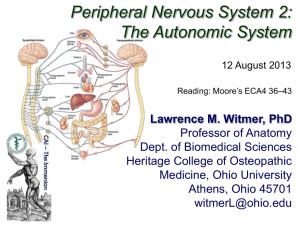
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Sensory Neurons
advertisement

The Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons y 解剖學科 江皓郁 Overview of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) General visceral motor (一般臟器運動) or General visceral efferent (一般臟器傳出) General visceral sense (一般臟器感覺)or General visceral afferent (一般臟器傳入) Comparison of somatic and autonomic nervous systems Somatic motor system Visceral motor system (ANS) Motor unit Motor unit A neuron A neuron skeletal muscle skeletal muscle Two neurons Two neurons muscles or or cells glands Myelination Heavily myelinated Lightly myelinated or unmyelinated li t d Impulse conduction fast slow Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) or Norepinephrine (正腎上腺素) Effect Stimulatory Stimulatory or inhibitory Stimulatory or inhibitory ANS: ‐‐‐ Pre‐ganglionic neuron (節前神經元): in CNS ‐‐‐ Pre‐ganglionic axon (節前神經纖維): light myelinated axon ‐‐‐ Post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元): in autonomic ganglia ‐‐‐ Post‐ganglionic axon (節後神經纖維): unmyelinated axon ANS: ‐‐‐ Pre‐ganglionic neuron (節前神經元): in CNS Pre ganglionic neuron (節前神經元): in CNS ‐‐‐ Pre‐ganglionic axon (節前神經纖維): light myelinated axon ‐‐‐ Post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元): in autonomic ganglia ‐‐‐ Post‐ganglionic axon (節後神經纖維): unmyelinated axon Sensory ganglia Motor ganglia Motor ganglia Division of the autonomic nervous system Sympathetic (交感: fight‐and‐flight) and parasympathetic (副交感: rest‐and‐digest) mostly innervate the same visceral organs, but cause opposite effects S Sympatheticdivision (交感神經系統) th ti di i i (交感神經系統) Parasympathetic division (副交感神經系 P th ti di i i (副交感神經系 統) Origin(出處來源) Thoracolumbar(胸腰) Craniosacral (顱薦) Locations of ganglion(神經節位 置) Near the spinal cord and vertebral column ( 靠近中樞 遠離臟器) 靠近中樞,遠離臟器) In or near the organs innervated (遠離中樞, 靠近臟器) Pre‐ganglionic axon(節前纖維) 短 長 post‐ganglionic axon(節後纖維) post‐ganglionic axon(節後纖維) 長 短 Branch (分支) extensive (多) minimal (少) Neurotransmitter released by pre‐ganglionic pre ganglionic neuron(節前神 neuron(節前神 經元釋放) Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Cholinergic Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Cholinergic Neurotransmitter released by post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神 經元釋放) Norepinephrine (正腎上腺素) Adrenergic Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Cholinergic Acetylcholine (乙醯膽鹼) Cholinergic 分佈範圍 bodywide (廣佈全身) Localized and discrete (侷限臟器) 影響範圍 大 小 Functional role (功能作用) 戰鬥‐逃跑(消耗能量) fight‐and‐flight 休息‐安眠(保存能量) rest‐and‐digest Parasympathetic division of the ANS (副交感神經系統) ‐‐‐Craniosacral division of ANS (顱薦系統):cranial outflow and sacral outflow 顱薦系統 Cranial outflow: ‐‐‐ oculomotor nerve (動眼神經, CN. III) oculomotor nerve (動眼神經, CN. III) 1. Innervate constrictor of iris and cause the pupil to constrict (控制瞳孔縮小) 2. Innervate ciliary muscle and control lens to bulge for focusing (調節水晶體以對焦) Pre‐ganglionic Pre ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):accessory oculomotor nucleus (副動眼神經核) in the neuron(節前神經元):accessory oculomotor nucleus (副動眼神經核) in the midbrain post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):ciliary ganglion(睫狀神經節) ‐‐‐ Facial nerve (顏面神經, CN. VII) 1. stimulate the secretion of glands 1 stimulate the secretion of glands lacrimal and nasal glands (淚腺及鼻腺) Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):lacrimal nucleus(淚腺核) in the pons post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):pterygopalatine ganglion(翼腭神經節) t li i (節後神經元): t l ti li (翼腭神經節) submandibular and sublingual glands (下頷下腺及舌下腺) Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):superior salivatory nucleus (上催涎核) post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):submandibular ganglion li i (節後神經元) b dib l li (下頷下神經節) ‐‐‐ Glossopharyngeal nerve (舌咽神經, CN. IX) stimulate the secretion of parotid gland Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):inferior salivatory nucleus(下催涎核) post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):otic ganglion(耳神經節) Cranial III, VII and IX supply the entire parasympathetic innervation of the head. , pp y p y p Only preganglionic fibers run within these three nerves. Ganglia and post‐ganglionic axons are in the routing by the way of the trigeminal nerve. ‐‐‐ Vagus nerve (迷走神經, CN. X) Innervate the visceral organs of the thorax and most of the abdomen (proximal half of the large i intestine) i ) secretion of digestive glands and increased motility of the smooth muscle of the digestive tract, reduction in the heart rate, constriction of the bronchi in the lungs Pre ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):dorsal motor nucleus (背運動核) in the medulla Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元):dorsal motor nucleus (背運動核) in the medulla post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):intramural ganglia within the walls of the organs(臟壁內 之神經節) vagus nerve send branches through autonomic plexus (自主神經叢) to the organs: Cardiac plexus (心神經叢)heart Pulmonary plexus (肺神經叢)lungs Esophageal plexus (食道神經叢) esophagus and stomach wall Celiac plexus (腹腔神經叢) abdominal organs Superior mesenteric plexus (上腸繫膜神經叢) abdominal organs Autonomic plexus fibers from both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions parasympathetic divisions Sacral outflow: Innervate organs in pelvis, including the distal half of the large intestine, the bladder and reproductive organs stimulation of defecation, voiding of urine and erection Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元): l (節前神經元) visceral motor region of the spinal gray matter in S2‐S4 i l i f h l spinal cord post‐ganglionic neuron(節後神經元):intramural ganglia (臟壁內之神經節, 終末神經節) Preganglionic fibers ventral root l ventral rami pelvic splanchnic nerves (骨盆內臟神經) inferior hypogastric plexus (腹下神經叢) Sympathetic division of the ANS (交感神經系統) ‐‐‐ Thoracolumbar division of ANS (胸腰系統) Thoracolumbar division of ANS (胸腰系統) ‐‐‐ Pre‐ganglionic neuron(節前神經元): visceral motor region of the spinal gray matter in T1‐L2 spinal cord, where they form the lateral gray horn(位在T1‐L2脊髓段之側角) The parasympathetic Th th ti division di i i d does not innervate sweat glands(汗腺), arrector pili (豎毛肌)or blood vessels Sympathetic ganglia(交感分系的神經節): ‐‐‐ sympathetic trunk ganglia (交感神經節) 交感 經節 or paravertebral ganglia (椎旁神經節 椎旁 經節 )sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chains) (交感神經幹(鏈)) ‐‐‐ collateral ganglia(側枝神經節) or prevertebral ganglia(椎前神經節) sympathetic trunk ganglia (交感神經節) or paravertebral ganglia (椎旁神經 節) sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chains) (交感神經幹(鏈)) sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chains) (交感神經幹(鏈)) White rami communicantes (白支), gray rami communicantes (灰支) 22‐24 sympathetic trunk ganglion per side Superior middle and inferior cervical ganglia(上、中、下頸神經節): (3) Superior, middle and inferior cervical ganglia(上、中、下頸神經節): # inferior cervical ganglia fuses with the first thoracic ganglion to form the stellate ganglion(星形神經節) Thoracic ganglia(胸神經節)(11) 胸神經節 Lumbar ganglia(腰神經節)(4) Sacral ganglia(薦神經節)(4) g g ( 神 )( ) Coccygeal ganglion(尾神經節)(1) ‐‐‐ collateral ganglia(側枝神經節) or prevertebral ganglia(椎前神經節) Celiac ganglion(腹腔神經節) 腹腔 經節 Superior mesenteric ganglion(上腸繫膜神經節) Inferior mesenteric ganglion(下腸繫膜神經節) Inferior hypogastric ganglia(下腹下神經節) lie within the autonomic nerve plexus Differ from the sympathetic trunk ganglia: (1) not paired and not segmentally (2) only in abdomen and pelvis (3) anterior to the vertebral column, mostly on the abdominal aorta Sympathetic pathways: (1) synapse at the same level (2) synapse at a higher or lower level (3) synapse in a distant collateral ganglion anterior to the vertebral column pathways to the body periphery(至全身體壁) Synapse in the sympathetic trunk ganglia Synapse in the sympathetic trunk ganglia Sweat glands, arrector pili muscles in the skin and peripheral blood vessels (汗腺、豎毛肌、 血管) pathways to the head(至頭部) T1‐‐T4sympathetic trunk T1 T4sympathetic trunk synapse in the superior cervical ganglion synapse in the superior cervical ganglion axons on arteries axons on arteries glands, smooth muscles and vessels throughout the head Functions: 1 Inhibit the lacrimal, nasal and salivary gland (害怕時會口乾舌燥) 1. Inhibit the lacrimal nasal and salivary gland (害怕時會口乾舌燥) 2. Stimulate the muscle in the iris that dilate the pupil in the eye (瞳孔放大) 3. Innervate superior tarsal muscle (眼睛張開時防止眼瞼下垂,害怕時眼睛睜大) pathways to the thoracic organs(至胸部器官) T1—T6: Fibers to the lungs (肺) and esophagus (食道) Fibers to the heart Cardiac, pulmonary and esophagus plexus pathways to the abdominal organs(至腹部器官) T5—L2 T5 L2 pass through the adjacent sympathetic trunk ganglia pass through the adjacent sympathetic trunk ganglia collateral ganglia collateral ganglia abdominal abdominal organs Thoracic splanchnic nerves (胸內臟神經): Thoracic splanchnic nerves (胸內臟神經): Greater splanchnic nerve (大內臟神經) Lesser splanchnic nerve (小內臟神經) Least splanchnic nerve (最小內臟神經) Least splanchnic nerve Collateral or Prevertebral ganglion: C li Celiac ganglion li (腹腔神經節) Superior mesenteric ganglia (上腸繫膜神經節) FFunctions: i (1) Innervate stomach, liver, kidney, spleen small intestine and the proximal half of the large intestine (2) Inhibit of the muscles and glands in these visceral organs pathways to the pelvic organs(至骨盆器官) T10—L2 (1) Synapse in the sympathetic trunk ganglia lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves (腰及薦內 臟神經) plexus in pelvis organs ( ) lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves (2) l b d l l h plexus in pelvis l l synapse in collateral ganglia ll l l organs Plexus in pelvis (骨盆腔的自主神經叢): Pl i l i (骨盆腔的自主神經叢) Inferior mesenteric plexus Aortic plexus H Hypogastric plexus i l Collateral or Prevertebral ganglion: Inferior mesenteric ganglia Inferior hypogastric ganglia Functions: (1) Innervate bladder (膀胱), reproductive organs (生殖器官) and the distal half of the large intestine (2) Inhibit urination and defecation and promote ejaculation (抑制排尿,排便及促進射精) The role of the adrenal medulla (腎上 腺髓質) i h 腺髓質) in the sympathetic division h i di i i Adrenal medulla (腎上腺髓質): sympathetic ganglion Adrenal medulla cells: modified postganglionic neurons preganglionic neurons: T8—L1 thoracic splanchnic nerves pass through the celiac splanchnic nerves pass through the celiac plexus adrenal medulla Hormone secreted: epinephrine (腎上腺素) and p p (正腎上腺素) norepinephrine (正腎上腺素) Visceral sensory neurons (臟器感覺神經元) General visceral sensation: stretch, temperature, chemical changes and irritation hunger, fullness, pain, nausea, or well‐being Sensory receptors: free (unencapsulated) nerve endings Difficult to localize Cell body of visceral sensory neurons: dorsal root ganglia or sensory ganglia of Cell body of visceral sensory neurons: dorsal root ganglia or sensory ganglia of cranial nerves The long peripheral process accompany the autonomic motor fibers to the visceral or ans organs parasympathetic fibers: monitor pain sympathetic fibers: monitor mechanical sensations Pathways: visceral input spinothalamic tract (脊髓丘腦徑) thalamus (丘腦) cerebral p p cortex for conscious perception visceral control centers in the hypothalamus (下丘腦) and medulla oblongata ( 延髓) Visceral pain (臟器痛) FFeels no pain when a visceral organs is l i h i l i cut or scraped Pain resulted from: chemical irritation ( 化學刺激) inflammation (器官發炎) , 化學刺激) i fl i (器官發炎) spasm of the smooth muscles (cramping)(器官平滑肌痙攣) and excessive stretching of the organs (器官 excessive stretching of the organs (器官 過度牽扯) Referred pain (牽涉痛) Perceive visceral pain to be somatic, as if it originated from the skin g Both affected organs and the region of body wall to which the pain is referred y p are innervated by the same spinal segment Visceral reflexes (臟器反射) Defecation reflex (排便反射) 排便反射 Micturition reflexes (排尿反射) Simple spinal reflex Visceral reflex involved cranial nerves and is integrated in the brain stem Central control of the autonomic nervous system(自主神經系統的中樞調控) ‐‐‐Control by the brain stem and spinal cord(腦幹與脊髓的調控) Control by the brain stem and spinal cord(腦幹與脊髓的調控) Brain stem (reticular formation) ex: cardiac centers: heart rate vasomotor center: diameter of blood vessels t t di t f bl d l digestive activities Spinal cord spinal visceral reflex: urination, defecation i l i l fl i i d f i ‐‐‐Control by the hypothalamus and amygdala(下丘腦與杏仁體的調控) Hypothalamus: integration center of the autonomic system medial and anterior part: parasympathetic function lateral and posterior part: sympathetic function hypothalamic center preganglionic neurons reticular formation Amygdala: emotion center through communications with the hypothalamus, amygdala stimulates sympathetic activity previous learned fear‐related behaviors ‐‐‐Control by the cerebral cortex(大腦皮質的調控) 雖然自主神經系統不受大腦皮質的意志控制,但人仍可利用其對情緒發展出的非常控 制,來學習間接控制一些自主神經功能 Disorders of the autonomic nervous system Raynaud’s disease (雷諾式症) : 過度交感性血管收縮反映 其臨床特點為兩側對稱的手指或足趾出現間歇性蒼白 紫紺或潮紅 並感 其臨床特點為兩側對稱的手指或足趾出現間歇性蒼白、紫紺或潮紅,並感 局部發涼、麻木或燒灼刺痛 Achalasia of the cardia (食道賁門弛緩不能): Achalasia of the cardia (食道賁門弛緩不能) 支配食道的自律神經受損, 支配食道的自律神經受損 食道和 胃接頭處(賁門)的括約肌無法順利的放鬆,無法順利地將食物往胃部推送 Congenital megacolon, Hirschsprung‘s disease (先天性巨結腸症): 先天性巨結腸症 胚胎發育時神 胚胎發育時 經脊細胞未移動到末端大腸,導致末端大腸沒有副交感神經支配 糞便淤滯的近端大腸,使該腸這肥厚、擴張 The autonomic nervous system throughout life Preganglionic neurons: neural tube Postganglionic neurons: neural crest Development of the sympathetic division