Polymer FACT-SHEETS ChE 412/512 Mini
advertisement

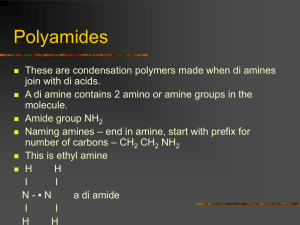
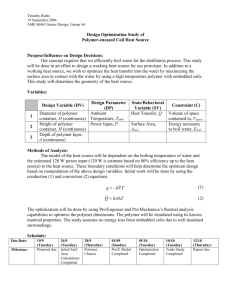
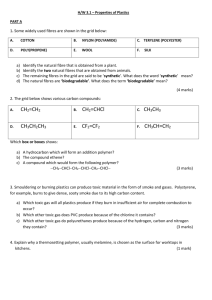
Polymer FACT-SHEETS ChE 412/512 Mini-Presentation Assignment Electronic Fact Sheets & PowerPoint Files due to cbrazel@eng.ua.edu by 5:00 pm March 10 Presentations on March 11 ASSIGNMENT Each student will select a different polymer on March 2. Compile a fact sheet (1 page) of chemical and physical properties, chemical structure, trade names, examples of products this polymer is used in, and what unique properties the polymer has (e.g., tough mechanical strength, optically clear, high temperature resistant, etc.). Something on the history of the material would be nice if you can find it- When was it discovered, first made industrially, what was it’s first use? Unfortunately, one polymer may have many properties that can be varied by copolymerization, additives, molecular weight, etc., so not all information will be appropriate or easily available for each polymer. Information that would be useful to include: What are some of the (common) trade names? What is the production rate per year? What products is it used in? What are the range of properties that it has- flexibility, Tg, tensile/impact strength What companies make this material? What is the chemical structure? Is it made by condensation or free radical plyztn? Is it used as a linear, branched or crosslinked polymer? What solvents dissolve it? How is it modified? (plasticizers??) How is it processed? gas-phase rxn, solution polymerization, reactive extrusion? Any crystallinity? HELPFUL RESOURCES Some useful resources include websites such as the macrogalleria at USM (http://www.pslc.ws/mactest/level2.htm) and other links from the course homepage (www.bama.ua.edu/~cbrazel). The Thomas Registry (link from homepage) requires free registration but can provide links to suppliers of particular chemical/industrial products. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for the monomer and polymer can also provide useful chemical data. I have two books in my office: Concise Polymeric Materials Encyclopedia (very good, brief overview of many polymers) and Polymer Handbook (mainly data, similar to the CRC handbook, but for polymers). The Rodgers Library is also an excellent resource. (Many polymers have their own entry in the Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology- in the reference section- 1st floor), as well as the Handbook of Material Selection for Engineering Applications (TA403.4.H37- reference@ Rodgers). TOPIC ASSIGNMENT Each person will be assigned a different polymer on Tuesday, Mar. 2. If you have a particular polymer that you want to investigate, you can request that on Mar. 2. IN-CLASS Prepare a 3-4 minute Powerpoint presentation of the polymer, and a 1-page ‘fact sheet’ for reference. I will make copies of the fact sheets & they will become part of your class notes. The Powerpoint presentations will be combined into a single presentation for in-class discussion on March 11. Visual aids- Examples of products or pictures (from a web site, etc.) that will help explain the products made from this polymer are encouraged. (right click, copy & paste works great for Powerpoint) GRADING This assignment counts for 5 % of the course grade. Grading will be on: 75 % accuracy, thoroughness, & technical presentation of the ‘fact sheet’, and 25 % in-class presentation- communication effectiveness ---- a list of polymers is included on page 2, and a sample FACT SHEET is on page 3 ---- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Polyethylene (HDPE/LDPE) Polypropylene, PP Poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET Poly(tetrafluoroethylene), PTFE, Teflon Poly(vinyl chloride), PVC Polystyrene, PS Poly(methyl methacrylate), PMMA Polycarbonates Polyamides (Nylon 6,6) Polyesters Polyurethanes, PU Poly(acrylic acid), PAA Poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone), PVP or PNVP also written as poly(vinyl pyrrolidinone) Polyisoprene Polybutadiene (cis, trans & vinyl) Poly(acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene), ABS Aramids Poly(cyanoacrylate)s Poly(p-phenylene sulfide) Poly(dimethyl siloxane), Silicone Poly(vinyl acetate) Poly(ethylene oxide) Starch (amylose & amylopectin) & Cellulose Polyimides POLY(2-HYDROXYETHYL METHACRYLATE) Abbreviations: PHEMA Trade Names: product no trade names of note, not sold as polymer; made directly into final Monomer Synonyms: 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, ethylene glycol monomethacrylate, glycol methacrylate, HEMA Chemical Structure: Repeat unit H2C=C(CH3)(COOCH2CH2OH) Monomer Properties: density 1.03 -1.08 g/ml boiling point 205-208 C melting point -12 C MW = 130.14 g/gmol Polymer Properties: hydrophilic thermoset biocompatible (low protein adsorption) usually crosslinked swellable in water (a hydrogel) can be made isotactic or syndiotactic chemically stable copolymers used to improve tensile strength gas permeability (O2) for contact lenses optically clear Reaction Mechanism: free radical; simultaneous crosslinking copolymerization; molded Products Used in: contact lenses (soft), biomaterials, drug delivery coatings, catheters, dialysis membranes; artificial cornea Historical: first used in contact lenses in the early 1970s Commercial Suppliers: because PHEMA is usually mold-casted into a final product, it is not available commercially as a polymer. The monomer is available from: Atofina, Dow Chemical, others