Linkage Work Analysis Tool: Identifying the KSAOs Most Important
advertisement

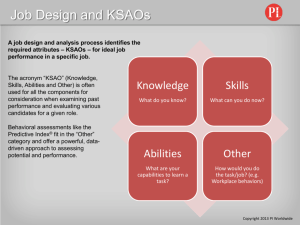
Linkage Work Analysis Tool: Identifying the KSAOs Most Important for Successful Linkage Work OVERVIEW This Linkage Work Analysis Tool (LWAT) is a process by which job experts in the organization identify the Performance Domains, Work Behaviors and Knowledges, Skills, Abilities, and Other Characteristics (KSAOs) that are important for successful performance in the target job. It is based on the General Model of Linkage Work (See Resource1) that describes Performance Domains, Important Work Behaviors and KSAOs required that for a generic representation of linkage work. Many of the Performance Domains, Work Behaviors and KSAOs identified by experts for the target job are likely to be the same as those shown in the General Model of Linkage Work. But some will be different than what are shown in the General Model because the target job may be different in important ways from the General Model, which was developed to represent generic linkage work. This tool was created with the intent of aiding decision making about improved selection processes by providing a comprehensive, accurate description of the KSAOs required for successful performance in the target job. For any job, these required KSAOs are the primary consideration in the design and development of an optimal selection process. In short, optimal selection processes assess the KSAOs that are most important for successful job performance. LWAT is a multiphase process by which participants who are experts about the target job perform the following major tasks. 1. They review the existing General Model for Linkage work and identify those Performance Domains, Important Work Behaviors and KSAOs that are also important for success in the target job. 2. They identify additional Performance Domains, Important Work Behaviors and/or KSAOs that are important for success in the target job but are not included in the General Model. 3. Later in the LWAT process, each expert independently rates the importance of each of the Performance Domains and Work Behaviors that were identified earlier in the process as important to success in the target job. 1 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE LINKAGE WORK ANALYSIS TOOL Getting Started 1. Select the participating job experts, including strong performing incumbents , supervisors and managers, as well as appropriate HR Staff and job Trainers . Two experts is a suggested minimum; Strive for 4 or 5, typically. The more the experts, the greater the accuracy of the results. 2. Gather and review all available, formal job documentation that describes the target job (e.g., job descriptions, appraisal forms, job training materials , etc.). 3. Review the General Model for Linkage Work. 4. Review this Linkage Work Analysis Tool (LWAT) including all phases. 5. LWAT is an iterative group process in which the experts work independently to generate information and then work as a group to review and collectively confirm information initially generated by individual experts. Phase 1. Identify and Confirm Performance Domains Individual Identification Important Performance Domains from the General Model. The experts should begin by individually reviewing Performance Domains provided in the General Model of Linkage Work. For each Performance Domain, each expert should independently judge whether it is important in the target job. For each of the Performance Domains (1st column of the Tool) that are important in the target job, place an X in the Applied space under the Performance Domain title. If a Performance Domain is not important in the target job, leave the Applied space blank. Refer to the General Model of Linkage Work in Resource1, for definitions and descriptions of the five Performance Domains in the General Model. Group Review of “Applied” Judgments. The group of experts should collectively review the individual judgments about the importance in the target job of each of the five General Model Performance Domains. Experts should review the definition of the Performance Domain in question and discuss why the Performance Domain may not be important in the target job. This will allow the facilitator and job experts to identify where 2 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com discrepancies exist and what may be contributing to varying ideas about the job. A group consensus is needed to exclude any one of the five Performance Domains provided in the General Model. It is essential to understand why a General Model Performance Domain may not be important in the target job. This discussion among the group of experts is intended to lead to a consensus about the importance of each General Model Performance Domain for the target job. A General Model Performance Domain may be excluded from the emerging target job model only if there is a consensus among the experts that it is not important enough to be included. Group Identification of Additional Performance Domains, If Any. Once the experts have collectively confirmed the inclusion and exclusion of the General Model Performance Domains, they should convene as a group to identify and define any additional Performance Domains that are important in the target job but were not identified in the General Model. In order to add a new Performance Domain, the experts must reach a consensus that the additional Performance Domain is important for successful performance in the target job. . This consensus-seeking process can provide critical insights and perspectives that will help define additional Performance Domains that do not overlap in meaning with other Performance Domains. Upon arriving at consensus, the newly created Performance Domains may be added to the additional Performance Domain areas at the end of the LWAT tool. Place an X in the Applied area under the title of the Performance Domain(s) that have been added. The primary aim of the focus group is to have a conversation between group members for the purpose of describing and understanding meanings and interpretations of the group members. The result is to gain an in-depth understanding of a specific topic or issue from the perspective of the group participants. If additional Performance Domains have been identified through group c onsensus, develop a definition and fill in the definition box provided. This will allow others using this Tool at later times to better understand the meaning of the additional Performance Domain in the target job and the way in which it differs from the General Model. 3 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com 4 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Phase 2. Identify and Confirm Important Work Behaviors Individual Identification of Important Work Behaviors from the Retained General Model Performance Domains. The experts should begin by reviewing all Important Work Behaviors identified in the Performance Domains that were retained from the General Model in Phase 1. Working separately, the experts should determine whether each Important Work Behavior is important for success in the target job. For each of the Important Work Behaviors (2 nd column of the Tool) that an expert judges to be important for success in the target job, place an X in the Applied column. For an Important Work Behavior that is not important for success in the target job, leave the Applied box blank. Refer to the General Model in Resource1 for descriptions of the Important Work Behaviors associated with each of the five Performance Domains included in the General Model. Group Review of “Applied” Judgments about Important Work Behaviors from the General Model. The group of experts should collectively review the individual judgments about the importance to the target job of each of the Important Work Behaviors aligned with the retained Performance Domains from the General Model. Their focus should be on any Work Behaviors that one or more of the experts have judged is not important for the same Performance Domain in the target job. Experts should review the Work Behaviors in question and discuss the reasons the Work Behaviors may not be important in the target job for the same Performance Domain they were aligned with in the General Model. This will allow the facilitator and job experts to identify where discrepancies exist and what may be contributing to varying ideas about the job. A group consensus is needed to exclude any Work Behavior that was previously aligned with a retained Performance Domain in the General Model. Group Development of Additional Important Work Behaviors. At this point in the process, the experts should collectively begin the process of identifying additional work behaviors that are important to success in the target job but are not included in the General Model. These may include additional Work Behaviors for Performance Domains that were retained from the General Model and additional Work Behaviors for new Performance Domains that were added in Phase 1, above. A round table process 5 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com can be effective and efficient for this activity. Individual experts should “nominate” specific work behaviors to be aligned to particular Performance Domains and explain why they are important to success in the target job. Other experts can then suggest improvements to the suggested work behavior or make a case that it is not important enough to include. All new work behaviors require a consensus of experts to be added to the target job model. Important Work Behaviors that are devised by the group and related to Performance Domains identified in the general model of Linkage Work, should be named in the bottom Additional box for that retained Performance Domain. For Important Work Behaviors that are devised by the group, but DO NOT relate to Performance Domains retained from the General Model, write them in the Definitions of Additional Important Work Behaviors box at the end of the LWAT Tool showing their alignment to a new Performance Domain from Phase 1. i. It is possible that new work behaviors are identified that are not aligned with any Performance Domain developed in Phase 1, either new or retained from the General Model or new. All Important Work Behaviors in the target job model must be aligned with a Performance Domain. The options are either to introduce another new Performance Domain to capture the new work behavior or to revise or discard the suggested new work behavior. If another new Performance Domain is added to accommodate an clearly important work behavior, then 2 or 3 additional important work behaviors should also be developed to be aligned with the new Performance Domain. For each added Work Behaviors that have group consensus place an X in the Applied column in the row where the new Work Behavior has been added.. If, and after, additional Important Work Behaviors have been identified through group consensus as required for success, develop a description and fill in the description boxes for Important Work Behaviors provided in Descriptions of Additional Important Work Behaviors box at the end of the Tool. Consensus should also be utilized to finalize the descriptions of the Important Work Behaviors. This will allow others using the target job model produced by this LWAT process at a later time to understand the meaning and importance of the additional Important Work Behaviors. 6 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Phase 3. Rate the Importance of Each Target Job Performance Domain. For each Performance Domain that has been identified in the target job model, each expert should independently rate the importance of the Performance Domain for overall success in the target job. Performance Domains should have been previously identified as important by placing an X in the Applied area under the title of the Performance Domain in the respective column. Each job expert should rate the importance of the Performance Domain by rating them from 1 (Not Important) to 5 (Critical) and placing their individual rating in the space provided on the LWAT tool. Definition of Performance Domain Importance A Performance Domain is important to the extent that successful performance of that particular domain contributes to overall success in the target job. Importance Rating Scale 5 4 3 2 1 – – – – – Critical to overall job success Very important, but not critical, to overall job success Important to overall job success Somewhat important to overall job success Not important to overall job success The objective is to determine which Performance Domains are more important than others. While some Performance Domains may be rated as less important, it does not necessarily mean that they are not critical for success in your specific job. Instead, the ratings can be used for other HR related tasks and decision making activities in the future, such as training and development or performance evaluations. Phase 4. Rate the Importance of Each Target Job Work Behavior. For each Work Behavior that has been identified in the target job model, each expert should independently rate the importance of the work behavior to the successful performance of the Performance Domain the work behavior is linked to. Work behaviors should have been previously identified as important by placing an X in the 7 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Applied area under the title of the Important Work Behavior column. Each job expert should rate the importance of the Performance Domain by rating them from 1 (Not Important) to 5 (Critical) and placing their individual rating in the space provided on the LWAT tool. Definition of Work Behavior Importance A Work Behavior is important to the extent that it contributes to the successful performance of that particular domain. That is, the importance of a Work Behavior is relative to the Performance Domain it is linked to. Importance Rating Scale 5 4 3 2 1 – – – – – Critical to successful Performance Domain performance Very important, but not critical, to successful Performance Domain performance Important to successful Performance Domain performance Somewhat important to successful Performance Domain performance Not important to successful Performance Domain performance The objective is to determine which Work Behaviors are more important than others. While some Work Behaviors may be rated as less important, it does not necessarily mean that they are not important for success in the target job. Instead, the ratings can be used for other HR related tasks and decision making activit ies in the future, such as training and development or performance evaluations. Phase 5. Compute Average Ratings for Each Performance Domain and Work Behavior in the Target Job Model. The objective of the Phases 5 and 6 is to identify the KSAOs required to successfully perform each Important Work Behavior. In order to (a) confirm that the Performance Domains and Work Behaviors are important enough to be retained and (b) provide valuable information for later activity, the average expert rating should be determined at this point for each Performance Domain and each Work Behavior. One purpose of the Work Behavior importance ratings gathered in Phase 4 is to confirm the level of importance for each Work Behavior. Only Work Behaviors that have an average importance rating of 3.0 or higher will be treated as Important Work Behaviors from this point forward in the LWAT process. 8 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com That is. in Phase 6 of this LWAT process, KSAOs will be identified only for Work Behaviors with average ratings of 3.0 or higher. There are any number of specific procedures for computing the average importance rating for each Performance Domain and each Work Behavior. Perhaps the simplest and most convenient for the group-based LWAT process is to simply have the experts read out their importance ratings as each Performance Domain and each Work Behavior is announced out loud. For example, the LWAT facilitator could announce the name of the first Performance Domain and then record on the board or paper the several ratings made by the experts as they read them out loud. Given that each rating is a single digit and there are likely to be only a few experts, the arithmetic of computing the average ratings will be simple. Example: Important Work Behavior – Know Available Health Resources. Five experts report out loud their importance ratings for Know Available Health Resources. Suppose the five ratings were: 4, 3, 4, 5, 4. Adding the scores = 20. Divide 20 by 5 (# of raters) = 4. In this example the average rating is 4. i. The same process would be utilized for computing the average rating for each Performance Domain. Phase 6. Identify Required KSAOs for Each Important Work Behavior . The objective of the Phase 6 is to identify the KSAOs required to successful perform each Important Work Behavior (average importance rating equal to 3.0 or higher), all of which should now be included in the target job model. This phase focuses solely on Important Work Behaviors, and not Performance Domains, because KSAOs are linked directly to specific work behaviors rather than broad categories of related work activities . As with Performance Domains and Work Behaviors, there are two sources of Required KSAOs. First, for the Important Work Behaviors and Performance Domains retained from the General Model, Required KSAOs are already identified. Second, for any Important Work Behavior, whether it was retained from the General Model or has been added be the experts, the experts may identify new KSAOs that are not identified in the General Model. Identify Required KSAOs from the General Model. For each Important Work Behavior that received an average rating of 3.0 or higher, move to the Required KSAOs column to 9 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com identify the KSAOs required to successfully perform a particular Important Work Behavior in the target job. Generally, all KSAOs should be retained from the General Model if they are linked to the same Important Work Behavior and same Performance Domain as in the General Model. Rarely will there be a persuasive reason for deleting such a KSAO. However, in the rare event that all experts agree that such a KSAO is not required for the Important Work Behavior, and the LWAT facilitator approves, that KSAO may be removed from the target job model. Identify Additional Required KSAOs. As the last activity, the experts should identify additional required KSAOs. These may be for new Work Behaviors that were not from the General Model or for Work Behaviors that were from the General Model which the job experts determine warrant additional KSAOs that were not from the General Model. Consensus of job experts is required to add a new KSAO. Careful thought and consideration are key to matching the correct Required KSAOs to their related Importa nt Work Behaviors. Our recommendation is that KSAO be suggested in a group, roundtable process in which individual experts suggest possible KSAOs, which are then vetted by the other group members. This vetting results either in a consensus to add the KSAO. If there is no consensus, the KSAO should not be added. Such consensus can provide critical insight and knowledge from varying view points of individuals who either perform or are familiar with the job. Upon arriving at consensus, the newly identified Required KSAOs may be added to their respective column and aligned to their related Important Work Behaviors. *Note: If the job experts cannot identify Required KSAOs for the additional Important Work Behaviors, we recommend consultation either with an HR professional or I/O Psychologist who has experience with employment selection and assessments. 10 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Linkage Work Analysis Tool Job Title: Reports to: Performance Domain Important Work Behaviors Department: Date: Applied Rating (1-5) Required KSAOs Client Engagement Know available health resources Applied _____ Know community resources Rating _____ Communicate effectively w ith served population Judge importance of client needs w ith respect to joining care Initiate and sustain action on behalf of client interests Judge and plan appropriate use of resources See and hear clients’ ow n frame of reference Build rapport and trust w ith clients Influence clients’ decisions 11 Additional: Additional: Relevant experience in and know ledge of health service work Relevant experience / know ledge of community resources Has a public health professional netw ork Extensive personal experience w ith served population Pr ofessional Judgment and Dec ision Making Related successful job experience Action-Oriented Dutifulness Achievement Striving Pr ofessional Judgment / Dec ision making Job Ex perience Orderliness Openness Extensive exper ience w ith served population Interpersonal Effectiveness Extensive exper ience w ith served population Communication Skills Empathy; Trust; Straightforw ardness Interpersonal Effectiveness; Communication Skills Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Work Process Management Applied _____ Rating _____ Write clearly and concisely Adhere to employers’ prescribed processes Appropriately judge roles, responsibilities and priorities Learning Ability Self-Discipline Dutifulness Orderliness Rule Follow ing Language Skills Self-Discipline Dutifulness Orderliness Judgment Learning Ability Competence Deliberation Judgment Learning Ability Competence Deliberation Pr oblem Solving Ability Self-Discipline Learning Ability Dutifulness Learning Ability Appropriately judge workload management priorities Investigate client information Manage time, performance, agreements Learn training content Additional: Additional: 12 Learn and use information management systems effectively Document actions on time, correctly and completely Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Collaboration with Others Team Orientation Self-Aw areness Team Orientation Interpersonal Effectiveness Collaborate w ith case management team Ask for help, support, input as needed Build effective relationships w ith other service providers Additional: Additional: Self Management Learn from ow n and others’ exper ience Applied _____ Know and plan search and safety procedures Persist on behalf of client Learning Orientation Openness Self- Management Planfulness Self- Management Persistence Self- Efficacy Self-Discipline Customer Orientation Res ilience Action-Oriented Achievement Striving Self-Discipline Client Orientation Self- Management Self-Discipline Achievement Striving Self- Efficacy Tolerance for Ambiguity Openness Self- Management Applied _____ Rating _____ Rating _____ 13 Maintain energy in the face of discouragement Grow ow n capabilities to perform linkage role Tolerate ambiguity / confusion / complexity Manage career Additional: Additional: Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Organization Support Stays in organizations Supports organization’s direction Helps others Suggests Improvements Additional: Additional: Additional Additional Additional Applied _____ Rating _____ Additional: Applied _____ Rating _____ Conscientiousness Agreeableness Loyalty Description of Performance Domain: Additional: Applied _____ Additional Additional Additional Rating _____ Description of Performance Domain: 14 Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com Definitions of Additional Important Work Behaviors Label 15 Description Selection & Assessment Consulting, LLC Email: jkehoe@selectionconsulting.com