Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes
advertisement

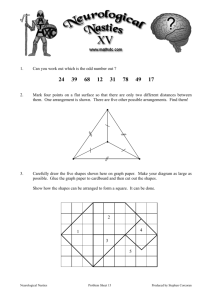
Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Lesson Plan Subject/Strand/Topic: Grade(s) / Course(s): Science – Structural Strength and Stability 7 Ontario Expectations: 7s85, 7s86, 7s87, 7s90, 7s102 Key Concepts: forces (compression, tension, bending, shear, torsion), loads (weight, soil, temp., wind, vibration, earthquake), materials (wood, plastic, aluminum, brick, concrete, iron, steel), shapes(rectangles, arches, triangles) Link: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/buildingbig/lab/forces.html Required Materials: Pre-Assessment/Answer Key, Student Activity Handout, Student Activity Answer Key, PostAssessment/Answer Key Before Starting: This activity works best during a double-period. Introduction (10 min including pre-assessment) 1. Ask students the following questions: Q: Predict what would happen if a building was built on soft soil. (It would sink into the soil and become unstable) Q: Predict what would happen if wood was used to build a large building in an area where it continually rained and snowed? (the wood would rot and weaken) 2. Introduce the learning object (this online activity will investigate factors involved in building structures) 3. Distribute the pre-assessment quiz and allow 5 min to complete; collect 4. Ensure students are in front of their computers prior to moving on Explanation of Activity Sheet (5 min) 1. Students should be placed in partners for this activity. 2. Distribute Activity sheet to each student 3. Provide direction on the organization and structure of the Activity sheet as needed 4. Inform students they will only by using the four headings at the top of the learning object and down the side of the screen and should not be using any other links on the page Use of Learning Object with Activity Sheet (45 minutes) 1. Teacher should circulate throughout the activity and ensure students are on task 2. Provide students with the following verbal time cues throughout the activity: • Forces section – 10 min • Loads section – 15 min • Materials section – 10 min • Shapes section – 10 min Consolidation Questions and Post-Assessment (10 minutes) Q: What are some important considerations when deciding what material to use for a building? (the environment it will be in, what it will be used for, how much material is needed (cost), etc.) Q: What kind of external factors must be considered in building structures? (Soil, temperature, natural events in the area, temperatures, safety, etc.) Q: Why is it important to plan the structure down to smallest details and make/test models prior to building? (you can only build once as repairs could be costly and involve loss of human life – by testing, you know how strong you need to make things to withstand the elements, you also know if your structure will be stable and strong) 1. Distribute post-assessment quiz and allow 5 min to complete; collect 2. Activity sheet can be taken up as a class or collected and marked © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Lesson Plan Page 1 of 1 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Pre-Assessment Birthday: __________________ Name: ____________________________ Complete the following questions below. Each correct response is worth 1 mark. 6 1. Torsion is an action that twists a material. True OR False 2. Cables in a suspension bridge are held by compression. True OR False 3. What is thermal load? 4. What is the difference between the dead load and the live load in a structure? 5. What building material is considered the strongest? 6. Draw the following structures in the table below in order of increasing strength (able to hold weight without collapsing). Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Pre-Assessment Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Pre-Assessment Name: Answer Key Complete the following questions below. Each correct response is worth 1 mark. 6 1. Torsion is an action that twists a material. True OR False 2. Cables in a suspension bridge are held by compression. True OR False 3. What is thermal load? The expanding or shrinking of a structure due to changes in temperature. 4. What is the difference between the dead load and the live load in a structure? The dead load is the weight of the materials used to build the building, the live load is the weight of the people, furniture, books, materials, etc. that are inside a building. 5. What building material is considered the strongest? Steel 6. Draw the following structures in the table below in order of increasing strength (able to hold weight without collapsing). Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Pre-Assessment Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ LINK: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/buildingbig/lab/forces.html 42 FORCES [12 marks] Use the FORCES section to complete the table below by filling in the empty boxes. Important: For the last column (the examples) look at the examples in each section by choosing Then think of an example of the force in everyday life and write it down. Action Name of Force Squeezing Compression What does the force do? What does it look like? (Draw the force in action!) Squeezes material together. Stretches material apart. Stretching Bending When a straight material becomes curved, one side squeezes together and the other side stretches apart. Sliding Sliding two materials past one another in opposite direction. Twisting © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Page 1 of 3 Example of the force in action! Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ LOADS [15 marks] 1. What are loads? [1 mark] 2. What is the dead load? Give an example of what a dead load would include. [2 marks] 3. What is the live load? Give an example of what a live load would include. [2 marks] 4. A library is built from concrete walls and will hold a collection of children’s books. Identify the dead load and live load in this example. [2 marks] 5. Complete the table below. [8 marks] What is the load called? Force acting on the structure Description of the load Deep piles (heavy concrete pillars) to support the structure Settlement load Temperature Earthquake load Wind load Preventing the load from occurring Shrinking or expanding due to changes in temperature Push and pull in a horizontal direction Roller joints (inserts into building material to allow it to expand or contract) Shear walls (walls of concrete reinforced with steel beams) Wind Vibration A load that changes over time © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Page 2 of 3 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ MATERIALS [9 marks] 1. Why is it important to take into account the direction of the fibers when building with wood? [1 mark] 2. Why are circus tents made from plastic? [2 marks] 3. Aluminum is a building material that when combined with magnesium and copper (both metals) is almost as strong as steel. What do we call materials that are a combination of metals? [1 mark] 4. Why is brick not used in building modern structures (excluding houses)? [1 mark] 5. What is the difference between concrete and reinforced concrete? [1 mark] 6. Which force is significantly improved by using reinforced concrete versus concrete? [1 mark] 7. Cast iron can be molded to any shape but is not used as a modern day building material, why? [1 mark] 8. Which material is stronger than any other in both compression and tension? [1 mark] SHAPES [6 marks] 1. Compare the structural strength of the three shapes by using the slider on the right side to add and remove weight. Draw the shapes below in the order of greatest structural strength to least structural strength. [3 marks] Note: Move to slider to the very bottom to return to the introductory screen Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength 2. Select each of the shapes to learn more about them. Complete the table below. [3 marks] Add a brace for support Add buttresses for support Circle the strongest point © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Page 3 of 3 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Answer Key Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ LINK: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/buildingbig/lab/forces.html 42 FORCES [12 marks] Use the FORCES section to complete the table below by filling in the empty boxes. Important: For the last column (the examples) look at the examples in each section by choosing Then think of an example of the force in everyday life and write it down. Action Squeezing Stretching Bending Sliding Name of Force Compression What does the force do? What does it look like? (Draw the force in action!) Squeezes material together. Columns in a skyscraper are under compression. Stretches material apart. Cables in a suspension bridge are in tension. Tension Bending Shear When a straight material becomes curved, one side squeezes together and the other side stretches apart. Sliding two materials past one another in opposite direction. Twisting a material. Twisting Example of the force in action! Torsion Bending a metal bar. Roadway sliding in opposite directions in the event of an earthquake. An unstable suspension bridge may twist during violent winds. NOTE FOR TEACHER: The answers in the last column will vary; the answers provided are those from the learning object which students are NOT to use in their answers. © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Answer Key Page 1 of 3 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Answer Key Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ LOADS [15 marks] 1. What are loads? [1 mark] Loads are forces that act on structures 2. What is the dead load? Give an example of what a dead load would include. [2 marks] The weight of the structure. Building materials such as concrete, nuts, bolts, beams are examples of dead load. 3. What is the live load? Give an example of what a live load would include. [2 marks] The weight of objects on the structure. People, furniture, materials are examples of live load. 4. A library is built from concrete walls and will hold a collection of children’s books. Identify the dead load and live load in this example. [2 marks] The dead load is the concrete walls of the library, the live load is the children’s books. 5. Complete the table below. [8 marks] What is the load called? Force acting on the structure Description of the load Soil beneath structure settles unevenly Settlement load Soft Soil Shrinking or expanding due to changes in temperature Thermal load Temperature Push and pull in a horizontal direction Earthquake load Earthquake Preventing the load from occurring Deep piles (heavy concrete pillars) to support the structure Roller joints (inserts into building material to allow it to expand or contract) Shear walls (walls of concrete reinforced with steel beams) Push in a horizontal direction Wind load Diagonal braces used to support and stabilize Wind A load that changes over time Dynamic load Vibration Thick beams are used in structures that experience dynamic loads. © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Answer Key Page 2 of 3 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Handout Answer Key Name: ___________________________ Date: ____________________________ MATERIALS [9 marks] 1. Why is it important to take into account the direction of the fibers when building with wood? [1 mark] The direction of the fibers is important because it is 3x easier to break wood if it is stretched across the direction of the fibers rather than in the direction of the fibers. 2. Why are circus tents made from plastic? [2 marks] Circus tents are made from plastic because the tents are pulled in many directions and cannot snap – the long chains of molecules that make up plastic can be pulled in many directions without snapping. 3. Aluminum is a building material that when combined with magnesium and copper (both metals) is almost as strong as steel. What do we call materials that are a combination of metals? [1 mark] Alloy 4. Why is brick not used in building modern structures (excluding houses)? [1 mark] Brick is very heavy and breaks easily (weak in tension) 5. What is the difference between concrete and reinforced concrete? [1 mark] Reinforced concrete has steel beams through it whereas concrete does not. 6. Which force is significantly improved by using reinforced concrete versus concrete? [1 mark] Tension 7. Cast iron can be molded to any shape but is not used as a modern day building material, why? [1 mark] Cast iron is brittle and snaps without warning. 8. Which material is stronger than any other in both compression and tension? [1 mark] Steel SHAPES [6 marks] 1. Compare the structural strength of the three shapes by using the slider on the right side to add and remove weight. Draw the shapes below in the order of greatest structural strength to least structural strength. [3 marks] Note: Move to slider to the very bottom to return to the introductory screen Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength 2. Select each of the shapes to learn more about them. Complete the table below. [3 marks] Add a brace for support Add buttresses for support Circle the strongest point © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Handout Answer Key Page 3 of 3 Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Post-Assessment Birthday: __________________ Name: ____________________________ Complete the following questions below. Each correct response is worth 1 mark. 6 1. Torsion is an action that twists a material. True OR False 2. Cables in a suspension bridge are held by compression. True OR False 3. What is thermal load? 4. What is the difference between the dead load and the live load in a structure? 5. What building material is considered the strongest? 6. Draw the following structures in the table below in order of increasing strength (able to hold weight without collapsing). Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Post-Assessment Forces, Loads, Materials, Shapes Student Activity Post-Assessment Name: Answer Key Complete the following questions below. Each correct response is worth 1 mark. 6 1. Torsion is an action that twists a material. True OR False 2. Cables in a suspension bridge are held by compression. True OR False 3. What is thermal load? The expanding or shrinking of a structure due to changes in temperature. 4. What is the difference between the dead load and the live load in a structure? The dead load is the weight of the materials used to build the building, the live load is the weight of the people, furniture, books, materials, etc. that are inside a building. 5. What building material is considered the strongest? Steel 6. Draw the following structures in the table below in order of increasing strength (able to hold weight without collapsing). Greatest amount of strength Moderate amount of strength Least amount of strength © 2007 University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT) ~ Permission to Copy Teacher-Created Resources: Student Activity Post-Assessment