Prehistoric Hunter–Gatherers: Emergence of Cultural Complexity. Edited by T. D. Price and J. A. Brown, pp. 99–119. New York: Academic Press. Collins, P. 2000. The Uruk Phenomenon: The Role of Social Ideology in the Expansion of the Uruk Culture during the Fourth Millennium B.C. BAR International Series 900. Oxford: Archaeopress. Collins, W. F. 2005. Cultural Transmission, Exchange and Complex Society in Late Fourth and Early Third Millenium BCE Inland West Syria. Doctoral Dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. Collon, D., and J. Reade. 1983. Archaic Nineveh. Baghdader Mitteilungen 14:33–41. Conolly, J. 1997. “Tools and Debitage of Obsidian and Flint,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring an Upper Mesopotamian Regional Centre, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 363–376. Cambridge and London: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and the British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Contenau, G. 1954. Everyday Life in Babylon and Assyria. London: E. Arnold. Cook, S. F., and R. F. Heizer. 1965. Studies on the Chemical Analysis of Archaeological Sites. Berkeley: University of California Press. Cook, S. F., and A. E. Treganza. 1947. The Quantitative Investigations of Aboriginal Sites: Comparative Physical and Chemical Analysis of Two California Indian Mounds. AA 13:135–141. 380 Costello, S. K. 2000. Memory Tools in Early Mesopotamia. AA 74:475–476. Courty, M. A., P. Goldberg, and R. Macphail. 1989. Soils and Micromorphology in Archaeology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Courty, M. A., R. Macphail, and J. Wattez. 1991. Soils and Micromorphological Indicators of Pastoralism; with Special Reference to Arene Candide, Finale Ligure, Italy. Revista di studi Liguri LVII:127–150. Crawford, H. E. W. 1985. A Note on the Vegetation on the Uruk Vase. Bulletin on Sumerian Agriculture 2:73–75. Creekmore, A. 2007. The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): A Summary and Synthesis of the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age Remains from the First Three Seasons at Kenan Tepe. Anatolica 33:75–128. Crowfoot, G. 1931. Methods of Hand Spinning in Egypt and the Sudan. Halifax: F. King and Sons. Çukur, A., and S. Kunç. 1989. Analyses of Tepecik and Tulintepe Metal Artifacts. Anatolian Studies 39:113–120. Dahl, J. L. 2006. “Early Swine Herding,” in De La Domestication Au Tabou: Le Cas Des Suidés Dans Le Proche–Orient Ancien. Edited by B. Lion and C. Michel, pp. 31– 38. Paris: Travaux de la Maison René–Ginouvès. D'Altroy, T. 2001. “A View of the Plains from the Mountains: Comments on Uruk by an Andeanist,” in UMN, pp. 445–477. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Damerow, P., and R. K. Englund. 1989. The Proto–Elamite Texts from Tepe Yahya. Cambridge: American School of Prehistoric Research. Daviau, P. M. M. 1993. Houses and Their Furnishings in Bronze Age Palestine: Domestic Activity Areas and Artefact Distribution in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages. Sheffield: JSOT. Deal, M. 1985. Household Pottery Disposal in the Maya Highlands: An Ethnoarchaeological Interpretation. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 4:243–291. DeBoer, W. R. 1983. “The Archaeological Record as Preserved Death Assemblage,” in Archaeological Hammers and Theories. Edited by J. A. Moore and A. S. Keene, pp. 19–36. New York: Academic Press. 381 del Olmo Lete, G., and J.–L. Montero Fenollos. Editors. 1999. Archaeology of the Upper Syrian Euphrates: The Tishrin Dam Area. Proceedings of the International Symposium Held in Barcelona, January 28th–30th, 1998. Barcelona: AUSA. Delougaz, P. P. 1933. Plano–Convex Bricks and the Methods of their Employment. Studies in Ancient Oriental Civilization 7. Chicago: Oriental Institute. Delougaz, P. P., and H. Kantor. 1996. Chogha Mish: The First Five Seasons of Excavations 1961–1971. Vol. 1. Chicago: Oriental Institute. Delougaz, P. P., and S. Lloyd. 1942. Pre–Sargonic Temples in the Diyala Region. Oriental Institute Publications, 58. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Dewdney, J. C. 1971. Turkey: An Introductory Geography. New York: Praeger. Dobney, K., D. Jaques, and W. van Neer. 2003. “Diet, Economy and Status: Evidence from the Animal Bones,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring a Regional Centre in Upper Mesopotamia, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 417–430. Cambridge: McDonald Institute and British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Dobres, M.–A., and J. E. Robb. Editors. 2000. Agency in Archaeology. London: Routledge. Dodd, L. S., B. J. Parker, A. Creekmore, and E. Healey. 2005. “The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): Research at Kenan Tepe in 2003,” in 26. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, Vol. 1, pp. 357–370. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanlığı Anıtlar ve Müzeler Genel Müdürlüğü. Dunnell, R. C., and J. K. Stein. 1989. Theoretical Issues in the Interpretation of Microartifacts. Geoarchaeology 4:31–42. Edens, C. 1999. The Chipped Stone Industry at Hacınebi: Technological Styles and Social Identity. Paléorient 25:23–33. Einwag, B. 1993. Vorbericht über die Archäologische Geländebegehung in der West– Gazira. Damaszener Mitteilungen 7:23–43. Emberling, G. 2002. “Political Control in an Early State: the Eye Temple and the Uruk Expansion in Northern Mesopotamia,” in Of Pots and Plans: Papers on the Archaeology and History of Mesopotamia and Syria presented to David Oates in Honour of his 75th birthday. Edited by L. A.–G. Werr, J. Curtis, H. Martin, A. McMahon, J. Oates, and J. Reade, pp. 82–91. London: Nabu Publications. 382 Emberling, G., J. Cheng, T. E. Larsen, H. Pittman, T. B. B. Skuldboel, J. Weber, and H. T. Wright. 1999. Excavations at Tell Brak 1998: Preliminary Report. Iraq 61:1– 42. Emberling, G., and H. McDonald. 2001. Excavations at Tell Brak 2000: Preliminary Report. Iraq 63:21–54. Emberling, G., and H. McDonald. 2003. Excavations at Tell Brak 2001–2002: Preliminary Report. Iraq LXV:1–77. Englund, R. K. 1995. “Late Uruk Pigs and Other Herded Animals,” in Beiträge zur Kulturgeschichte Vorderasiens: Festschrift für Rainer Michael Boehmer. Edited by U. Finkbeiner, R. Dittmann, and H. Hauptmann, pp. 121–133. Mainz: Verlag Philipp von Zabern. Erinç, S. 1980. “Human Ecology in Southeastern Anatolia,” in The Joint Istanbul– Chicago Universities Prehistoric Research in Southeastern Anatolia, vol. I. Edited by H. Çambel and R. J. Braidwood, pp. 73–91. Istanbul: Edebiyat Fakültesi Basimevi. Erinç, S., and N. Tunçdilek. 1952. The Agricultural Regions of Turkey. The Geographical Review 42:179–204. Erentöz, C., and I. Ketin. 1962. Explanatory Text of the Geological Map of Turkey. Diyarbakır 1:500,000. Maden Tetkik Ve Arama Enstutusu Yayinlarindan. Ankara: Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitusu. Esin, U. 1970. “Tepecik Excavation 1968 Campaign, Preliminary Report,” in METU: 1968 Summer Work. Edited by I. Acaroglu, pp. 147–172. Ankara: Turk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Esin, U. 1971. “Tepecik Excavations, 1969,” in METU: 1969 Activities. Edited by S. Pekman, pp. 119–129. Ankara: Turk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Esin, U. 1972a. “Tepecik Excavations, 1970,” in METU: 1970 Activities. Edited by S. Pekman, pp. 139–158. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Esin, U. 1972b. Tepecik and Tulin Tepe, 1971. Anatolian Studies 22:29–31. Esin, U. 1975. Tepecik 1974. Anatolian Studies 25:46–49. Esin, U. 1976. “Tepecik Excavations, 1972,” in METU: 1972 Activities. Edited by S. Pekman, pp. 101–117. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Esin, U. 1979. “Tepecik Excavations, 1973,” in METU: 1973 Activities. Edited by S. Pekman, pp. 79–112. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. 383 Esin, U. 1982. “Tepecik Excavations, 1974,” in METU: 1974–75 Activities. Edited by S. Pekman, pp. 95–118. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Falkenstein, A. 1936. “Archaische Texte Aus Uruk,” in UA, Vol. 2. Berlin: Harrassowitz. Fassbinder, J. W. E., H. Becker, and M. van Ess. 2003. “Magnetometry at Uruk (Iraq): The city of King Gilgamesh,” in Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 5, 09152: Copernicus Publications on behalf of the European Geosciences Union. Last accessed: 02 December 2008. < http://www.geophys–res–abstr.net> Fehon, J. R., and S. C. Scholtz. 1978. A Conceptual Framework for the Study of Artifact Loss. AA 43:271–273. Felli, C. 2003. “Developing Complexity. Early to Mid Fourth–Millenium Investigations: The Northern Middle Uruk Period,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring an Upper Mesopotamian Regional Centre, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 53–96. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Finet, A. 1973. Les Fouilles du Secteur Ouest au Tell Kannâs. Archiv fur Orientforschung 24:171–175. Finet, A. 1975. Les Temples Sumtriens Du Tell Kannâs. Syria 52:157–174. Finet, A. 1977. Bilan Provisoire des Fouilles Belges du Tell Kannâs. The Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 44:79–96. Finet, A. 1982. Lorsque la royauté descendit du ciel..." Les fouilles belges du Tell Kannâs sur l'Euphrate en Syrie. Morlanwelz: Musée royal de Mariemont. Fladmark, K. R. 1982. Microdebitage Analysis: Initial Considerations. Journal of Archaeological Science 9:205–220. Flannery, K. V. 1972. “The Origins of the Village as a Settlement Type in Mesoamerican and the Near East: a Comparative Study,” in Man, Settlement and Urbanism. Edited by P. Ucko, R. Tringham, and G. W. Dimbleby, pp. 23–53. London: Duckworth. Flannery, K. V. Editor. 1976. The Early Mesoamerican Village. New York: Academic Press. Forbes, R. J. 1956. Studies in Ancient Technology. Vol. IV. Leiden: Brill. Forrest, J.D. 1987. “Les Bevelled–Rim Bowls. Nouvelle Tentative d’Interprétation.” Akkadica 53:1–24. 384 Fortes, M. 1949. “Time and Social Structure: An Ashanti Case Study,” in Social Structure: Studies presented to A. R. Radcliffe–Brown. Edited by M. Fortes, pp. 54–84. London: Oxford University Press. Fortes, M. 1958. “Introduction,” in The Developmental Cycle in Domestic Groups, Cambridge Papers in Social Anthropology 1. Edited by J. Goody, pp. 1–14. Cambridge: Cambridge University. Frangipane, M. 1993. “Local Components in the Development of Centralized Societies in the Syro–Anatolian Region,” in Between the Rivers and Over the Mountains: Archaeologica Anatolica et Mesopotamica Alba Palmieri Dedicata. Edited by M. Frangipane, H. Hauptmann, M. Liverani, P. Matthiae, and M. Mellink. Rome: Universita di Roma “La Sapienza.” Frangipane, M. 1997a. “Arslantepe–Malatya: External Factors and Local Components in the Development of an Early State Society,” in Emergence and Change in Early Urban Societies. Edited by L. Manzanilla, pp. 43–58. New York: Plenum Press. Frangipane, M. 1997b. A Fourth Millennium Temple/Palace Complex at Arslantepe– Malatya: North–South Relations and the Formation of Early State Societies in the Northern Regions of Greater Mesopotamia. Paléorient 23:45–73. Frangipane, M. 2001. “Centralization Processes in Greater Mesopotamia: Uruk “Expansion” as the Climax of Systemic Interactions Among Areas of the Greater Mesopotamian Region,” in UMN, pp. 307–349. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Frangipane, M., and F. Balossi. 2004. “The 2002 Exploration Campaign at Arslantepe– Malatya,” in 25. Kazi Sonuçlari Toplantisi, Vol. 1, pp. 397–404. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanligi Anitlar ve Müzeler Genal Müdürlügü. Frangipane, M., G. M. Di Nocera, H. Hauptmann, P. Morbidelli, A. Palmieri, L. Sadori, M. Schultz, and T. Schmidt–Schultz. 2001. New Symbols of New Power in a “Royal” Tomb from 3000 B.C. Arslantepe, Malatya (Turkey). Paléorient 27:105– 139. Frangipane, M., and A. Palmieri. 1983. Perspectives on Protourbanization in Eastern Anatolia: Arslantepe (Malatya), an Interim Report on the 1975–1983 Campaigns. Origini 12:287–668. Frangipane, M., and A. Palmieri. 1987. “Urbanization in Perimesopotamian Areas: The Case of Eastern Anatolia,” in Studies in the Neolithic and Urban Revolutions. Edited by K. Manzanilla, pp. 295–326. Oxford: BAR International Series 349. Frankfort, H. 1950. Town Planning in Ancient Mesopotamia. Town Planning Review 21:99–115. 385 Frankfort, H. 1951. The Birth of Civilization in the Near East. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. Garstang, J. 1953. Prehistoric Mersin: Yümük Tepe in Southern Turkey. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Gardner, A. 2004. “Introduction: Social Agency, Power, and Being Human,” in Agency Uncovered: Archaeological Perspectives on Social Agency, Power, and Being Human. Edited by A. Gardner, pp. 1–18. London: UCL Press. Gé, T., M. A. Courty, W. Matthews, and J. Wattez. 1993. “Sedimentary Formation Processes of Occupation Surfaces,” in Formation Processes in Archaeological Context. Edited by P. Goldberg, D. T. Nash, and M. D. Petraglia, pp. 149–164. Madison: Prehistory Press. George, A. 1999. The Epic of Gilgamesh. A New Translation. London: Penguin Press. Gibson, M. 2000. Hamoukar: Early City in Northeastern Syria. Antiquity 74:477–478. Gibson, M., A. al–Azm, C. Reichel, S. Quntar, J. A. Franke, L. Khalidi, C. Hritz, M. Altaweel, C. Coyle, C. Colantoni, J. Tenney, G. Abdul Aziz, and T. Hartnell. 2002a. Hamoukar: A Summary of Three Seasons of Excavation. Akkadica 123:11–34. Gibson, M., M. Maktash, J. A. Franke, A. al–Azm, J. C. Sanders, T. J. Wilkinson, C. Reichel, J. Ur, P. Sanders, A. Salameh, C. Hritz, B. Watkins, and M. Kattab. 2002b. First Season of Syrian–American Investigations at Hamoukar, Hasekeh Province. Iraq 64:45–68. Gifford, D. P. 1978. “Ethnoarchaeological Observations of Natural Processes Affecting Cultural Materials,” in Explorations in Ethnoarchaeology. Edited by R. A. Gould, pp. 77–102. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Gifford, E. W. 1916. Composition of California Shell–Mounds. Berkeley: University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology, Vol. 12, no. 1. Goff, B. L. 1963. Symbols of Prehistoric Mesopotamia. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. Goldberg, P., and S. C. Sherwood. 1994. Micromorphology of Dust Cave Sediments: Some Preliminary Results. Journal of Alabama Archaeology 40:57–65. Goldberg, P., and I. Whitbread. 1993. “Micromorphological Study of a Bedouin Tent Floor,” in Formation Processes in Archaeological Context. Edited by P. Goldberg, D. T. Nash, and M. D. Petraglia, pp. 165–188. Madison: Prehistory Press. 386 Goldman, H. 1956. Excavations at Gözlü Kule, Tarsus. Vol. II: From the Neolithic through the Bronze Age. Princeton: Princeton University Press. Goody, J. 1972. "The Evolution of the Family," in Household and Family in Past Time. Edited by P. Laslett and P. Wall, pp. 103–124. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Gould, R. A. 1980. Living Archaeology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Green, A. Editor. 1993. Abu Salabikh Excavations 4: The 6Gash–Tip and its Contents: Cultic or Administrative Discard from the Temple? London: British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Green, M.W. 1981. The Construction and Implementation of the Cuneiform Writing System. Visible Languages 15:345–372. Grigson, C. 2007. “Culture, Ecology, and Pigs from the 5th to the 3rd Millennium BC around the Fertile Crescent,” in Pigs and Humans: 10,000 Years of Interaction. Edited by U. Albarella, K. Dobneym, A. Ervynck, and P. Rowley–Conwy, pp. 83–108. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Gülçur, S. 2000. “Norşun Tepe: Die Chalkolithische Keramik (Elazig/Ostanatolien),” in Chronologies des Pays du Caucase et de l'Euphrate aux IVe–IIIe Millenaires. Edited by C. Marro and H. Hauptmann, pp. 375–418. Paris: Français d'Etudes Anatoliennes d'Istanbul. Günay, D., and R. Whallon Jr. 1980. “History of Travel and Previous Research in the Survey Area,” in Prehistoric Research in Southwestern Anatolia I. Edited by H. Çambel and R. J. Braidwood, pp. 91–150. Istanbul: Edebiyat Fakültesi Basımevi. Gut, R. V. 1995. Das Prähistorische Nineve. Mainz: Verlag Philipp von Zabern. Gut, R. V. 2002. “The Significance of the Uruk Sequence at Nineveh,” in AC, pp. 17–48. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Hammade, H. 1989. Syrian Excavations at Tell Qumloq and Tell al–'Abr, 1989 Season. Les Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 39:15–20. Hammade, H., and Y. Koike. 1992. Syrian Archaeological Expedition in the Tishreen Dam Basin––Excavations at Tell el–'Abr 1990 and 1991. Damaszener Mitteilungen 6:109–175. Hammade, H., and Y. Yamazaki. 1993. Some Remarks on the Uruk Levels at Tell al–Abr on the Euphrates. Akkadica 84/85:53–62. 387 Hammade, H., and Y. Yamazaki. 1995. A Preliminary Report on the Excavations at Tell al–'Abr on the Upper Euphrates, 1992. Akkadica 93:4–10. Hammade, H., and Y. Yamazaki. 2006. Tell al–'Abr (Syria): Ubaid and Uruk Periods. Louvain: Peeters. Hammel, E. A., and P. Laslett. 1974. Comparing Household Structure Over Time and Between Cultures. Comparative Studies in Society and History 16:73–109. Hanbury Tenison, J. 1983. The 1982 Flaked Stone Assemblage at Jebel Aruda, Syria. Akkadica 33:27–33. Hanks, W. F. 1990. Referential Practice: Language and Lived Space Among the Maya. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Hardin, J. W. 2001. An Archaeology of Destruction: Households and the Use of Domestic Space at Iron II Tel Halif. Ph.D. thesis, University of Arizona. Hardin, J. W. 2004. Understanding Domestic Space: An Example from Iron Age Tel Halif. Near Eastern Archaeology 67:71–83. Harris, M. 2007. “The Abominable Pig,” in Food and Culture: A Reader. Second Edition. Edited by C. M. Counihan and P. van Esterik, pp. 654–66. New York: Routledge. Hassan, F. A. 1978. Sediments in Archaeology: Methods and Implications for Palaeoenvironmental and Cultural Analysis. Journal of Field Archaeoelogy 5:97– 213. Hastorf, C. A. 1990. The Effect of the Inka State on Sausa Agricultural Production and Crop Consumption. AA 55:262–290. Hastorf, C. A., and T. N. D'Altroy. 2001. “The Domestic Economy, Households, and Imperial Transformation,” in Empire and Domestic Economy. Edited by T. N. D'Altroy and C. A. Hastorf, pp. 3–26. New York: Kluwer Academic and Plenum Publishers. Hauptmann, H. 1976. “Die Graubungen auf dem Norşun–Tepe, 1972,” in METU: 1972 Activities, pp. 71–90. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Hauptmann, H. 1979. “Die Graubungen auf dem Norşun–Tepe, 1973,” in METU: 1973 Activities, pp. 61–96. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. 388 Hauptmann, H. 2000. “Zur Chronologie des 3.Jahrtausends v.Chr. am oberen Euphrat Aufgrund der Stratigraphie des Norşuntepe,” in Chronologies des Pays du Caucase et de l'Euphrate aux IVe–IIIe Millenaires. Edited by C. Marro and H. Hauptmann, pp. 419–438. Paris: Français d'Etudes Anatoliennes d'Istanbul. Hayden, B., and A. Cannon. 1983. Where the Garbage Goes: Refuse Disposal in the Maya Highlands. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 2:117–163. Heinrich, E. 1936. “Kleinfunde Aus Den Archaischen Tempelschichten in Uruk,” in UA, Vol. 1. Berlin: Harrassowitz. Heinrich, E. 1937. VIII. UVB. Berlin: Ger. Mann Verlag. Heinrich, E. 1938. “Grabungen Im Gebiet Des Anu–Antum–Tempels,” in IXX. UVB, pp.19–30. Berlin: Ger. Mann Verlag. Heinrich, E. 1982. Die Tempel und Heiligtümer im Alten Mesopotamien. Typologie, Morphologie und Geschichte. Berlin: Verlag Walter de Gruyter. Helwing, B. 1999. Cultural Interaction at Hassek Höyük, Turkey: New Evidence from Pottery Analysis. Paléorient 25:91–101. Helwing, B. 2002. Hassek Höyük II: Die spätchalkolithische Keramik. Istanbuler Forschungen Band 45. Tübingen: Ernst Wasmuth. Hendon, J. A. 1996. Archaeological Approaches to the Organization of Domestic Labor: Household Practice and Domestic Relations. Annual Review of Anthropology 25:45–61. Hendon, J. A. 2004. “Living and Working at Home: The Social Archaeology of Household Production and Social Relations,” in A Companion to Social Archaeology. Edited by L. Meskell and R. Pruecel, pp. 272–286. Malden: Blackwell. Hillier, B., and J. Hanson. 1984. The Social Logic of Space. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Hirth, K. G. 1993. “The Household as an Analytical Unit: Problems in Method and Theory,” in Prehispanic Domestic Units in Western Mesoamerica: Studies of the Household, Compound, and Residence. Edited by R. Santley and K. G. Hirth, pp. 21–36. Boca Raton: CRC Press. Hodder, I. 1983. The Present Past: An Introduction to Anthropology for Archaeologists. New York: Pica Press. Hodder, I. 1990. The Domestication of Europe. Oxford: Blackwell. 389 Hodder, I. 1992. Theory and Practice in Archaeology. London: Routledge. Hodder, I. 1998. “The Domus: Some Problems Reconsidered,” in Understanding the Neolithic of North–western Europe. Edited by M. Edmonds and C. Richards, pp. 84–101. Glasgow: Cruithne Press. Hodder, I., and C. Cessford. 2004. Daily Practice and Social Memory at Çatalhöyük. AA 69:17–40. Hoh, M. 1981. Die Keramik von Hassek Höyük. Istanbuler Mitteilungen 31:31–82. Hoh, M. 1984. Die Keramik von Hassek Höyük. Istanbuler Mitteilungen 34:66–91. Hole, F. 1978. “Pastoral Nomadism in Western Iran,” in Explorations in Ethnoarchaeology, School of American Research. Edited by R. A. Gould, pp. 127–168. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Hole, F. 1990. “Cemetery or Mass Grave? Reflections on Susa I,” in Melanges Jean Perrot. Edited by F. Vallat, pp. 1–13. Paris: Editions Recherche sur les Civilisations. Hole, F. 1994. “Environmental Instabilities and Urban Origins,” in Chiefdoms and Early States in the Near East: The Organizational Dynamics of Complexity. Edited by G. Stein and M. S. Rothman, pp. 121–151. Madison: Prehistory Press. Hopkins, L. 1996. “The Rise of Social Complexity in East Central Anatolia in the Early Bronze Age,” in Cultural Interaction in the Ancient Near East: Papers Read at a Symposium Held at the University of Melbourne, Department of Classics and Archaeology (29–30 September 1994). Edited by G. Bunnens, pp. 17–26. Louvain: Peeters Press. Hopwood, D. E. 2008. “The Changing Relationship Between the Living and the Dead: Child Burial at the Site of Kenan Tepe, Turkey,” in Babies Reborn: Infant/Child Burials in Pre– and Protohistory. Proceedings of the XV World Congress (Lisbon, 4–9 September 2006). Vol. 24. BAR International Series. Edited by K. Bacvarov, pp. 113–121. Oxford: Archaeopress. Horne, L. 1994. Village Spaces: Settlement and Society in Northeastern Iran. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. Horwitz, L. K. 1989. “Sedentism in the Early Bronze IV: A Faunal Perspective.” Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research 275: 15–25. Howell–Meurs, S. 2001. Archaeozoological Evidence for Pastoral Systems and Herd Mobility: The Remains from Sos Hoyuk and Buyuktepe Hoyuk. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology 11:321–328. 390 Hull, K. L. 1987. Identification of Cultural Site Formation Processes through Microdebitage Analysis. AA 52:772–783. Huntington, E. 1903. The Hittite Ruins of Hilar, Asia Minor. Records of the Past II: 131– 140. Jasim, S. A., and J. Oates. 1986. Early Tokens and Tablets in Mesopotamia: New Information from Tell Abada and Tell Brak. World Archaeology 17:348–362. Joffe, A. H. 1994. Review of The Uruk World System: The Dynamics of Expansion of Early Mesopotamian Civilization, by Guillermo Algaze (1993). Journal of Field Archaeoelogy 21:512–516. Joffe, A. H. 2000. Egypt and Syro–Mesopotamia in the 4th Millennium: Implications of the New Chronology. CA 41:113–129. Johnson, G. A. 1973. Local Exchange and Early State Development in Southwestern Iran. Museum of Anthropology Anthropological Papers 51. Ann Arbor: Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan. Johnson, G. A. 1975. “Locational Analysis and the Investigations of Uruk Local Exchange Systems,” in Ancient Civilizations and Trade. Edited by J. A. Sabloff and C. C. Lamberg–Karlovsky, pp. 285–339. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Johnson, G. A. 1976. “Early State Organization in Southwestern Iran: Preliminary Field Report,” in Proceedings of the IVth Annual Symposium on Archaeological Research in Iran, pp. 190–223. Iranian Center for Archaeological Research. Johnson, G. A. 1987. “The Changing Organization of Uruk Administration in the Susiana Plain,” in The Archaeology of Western Iran: Settlement and Society from Prehistory to the Islamic Conquest. Edited by F. Hole, pp. 107–39. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. Johnson, G. A. 1988/89. Late Uruk in Greater Mesopotamia: Expansion or Collapse? Origini 14:595–613. Jordan, J. 1913. Aus den Berichten aus Warka: Oktober 1912 bis März 1913. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Orient–Gesellschaft 51:47–76. Jordan, J. 1914. Aus den Berichten aus Warka: März bis Mai 1913. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Orient–Gesellschaft 53:9–17. 391 Joyce, R. A. 2000. “Heirlooms and Houses: Materiality and Social Memory,” in Beyond Kinship: Social and Material Reproduction in House Societies. Edited by R. A. Joyce and S. D. Gillespie, pp. 189–212. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. Kamp, K. A. 2000. From Village to Tell: Household Ethnoarchaeology in Syria. Near Eastern Archaeology 63:84–93. Kamp, K. A. 2001. Prehistoric Children Working and Playing: A Southwestern Case Study in Learning Ceramics. Journal of Anthropological Research 57:427–450. Kantor, H. 1952. Further Evidence for Early Mesopotamian Relations with Egypt. JNES 11:239–250. Karg, N. 1999. “Gre Dimse 1998: Preliminary Report,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 1998. Edited by N. Tuna and J. Öztürk, pp. 271–318. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Karg, N. 2001. “First Soundings at Grê Dimsê 1999,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 1999. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 671–714. Anakara: Middle East Technican University. Keith, K. 1998. Spindle Whorls, Gender, and Ethnicity at Late Chalcolithic Hacınebi Tepe. Journal of Field Archaeology 25:497–515. Kent, S. 1984. Analyzing Activity Areas: an Ethnoarchaeological Study of the Use of Space. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Kent, S. 1987. “Understanding the Use of Space: An Ethnoarchaeological Approach,” in Method and Theory for Activity Area Research: An Ethnoarchaeological Approach. Edited by S. Kent, pp. 1–62. New York: Columbia University Press. Kent, S. 1990. “A Cross–Cultural Study of Segmentation, Architecture, and the Use of Space,” in Domestic Architecture and the Use of Space: An Interdisciplinary Cross–Cultural Study. Edited by S. Kent, pp. 127–152. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. King, P. J., and L. E. Stager. 2001. Life in Biblical Israel. Louisville: Westminster John Knox Press. Kirkby, A., and M. J. Kirkby. 1976. “Geomorphic Processes and the Surface Survey of Archaeological Sites in Semi–Arid Areas," in Geoarchaeology: Earth Science and the Past. Edited by D. A. Davidson and M. L. Shackley, pp. 229–254. London: Duckworth. 392 Kirkby, M. J. 1977. “Land and Water Resources of the Deh Luran and Khuzistan Plains,” in Studies in the Archaeological History of the Deh Luran Plain: The Excavation of Chagha Sefid. Edited by F. Hole, pp. 251–288. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan. Kohl, P. 1987. “The Use and Abuse of World Systems Theory: The Case of the “Pristine” West Asian State,” in Advances in Archaeological Method and Theory, vol. 11. Edited by M. B. Shiffer, pp. 1–35. New York: Academic Press. Köhler, C. E. 1992. “The Pre– and Early Dynastic Pottery of Tell el–Fara'in/Buto,” in The Nile Delta in Transition: 4th – 3rd Millennium B.C. Edited by E. C. M. van den Brink, pp. 11–22. Jerusalem: Israel Exploration Society. Kohlmeyer, K. 1996. “Houses in Habuba Kabira South: Spatial Organization and Planning of Late Uruk Residential Architecture,” in Houses and Households in Ancient Mesopotamia. Papers read at the 40e Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Leiden, July 5–8, 1993. Edited by K. R. Veenhof, pp. 89–104. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archaeologisch Instituut. Kökten, I. K. 1947. 1946 yılı Tarihöncesi araştırmaları. Türk Tarih Kurumu Belleten XI:161–163. Kozbe, G., K. Köroğlu, and H. Sağlamtemir. 2003. “Kavuşan Höyük 2001 Yılı Kazısı,” in 24. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, vol. 1, pp. 139–150. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanlığı Anıtlar ve Müzeler Genel Müdürlüğü. Kozbe, G., K. Köroğlu, and H. Sağlamtemir. 2004. “2001 Excavations at Kavuşan Höyük,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Greenhalgh, and J. Velibeyoglu, pp. 463–501. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Králík, M., and M. Hložek. 2007. “Neolithic Miniature Ceramic Vessels – Production of Children?” Paper given at Vessels Inside and Out: 9th European Meeting on Ancient Ceramics, Budapest, 2007. Kramer, C. 1982. Village Ethnoarchaeology: Rural Iran in Archaeological Perspective. New York: Academic Press. Kuijt, I. 2000. People and Space in Early Agricultural Villages: Exploring Daily Lives, Community Size, and Architecture in the Late Pre–Pottery Neolithic. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 19:75–102. Kupper, J.–R. 1950. Correspondance de Kibri–Dagan, Gouverneur de Terqa. Archives Royales de Mari III. Paris: Imprimerie. 393 Lamberg–Karlovsky, C. C. 1984. "The Long Dureé of the Ancient Near East," in De L'indus Aux Balkans: Recueil À La Mémoire De Jean Deshayes. Edited by J.–L. Huot, M. Yon, and Y. Calvet, pp. 55–72. Paris: Editions Recherche sur les Civilisations. Lampl, P. 1968. Cities and Planning in the Ancient Near East. New York: Braziller. Laneri, N. 2005. “Hirbemerdon Tepe 2003: A Preliminary Report,” in 26. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, vol. 2, pp. 63–72. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanlığı Anıtlar ve Müzeler Genel Müdürlüğü. Laneri, N., A. D'Agostino, M. Schwartz, S. Valentini, and G. Pappalardo. 2006. A Preliminary Report of the Archaeological Excavations at Hirbemerdon Tepe, Southeastern Turkey. Anatolica 32:153–188. Layard, A. H. 1846. Description of the Plain of Khuzistan. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society 16:78–86. Lebeau, M. 1989. “Notes sur l'Expansion Urukéenne,” in Archeologica Iranica Et Orientalis, Miscellannea in Honorem Louis Vanden Berghe. Edited by L. de Meyer and E. Haerinck, pp. 33–47. Gent: Peeters. Le Breton, L. 1957. The Early Periods at Susa, Mesopotamian Relations. Iraq 19:79–124. LeBrun, A. 1978. Suse, chantier “Acropole 1.” Paléorient 4:177–192. Lehmann–Haupt, C. F. 1910. Armenien Einst und Jetzt, I: Vom Kaukasus zur Tigris und Nach Tigranokerta. Berlin: B. Behr. Leick, G. 1988. A Dictionary of Ancient Near Eastern Architecture. London and New York: Routledge. Lenzen, H. 1941. UA, Vol. 4. Berlin: Harrowitz. Lenzen, H. 1950. Die Tempel der Schicht Archaisch IV in Uruk. ZA 49 (NF 15). Lenzen, H. 1960. “Die Kleinfunde,” in, XVI. UVB, Edited by H. Lenzen, pp. 47–56. Berlin: Verlag Gebr. Mann. Lenzen, H. 1965. XXI. UVB. Berlin: Gebr. Mann Verlag. Lenzen, H. 1974a. Die Architektur in Eanna in der Uruk IV Periode. Iraq 36 (1/2): 111– 128. Lenzen, H. 1974b. XXV. UVB Winter 1966/1967. Berlin: Gebr. Mann Verlag. 394 Lévi–Strauss, C. 1966. The Savage Mind. Chicago: University of Chicago. Lévi–Strauss, C. 1979. La Voie des Masques. Paris: Plon. Lightfoot, C. S. 1986. “Tilli–A Late Roman Equites Fort on the Tigris,” in The Defence of the Roman and Byzantine East: Proceedings of a Colloquium Held at the University of Sheffield in April 1986. Edited by P. Freeman and D. Kennedy, pp. 509–529. Oxford: B.A.R. Liu, R. 1978. Spindle Whorls: Pt. I, Some Comments and Speculations. The Bead Journal 3:87–103. Loftus, W. K. 1857. Travels and Researches in Chaldaea and Susiana: With an Account of Excavations at Warka, the "Erech" of Nimrod, and Shush, "Shushan the Palace" of Esther, in 1849–52. New York: Robert Carter & Brothers. Lupton, A. 1996. Stability and Change: Socio–Political Development in Northern Mesopotamia and South–East Anatolia 4000–2700 B.C. Bar International Series. Oxford: Tempvs Reparatvm. Malinowski, B. 1963. The Family among the Australian Aborigines: A Sociological Study. Second edition. New York: Schocken. Mallowan, M. E. L. 1947. Excavations at Brak and Chagar Bazar. Iraq 9:1–259. Manzanilla, K., and L. Barba. 1990. The Study of Activities in Classic Households: Two Case Studies from Coba and Teotihuacan. Ancient Mesoamerica 1:41–49. Marfoe, L., G. Algaze, K. Ataman, I. Ingraham, H. McDonald, N. Miller, C. Snow, G. Stein, B. Verhaaren, P. Wattenmaker, T. J. Wilkinson, and K. A. Yener. 1986. The Chicago Euphrates Archaeological Project 1980–1984: An Interim Report. Anatolica 13:37–148. Matney, T., J. MacGinnis, H. McDonald, K. Nicoll, L. Rainville, M. Roaf, M. L. Smith, and D. Stein. 2003. Archaeological Investigations at Ziyaret Tepe – 2002. Anatolica 29:175–221. Matney, T., and L. Rainville. 2005. Archaeological Investigations at Ziyaret Tepe, 2003– 2004. Anatolica 31:19–68. Matney, T., L. Rainville, K. Köroglu, A. Keskin, T. Vorderstrasse, N. Ö. Findik, and A. Donkin. 2007. Report on Excavations at Ziyaret Tepe, 2006 Season. Anatolica 33:23–74. Matthews, R. J. 1989. Excavations at Jemdet Nasr, 1988. Iraq 51:225–248. 395 Matthews, R. J. 1990. Excavations at Jemdet Nasr, 1989. Iraq 52:25–39. Matthews, R. J. 1995. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1995. Iraq 57:87–111. Matthews, R. J. 1996. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1996. Iraq 58:65–78. Matthews, R. J. 2002. Secrets of the Dark Mound: Jemdet Nasr 1926–1928. Warminster: Arys and Phillips for the British School of Archeology in Iraq. Matthews, R. J. 2003a. “Traces of Early Complexity. Late Fifth– to Early Fourth– Millenia Investigations: the Early Northern Uruk Period,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring an Upper Mesopotamian Regional Centre, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 25–52. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Matthews, R. J. 2003b. “A Chiefdom on the Northern Plains. Early Third–Millennium Investigations: the Ninevite 5 Period,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring an Upper Mesopotamian regional centre, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 97–194. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and the British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Matthews, R.J. and T. Wilkinson. 1991. “Excavations in Iraq, 1989–1990.” Iraq 53:169– 182. Matthews, R. J., W. Matthews, and H. McDonald. 1994. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1994. Iraq 56:177–194. Matthews, W. 1993. “Analysis of field section from 1960's excavations,” in Çatalhöyük 1993 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1993/ar93_02.html> Matthews, W. 1994. “Analysis of Field sections from the 1960s' excavations,” in Çatalhöyük 1994 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1994/ar94_02.html> Matthews, W. 1995a. “Micromorphological Characterization and Interpretation of Occupation Deposits and Microstratigraphic Sequences at Abu Salabikh, Iraq,” in Archaeological Sediments and Soils, Analysis, Interpretation and Management. Edited by A. J. Barham and R. I. Macphail, pp. 41–76. London: Archetype Books. Matthews, W. 1995b. “Sampling Report and Micromorphology,” in Çatalhöyük 1995 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1995/ar95_08.html> 396 Matthews, W. 1996. “Microstratigraphy, Micromorphology and Sampling Report,” in Çatalhöyük 1996 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1996/ar96_07.html> Matthews, W. 1997. “Report on Sampling Strategies, and Analyses of the Microstratigraphy and Micromorphology of Depositional Sequences at Çatalhöyük, 1997,” in Çatalhöyük 1997 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1997/ar97_09.html> Matthews, W. 1998. “Report on Sampling Strategies, Microstratigraphy and Micromorphology of Depositional Sequences, and Associated Ethnoarchaeology at Çatalhöyük, 1998,” in Çatalhöyük 1998 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008.<http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1998/ar98_06.html> Matthews, W. 1999. “Micromorphology Archive Report,” in Çatalhöyük 1999 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1999/ar99_06.html> Matthews, W. 2001a. “Methodological Approaches in Microstratigraphic Analysis of Uses and Concepts of Space at Tell Brak,” in Recherches en archéométrie. Edited by M. Forth, pp. 177–197. Quebec: CELAT. Matthews, W. 2001b. “Micromorphological Analysis of Cccupational Sequences,” in Contextual Analysis of the Use of Space at Two Near Eastern Bronze Age Sites. Edited by R. J. Matthews and J. N. Postgate. Last accessed: 21 January 2008. <http://ads.ahds.ac.uk/catalogue/resources.html?tellbrak> Matthews, W. 2003. “Microstratigraphic Sequences: Indications of Uses and Concepts of Space,” in Excavations at Tell Brak: Exploring an Upper Mesopotamian Regional Centre, 1994–1996. Vol. 4. Edited by R. J. Matthews, pp. 377–388. Cambridge and London: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and the British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Matthews, W. 2005. “Micromorphological and Microstratigraphic Traces of Uses and Concepts of Space,” in Inhabiting Çatalhöyük: Reports from the 1995–1999 Seasons. Edited by I. Hodder, pp. 217–255. Cambridge: McDonald Institute Monographs. Matthews, W., C. A. I. French, T. Lawrence, D. F. Cutler, and M. K. Jones. 1997. Microstratigraphic Traces of Site Formation Processes and Human Activities. World Archaeology 29:281–308. 397 Matthews, W., and J. N. Postgate. 1994. “The Imprint of Living in an Early Mesopotamian City: Questions and Answers,” in Whither Environmental Archaeology?, Oxbow Monograph 38. Edited by R. Luff and P. Rowley–Conwy, pp. 171–212. Oxford: Oxbow Books. Matthews, W., L.–M. Shillito, and M. Almond. 2004. “Micromorphology: Investigation of Neolithic Social and Ecological Strategies at Seasonal, Annual and Life–Cycle Timescales,” in Çatalhöyük 2004 Archive Report. Last accessed: 14 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/2004/ar04_22.html> McCorriston, J. 1997. The Fiber Revolution: Textile Extensification, Alienation, and Social Stratification in Ancient Mesopotamia. CA 38:517–551. McCown, D. E., and R. C. Haines. 1967. Nippur. Excavations of the Joint Expedition to Nippur of the University Museum of Philadelphia and the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. Chicago: Chicago University Press. McGovern, P. E. 2003. Ancient Wine: The Search for the Origins of Viniculture. Princeton: Princeton University Press. McGovern, P. E., V. R. Badler, and D. L. Glusker. 1996. Chemical Evidence for a Wine Residue from Warka (Uruk) inside a Late Uruk Period Spouted Jar. Baghdader Mitteilungen 27:39–43. McKellar, J. A. 1983. Correlations and the Explanation of Distributions. Atlatl: Occasional Papers in Anthropology 4:2–5. Meijer, D. J. W. 1988. “Tell Hammam: Architecture and Stratigraphy,” in Hammam et– Turkman. Report on the University of Amsterdam's 1981–84 Excavations in Syria, Vol. I. Edited by M. N. van Loon, pp. 69–128. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch– Archeologisch Instituut. Meijer, D. J. W. 1989. Hammam al Turkman on the Balikh: First Results of the Fifth Campaign, 1988. Akkadica 64/65:1–12. Meijer, D. J. W. 1996. Tell Hammam al–Turkman: Preliminary Report on the Seventh Campaign, May–July 1995. Anatolica 22:181–193. Mellink, M. 1989. Archaeology in Asia Minor, Samsat. American Journal of Archaeology 93:113–114. Metcalfe, D., and K. M. Heath. 1990. Microrefuse and Site Structure: The Hearths and Floors of the Heartbreak Hotel. AA 55:781–796. Meyers, C. 2002. Having Their Space and Eating There Too: Bread Production and Female Power in Ancient Israelite Households. Nashim 5:14–44. 398 Meyers, C. 2003. "Where the Girls are: Archaeology and Women's Lives in Ancient Israel," in Between Text and Artifact: Integrating Archaeology in Biblical Studies Teaching, Archaeology and Biblical Studies, No. 8. Edited by M. C. Moreland, pp. 31–53. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature. Middleton, W., and T. D. Price. 1996. Identification of Activity Areas by Multi–Element Characterization of Sediments from Modern and Archaeological House Floors Using Inductively Coupled Plasma–Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. Journal of Archaeological Science 23:673–687. Millard, A. R. 1988. The Beveled–Rim Bowls: Their Purpose and Significance. Iraq 50:49–57. Minnis, P. E. 1981. Seeds in Archaeological Sites: Sources and Some Interpretive Problems. AA 46:143–152. Miroschedji, P. 1999. De la Mésopotamie Urukéenne à l’Égypte Prédynastique: Commentaire sur les Articles de G. Stein et al. et de B. Helwing. Paléorient 25:159–65. Monchambert, J.–Y. 1985. Mashnaqa 1985. Rapport Préliminaire sur la 1re Campagne de Fouilles. Syria 62:219–250. Monchambert, J.–Y. 1987. Mashnaqa 1986. Rapport Préliminaire sur la Deuxième Campagne de Fouilles. Syria 64:47–78. Moore, H. 1988. Feminism and Anthropology. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. Moorey, P. R. S. 1987. “On Tracking Cultural Transfers in Perhistory: the Case of Egypt and Lower Mesopotamia in the Fourth Millennium BC,” in Centre and Periphery in the Ancient World. Edited by M. Rowlands, M. Larsen, and K. Kristiansen. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Moorey, P. R. S. 1994. Ancient Mesopotamian Materials and Industries: The Archaeological Evidence. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Moorey, P. R. S. 2003. Idols of the People: Miniature Images of Clay in the Ancient Near East. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Morris, J. 2004. “ “Agency” Theory Applied: A Study of Later Prehistoric Lithic Assemblages from Northwest Pakistan,” in Agency Uncovered: Archaeological Perspectives on Social Agency, Power, and Being Human. Edited by A. Gardner, pp. 51–64. London: UCL Press. Murdock, G. P. 1949. Social Structure. New York: Macmillan. 399 Needler, W. 1984. Predynastic and Archaic Egypt in the Brooklyn Museum. Brooklyn: Brooklyn Museum. Nesbitt, M. 1995. “Recovery of Archaeological Plant Remains at Kaman–Kalehoyuk,” in Essays on Ancient Anatolia and its Surrounding Civilizations. Bulletin of the Middle East Culture Centre in Japan, Vol. 8. Edited by H. I. H. P. T. Mikasa. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. Nesbitt, M., and D. Samuel. 1989. The Recovery of Ancient Botanical Remains from Near Eastern Excavations: a Practical Guide. Ankara: British Institute of Archaeology. Netting, R. M. 1993. Smallholders, Householders: Farm Families and the Ecology of Intensive, Sustainable Agriculture. Stanford: Stanford University Press. Netting, R. M., R. R. Wilk, and E. J. Arnould. 1984. “Introduction,” in Households: Comparative and Historical Studies of the Domestic Group. Edited by R. M. Netting, R. R. Wilk, and E. J. Arnould, pp. xiii–xxxviii. Berkeley: University of California Press. Newcomer, M. H., and G. d. G. Sieveking. 1980. Experimental Flake Scatter–Patterns: a New Interpretative Technique. Journal of Field Archaeology 7:345–352. Nielsen, A. E. 1991. Trampling the Archaeological Record: An Experimental Study. AA 56:483–503. Nilhamn, B. 2002. Tokens of Identity? Small Clay Objects in near Eastern Archaeology. Swedish Seminar Papers in Archeology. Uppsala: Uppsala University. Nishiaki, Y. 1999. “Tell Kosak Shamali: Preliminary Report of the Excavations (1994– 1997),” in Archaeology of the Upper Syrian Euphrates: The Tishrin Dam Area. Edited by G. del Olmo Lete and J.–L. Montero Fenollós, pp. 71–82. Barcelona: Institut del Pròxim Orient Antic, Universitat de Barcelona. Nishiaki, Y., T. Koizumi, M. le Mière, and T. Oguchi. 2000. Prehistoric Occupations at Tell Kosak Shamali, the Upper Euphrates, Syria. Akkadica 113:13–68. Nissen, H. J. 1968. Survey of an Abandoned Modern Village in Southern Iraq. Sumer 24:107–114. Nissen, H.J. 1970. Grabung in den Qadraten K/L XII in Uruk–Warka. Baghdader Mitteilungen 5: 137. Nissen, H. J. 1986. The Archaic Texts from Uruk. World Archaeology 17:317–334. Nissen, H. J. 1988. The Early History of the Ancient Near East 9000–2000 BC. Chicago: University of Chicago. 400 Nissen, H. J. 2001. “Cultural and Political Networks in the Ancient Near East during the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C.,” in UMN, pp. 149–179. Santa Fe: School of American Research. Nissen, H. J. 2002. “Uruk: Key Site of the Period and Key Site of the Problem,” in AC, pp. 1–16. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Nissen, H. J., P. Damerow, and R. K. Englund. 1993. Archaic Bookkeeping: Writing and Techniques of Economic Administration in the Ancient Near East. Chicago: Chicago University Press. Nöldeke, A. 1932. IV. UVB. Berlin: Gebr. Mann Verlag. Nunn, A. 1985. Die Wandmalereifragmente aus Uruk–Warka. Baghdader Mitteilungen 16: 7–16. Oates, D. 1977. The Excavations at Tell Brak, 1976. Iraq 39:233–244. Oates, D. 1982a. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1978–81. Iraq 44:187–204. Oates, D. 1982b. “Tell Brak,” in Fifty Years’ of Mesopotamian Discovery: The Work of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq, 1932–1982. Edited by J. Curtis, pp. 62– 71. London: British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Oates, D. 1985. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1983–84. Iraq 47:159–173. Oates, D. 1987. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1985–86. Iraq 49:175–191. Oates, D., and J. Oates. 1989. Akkadian Buildings at Tell Brak. Iraq 51:193–211. Oates, D., and J. Oates. 1991. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1990–1991. Iraq 53:127–145. Oates, D., and J. Oates. 1993a. Excavations at Tell Brak, 1992–1993. Iraq 55:155–199. Oates, D., and J. Oates. 1993b. Excavations at Tell Brak, Syria. Cambridge Archaeological Journal 3:137–140. Oates, D., and J. Oates. 1994. Tell Brak: a Stratigraphic Summary, 1976–1993. Iraq 56:167–176. Oates, D., J. Oates, and H. McDonald. 1997. Excavations at Tell Brak: The Mitanni and Old Babylonian Periods. Vol. 1. McDonald Institute Monographs. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and British School of Archaeology in Iraq. 401 Oates, D., J. Oates, and H. McDonald. 2001. Excavations at Tell Brak: Nagar in the Third Millennium. Vol. 2. McDonald Institute Monographs. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Oates, J. 1985. Tell Brak: Uruk Pottery from the 1984 Season. Iraq 47:175–186. Oates, J. 1986. “Tell Brak: The Uruk/Early Dynastic Sequence,” in Ğamdat Nasr: Period or Regional Style?: Papers given at a symposium held in Tübingen, November 1983. Edited by U. Finkbeiner and W. Röllig, pp. 245–273. Wiesbaden: Dr. Ludwig Reichert. Oates, J. 1993. Trade and Power in the Fifth and Fourth Millennia BC: New Evidence from Northern Mesopotamia. World Archaeology 24:403–422. Oates, J. 2002. “Tell Brak: The 4th Millennium Sequence and Its Implications," in AC, pp. 111–122. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Oates, J., and D. Oates. 1997. An Open Gate: Cities of the Fourth Millennium BC (Tell Brak 1997). Cambridge Archaeological Journal 7:287–296. Oates, J., and D. Oates. 2004. “The Role of Exchange Relations in the Origins of Mesopotamian Civilizations,” in Explaining Social Change: Studies in Honour of Colin Renfrew. Edited by J. Cherry, C. Scarre, and S. Shennan, pp. 177–192. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research. Ökse, A. T. 1999. “Salat Tepe: Research in 1998,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 1998. Edited by N. Tuna and J. Öztürk, pp. 345–361. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Ökse, A. T. 2002. “Excavations at Gre Virike in 2000,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2000. Edited by N. Tuna and J. Velibeyoglu, pp. 270–285. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Ökse, A. T. 2004. “2001 Rescue Excavations at Salat Tepe,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 603–640. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Ökse, A. T., A. O. Alp, H. U. Dağ, A. Engin, A. Görmüş, and G. Mustafaoğlu. 2001. “Salat Tepe–1999 Survey,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 1999. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 620–642. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Ökse, A. T., and A. O. Alp. 2002. “2000 Excavation at Salat Tepe,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2000. Edited by N. Tuna and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 662–687. Anakara: Middle East Technical University. 402 Oppenheim, A. L. 1977. Ancient Mesopotamia: Portrait of a Dead Civilization. Second Edition. Chicago: University of Chicago. Özbal, H., A. M. Adriaens, and B. Earl. 1999. Hacınebi Metal Production and Exchange. Paléorient 25:57–65. Özbal, R. 2006. Households, Daily Practice, and Cultural Appropriation at Sixth Millennium Tell Kurdu. Doctoral Dissertation, Northwestern University. Özbal, R., F. Gerritsen, B. Diebold, E. Healey, N. Aydin, M. Loyet, F. Nardulli, D. Reese, H. Ekstrom, S. Sholts, N. Mekel–Bobrov, and B. Lahn. 2004. Tell Kurdu Excavations 2001. Anatolica 30:37–108. Özdoğan, M. 1977. Lower Euphrates Basin 1977 Survey. Lower Euphrates Publications, Series 1, No. 2. Istanbul: Middle East Technical University. Özgüç, N. 1987. Samsat Muhurleri. Belleten 51(2):429–440. Özgüç, N. 1988. Samsat Kazilari, 1987. Belleten 52:291–294. Özgüç, N. 1992. “The Uruk Culture at Samsat,” in Von Uruk nach Tuttul, Eine Festschrift für Eva Strommenger: Studien und Aufsätze von Kollegen und Freunden. Edited by B. Hrouda, S. Kroll, and P. Z. Spanos, pp. 151–157. Munich: Profil. Özgüç, N. 1993. “An Early Bronze Age Pot Grave of a Child from Acemhöyük,” in Between the Rivers and over the Mountains: Archaeologica Anatolica Et Mesopotamica Alba Palmieri Dedicata. Edited by M. Frangipane, H. Hauptmann, M. Liverani, P. Matthiae, and M. Mellink, pp. 517–520. Rome: Dipartimento di Scienze Storiche Archaeologiche e Antropologiche dell'Antichità, Università di Roma, “La Sapienza.” Özten, A. 1984. Two Pots Recovered in the Excavations at Samsat Belonging to the Late Chalcolithic Period. Anadolu 20:267–271. Palmieri, A. 1977. The 1973 and 1975 Campaigns at Arslantepe (Malatya). Turk Arkeoloji Dergisi 24:123–132. Palmieri, A. 1981. Excavations at Arslantepe (Malatya). Anatolian Studies XXXI:101– 119. 403 Palmieri, A., K. Sertok, and E. Chernykh. 1993. “From Arslantepe Metalworks to Arsenical Copper Technology in Eastern Anatolia,” in Between the Rivers and over the Mountains: Archaeologica Anatolica Et Mesopotamica Alba Palmieri Dedicata. Edited by M. Frangipane, H. Hauptmann, M. Liverani, P. Matthiae, and M. Mellink, pp. 573–599. Rome: Dipartimento di Scienze Storiche Archaeologiche e Antropologiche dell'Antichità, Università di Roma, “La Sapienza.” Parker, B. J. 2001. The Mechanics of Empire: The Northern Frontier of Assyria as a Case Study in Imperial Dynamics. Helsinki: Neo–Assyrian Text Corpus Project. Parker, B. J., A. Creekmore, E. Moseman, and R. Sasaki. 2002a. “The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): Preliminary Report from the Year 2000 Excavations at Kenan Tepe,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2000. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 613–643. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Parker, B. J., A. Creekmore, L. S. Dodd, E. Moseman, M. Abraham, and J. Schnereger. 2002b. “The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP) Year 2000 Excavations at Kenan Tepe,” in 23. Kazi Sonuçlari Toplantisi, pp. 435–445. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanligi Anitlar ve Müzeler Genal Müdürlügü. Parker, B. J., A. Creekmore, L. S. Dodd, C. Meegan, E. Moseman, R. Paine, M. Abraham, and P. Cobb. 2003. The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): A Preliminary Report from the 2001 Field Season. Anatolica 29:103– 174. Parker, B. J., A. Creekmore, L. S. Dodd, E. Moseman, C. Meegan, and P. Cobb. 2004. “The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): A Preliminary Synthesis of the Cultural History of Kenan Tepe,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 547–602. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Parker, B. J., L. S. Dodd, A. Creekmore, E. Healey, R. Paine, E. Moseman, and M. Marley. 2005. The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project: A Preliminary Report from the 2002 Field Season. Anatolica 31:69–89. Parker, B. J., L. S. Dodd, A. Creekmore, E. Healey, and C. Painter. 2006. The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): A Preliminary Report from the 2003 and 2004 Field Seasons at Kenan Tepe. Anatolica 32:72–151. Parker, B. J., C. P. Foster, J. Henecke, M. Hopwood, D. Hopwood, A. Creekmore, A. Demirergi, and M. Eppihimer. 2008. A Preliminary Report from the 2005 and 2006 Field Seasons at Kenan Tepe. Anatolica 34:103–176. 404 Parker, B. J., C. P. Foster, K. Nicoll, J. R. Kennedy, P. Graham, A. Smith, D. E. Hopwood, M. Hopwood, K. Butler, E. Healey, M. B. Uzel, and R. Jensen. Forthcoming. The Upper Tigris Archaeological Research Project (UTARP): A Preliminary Report from the 2007 and 2008 Field Seasons at Kenan Tepe. Anatolica 35. Parker, B. J., and C. P. Foster. Forthcoming. “An Overview of the Ceramic Sequence at Kenan Tepe,” in Studies in Honour of Altan Çilingiroğlu. Edited by Z. Derin, H. Sağlamtimur, and E. Abay. Istanbul: Arkeoloji ve Sanat Yayinlari. Parker, B. J., and M. B. Uzel. 2007. “The Tradition of Tandır Cooking in Southeastern Anatolia: An Ethnoarchaeological Perspective,” in Ethnoarchaeological Investigations in Rural Anatolia. Vol. 4. Edited by T. Takaoğlu, pp. 7–43. Istanbul: Ege Yayınları. Paynter, R. 1981. “Social Complexity in Peripheries: Problems and Models,” in Archaeological Approaches to the Study of Complexity. Edited by S. E. van der Leeuw, pp. 118–143. Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam. Pearce, J. 2000. Investigating Ethnicity at Hacınebi: Ceramic Perspectives on Style and Behavior in 4th Millennium Mesopotamian– Anatolian Interaction. Paléorient 25:35–42. Peltenburg, E. 1999. “Tell Jerablus Tahtani 1992–1996: A Summary,” in Archaeology of the Upper Syrian Euphrates: The Tishrin Dam Area. Proceedings of the International Symposium Held in Barcelona, January 28th–30th, 1998. Edited by G. Del Olmo Lete and J.–L. Montero Fenollos, pp. 97–105. Barcelona: AUSA. Peltenburg, E., D. Bolger, S. Campbell, M. A. Murray, and R. Tipping. 1996. Jerablus Tahtani, Syria 1995: Preliminary Report. Levant 28:1–25. Peltenburg, E., S. Campbell, P. Croft, D. Lunt, M. A. Murray, and M. E. Watt. 1995. Jerablus–Tahtani, Syria, 1992–4: Preliminary Report. Levant 27:1–28. Peltenburg, E., S. Campbell, S. Carter, F. M. K. Stephen, and R. Tipping. 1997. Jerablus– Tahtani, Syria, 1996: Preliminary Report. Levant 29:1–18. Peltenburg, E., E. Eastaugh, M. Hewson, A. Jackson, A. McCarthy, and T. Rymer. 2000. Jerablus Tahtani, Syria, 1998–9: Preliminary Report. Levant 32:53–75. Perkins, A. L. 1963. The Comparative Archeology of Early Mesopotamia, Fourth edition. Studies in Ancient Oriental Civilization #25. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. 405 Pfälzner, P. 1990. “Tell Bderi: The Development of a Bronze Age Town,” in The Near East in Antiquity I. Edited by S. Kerner, pp. 63–80. Amman: Goethe–Institut, Al Kutba. Pfälzner, P. 1996. “Activity and the Social Organization of Third Millennium B.C. Households," in Houses and Households in Ancient Mesopotamia. Papers read at the 40e Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Leiden, July 5–8, 1993. Edited by K. R. Veenhof, pp. 117–128. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archaeologisch Instituut. Philip, G. 2002. “Contacts Between the “Uruk” World and the Levant During the Fourth Millennium BC: Evidence and Interpretation,” in AC, pp. 207–236. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Pittman, H. 1996. “Constructing Context: The Gebel el–Arak Knife. Greater Mesopotamian and Egyptian Interaction in the Late Fourth Millennium BCE,” in The Study of the Ancient Near East in the Twenty–First Century: The William Foxwell Albright Centennial Conference. Edited by J. S. Cooper and G. M. Schwartz, pp. 9–32. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns. Pittman, H. 1999. Administrative Evidence from Hacınebi Tepe: An Essay on the Local and the Colonial. Paléorient 25:43–50. Pittman, H. 2001. “Mesopotamian Intraregional Relations Reflected through Glyptic Evidence in the Late Chalcolithic 1–5 Periods,” in UMN, pp. 403–444. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Pittman, H. 2002. “Bears at Brak,” in Of Pots and Plans: Papers on the Archaeology and History of Mesopotamia and Syria Presented to David Oates in Honour of His 75th birthday. Edited by L. A.–G. Werr, J. Curtis, H. Martin, A. McMahon, J. Oates, and J. Reade, pp. 287–96. London: Nabu Publications. Polanyi, K. 1944. The Great Transformation. New York: Farrar & Rinehart. Pollock, S. 1987. Abu Salabikh, the Uruk Mound 1985–86. Iraq 49:121–141. Pollock, S. 1989. “Power Politics in the Susa A Period,” in Upon this Foundation – The 'Ubaid Reconsidered. Proceedings from the 'Ubaid Symposium Elsinore May 30th – June 1st 1988. Edited by E. F. Henrickson and I. Thuesen, pp. 281–292. Copenhagen: Carsten Niebuhr Institute of Ancient Near East Studies, University of Copenhagen : Museum Tusculanum Press. Pollock, S. 1990a. Archaeological Investigations on the Uruk Mound, Abu Salabikh, Iraq. Iraq 52:85–93. 406 Pollock, S. 1990b. Political Economy as Viewed from the Garbage Dump: Jemdet Nasr Occupation at the Uruk Mound, Abu Salabikh. Paléorient 16:57–75. Pollock, S. 1992. Bureaucrats and Managers, Peasants, Imperialists and Traders: Research on the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr Periods in Mesopotamia. Journal of World Prehistory 6:297–336. Pollock, S. 1999. Ancient Mesopotamia: The Eden That Never Was. Cambridge: Cmabridge University Press. Pollock, S. 2001. “The Uruk Period in Southern Mesopotamia,” in UMN, pp. 181–233. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Pollock, S., C. Steele, and M. Pope. 1991. Investigations on the Uruk Mound, Abu Salabikh, Iraq. Iraq 53:59–68. Pollock, S., and C. Coursey. 1995. Ceramics from Hacınebi Tepe: Chronology and Connections. Anatolica XXI:101–141. Pollock, S., M. Pope, and C. Coursey. 1996. Household Production at the Uruk Mound, Abu Salabikh, Iraq. American Journal of Archaeology 100:683–698. Pope, M. 1994. Mississippian Microtools and Uruk Blades: A Comparative Study of Chipped Stone Production, Use, and Economic Organization. Lithic Technology 19:128–145. Porada, E. 1965. “The Relative Chronology of Mesopotamia. Part I. Seals and Trade (6,000–1,600 B.C.),” in Chronologies in Old World Archaeology. Edited by R. Ehrich, pp. 133–181. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Postgate, J. N. 1977. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1976. Iraq 39:269–299. Postgate, J. N. 1978. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1977. Iraq 40:77–87. Postgate, J. N. 1980. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1978–1979. Iraq 42:87–104. Postgate, J. N. 1983. Abu Salabikh Excavations, Vol. 1. The West Mound Surface Clearance. London: British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Postgate, J. N. 1990. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1988–1989. Iraq 52:95–106. Postgate, J. N. Editor. 2002. Artefacts of Complexity: Tracking the Uruk in the Near East. Iraq Archaeological Reports 5. Baghdad: British School of Archaeology in Iraq. Postgate, J. N., and J. Moon. 1982. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1981. Iraq 44:103–136. 407 Postgate, J. N., and P. R. S. Moorey. 1976. Excavations at Abu Salabikh, 1975. Iraq 38:133–169. Potts, D. T. 1999. The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Potts, D. T. 2004. The Uruk Explosion: More Heat Than Light? Review of Archaeology 25:19–29. Pyburn, K. A. 1998. Smallholders in the Maya Lowlands: Homage to a Garden Variety Ethnographer. Human Ecology 26:267–286. Raheel, M. 1994. “History, Identification, and Characterization of Old World Fibers and Dyes,” in Ancient Technologies and Archaeological Materials. Edited by S. U. Wisseman and W. S. Williams, pp. 121–156. Langhorne: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers. Rainville, L. 2000. Microdebris Analysis in Early Bronze Age Mesopotamian Households. Antiquity 74:291–292. Rainville, L. 2005. Investigating Upper Mesopotamian Households using Micro– Archaeological Techniques. BAR International Series 1368. Oxford: Archaeopress. Rapoport, A. 1969. House Form and Culture. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice–Hall. Rapoport, A. 1986. “Culture and Built Form – A Reconsideration,” in Architecture in Cultural Change: Essays in Built Form and Culture Research. Edited by D. G. Saile, pp. 159–160. Lawrence: School of Architecture and Urban Design, University of Kansas. Reade, J. 1992. “An Early Warka Tablet,” in Von Uruk Nach Tuttul, Eine Festschrift Für Eva Strommenger: Studien Und Aufsatze Von Kollegen Und Freunden. Edited by B. Hrouda, S. Kroll, and P. Z. Spanos, pp. 177–179. Munich: Profil Verlag. Redding, R. W. 1981. “The Faunal Remains,” in An Early Town on the Deh Luran Plain: Excavations at Tepe Farukhabad. Edited by H. T. Wright, pp. 233–261. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Museum. Redman, C. 1987. Surface Collection, Sampling, and Research Design: A Retrospective. AA 52:249–265. Reichel, C. 2002. Administrative Complexity in Syria during the 4th Millennium B.C.— the Seals and Sealings from Tell Hamoukar. Akkadica 123:35–56. Reimer, S. 1989. Tell Qraya on the Middle Euphrates. Paléorient 15:284. 408 Renfrew, C. 1986. "Introduction: Peer Polity Interaction and Socio–Political Change," in Peer Polity Interaction and Socio–Political Change. Edited by C. Renfrew and J. F. Cherry, pp. 1–18. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Roaf, M. Editor.1984. Tell Madhhur: A Summary Report on the Excavation. Sumer 43:108–167. Roaf, M. 1989. “Social Organization and Social Activities at Tell Madhhur,” in Upon This Foundation–the 'Ubaid Reconsidered. Edited by E. F. Henrickson and I. Thuesen, pp. 91–146. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press. Roberts, N., and H. E. Wright, Jr. 1993. “Vegetational, Lake–Level, and Climatic History of the Near East and Southwest Asia,” in Global Climates since the Last Glacial Maximum. Edited by H. E. Wright, Jr., J. E. Kutzbach, T. Webb III, W. F. Ruddiman, F. A. Street–Perrott, and P. J. Bartlein, pp. 194–220. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. Rodman, M. C. 1992. Empowering Place: Multilocality and Multivacality. American Anthropologist 94:640–656. Röllig, W., and H. Kühne. 1977–78. The Lower Habur. A Preliminary Report on a Survey Conducted by the Tübinger Atlas des Vorderen Orients in 1975. Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 27–28:115–140. Rosen, A. M. 1986. Cities of Clay: The Geoarcheology of Tells. Prehistoric Archeology and Ecology Series. Chicago: University of Chigaco Press. Rosen, A. M. 1989. Ancient Town and City Sites: A View From the Microscope. AA 54:564–578. Rosen, A. M. 1991. “BA” Guide to Artifacts: Microartifacts and the Study of Ancient Societies. The Biblical Archaeologist 54:97–103. Rosen, A. M. 1992. “Preliminary Identification of Silica Skeletons from Near Eastern Archaeological Sites: An Anatomic Approach,” in Phytolith Systematics: Emerging Issues. Edited by G. Rapp Jr. and S. C. Mulholland, pp. 129–147. New York: Plenum Press. Rosen, A. M. 1993. “Microartifacts as a Reflection of Cultural Factors in Site Formation,” in Formation Processes in Archaeological Context. Edited by P. Goldberg, D. T. Nash, and M. D. Petraglia, pp. 141–148. Madison: Prehistory Press. Rosen, A. M. 2007. Civilizing Climate: Social Responses to Climate Change in the Ancient Near East. Plymouth: Altamira Press. 409 Rosen, S. A. 1997. Lithics After the Stone Age: A Handbook of Stone Tools from the Levant. Walnut Creek: AltaMira Press. Rosenberg, M., and H. Togul. 1991. The Batmen River Archaeological Site Survey, 1990. Anatolica 17:241–254. Rothman, M. S. 1988. Centralization, Administration, and Function at Fourth Millennium B.C. Tepe Gawra, Northern Iraq. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Pennsylvania. Rothman, M. S. 1993. “Another Look at the Uruk Expansion from the Tigris Piedmont,” in Between the Rivers and over the Mountains: Archaeologica Anatolica Et Mesopotamica Alba Palmieri Dedicata. Edited by M. Frangipane, H. Hauptmann, M. Liverani, P. Matthiae, and M. Mellink. Rome: Dipartimento di Scienze Storiche Archaeologiche e Antropologiche dell'Antichità, Università di Roma, "La Sapienza". Rothman, M. S. 2001. “The Local and the Regional: An Introduction,” in UMN, pp. 3– 26. Santa Fe: School of American Research Press. Rothman, M. S. 2002. Tepe Gawra: The Evolution of a Small, Prehistoric Center in Northern Iraq. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum. Rothman, M. S. 2004. Studying the Development of Complex Society: Mesopotamia in the Late Fifth and Fourth Millennia BC. Journal of Archaeological Research 12:75–119. Rothman, M. S., and M. J. Blackman. 1990. “Monitoring Administrative Spheres of Action in Late Prehistoric Northern Mesopotamia with the Aid of Chemical Characterization (INAA) of Sealing Clays,” in Economy and Settlement in the Near East: Analyses of Ancient Sites and Materials. Edited by N. F. Miller, pp. 19–46. Philadelphia: MASCA, The University Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, University of Pennsylvania. Rova, E. 1999–2000. A Tentative Synchronisation of the Local Late Chalcolithic Ceramic Horizons of Northern Syro–Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia XXXIV– XXXV:175–201. Safar, F., M. A. Mustafa, and S. Lloyd. 1981. Eridu. Baghadad: Republic of Iraq, Ministry of Culture and Information and State Organization of Antiquities and Heritage. Saggs, H. W. F. 1965. Everyday Life in Babylonia and Assyria. New York: Dorset. Sahlins, M. 1972. Stone Age Economics. Chicago: Aldine. 410 Schachner, A. 2003. “2000–2001 Yılı Giricano Kazıları,” in 24. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı. Vol. 2, pp. 447–460. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanlığı Anıtlar ve Müzeler Genel Müdürlüğü. Schachner, A. 2004. “Vorbericht über die Ausgrabungen in Giricano, 2001,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 505–546. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Schachner, A., M. Roaf, K. Radner, and R. Pasternak. 2002. “Vorläufiger Bericht über die Ausgrabungen in Giricano,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2000. Edited by N. Tuna and J. Velibeyoglu, pp. 587–630. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Schiffer, M. B. 1972. Archeological Context and Systemic Context. AA 37:156–165. Schiffer, M. B. 1983. Toward the Identification of Formation Process. AA 48:675–707. Schiffer, M. B. 1987. Formation Processes of the Archaeological Record. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Schiffer, M. B., and W. L. Rathje. 1973. “Efficient Exploitation of the Archaeological Record: Penetrating Problems,” in Research and Theory in Current Archeology. Edited by C. Redman, pp. 169–179. New York: John Wiley and Sons. Schloen, J. D. 2001. The House of the Father as Fact and Symbol: Patrimonialism in Ugarit and the Ancient near East. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns. Schmandt–Besserat, D. 1992. Before Writing, Volumes I and II: From Counting to Cuneiform and A Catalogue of Near Eastern Tokens. Austin: University of Texas Press. Schwartz, G. M. 1988a. A Ceramic Chronology from Tell Leilan: Operation 1. Yale Tell Leilan Researc, Vol. 1. New Haven: Yale University Press. Schwartz, G. M. 1988b. Excavation at Karatut Mevkii and Perspectives on the Uruk/Jemdet Nasr Expansion. Akkadica 56:1–41. Schwartz, G. M. 2001. “Syria and the Uruk Expansion,” in UMN, pp. 233–264. Santa Fe: School of American Research. Schwartz, G. M., and S. E. Falconer. Editors. 1994. Archaeological Views from the Countryside: Village Communities in Early Complex Societies. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. 411 Schwartz, M., D. Hollander, and G. Stein. 1999. Reconstructing Mesopotamian Exchange Networks in the Fourth Millennium BC: Geochemical and Archaeological Analyses of Bitumen Artifacts from Hacınebi, Turkey. Paléorient 25:67–82. Seddon, D. 1976. “Aspects of Kinship and Family Structure among the Ulad Stut of Zaio Rural Commune, Nador Province, Morocco,” in Mediterranean Family Structures. Edited by J. G. Peristiany, pp. 173–194. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Serdaroğlu, Ü. Editor. 1977. 1975 Surveys in the Lower Euphrates Basin. METU Lower Euphrates Project Publications, Series 1, no. 1. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Sertok, K., and R. Ergeç. 1999. A New Early Bronze Age Cemetery: Excavations Near the Birecik Dam, Southestern Turkey, Preliminary Report (1997–98). Anatolica 25:87–107. Şenyurt, S. Y. 2002a. “2000 Excavations at Aşağı Salat,” in TAÇDAM: Activities in 2000. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Öztürk, and J. Velibeyoğlu, pp. 688–722. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Şenyurt, S. Y. 2002b. “Ilısu Barajı–Aşağı Salat 2000 Yılı Kazısı,” in 23. Kazı Sonuçları Toplantısı, vol. 2, pp. 445–452. Ankara: T.C. Kültür Bakanlığı Anıtlar ve Müzeler Genel Müdürlüğü. Şenyurt, S. Y. 2004. “2001 Excavations at Aşağı Salat,” in TAÇDAM Activities in 2001. Edited by N. Tuna, J. Greenhalgh, and J. Velibeyoglu, pp. 641–668. Ankara: Middle East Technical University. Sherwood, S. C., and S. D. Ousley. 1995. Quantifying Microartifacts Using a Personal Computer. Geoarchaeology 10:423–428. Sherwood, S. C., J. F. Simek, and R. R. Polhemus. 1995. Artifact Size and Spatial Process: Macro– and Microartifacts in a Mississippian House. Geoarchaeology 10:429–455. Simpson, K. 1988. Qraya Modular Reports, No. 1. Early Soundings. Syro–Mesopotamian Studies 4:3–44. Siracusano, G. 2002. “Animal Husbandry and Centralized Cultures: How Social and Political Factors Can Influence Rural Lifestyle,” in Behavior Behind Bones: The Zooarchaeology of Ritual, Religion, Status and Identiy. Edited by S. J. O'Day, W. van Neer, and A. Ervynck, pp. 190–197. Oxford: Oxbow Books. Speiser, E. A. 1935. Excavations at Tepe Gawra 1. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. 412 Spoor, R. H. and Collet, P. 1996. “The Other Small Finds,” in Tell Sabi Abyad – The Late Neolithic Settlement. Edited by P.M.M.G. Akkermans, pp. 439–473. Istanbul: Nederlands–Historisch Archaeologisch Instituut. Stanislawski, M. B. 1965. What Good is a Broken Pot? An Experiment in Hopi–Tewa Ethno–Archaeology. Southwestern Lore 31:11–18. Steadman, S. 1996. Isolation or Interaction: Prehistoric Cilicia and the Fourth Millennium Uruk Expansion. Journal of Mediterranean Archaeology 9:131–165. Stein, G. J. 1999a. Material Culture and Social Identity: The Evidence for a 4th Millennium BC Uruk Mesopotamian Colony at Hacınebi, Turkey. Paléorient 25:11–22. Stein, G. J. 1999b. Rethinking World Systems: Diasporas, Colonies, and Interaction in Uruk Mesopotamia. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. Stein, G. J. 2002a. From Passive Periphery to Active Agents: Emerging Perspectives in the Archaeology of Interregional Interaction. American Anthropologist 104:903– 916. Stein, G. J. 2002b. “The Uruk Expansion in Anatolia: a Mesopotamian Colony and Its Indigenous Host Community at Hacınebi, Turkey,” in AC, pp. 149–172. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Stein, G. J., R. Bernbeck, C. Coursey, A. McMahon, N. F. Miller, A. Misir, J. Nicola, H. Pittman, S. Pollock, and H. T. Wright. 1996a. Uruk Colonies and Anatolian Communities: an Interim Report on the 1992–1993 Excavations at Hacınebi, Turkey. American Journal of Archaeology 100:205–260. Stein, G., C. Edens, N. Miller, R. Ozbal, J. Pearce, and H. Pittman. 1996b. Hacınebi, Turkey: Preliminary Report on the 1995 Excavations. Anatolica 22:85–128. Stein, G., K. Boden, C. Edens, J. P. Edens, K. Keith, A. McMahon, and H. Ozbal. 1997. Excavations at Hacınebi, Turkey – 1996: Preliminary Report. Anatolica 23:111– 171. Stein, G. J., C. Edens, J. Pearce Edens, K. Boden, N. Laneri, H. Özbal, B. Earl, A. M. Adriaens, and H. Pittman. 1998. Southeast Anatolia Before the Uruk Expansion: Preliminary Report on the 1997 Excavations at Hacınebi, Turkey. Anatolica 24:143–194. 413 Stein, G. J., and P. Wattenmaker. 1990. “The 1987 Tell Leilan Regional Survey: Preliminary Report,” in Economy and Settlement in the Near East: Analyses of Ancient Sites and Materials. Edited by N. F. Miller, pp. 8–19. Philadelphia: MASCA, The University Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology, University of Pennsylvania. Stein, J. K., and P. A. Teltser. 1989. Size Distributions of Artifact Classes: Combining Macro– and Micro–Fractions. Geoarchaeology 4:1–30. Stephen, F. M. K., and E. Peltenburg. 2002. “Scientific Analyses of Uruk Ceramics from Jerablus Tahtani and Other Middle–Upper Euphrates Sites,” in AC, pp. 173–190. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Stevanovic, M. 1997. The Age of Clay: The Social Dynamics of House Destruction. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 16:334–395. Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 1998. “The BACH 1 Area,” in Çatalhöyük 1998 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1998/ar98_04.html> Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 1999. “The Excavation of the BACH 1 Area,” in Çatalhöyük 1999 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1999/ar99_05.html> Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 2000. “The Excavation of the BACH 1 Area,” in Çatalhöyük 2000 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/2000/ar00_04.html> Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 2001. “The Excavation of the BACH 1 Area, 2001,” in Çatalhöyük 2001 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/2001/ar01_03.html> Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 2002. “The Excavation of the BACH 1 Area 2002,” in Çatalhöyük 2002 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/2002/ar02_03.html> Stevanovic, M., and R. Tringham. 2003. “The Excavation of the BACH 1 Area 2003,” in Çatalhöyük 2003 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/2003/ar03_06.html> Stone, E. 1981. Texts, Architecture and Ethnographic Analogy: Patterns of Residence in Old Babylonian Nippur. Iraq 43:19–33. Stone, E. 1987. Nippur Neighborhoods. Chicago: Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago 414 Stone, E., and P. Zimansky. 2004. The Anatomy of a Mesopotamian City: Survey and Soundings at Mashkan–shapir. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns. Stordeur, D., C. Maréchal, and M. Molist. 1982. El Kowm 2–Caracol. Campagne 1978– 1979–1980. Stratigraphie et Architectures. Cahiers de l'Euphrate 3:33–49. Strommenger, E. 1964. 5000 Years of the Art of Mesopotamia. New York: H. N. Abrams. Strommenger, E. 1980. Habuba Kabira: eine Stadt vor 5000 Jahren, Ausgrabungen der Deutschen Orient–Gesellschaft am Euphrat in Habuba Kabira, Syrien. Mainz am Rhein: Verlag Philipp von Zabern. Strommenger, E. 1985. “Habuba Kabira South/Tell Qannas and Jebel Aruda,” in Ebla to Damascus: Art and Archaeology of Ancient Syria. Edited by H. Weiss, pp. 83–86. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Traveling Exhibition Service. Stronach, D. 1994. “Village to Metropolis: Nineveh and the Beginnings of Urbanism in Northern Mesopotamia,” in Nuovo Fondazione nel Vicino Oriente Antico: Realtà ed Ideologia. Edited by S. Mazzoni, pp. 85–108. Pisa: Giardini. Sürenhagen, D. 1974/5. Untersuchungen zur Keramikproduktion innerhalb der Spät– Urukzeitlichen Siedlung Habuba Kabira–Süd in Nordsyrien. Acta Praehistorica et Archaeologica 5/6:43–164. Sürenhagen, D. 1986. “The Dry–Farming Belt: The Uruk Period and Subsequent Developments,” in The Origins of Cities in Dyr–Farming Syria and Mesopotamia in the Third Millennium B.C. Edited by H. Weiss, pp. 7–43. Guilford: Four Quarters Publishing Co. Sweet, L. E. 1960. Tell Toqaan: A Syrian Village. Anthropological Papers. Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan. No. 14. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan. Szarzynska, K. 1988. Records of Garments and Cloths in Archaic Uruk/Warka. Altorientalische Forschungen 15:220–230. Taylor, J. E. 1855. Notes on Abu Shahrein and Tel al–Lahm. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society 15:404–415. Taylor, J. G. 1865. Travels in Kurdistan, with Notices of the Sources of the Eastern and Western Tigris, and Ancient Ruins in their Neighbourhood. Journal of the Royal Geographical Society XXXV:21–58. Teissier, B. 1987. Glyptic Evidence for a Connection between Iran, Syro–Palestine and Egypt in the Fourth and Third Millenia. Iran XXV:27–55. 415 Thuesen, I. 1988. Hama: Fouilles et Recherches 1931–1938. Vol. I: The Pre– and Protohistoric Periods. Copenhagen: Fondation Carlsberg. Thuesen, I. 1991. The Danish Archaeological Expedition to Tell Mashnaqa 1991. Orient Express 1991/2:11. Tobler, A. J. 1950. Excavations at Tepe Gawra 2. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum. Tolun, N. 1962. Türkiye Jeoloji Haritası: Geological Map of Turkey. Vol. 6: Diyarbakır. Ankara: Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü. Trigger, B. G. 1989. A History of Archaeological Thought. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Tringham, R. 1991. “Households with Faces: The Challenge of Gender in Prehistoric Architectural Remains,” in Engendering Archaeology: Women and Prehistory. Edited by J. M. Gero and M. H. Conkey, pp. 93–131. Oxford: Blackwell. Tringham, R. 1995. “Archaeological Houses, Households, Housework and the Home,” in Home: Words, Interpretations, Meanings and Environments. Edited by D. N. Benjamin, pp. 79–107. Aldershot: Avebury. Tringham, R. 1997. “BACH Area,” in Çatalhöyük 1997 Archive Report. Last accessed: 6 February 2008. <http://www.catalhoyuk.com/archive_reports/1997/ar97_06.html> Tringham, R. 2000. “The Continuous House: a View from the Deep Past,” in Beyond Kinship: Social and Material Reproduction in House Societies. Edited by R. A. Joyce and S. D. Gillespie. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. Tringham, R., B. Brukner, and B. Voytek. 1985. The Opovo Project: a Study of Socioeconomic Change in the Balkan Neolithic. Journal of Field Archaeoelogy 12:425–444. Tringham, R., B. Brukner, T. Kaiser, K. Borojevic, L. Bukvic, P. Steli, N. Russel, M. Stevanovic, and B. Voytek. 1992. Excavations at Opovo 1985–1987: Socioeconomic Change in the Balkan Neolithic. Journal of Field Archaeoelogy 19:351–386. Tsuneki, A., and Y. Miyake. 1998. Excavations at Tell Umm Qseir in the Middle Khabur Valley, North Syria. Tennodai: University of Tsukuba, Department of Archaeology. Ucko, P. 1968. Anthropomorphic Figurines of Predynatic Egypt and Neolithic Crete. London: Royal Anthropological Institute. 416 Ur, J. 2002a. Surface Collection and Offsite Studies at Tell Hamoukar, 1999. Iraq 64:15– 44. Ur, J. 2002b. Settlement and Landscape in Northern Mesopotamia: The Tell Hamoukar Survey 2000–2001. Akkadica 123:57–88. van den Driesch, A. 1993. “Faunal Remains from Habuba Kabira in Syria,” in Archaeozoology of the Near East. Edited by H. Buitenhuis and A. T. Clason, pp. 52–59. Leiden: Universal Book Services. van der Kooij, G. 2002. “Ethnoarchaeology in the Near East: Practice and Theory,” in Moving Matters: Ethnoarchaeology in the Near East. Proceedings of the International Seminar held in Cairo, 7–10 December 1998. Edited by W. Wendrich and G. van der Kooij, pp. 13–28. Leiden: Research School of Asian, African, and Amerindian Studies, Universiteit Leiden. van Driel, G. 1979. “The Uruk Settlement on Jebel Aruda: a Preliminary Report,” in Le Moyen Euphrate. Edited by J. Margueron, pp. 75–93. Leiden: Brill. van Driel, G. 1983. Seals and Sealings from Jebel Aruda, 1974–1978. Akkadica 33:34– 62. van Driel, G. 2002. “Jebel Aruda: Variations on a Late Uruk Domestic Theme,” in AC, pp. 191–206. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. van Driel, G., and C. van Driel–Murray. 1979. Jebel Aruda 1977–1978. Akkadica 12:2– 28. van Driel, G., and van Driel–Murray. 1983. Jebel Aruda, The 1982 Season of Excavation, Interim Report. Akkadica 33:1–26. van Loon, M. N. 1967. The Tabqa Reservoir Survey, 1964. Damascus: Directorate General of Antiquities and Museums. van Loon, M. N. 1971. “Korucutepe Excavations, 1969: Architecture and General Finds,” in METU: 1969 Activities, pp. 59–80. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. van Loon, M. N. 1973. The Excavations at Korucutepe, Turkey, 1968–70: Preliminary Report. JNES 32:357–423. van Loon, M. N. Editor. 1975. Korucutepe: Final Report on the Excavations of the Universities of Chicago, California (Los Angeles) and Amsterdam in the Keban Reservoir, Eastern Anatolia, 1968–1970, Volume 1. Amsterdam: North–Holland Publishers. 417 van Loon, M. N. 1982. Hammam et–Turkman on the Balikh: Background and First Results of the University of Amsterdam's 1981 Excavations. Akkadica 27:30–45. van Loon, M. N. 1983. Hammam et–Turkman on the Balikh: First Results of the University of Amsterdam's 1982 Excavation. Akkadica 35:1–23. van Loon, M. N. 1985. Hammam et–Turkman on the Balikh: First Results of the University of Amsterdam's 1984 Excavation. Akkadica 44:21–40. van Loon, M. N. Editor. 1988. Hammam et–Turkman. Report on the University of Amsterdam's 1981–84 Excavations in Syria. Vol. I and II. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archeologisch Instituut. van Loon, M., and G. Buccellati. 1970. “The University of Chicago—University of California Excavations at Korucutepe–1968,” in METU: 1968 Summer Work, pp. 89–114. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. van Loon, M., and H. G. Güterbock. 1972. “Korucutepe Excavations, 1970,” in METU: 1970 Activities, pp. 83–102. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. van Loon, M. N., and D. J. W. Meijer. 1982. Hammam et–Turkman on the Balikh: First Results. Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 33:131–152. van Loon, M. N., D. J. W. Meijer, and P. M. M. G. Akkermans. 1986/1987. Hammam et– Turkman and Sabi Abyad on the Balikh: The University of Amsterdam's 1986 Excavations. Annales Archéologiques Arabes Syriennes 36/37:309–324. van Zeist, W., and J. A. H. Bakker–Heeres. 1975. Evidence for Linseed Cultivation Before 6000 BC. Journal of Archaeological Science 2:215–219. van Zeist, W., and S. Bottema. 1982. “Vegetational history of the Eastern Mediterranean and the Near East During the Last 20,000 Years,” in Palaeoclimates, Palaeoenvironments and Human Communities in the Eastern Mediterranean Region in Later Prehistory. Vol. 2. Edited by J. L. Bintliff and W. van Zeist, pp. 277–321. Oxford: BAR International Series, 133. Veenhof, K. R. Editor. 1996. Houses and Households in Ancient Mesopotamia: Papers Read at the 40e Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Leiden, July 5–8, 1993. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archaeologisch Instituut te Istanbul. Verhoeven, M. 1999. An Archaeological Ethnography of a Neolithic Community : Space, Place and Social Relations in the Burnt Village at Tell Sabi Abyad, Syria. Istanbul: Nederlands Historisch–Archaeologisch Instituut te Instanbul. 418 Vértesalji, P. 1987. “The Chronology of the Chalcolithic in Mesopotamia (6200–3400 B.C.),” in Chronologies in the Near East. Edited by O. Aurenche, J. Evin, and F. Hours, pp. 483–509. Oxford: BAR International. Vértesalji, P. 1989. “Were there Supralocal Cemeteries in Southern Mesopotamia in Late Chalcolithic Times?,” in Upon this Foundation – the 'Ubaid Reconsidered. Proceedings from the 'Ubaid Symposium Elsinore May 30th – June 1st 1988. Edited by E. F. Henrickson and I. Thuesen, pp. 181–198. Copenhagen: Carsten Niebuhr Institute of Ancient Near East Studies, University of Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press. Vila, E. 1998. “Interpreting the Faunal Remains of El Kowm 2–Caracol (IVth Millennium BC, Syria),” in Archaeozoology of the Near East III. Edited by H. Buitenhuis, L. Bartosiewicz, and A. M. Choyke, pp. 120–129. Groningen: Centre for Archaeological Research and Consultancy. Villa, P. 1982. Conjoinable Pieces and Site Formation Processes. AA 47:276–290. Voigt, M. 1983. Hajji Firuz Tepe, Iran: The Neolithic Settlement. Philadelphia: University Museum. von der Way, T. 1992. “Excavations at Tell el–Fara'in/Buto in 1987–1989,” in The Nile Delta in Transition: 4th – 3rd Millennium B.C. Edited by E. C. M. van den Brink, pp. 1–10. Jerusalem: Israel Exploration Society. von Haller, A. 1931. Die Keramik der archaischen Schichten von Uruk. IV. UVB. Berlin: Ger. Mann Verlag Waetzoldt, H. 1972. Untersuchungen zur Neusumerischen Textilindustrie. Rome: Centro per le Antichità e la Storia dell’Arte del Vicino Oriente. Wallerstein, I. 1974. The Modern World System I. New York: Academic Press. Wallerstein, I. 1996. “World System Versus Worlds–Systems: A Critique,” in The World System: Five Hundred Years or Five Thousand? Edited by A. G. Frank and B. K. Gills, pp. 292–296. London and New York: Routledge. Watkins, T. 1990. The Origins of House and Home? World Archaeology 21:336–347. Watson, P. J. 1979. Archaeological Ethnology in Western Iran. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. Watson, P. J., and S. A. LeBlanc. 1990. Girikihacıyan: A Halafian Site in Southeastern Turkey. Los Angeles: Institute of Archaeology, University of California. 419 Wattenmaker, P. 1994a. “State Formation and the Organization of Domestic Craft Production at Third–Millennium B.C. Kurban Hoyuk, Southeast Turkey,” in Archaeological Views from the Countryside: Village Communities in Early Complex Societies. Edited by G. M. Schwartz and S. E. Falconer, pp. 109–120. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. Wattenmaker, P. 1994b. “Household Economy in Early State Society: Material Value, Productive Context and Spheres of Exchange,” in The Economic Anthropology of the State. Edited by E. M. Brumfiel, pp. 93–118. Lanham: University Press of America. Wattenmaker, P. 1998. Household and State in Upper Mesopotamia: Specialized Economy and the Social Uses of Goods in an Early Complex Society. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. Wattenmaker, P., and G. Stein. 1986. Early Pastoral Production in Southeast Anatolia: Faunal Remains from Kurban Hoyuk and Gritille Hoyuk. Anatolica 13:90–96. Weiss, H. 1983. Excavations at Tell Leilan and the Origins of North Mesopotamian Cities in the Third Millennium B.C. Paléorient 9:39–52. Weiss, H. C., and T. C. Young 1975. The Merchants of Susa: Godin V and Plateu– Lowland Relations in the Late Fourth Millennia. Iran 13:1–18. Wengrow, D. 2003. “Interpreting Animal Art in the Prehistoric Near East,” in Culture through Objects: Ancient near Eastern Studies in Honour of P.R.S. Moorey. Edited by T. Potts, M. Roaf, and D. Stein, pp. 139–160. Oxford: Griffith Institute. Whallon Jr., R. 1973. Spatial Analysis of Occupation Floors I: Application of Dimensional Analysis of Variance. AA 38:266–278. Whallon Jr., R. 1979. An Archaeological Survey of the Keban Reservoir Area of East– Central Turkey. Ann Arbor: Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan. Whallon Jr., R., and S. Kantman. 1970. “The Survey of the Keban Dam Reservoir,” in METU: 1968 Summer Work, pp. 7–21. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basımevi. Whiting, J. W. M., and B. Ayres. 1968. "Inferences from the Shape of Dwellings," in Settlement Archaeology. Edited by K. C. Chang, pp. 117–133. Palo Alto: National Press Books. Wilk, R. R. 1989. “Decision Making and Resource Flows within the Household: Beyond the Black Box,” in The Household Economy: Reconsidering the Domestic Mode of Production. Edited by R. R. Wilk, pp. 23–54. Boulder: Westview Press. 420 Wilk, R. R., and W. Ashmore. Editors. 1988. Household and Community in the Mesoamerican Past. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. Wilk, R. R., and R. M. Netting. 1984. “Households: Changing Forms and Functions,” in Households: Comparative and Historical Studies of the Domestic Group. Edited by R. M. Netting, R. R. Wilk, and E. J. Arnould, pp. 1–28. Berkeley: University of California Press. Wilk, R. R., and W. L. Rathje. 1982. Household Archaeology. American Behavioral Scientist 25:617–639. Wilkinson, T. A. H. 2002. “Uruk into Egypt: Imports and Imitations,” in AC, pp. 237– 248. Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press. Wilkinson, T. J. 1990a. Town and Country in Southeastern Anatolia: Settlement and Land Use at Kurban Hoyuk and Other Sites in the Lower Karababa Basin. Vol. 1. Chicago: Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. Wilkinson, T. J. 1990b. The Development of Settlement in the North Jazira Region between the 7th and 1st Millennia BC. Iraq 52:49–62. Williams, D. 1973. Flotation at Siraf. Antiquity 47:198–202. Wilson, K. L. 1986. “Nippur: The Definition of a Mesopotamian Gamdat Nasr Assemblage,” in Gamdat Nasr: Period or Regional Style?: Papers Given at a Symposium Held in Tübingen, November 1983. Edited by U. Finkbeiner and W. Röllig, pp. 57–89. Wiesbaden: Dr. Ludwig Reichert Verlag. Woolley, S. L. 1952. Carchemish: Report on the Excavations at Jerablus on Behalf of the British Museum. Vol. III: The Excavations in the Inner Town and the Hittite Inscriptions. London: British Museum Publications Limited. Woolley, S. L. 1955. Ur Excavations, Volume IV: The Early Periods. London and Philadelphia: British Museum and the Museum of the University of Pennsylvania. Wong, D. 1984. “The Limits of Using the Household as a Unit of Analysis," in Households and the World Economy. Edited by J. Smith, I. Wallerstein, and H.– D. Evers, pp. 56–63. Beverly Hills: Sage. Wright, H. T. 1972. “A Consideration of Interregional Exchange in Greater Mesopotamia, 4000–3000 B.C.," in Social Exchange and Interaction, vol. 46, Anthropological Papers: Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan. Edited by E. N. Wilmsen, pp. 95–105. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan. Wright, H. T. 1981. An Early Town on the Deh Luran Plain. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan. 421 Wright, H. T. 2001. “Cultural Action in the Uruk World,” in UMN, pp. 123–148. Santa Fe: School of American Research. Wright, H. T., and G. A. Johnson. 1975. Population, Exchange, and Early State Formation in Southwestern Iran. American Anthropologist 77:267–289. Wright, H. T., and G. A. Johnson. 1985. Regional Perspectives on Southwest Iranian State Development. Paléorient 11:25–30. Xenophon. 1998. Anabasis. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. Yakar, J. 2000. Ethnoarchaeology of Anatolia: Rural Socio–Economy in the Bronze and Iron Ages. Tel Aviv: Emery and Claire Yass Publications in Archaeology of the Institute of Archaeology, Tel Aviv University. Yamazaki, Y. 1999. “Excavations at Tell al–'Abr,” in Archaeology of the Upper Syrian Euphrates: The Tishrin Dam Area. Proceedings of the International Symposium Held in Barcelona, January 28th–30th, 1998. Edited by G. Del Olmo Lete and J.– L. Montero Fenollos, pp. 83–96. Barcelona: AUSA. Yanagisako, S. J. 1979. Family and Household: The Analysis of Domestic Groups. Annual Review of Anthropology 8:161–205. Yellen, J. E. 1977. Archaeological Approaches to the Present: Models for Reconstructing the Past. New York: Academic Press. Yener, K. A. 2000. The Domestication of Metals: The Rise of Complex Metal Industries in Anatolia. Leiden: Brill. Yener, K. A., C. Edens, J. Casana, B. Diebold, H. Ekstrom, M. Loyet, and R. Özbal. 2000. Tell Kurdu Excavations 1999. Anatolica 26:31–117. Yoffee, N. 1989. Review of Nippur Neighborhoods, by Elizabeth Stone (1987). American Anthropologist 91/3:786-787. Young, T. C. 1969. Excavations at Godin Tepe: First Progress Report. Toronto: Royal Ontario Museum. Young, T. C., and L. D. Levine. 1974. Excavations of the Godin Project: Second Progress Report. Toronto: Royal Ontario Museum. Zagarell, A. 1986. Trade, Women, Class and Society in Ancient Southwestern Asia. CA 27:415–430. Zeder, M. A. 1991. Feeding Cities: Specialized Animal Economy in the Ancient near East. Washington and London: Smithsonian Institution Press. 422 Zeder, M. A. 1998. Pigs and Emergent Complexity in the Ancient Near East. MASCA Research Papers in Science and Archaeology 15:99–122. Zimansky, P. 1993. Review of Before Writing. Volume I: From Counting to Cuneiform and Volume II. A Catalogue of Near Eastern Tokens, by Denise Schmandt– Besserat (1992). Journal of Field Archaeology 20:513–517. 423