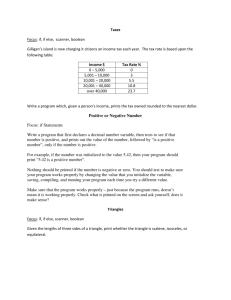
Assignment 5
advertisement

Assignment 4
Software Testing
Software Testing :Q1
• Q1. Using your java, C# or other
programming language skill, derive a
checklist of common errors (NOT syntax
errors) that could not be detected by a
compiler but that could be detected in a
program inspection?
Software Testing :Q1
• Dynamic variables are cleared properly when
they’re no longer needed
• Recursive functions have logic to prevent
infinite recursion
• Iterative loops have logic to prevent infinite
loops
• Variables are not in danger of being too
limited with large numbers
• Logic statements are defined correctly
Software Testing :Q2
• Q2. Let P be a program that is using as input a
number of 5 digits to compute some
function. Derive test cases for black box
testing from this specification using partition
testing.
• black box testing?
• partition testing ?
Software Testing :Q2
• equivalence classes:
1. x < 10000
2. 10000 ≤x ≤99999
3. x ≥100000
we'll have to test the following numbers:
Software Testing :Q3
• Q3. Derive test cases for black box testing
using partition testing of a procedure that
given an integer n computes its factorial n!
Software Testing :Q3
• If n<o then an error message is printed ("
number is negative");
• If 0=<n<20 then the exact value of n! is
printed ;
• If 20=<n=<200 then a floating number
approximation of n! is printed (because there
will be an overflow);
• If n>200 then an error message is printed
("number is too big");
Software Testing :Q3
•
•
•
•
D1 = {n: n<0}
D2 ={n: 0≤n<20}
D3 ={n: 20≤n≤200}
D4 ={n: n>200}
Software Testing :Q3
•
•
•
•
D1 = {n: n<0}
D2 ={n: 0≤n<20}
D3 ={n: 20≤n≤200}
D4 ={n: n>200}
• a set of test data could be T ={-12, 6, 56, 352}
which covers the whole input data set.
Software Testing :Q4
• Q4. Derive test cases for black box testing
using partition testing of a procedure for
detecting the type of triangle. The
specification of a procedure is as follows:
• Input: 3 numbers (representing edge lengths)
• Output: the type of triangle represented by
the 3 numbers (equilateral, isosceles, right
triangle, other)
Software Testing :Q4
• Triangle
– The sum of the lengths of any two sides of
a triangle is always greater than the length of the
third side
• Equilateral
– All sides are equal.
• isosceles
– If two of the sides of a triangle are of equal size the
triangle
• right triangle
Software Testing :Q4
•
•
•
•
D1= {(a, b, c): abc is equilateral}
D2= {(a, b, c): abc is isosceles }
D3= {(a, b, c): abc is right}
D4= {(a, b, c): abc is not a triangle}
Software Testing :Q4
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
D1 = {(a, b, c): is equilateral : a=b=c}
D21= {(a, b, c): is isosceles and a=b, a<>c}
D22= {(a, b, c): is isosceles and a=c, b<>c}
D23= {(a, b, c): is isosceles and b=c, a<>b}
D3= {(a, b, c): is right and a<>b<>c}}
D41= {(a, b, c): pas un triangle et a >= b+c}
D42= {(a, b, c): pas un triangle et b >= a+c}
D43= {(a, b, c): pas un triangle et c >= a+b}
Software Testing :Q4
• Test cases:
1. (3, 3, 3)
2. (2, 2, 3)
3. (2, 3, 2)
4. (3, 2, 2)
5. (3, 4, 5)
6. (6, 3, 3)
7. (3, 6, 3)
8. (3, 3, 6)
Software Testing :Q5
•
•
•
Q5. Write a scenario that could be used to help design tests for the
wilderness weather station system example (Chapter 7).
A possible scenario for high-level testing of the weather station system is:
John is a meteorologist responsible for producing weather maps for the
state of Minnesota. These maps are produced from automatically
collected data using a weather mapping system and they show different
data about the weather in Minnesota. John selects the area for which the
map is to be produced, the time period of the map and requests that the
map should be generated. While the map is being created, John runs a
weather station check that examines all remotely collected weather
station data and looks for gaps in that data – this would imply a problem
with the remote weather station.
– Note: There are many possible alternative scenarios here. You should identify
the role of the actors involved and should discuss a typical task that might be
carried out by that role.