2014 Academic Super Bowl Senior Science Physics Concepts and
advertisement

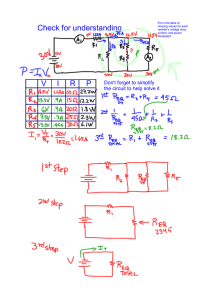
2014 Academic Super Bowl Senior Science Physics Concepts and References Electricity Ohm's Law Holt Physics by Serway and Faughn (c. 1999) Chapters 19 and 20 Must be comfortable with Ohm’s Law relating voltage, current and resistance Understand combinations of resistors, series and parallel connections Induced currents and Power Generation Holt Physics by Serway and Faughn (c. 1999) Chapter 22 Faraday’s Law of Induction http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/farlaw.html Compute the power for simple generators by combining Faraday’s Law and Ohm’s Law Thermodynamics Holt Physics by Serway and Faughn (c. 1999) Chapter 11 First Law of Thermodynamics U = Q-W Change in internal energy of system = Heat added to the system - Work done by the system Four processes: Isobaric - system stays at constant pressure. Work = Pressure* Volume Change = P V Isothermal - system stays a constant temperature U = 0 Isovolumatric (Isochoric) - system stays at constant volume, W = 0 Adiabatic - no heat enters or leaves the system, Q = 0 Heat Engines - Pressure Volume Diagrams http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/heaeng.html http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/members/courses/teachers_corner/44428.html Understand Cyclical processes on PV diagram Work done equals area under the curve Efficiency = 1 - Qc/Qh or 1 - Tc/Th Q is quantity of heat, T is temperature in Kelvin. The subscripts refer to cold and hot reservoirs. Qc is waste heat. Qh is heat added to the system.