reaction rates
advertisement

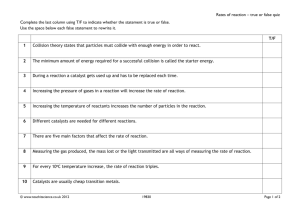
MODULE 4 15 WORKSHEET WORKSHEET REACTION RATES Syllabus reference 8.5.5 1 Complete the following to check your understanding. a slow Combustion reactions occur at very different rates. The reaction will be _____________ when large lumps of coal and a limited supply of air is used. This is because the burning only takes surface place on the _____________ of the coal. When the coal is ground into very fine particles the fast surface reaction is _____________ because there is a large _____________ area of fuel exposed to the oxygen. In diesel engines the liquid fuel reacts within a few milliseconds producing an explosion _____________, which is an extremely rapid reaction. b Combustion is just one example of a chemical reaction which occurs at different rates. One activation factor that determines the speed or rate at which a reaction occurs is the _____________ high energy. Usually slow reactions have _____________ values for this. Chemists alter the rate at concentration which a reaction occurs by changing one or more of the following factors: _______________, temperature particles catalyst _______________, size of the _______________ or by using a _______________. c collide For any reaction to occur the reacting particles must _______________. Increasing the rate at increase which this occurs will _______________ the rate of the reaction. d particles Concentration is a measure of the number of _______________ per unit volume. more Increasing the concentration means there are _______________ particles per unit volume increases so the chance of collisions between particles _______________ and this, in turn, increases the reaction rate. e surface Breaking solid substances into smaller pieces increases the _______________ area of the solid. increases The greater this is, the more collisions can occur so reaction rate _______________. Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 4 WS 15 average kinetic energy of the particles. This means As temperature increases so does the _______________ f increase that the rate of collisions will _______________ and so cause an increase in the reaction rate. g For the particles to successfully react they must not only collide but collide with enough activation energy energy to overcome an ____________________ barrier. If particles have insufficient energy reactants they bounce apart and stay as _____________. An increase in temperature means the average higher kinetic energy of the reactant particles will be ____________. Therefore more particles will proceed have enough energy to overcome the energy barrier and the reaction will _______________. h catalyst The fourth factor which changes the rate of reaction is using a _______________. This is a consumed substance which increases the rate of reaction without being _______________ in the reaction. lower Catalysts work by providing a reaction pathway with a _______________ activation energy. i lower Catalysts play an important role in industry by allowing reactions to occur at _____________ reducing temperatures thus saving energy and _______________ production costs. In oil refining cracking catalytic _______________ is used to break large molecules into smaller ones and so produce catalytic more petrol. In motor vehicles _______________ converters remove pollutants from exhaust enzymes gases. Biological catalysts are called _______________. These are very specific in their activity slowly and without them biological reactions would proceed extremely _______________. j Catalysts generally operate by forming compounds where the bond breaking and rearrangement less to form new compounds requires _______________ energy. With solid catalysts the reactant absorb/stick to the surface of the catalyst. In doing this bonds may be weakened particles _______________ broken or _______________ and other reactant particles collide with those on the catalyst allowing surface a reaction _______________ to occur and the products to leave the _______________ of the catalyst. 2 A common method of preparing hydrogen for industrial purposes is to heat methane and steam with a catalyst at high temperature. The endothermic reaction is: CH4(g) H2O(g) → 3H2(g) CO(g) When 1 mole of methane was reacted with excess steam at 1100°C in a vessel of fixed volume, curve A in the following diagram was obtained. When the experiment was repeated at a different temperature, curve B was obtained. Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 4 WS 15 Moles of CO formed 1.0 B A 0.5 0 a 10 Time (min) 20 What do the initial slopes of the curves tell you about the initial rates at the two temperatures? What is the reason for this difference? Reaction B has a steeper slope so this reaction occurs faster. Temperature affects the rate at which a reaction occurs. b Was the temperature for curve B greater or less than that for curve A? Explain. Temperature for B was greater because the reaction occurred at a faster rate and there were more moles of CO (product) formed in the same time as reaction A. 3 Explain why food spoils less quickly when stored in the refrigerator. Refrigerator lowers the temperature so the reaction which causes the food to spoil occurs at a slower rate. 4 The following observations were made in simple experiments. i If a lump of iron is heated with sulfur, a slow reaction starts and continues slowly. ii If a mixture of iron filings and sulfur is heated for only a few seconds a vigorous reaction occurs, which becomes self-sustaining. iii When iron filings are mixed with sulfur no apparent reaction occurs. Explain the reasons for the difference in reaction rates between: a the first and second reaction In the first reaction a lump of iron is used while in the second reaction iron filings are used. The filings have a greater surface area so the reaction proceeds more rapidly. b the second and third reaction In the second reaction the mixture is heated so this provides the energy to overcome the activation energy barrier and allows the reaction to proceed, whereas in the third reaction no energy is provided so reaction does not occur. 5 When a match is put to a plate of flour it goes out, but workers in a flour mill must be extremely careful to avoid explosions. Explain why this could be so. The flour particles are dispersed through a volume of air providing a large surface area for reaction. Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 4 WS 15 6 In an experiment in which calcium carbonate reacted with hydrochloric acid, the carbon dioxide gas (CO2) was collected in a tube and the volume of gas produced over a period of time was recorded as shown below. a Time (s) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Volume of CO2 (mL) 0 10 17 22 29 29 30 31 31.5 31.5 Plot a graph showing volume of CO2 produced vs time. �� ��������������� �� �� �� �� �� � � b � � � �� �� �������� �� �� �� From your graph state the way in which the rate of the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid varies with time. How did you decide this? Explain why rate changes this way. Reaction rate decreases as the reaction proceeds which can be seen by the decrease in slope of the graph. The rate decreases because the reactants are being used up and there are less reactant particles to collide to produce the CO product. c Suggest one way in which the rate of this reaction can be increased and explain why the increase occurs. Reaction rate could be increased by: • grinding up the calcium carbonate creating a greater surface area • increasing the concentration of hydrochloric acid so there are more particles available for collision • increasing the temperature causing more successful collisions to occur between particles. Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 4 WS 15 7 Describe one example of the role of a catalyst used in industry. • Synthesis of ammonia for fertiliser from N2 and H2 using an iron catalyst • Sulfuric acid synthesis using a vanadium pentoxide catalyst for the SO2 O2 step • Hydrogenation of liquid vegetable oils into semi-solid fats for use in margarine using a nickel catalyst • Catalytic cracking (using zeolites) of hydrocarbons in oil refining to convert higher boiling point fractions into petrol • Catalytic reforming of gasoline using a platinum catalyst to improve octane rating and eliminate the need for lead compounds Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 4 WS 15