Ch. 8 Practice MC
advertisement

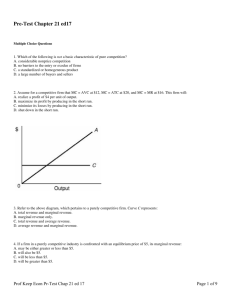
Ch. 8 Practice MC 1. In which of the following market structures is there clear-cut mutual interdependence with respect to price-output policies? A. pure monopoly B. oligopoly C. monopolistic competition D. pure competition 2. An industry comprised of 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market for a differentiated product is an example of: A. monopolistic competition. B. oligopoly. C. pure monopoly. D. pure competition. 3. An industry comprised of four firms, each with about 25 percent of the total market for a product is an example of: A. monopolistic competition. B. oligopoly. C. pure monopoly. D. pure competition. 4. A purely competitive seller is: A. both a "price maker" and a "price taker." B. neither a "price maker" nor a "price taker." C. a "price taker." D. a "price maker." 5. The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual purely competitive firm is: A. relatively elastic, that is, the elasticity coefficient is greater than unity. B. perfectly elastic. C. relatively inelastic, that is, the elasticity coefficient is less than unity. D. perfectly inelastic. In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. 6. Refer to the above information. For a purely competitive firm, total revenue graphs as a: A. straight, upsloping line. B. straight line, parallel to the vertical axis. C. straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis. D. straight, downsloping line. 7. Refer to the above information. For a purely competitive firm, marginal revenue graphs as a: A. straight, upsloping line. B. straight line, parallel to the vertical axis. C. straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis. D. straight, downsloping line. 8. For a purely competitive seller, price equals: A. average revenue. B. marginal revenue. C. total revenue divided by output. D. all of these. 9. For a purely competitive firm total revenue: A. is price times quantity sold. B. increases by a constant absolute amount as output expands. C. graphs as a straight upsloping line from the origin. D. has all of these characteristics. 10. The fact that a purely competitive firm's total revenue curve is linear and upsloping to the right implies that: A. product price increases as output increases. B. product price decreases as output increases. C. product price is constant at all levels of output. D. marginal revenue declines as more output is produced. 11. Which of the following statements is correct? A The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely . competitive industry is downsloping. B The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is downsloping, but the demand curve for a purely . competitive industry is perfectly elastic. C. The demand curves are downsloping for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. D. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. 12. Firms seek to maximize: A. per unit profit. B. total revenue. C. total profit. D. market share. 13. A competitive firm in the short run can determine the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output by equating: A. price and average total cost. B. price and average fixed cost. C. marginal revenue and marginal cost. D. price and marginal revenue. 14. In the short run a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit will produce: A. where the demand and the ATC curves intersect. B. where total revenue exceeds total cost by the maximum amount. C. that output where economic profits are zero. D. at any point where the total revenue and total cost curves intersect. 15. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. 16. The MR = MC rule applies: A. to firms in all types of industries. B. only when the firm is a "price taker." C. only to monopolies. D. only to purely competitive firms. 17. When a firm is maximizing profit it will necessarily be: A. maximizing profit per unit of output. B. maximizing the difference between total revenue and total cost. C. minimizing total cost. D. maximizing total revenue. 18. In the short run the individual competitive firm's supply curve is that segment of the: A. average variable cost curve lying below the marginal cost curve. B. marginal cost curve lying above the average variable cost curve. C. marginal revenue curve lying below the demand curve. D. marginal cost curve lying between the average total cost and average variable cost curves. Answer the question on the basis of the following data confronting a firm: 19. Refer to the above data. At the profit-maximizing output the firm's total revenue is: A. $48. B. $32. C. $80. D. $64. 20. If a firm is confronted with economic losses in the short run, it will decide whether or not to produce by comparing: A. marginal revenue and marginal cost. B. price and minimum average variable cost. C. total revenue and total cost. D. total revenue and total fixed cost. 21. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A. P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4. 22. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: A. above P1. B. above P3. C. above P4. D. between P2 and P3. 23. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A. the abcd segment and above on the MC curve. B. the bcd segment and above on the MC curve. C. the cd segment and above on the MC curve. D. not shown. 24. In the short run a purely competitive seller will shut down if: A. it cannot produce at an economic profit. B. price is less than average variable cost at all outputs. C. price is less than average fixed cost at all outputs. D. there is no point at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal. 25. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: A. K units at price C. B. D units at price J. C. E units at price A. D. E units at price B. 26. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total fixed cost is equal to: A. 0AHE. B. 0BGE. C. 0CFE. D. BCFG. 27. If a purely competitive firm is producing at some level less than the profit-maximizing output, then: A. price is necessarily greater than average total cost. B. fixed costs are large relative to variable costs. C. price exceeds marginal revenue. D. marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market: 28. Refer to the above data. If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will: A. produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40. B. produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00. C. shut down in the short run. D. produce 6 units at a loss of $23.80. 29. Refer to the above data. If there were 1,000 identical firms in this industry and total or market demand is as shown below, equilibrium price will be: A. $32. B. $42. C. $36. D. $20. 30. Refer to the above diagram. The short-run supply curve for this firm is the: A. entire MC curve. B. segment of the AVC curve lying to the right of the MC curve. C. segment of the MC curve lying to the right of output level k. D. segment of the MC curve lying to the right of output level h. 31. The principle that a firm should produce up to the point where the marginal revenue from the sale of an extra unit of output is equal to the marginal cost of producing it is known as the: A. output-maximizing rule. B. profit-maximizing rule. C. shut-down rule. D. break-even rule. 32. Refer to the above diagram. At P4, this firm will: A. shut down in the short run. B. produce 30 units and incur a loss. C. produce 30 units and earn only a normal profit. D. produce 10 units and earn only a normal profit. 33. If a purely competitive firm is maximizing economic profit: A. it is necessarily maximizing per-unit profit. B. it may or may not be maximizing per unit profit. C. then per-unit profit will be minimized. D. it is necessarily overallocating resources to its product. 34. Refer to the above diagram. The firm will realize an economic profit if price is: A. P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4. Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: 35. The above data are for: A. the long run. B. the short run. C. both the short run and the long run. D. the intermediate market period only. 36. Refer to the above data. The marginal cost of the fifth unit of output is: A. $80. B. $90. C. $50. D. $20. 37. Refer to the above data. Given the $75 product price, at its optimal output the firm will: A. realize a $25 economic profit. B. realize a $30 economic profit. C. incur a $25 loss. D. realize a $30 loss. The following table applies to a purely competitive industry composed of 100 identical firms. 38. Refer to the above table. The equilibrium price in this purely competitive market is: A. $5. B. $4. C. $3. D. $2. 39. Refer to the above table. If each of the 100 firms in the industry is maximizing its profit and earning only a normal profit, each must have a total cost of: A. $18,000. B. $20,000. C. $22,000. D. $14,000. 40. (Consider This) An unprofitable motel will stay open in the short-run if: A. price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average variable cost. B. marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. C. price (average nightly room rate) exceeds average fixed cost. D. marginal revenue exceeds price. 41. (Last Word) Oil wells and seasonal resorts will often shut down temporarily because: A. prices for their output temporarily fall below their average variable costs of production. B. fixed costs temporarily rise, making production unprofitable. C. variable costs for pumping oil and operating resorts fluctuate significantly. D. government regulations require seasonal shutdowns for maintenance purposes. 42. Oligopoly firms may produce either standardized or differentiated products. True False 43. The term imperfect competition refers to every market structure besides pure competition. True False 44. Although individual purely competitive firms can influence the price of their product, these firms as a group cannot influence market price. True False 45. In the short run a competitive firm will always choose to shut down if product price is less than the lowest attainable average total cost. True False 46. A competitive firm will produce in the short run so long as its price exceeds its average fixed cost. True False 47. Refer to the above diagram. This firm will maximize profits by producing output D. True False 48. Refer to the above diagram. At output C production will result in an economic profit. True False 49. Refer to the above diagram. At any price below R the firm will shut down in the short run. True False 50. Refer to the above diagram. If demand fell to the level of FNJ, there would be no output at which the firm could realize an economic profit. True False Ch. 8 Practice MC Key 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. B 6. A 7. C 8. D 9. D 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. B 15. A 16. A 17. B 18. B 19. A 20. B 21. B 22. D 23. B 24. B 25. C 26. D 27. D 28. B 29. C 30. D 31. B 32. A 33. B 34. D 35. B 36. A 37. B 38. C 39. A 40. A 41. A 42. TRUE 43. TRUE 44. FALSE 45. FALSE 46. FALSE 47. FALSE 48. TRUE 49. TRUE 50. FALSE Ch. 8 Practice MC Summary Category AACSB: Analytic AACSB: Reflective Thinking Blooms: Level 1 Remember Blooms: Level 2 Understand Blooms: Level 3 Apply Blooms: Level 4 Analyze Difficulty: 1 Easy Difficulty: 2 Medium Difficulty: 3 Hard Learning Objective: 08-01 Give the names and summarize the main characteristics of the four basic market models. Learning Objective: 08-02 List the conditions required for purely competitive markets. Learning Objective: 0803 Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Learning Objective: 08-04 Explain why a competitive firms marginal-cost curve is the same as its supply curve. McConnell - Chapter 08 Status: New Topic: Demand as seen by a purely competitive seller Topic: Four Market Models Topic: Marginal cost and short-run supply Topic: Profit maximization in the short run Topic: Pure competition: characteristics and occurrence Type: Graph Type: Table # of Questions 18 32 14 14 10 12 14 24 12 5 9 31 5 62 1 7 5 5 31 2 13 8