Rights of the Accused and Separation of Church and State
advertisement

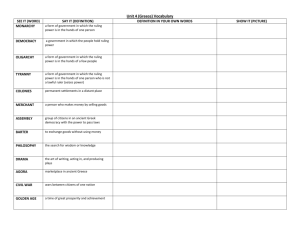
Rights of the Accused and Separation of Church and State Directions: Using www.oyez.com, summarize the case background, legal question, and ruling in the following Supreme Court cases related to religion and government. Case: Everson v. Board (1947) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1940-1949/1946/1946_52/ Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Engel v. Vitale (1962) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1961/1961_468 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Abington v. Schempp (1963) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1962/1962_142 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling What does it mean to not create a “religion of secularism”? ______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Case: Lemon v. Kurtzman (1971) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1970-1979/1970/1970_89 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Mapp v. Ohio (1961) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1960/1960_236 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Gideon v. Wainwright (1964) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1962/1962_155 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Escobedo v. Illinois (1964) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1963/1963_615 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Case: Miranda v. Arizona (1966) http://www.oyez.org/cases/1960-1969/1965/1965_759 Facts of the Case/Background Legal Question Ruling Rights of the Accused and Separation of Church and State Review Quiz Directions: Match the Supreme Court case with the ruling. One choice will have two answers. _____. Everson v. Board _____. Engel v. Vitale _____. Abington v. Schempp _____. Lemon v. Kurtzman _____. Mapp v. Ohio _____. Gideon v. Wainwright _____. Escobedo v. Illinois _____. Miranda v. Arizona a. accused persons must be “read the rights” (right to remain silent, anything they say can be used against them, right to a lawyer before & during interrogation) b. The first Supreme Court case to directly state that a “wall of separation between church and state” exists and that it is “high and impregnable”. c. This case created a constitutional test to determine if a government action violated “separation of church and state”—1. The law must have a secular (non-religious) purpose, 2. The law must neither advance nor inhibit religion, and 3. It must not create excessive entanglement between government and religion. This case also kept government money from being used for “church-related educational institutions” d. criminal courts must provide free lawyers to those who cannot afford it e. The Supreme Court case that said busing schoolchildren was so far removed from an establishment of religion that it was not a violation of “separation of church and state” to give government money to Catholic schools in order to transport children to school f. evidence seized illegally cannot be used to prosecute accused persons in state courts g. The state government of NY’s voluntary, nondenominational prayer was struck down as unconstitutional here, as it allegedly showed that NY was officially approving of religion; this was the first of many Court cases that disallowed public religious ceremonies h. In this case, the Court ruled that required Bible reading in a PA school was unconstitutional because it violated the Establishment and Free Exercise Clause i. an accused person has the right to have a lawyer present while being questioned by police