Staphylococcus
advertisement
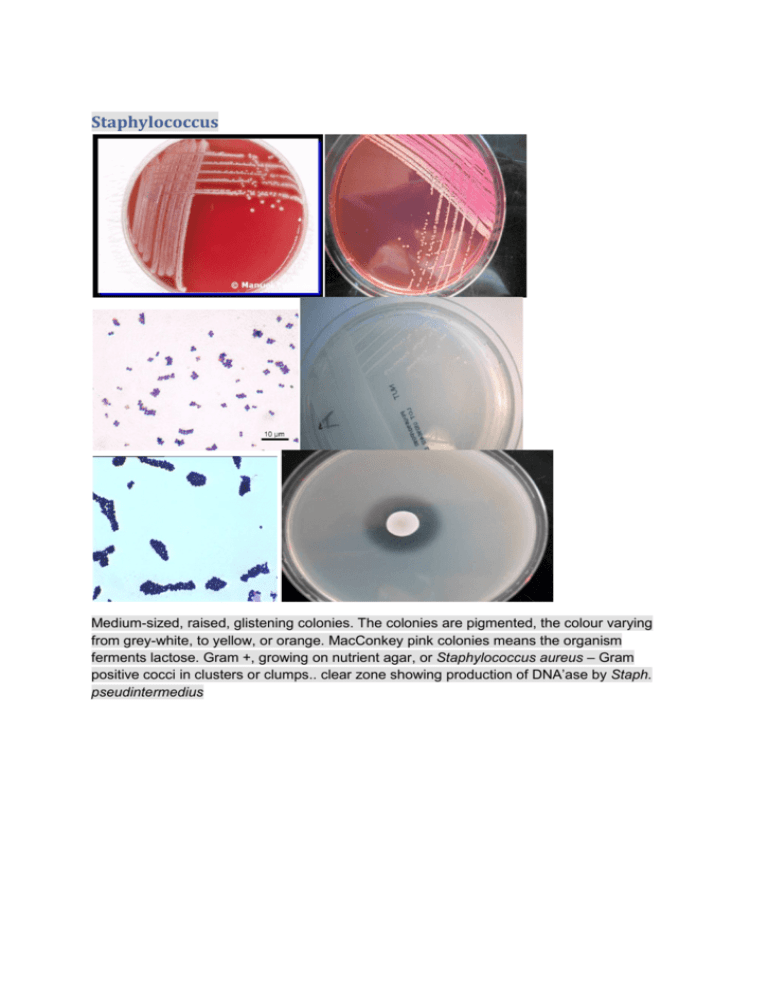
Staphylococcus Medium-sized, raised, glistening colonies. The colonies are pigmented, the colour varying from grey-white, to yellow, or orange. MacConkey pink colonies means the organism ferments lactose. Gram +, growing on nutrient agar, or Staphylococcus aureus – Gram positive cocci in clusters or clumps.. clear zone showing production of DNA’ase by Staph. pseudintermedius Streptococcus Gram-positive cocci. Catalase-negative. Attacks sugars by fermentation. Non-motile. Gram positive cocci in chains. MacConket negative (sensitive to bile salts). Alpha and beta haemolytic. Step. Uberis positive on Edwards medium ( produce aesculin Positive catalase test to differentiate Streptococci (-ve) from Staphylococci (+ve). DNA’ase test – pathogenic Staphylococci break down DNA in the medium because they have the enzyme DNA’ase (A) Staph epidermidis (-ve), (B) Staph. aureus (+ve), and (C), Staph pseudintermedius (+ve). Arcanobacterium pyogenes Gram-positive. Catalase-negative. Non-motile. Attacks sugars by fermentation, but the reaction is weak. Blood Agar plate which has been incubated with 5% carbondioxide for 24 hours. Small, grey-white, convex colonies.B haemolysis. Listeria monocytogenes Gram-positive rods. Catalase-positive. Attacks sugars fermentatively. Motile with characteristic slow, tumbling and rotary movements. Gram-positive short rodes with rounded ends. Some cells may be curved. Pinpoint to small, semi-transparent colonies. Clostridium perfringens Gram-positive, large, spore-forming rods. Spores are rarely seen as the sporulation process requires a pH around 7.5. Catalase-negative. Anaerobic, although requirements for anaerobiosis are not as strict as for many Clostridia. Non-motile. on blood agar grown anaerobically – note zones of Beta haemolysis colonial morphology varies considerably, sometimes even within the same culture. The colonies are small to medium sized and typically grey to grey-yellow and translucent. Some are smooth and dome-shaped with an entire margin, whilst others are rough with a lobate margin, still others are flat with an irregular surface and a filamentous margin. Large Gram positive rods Clostridium perfringens is non-proteolytic and is not associated with a distinct odour. sheep blood agar incubated anaerobically, - 2 colonial forms. Colony 1 = Gram negative rods – Escherichia coli grows anaerobically. Colony 2 = Large Gram positive rods – only grows on anaerobic plate = Clostridium species (Clostridium perfringens). Gram stain – Gram positive rods – Clostridium perfringens Gram negative: E.coli Medium-sized grey colonies. The colonies have a characteristic odour. Gram-negative rods. Catalase-positive and oxidase-negative. Attacks sugars by fermentation and gas is produced. Motile. Mesophilic. MacConkey pink (resistant) Gram-negative rods with parallel sides and rounded ends. Escherichia coli growing on nutrient agar. E. coli (C) grows on MacConkey with pink colonies (lactose fermenter) sheep blood agar incubated aerobically, Large grey colonies, circular, entire edged 3mm in diameter – Escherichia coli. Gram negative rods/coccobacilli – Escherichia coli. MacConkey agar. Large lactose fermenting colonies – Escherichia coli Salmonella: Gram-negative rods. Medium-sized, greyish colonies which cause no alteration of the blood. Catalase-positive and oxidase-negative. Attacks sugars by fermentation and gas is produced (Salmonella Gallinarum is anaerogenic and Salmonella Pullorum is variable). Motile with the exception of Salmonella Gallinarum and Salmonella Pullorum. Salmonella typhimurium growing on nutrient agar. S. typhimurium (D) grows on MacConkey with colourless colonies (non-lactose fermenter . Salmonella isolation - DCA plate (Desoxycholate Citrate Agar) – colonies grown from tetrathionate enrichment broth cultures. Black colonies are because of hydrogen sulphide production. Colonies are colourless because this organism is a non lactose fermenter on DCA. – Possible Salmonella species Actinobacillus Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae growing on Chocolate (heated blood) agar. A. pleuropneumoniae (B) does not grow on MacConkey. A. pleuropneumoniae (B) does not grow on Blood agar. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae – growing on blood agar in the presence of Staph. aureus producing NAD. A. pleuropneumoniae forms tiny colonies using the NAD provided by S. aureus as a growth factor. Gram-negative rods/coccobacilli Pasteurella multocida Gram negative cocci/coccobacilli Cat bite abscess. Plate 3A – sheep blood agar aerobic, - Pasteurella multocida. No growth MacConkey Mannheimia haemolytica blood agar – Beta haemolytic colonies. Gram negative cocco-bacilli Bordetella bronchiseptica Grow on MacConkey. Gram negative rods Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa on blood agar. The ‘holes’ in the initial inoculum is the lytic action of a bacteriophage killing the bacterial cells. Note the metallic sheen of the colonies. Pseudomonas aeruginosa sensitivity – this organism is naturally resistant to many antibiotics sheep blood agar – organism shows metallic glistening colonies with a characteristic smell. The organism is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. P. aeruginosa is normally resistant to many antibiotics and causes otitis externa in dogs. Confirm with an oxidase test. MacConkey agar. Pseudomonas aeruginosa – non lactose fermenting colonies. Gram stain – Gram negative rods – Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proteus mirabilis Gram-negative rods. Catalase-positive and oxidase-negative. Attacks sugars fermentatively and gas is produced. Motile. MacConkey agar. This organism is a non lactose fermenter and spread is inhibited on this medium. aeruginosa on MaConkey agar. This organism is a non lactose fermenter. Positive oxidase test. Negative control on the left (E. coli). Positive test on the right (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) Klebsiella Medium sized, grey colonies, which cause no alteration of the blood. Gram-negative short rods. Catalase-positive and oxidase-negative. Attacks sugars fermentatively and gas is produced. Non-motile. Mesophile. Note the large domed mucoid colonies. The colonies are large because this organism produces abundant capsular material. MacConkey agar. This organism is a lactose fermenter. Note the large domed mucoid colonies. The colonies are large because this organism produces abundant capsular material Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter jejuni growing on ‘Campylobacter selective agar’ after 48 hours incubation in a microaerophilic atmosphere. Colonies are moist and spreading. campylobacter jejuni growing on ‘Campylobacter selective agar’ after 48 hours incubation in a microaerophilic atmosphere. Colonies are moist and spreading. Gram negative spiral bacteria and ‘seagulls wings forms’. . Plate A – sheep blood agar, plate B, MacConkey agar, plate C, Campylobacter selective agar, plate D, sheep blood agar incubated anaerobically. Plates have been inoculated with faeces from a pig with diarrhoea. Campylobacter selective agar – grown for 48 hours in microaerophilic conditions – the organism is Campylobacter jejuni. Campylobacter jejuni – Gram negative spiral bacteria and ‘seagulls wings forms’ Bacteroides fragilis Growing on blood agar incubated anaerobically. Gram negative rods. Fusobacterium necrophorum growing anaerobically on blood agar. The organism shows target haemolysis = double zones of beta haemolysis. growing anaerobically on blood agar. The organism shows target haemolysis = double zones of beta haemolysis. pleomorphic Gram negative rods otitis externa in a dog. Pustular dermatitis in a dog. Plate 2A – sheep blood agar aerobic, 2B – MacConkey agar aerobic, 2C DNA’ase plate, 2D – sensitivity test Yeast: Microsporum canis Microsporum canis - Top surface - Sabarauds dextrose agar - White silky surface, yellow reverse showing through. Reverse surface - yellow reverse. hyphae and microconidia. hyphae and young macroconidia . hyphae and mature macroconidia. close up hyphae and macroconidia Candida albicans Candida albicans plate culture on Sabarauds dextrose agar. Gram positive oval budding yeast (Arrow = budding yeast) Malassezia pachydermatis Plate culture of Malassezia pachydermatis on Sabarauds dextrose agar. bottle shaped elongated yeasts Trichophyton mentagraphytes isolated from the skin of a dog with focal alopecia – soft cottony powdery texture on upper surface – Sabarauds dextrose agar – Trichophyton mentagraphytes. isolated from the skin of a dog with focal alopecia – soft cottony powdery texture on lower surface, yellow/orange colour – Sabarauds dextrose agar – Trichophyton mentagraphytes. Sabarauds dextrose agar – Trichophyton mentagraphytes. Lactophenol cotton blue prepn – club shaped and round microconidia along the sides of the hyphae . Trichophyton mentagraphytes Lactophenol cotton blue prepn –spiral hyphae . Trichophyton mentagraphytes .Lactophenol cotton blue prepn – cigar shaped macroconidia and round microconidia





