WORLD RELIGIONS VOCABULARY
advertisement

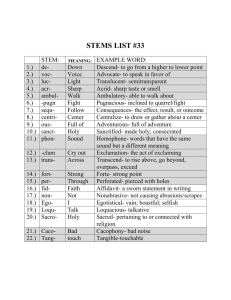
7.1.spi.3 How do you compare and contrast the tenets of the five major world religions? WORLD RELIGIONS VOCABULARY A child sits near idols of Hindu Goddess Lakshmi, the Goddess of wealth, on the eve of Diwali in Hyderabad, India. BELIEFS • religion: relationship w/ a higher power • monotheism: belief in one god • polytheism: belief in many gods • atheists: people who do not believe in a god or gods 5 MAJOR WORLD RELIGIONS Christianity Hinduism Judaism Buddhism Islam DEITY: HIGHER POWER •God­Christian deity •Yahweh­Jewish deity •Allah­Islamic deity •Brahman­Hindu universal spirit translated as God • goddesses­female gods •Buddha­Buddhist deity Buddhist monks and other devotees walk back to their camps through a field after attending a teaching session of Tibetan spiritual leader the Dalai Lama during the Kalachakra. FIGURES • Jesus Christ: believed by Christians to be the son of God (Messiah), sent to save the Jewish people • Rabbi: Jewish teacher of the Torah • Hebrews: Jews that began praying to one God in 2000 BC that speak Yiddish (Hebrew/Jewish language) • Abraham: Hebrew leader that made a covenant (holy agreement) w/ God • Moses: Jewish man believed to have been given the 10 Commandments (instructions for holy living) directly from God • Muhammad: prophet that is believed by Muslims (people of Islamic faith) to have received messages from Allah • guru: religious teacher that leads Hindu worship • Dalai Lama: spiritual leader of Tibet associated with Hindu • Siddhartha Gautama: Indian prince that witnessed ppl. Suffering in India, became known as Buddha • monks: men responsible for preserving and teaching Buddhist teachings/guiding lay followers An elderly couple read from the Quran together near Orlando, Florida. HOLY BOOKS • Bible: Christian holy book, especially the New Testament • Gospels: first 4 books of the New Testament which tell the life and teachings of Jesus Christ • Torah: Jewish holy book, first 5 books of the Old Testament in the Bible • Koran/Quran: holy text of Islam, messages recorded by Muhammad from Allah • The Vedas: Hindu holy book • Dhamma: Buddhist collection of sayings/teachings from Buddha Tens of thousands of Muslim pilgrims move around the Kaaba (center) inside the Grand Mosque in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. RELIGIOUS PLACES • church: Christian place of worship, typically attended on Sunday • synagogue: Jewish place of worship, also known as temple, typically attended on Saturday • mosque: Islamic place of worship, often visited on Friday by men for prayer • Mecca: holy city for followers of Islam • temple: Hindu place of worship in addition to shrines to god/goddesses CEREMONIES/OBSERVANCES • Sabbath: Saturday, day of rest, day that Jews attend synagogue to worship • Ramadan: fasting during daylight hours as observance of month that Muhammad received messages from Allah • pilgrimage: religious journey Orthodox Christians immerse themselves in the Jordan River at a baptism ceremony, during Holy Week, in Jericho, where Jesus is believed to have been baptized. TEACHINGS • baptism: Christian teaching of being immersed in water for forgiveness of sins • crucifixion: death by being nailed to a cross; the way religious/political leaders killed Jesus • resurrection: to raise from the dead; Christians believe that Jesus Christ was resurrected after being crucified on the cross • Trinity: Christian belief in God, Jesus, and the Holy Spirit • Kosher: food that is fit or allowed to be eaten or used, according to the Jewish dietary or ceremonial laws • covenant: religious promise or agreement • 10 Commandments: instructions for Hebrew people on how to live/worship • Five Pillars of Islam: ways in which to worship and pray to Allah • reincarnation: rebirth in which a soul moves to another body depending on how well a person lives his/her life • karma: actions that affect future lives • nirvana: an end to imperfection, state of perfect peace • meditation: the practice of training your mind to focus only on the important things • Four noble truths: Buddhist teachings about suffering