Earth's Interior Objective 12: Section 2 Assessment Questions
advertisement

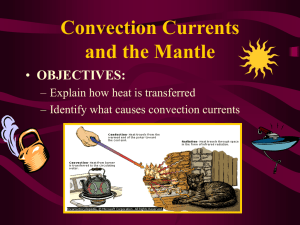
Earth’s Interior Objective 12: Section 2 Assessment Questions 1 a) What are the three types of heat transfer? The three types of heat transfer are convection, conduction, and radiation. 2 a) What is a convection current? A convection current is the movement of fluids, due to a difference in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of a fluid to another. 2 b) In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it becomes hotter? In general, as a fluid gets hotter, the density decreases. This is due to the fact that the particles receive more energy, which in turn makes them move faster and further apart. Even though the mass is the same, the volume increases, which makes the fluid less dense. 2 c) Describe how convection currents form. A convection current forms when there is a temperature difference between two parts of a fluid. The colder fluid, that is originally at the top, sinks as it has become more dense. Once it has sunk, the fluid then warms up and gains energy. This makes the fluid less dense so it rises. This continues as long as there is a heat source. 3 a) Name two layers of Earth in which convection currents take place. The two layers of the Earth in which convection currents take place are the outer core and mantle. 3 b) What causes convection currents in the mantle? The convection currents in the mantle are caused by the heat of the mantle and core. The internal heat generated in the core is created by radioactive decay, the Earth’s formation, and friction. 3 c) What will happen to the convection currents in the mantle if Earth’s interior eventually cools down? Explain As long as there is a heat source, convection currents will continue. This is due to the fact that there is a temperature difference between the upper and lower mantle. If the interior of the Earth were to cool off enough that there is no longer a temperature difference between the upper and lower mantle, then convection currents would stop. Until that time though, there will always be convection currents as long as there is a heat source and, thus, a temperature difference.