AP LAB 5: Cell Respiration
advertisement

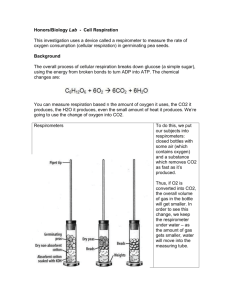
cAn0uilA Name/Group# Date StudentGuide AP' Biology Laboratory 5 Cell Respiration Objectives . Measurethe consumptionof oxygenby respiring seeds . Comparerespirationratesat two different temperatures Background Many cellularprocesses requireenergy.Aerobic cellularrespirationsupplies energyby the oxidation of glucose'This is a complexprocessinvolving a number of reactions;however,we can summarizethe processin termsof input ".ry-.--ediated output produ.tr'riil-, n ,r"ry simpleequation: "r-rJ C6Hr206+ 602 -+ 6CO, + 6HrO * enersy Introduction Youwill usea respirometerto measurethe rate of respirationof germinatingand nongerminatingpea seedsat two different temperatures.The respiromerer consisrsoia vial,hui.o.,ru-r-?h" p.u, u'd u volume of air' The mouth of the vial is sealel with a rubber t -hole sropperthat has a pipet inserted in it. The respirometeris submergedin water.If the peas nr" ,"rpi.i.rg, they will useoxygenand releasecarbon dioxide' since 1 mole of carbondioxide is released fo..u.h oro*ygen consumed,rhereis no changein the volume of gasin the respirometer.(Avogadro's -oi" Law: At constanttemperarureand pressure'I mole of any gashas the samevolume as 1 riole of any other gas.)you ,ltintt". thi, equilibriumby placinga-solution of potassiumhydroxide (KoH)'in the iiul. potrrri,,^ hydroxide reacts with carbondioxide to form potassiumcarbonate, which i, u soiid. CO, + Z KOH -+ KrCO, + H2O since the carbondioxide producedis removed by reactionwith potassiumhydroxide,asoxygen is used by cellularrespirationthe volume of gasin the respirom","r.,"iil?".rease.As the volume of gas decreases, water will move into th" pip"t. Youwill usethis decreaseof volume,asread from the scale printed on the pipet, as a measureof th. rat" of cellular;r;i;;;" 02 00 5 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y 5- 1 Measuring Respiration of Germinating and Nongerminating Peas Materials Room-temperaturewater bath, cold water bath, container of ice, paper (white or lined), water, germinating peas, nongerminating peas, glassbeads, respirometers, graduated tube, absorbent cotton balls, nonabsorbent cotton, 15olopotassium hydroxide (KOH) solution, dropping pipets, forceps, thermometers,stopwatch or timer or clock with second hand, calculators (optional). Procedure Setupof Respirometers andWaterBatlx You will use two water baths (uays of water) to buffer the respirometersagainst tenperature change and to provide two tenperatures for testing: room temperature and a colder temperature (approximately 10'C). Place a sheet of paper in the bottom of each water bath. This will make the graduated pipet easier to read. Next, place a thermometer in each tray. If necessary,add ice to the cold-temperature tray to further cool the water to get it as close to 10'C as possible.While waiting for the cold-water temperature to stabilize at 10'C, two of you should prepare three respirometers to test at room temperature, and two of you should prepare an identical set of three respirtlneters to test at the colder temperature. Preparing Peasand Gloss Beads You will need a set of peas and/or beadsfor testing at each temperature. Respirometer 1: Put 25 mL of H'O in your 50-mL graduated plastic tube. Drop in 25 germinaring peas. Determine the volume of water that is displaced (equivalent to the volume of peas). Record the volume of the 25 germinating peas. Remove these peas and place them on a paper towel. Respirometer 2: Refill the graduated tube to 25 rnl with HrO. Drop 25 dry, nongerminating peas into the graduated cylinder. Next, add enough glassbeads to equal the volume of the germinating peas. Remove the nongerminating peas and beads and place thern on a paper towel. Respirometer 3: Refill the graduated tube to 25 mL with of H2O. Add enough glassbeads to equal the volume of the germinating peas. Remove these beads and place them on a paper towel. Respirometer Assembly Youwill need three respirometers for room-temperaturetestingand three respirometers for coldtemperaturetesting. placean absorbentcotton ball in the bottom of eachrespirometervial. Use a To assemblea respirometer, withKOH. droppingpipet to saturatethe cotton with 2 mL of 15% KOH. (Caution: Auoidskincontctct uialsare dr1on the inside.Do notget KOH on the sidesof therespirometer.) Be certainthat the respirometer Placea smallwad of dry,nonabsorbentcotton on top of the KOH-soakedabsorbentcotton. The nonabsorbentcotton will prevent the KOH solution from contactingthe peas.It is important that the amountsof cotton and KOH soludonbe the samefor eachrespirometer. . Place25 germinatingpeasin your respirometer vial(s) 1. . vial(s)2. Place25 drypeasand beadsin your respirometer . Placebeadsonly in your respirometervial(s) 3. Insert a stopperfitted with a calibratedpipet into eachrespirometervial. The stoppermust fit tightly. If the respirometersleak during the experiment,you will have to start over. @2 00 5 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y 5-2 Placementof RespirometersinWater Baths Place a set of respirometers (1, 2, and 3) in each water bath with their pipet tips resting on one lip of the tray. See Figure 1. Vait five minutes before proceeding. This is to allow time for the respirometers to reach thermal equilibrium with the water. If any of the respirometers begins to fill with water, you have a leak and must start over. Figure 1. Respirometersin the water bath. After the equilibrationperiod,immerseall respirometers(includingpipet tips) in the water bath. Positionthe respirometers so that you can read the scaleson the pipets.The papershouldbe under the pipetsto make readingthem easier.Do not put anythingelseinto the water bath or take anythingout until all readingshave been completed. Tal<eReadings Allow the respirometersto equilibratefor another five minutes.Then, observethe initial volune reading on the scaleto the nearest0.01 mL. Recordthe data in Table 1 for Time O.Also, observeand record the temperature.Repeatyour observationsand record them everyfive minutesfor 20 minutes. Table 1: Respirationof Peasat Room Temperature Respirometer1 GerminatingPeas oc Time V of (Mi n ) Pipet Respirometer 2 Dry Peas+ Beads Vof AV Corrected Pipet AV Respirometer 3 BeadsOnly AV Corrected V o f AV Pipet AV 0 5 10 15 20 AV = V at Time0 - V attimeof currentre a d in g AV = AV (forResoirometer Corrected 1 o r Re s p iro me t 2e )r- A V o f Re s p iro me t 3 er O20 05 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y 9-3 Table 2: Respirationof Peasat Colder Temperature Respirometer1 GerminatingPeas oc 'l'ime V o f (Min) Pipet AV 2 Respirometer Dry Peas+ Beads Corrected V o f Pipet AV Respirometer 3 BeadsOnly Vof AV Gorrected AV Pipet AV 0 5 10 15 20 AV = V at Time0 - V at time of currentreading AV = AV (forRespirometer 1 or Respirometer 2l - LV of Respirometer Corrected 3 Analysis of Results: Measuring Respiration of Germinating and Nongerminating Peas Graphthe datafor respirometers 1 and2 fromyourgroup'stables.Tide the graphandsupplythe following information: a. The independent variable is b. The dependentvariableis Plot the independentvariableon the x-axis,and the dependentvariableon the y-axis.Labeleach plotted line. 1. Write two hypothesesthat this experimentis designedto test. 2. In this experiment,you measuredthe changein volume of the gasinsidethe respirometers. The generalgaslnw describesthe stateof a gasunder given conditions: pV: nRT where p : V : n : R: T : pressureofthe gas volume of the gas kmoles (numberof molecules)of gas (K)] universalgasconsrant[8314joules/(kmole) gas temperatureof the in K O2 OO5 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y 5-4 Since you have been measuring changes in volume, restate the general gas law to solve for volume: nRT \/ v- - _ D Using the generalgaslaw and your experiencein this lab, give the variablesthat had to be controlledfor your data to be valid. State the controlsusedfor eachvariableand any meansusedto correct for the influenceof a variable(s). (1,2, or 3) servesasa negativecontrol?Explainyour answer. 3. Which of the respirometers 4. In referenceto the generalgaslaw, and assumingyour conffol measuresworked,a changeto which of the variablesled to the observedchangein volume (CorrectedAV in Tables1 and 2) / Explain your answer. O2 00 5 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y 5-5 5. Using your graph and data tables,summarizeyour findings,comparingresultsfrom respirometers1 and2, and resultsobtainedat room temperaturevs. resultsat the colder temperature.Speculateas to the cause(s)of any differencesbetweenthe ffeatments. 6. From your graph, calculate the rate of oxygen consumption for each treatment: a. germinating seedsat room temperature : mL/min b. germinating seedsat colder temperature : c. dry seedsat room temperature: d. d.V seedsat colder temperature: @2 00 5 Car olina Biologic al Supply C o m p a n y mL/min mL/min mL/min 5-6 BlacklineMaster Analvsis of Results Name Date Graphthe resultsfrom the correcteddifferencecolumnforthe g€rminatingpeasand dry peasat both room temperatureand at 10'C. Placenme rn m,ftrtes on the x-axisand mL oxyge, consumedonthe y axis, No*h caro'inaz721s cardina Bi0l0gical$ullilU C0mDanU ffiil:ll,T?11",?""ns'1on, c8271540205