Biomes - Y9-Environmental-Management-SG
advertisement

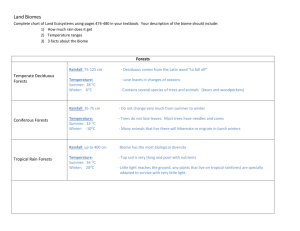
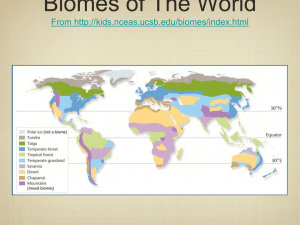
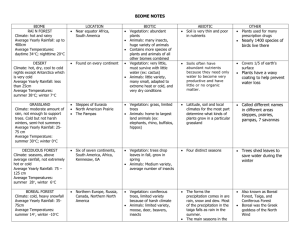
Biomes By: Trinidad By: Trinidad GenoveseGenovese Savannas A savanna is a grassland in which there are shrubs and isolated trees. Trees are isolated and not in a forest because there is not enough rainfall in a savanna for it. Savannas temperature is warm and they have two different seasons: dry season, in winter, and a really wet season, in summer. Dry season Wet season very few rain (average of 4 inches) lots of rain (average of 15 to 25 inches) cool (not cooler than 21°c) hot and very humid Human Impacts Animals Vegetation Most have longs wings or legs so they can be able to go on long migrations. Many of they stay under the ground so they can avoid the heat or raise their babies They are highly specialized to survive to long periods of drought. Their roots are long so that they can reach the water that is really under the soil, they have thick barks so that they resist fires. The grass is different in different parts so animals eat depending on what they like. The main human impact on savannas is that there live native people who are nomades. They farm in one place, cultivate and then to other area. This benefits the soil because it is not used, meaning it will recover and will still be useful in the future. Other human impact is tourism. People do safaris to get to know the place while being in contact with it. Tropical Rainforest A tropical rainforest is a forest where there are Animals Vegetation really tall trees and its temperature is warm. Many different kinds of monkeys. Some characteristics present on animals living there are bright colors and sharp patterns, loud vocalization and a diet heavy on fruits. has more kinds of trees than any other area in the world. It has more than a hundred species. Most of the trees have straight and are higher than 100 feet or even more. Many trees can only be identified by their flowers. Leaves are very large so that they can absorb as much light as possible Its temperature is between 34° and 20°. Rainfall there is more than a hundred inches per year. And its humidity is between 77 and 88% . They are very important because a half of the world’s vegetation is there, meaning it provides a lot of oxygen, necessary for human life. Human impact on rainforests Deforestation is the main human impact of rainforests. Every year over 90,000 square miles of the forest are harvested for human use. Apart from destroying the environment, deforestation is proved to accelerate global warming leading to a climate change in the rainforest layers of rainforest Temperate rainforest This kind of forests are found in North and South America. There it rains between 60 and Human Impacts 200 inches of rain per year. Summers are extremely hot (more than 80°f) and Winter is really cold, sometimes even snows. animals vegetation mammals like (bears, deers, coyotes) big coniferous trees big slug variety mosses and lichens Timber cutting is the number one threat of these forests. If it is done wrongly it can cause erosion of the soil, destroying it. Deserts Vegetation Animals Cold -widely scattered plants -pretty covered ground -most plants: deciduous, having spiny leaves -jack rabbits -kangaroo rats -also other carnivores like coyote Hot -rocky course textured soils -No surface water -shrubs -short woody trees -small thick leaves -cacti -nocturnal carnivores -main animals: kangaroo rats and burrowers insects, arachnids, reptiles and birds Cover ⅕ of the surface of the earth. Rainfall is less than 50 cm per year. Deserts loose almost twice as much heat at night Cold Desert Hot Desert cold winters with snowfall Seasons warm during the year and very hot in summer high rainfall in winter and little rainfall in winter a little in summer mean winter t° -2°- 4°c mean summer t° 21°-26° c mean t° 20-25°c, high 43.5°-49°c. They drop to -18°c Human Impacts -off roading -military exercise Taiga is the largest biome in the world. Very cold winters with snowfall and summers are warm, humid and rainy. Winter average temperature is -54°-1°c. Summer can be from -7°-21°c. Total precipitation on a year is 30-85 cm Vegetation Animals lots of coniferous trees (pines, white spruce, hemlock and douglas fir) millions of insects in the summer times lichens and mosses Tend to be predators (wolverine, bobcat) snowshoe rabbits, red squirrels and voles and birds Main human impact: Deforestation Tundra treeless land and the youngest biome, it was formed 10,000 years ago. Usually is very cold. Mostly all tundras are located in the Northern hemisphere. In winter it is cold and dark In summer it is very soggy and the tundra is covered with Human Impact pollution from mines is the main human impact on tundra. in a tundra of Russia got so polluted that all plants had died marshes, lake, bogs and streams. There is sunlight almost the 24 hrs Vegetation Animals drop to -70°c rocky ground insects Precipitation 6-10 inches per year mosses, heath, lichen, grasses and 400 varieties of flowers rodents,wolves,foxes bears and deer Average temperature -28°c. at night temperature can Grasslands Large terrains of grass, flowers and herbs. In winter t° can be of -40°c and in summer it can be 21.1°c Temperate average of rainfall per year 10-30 inches TropicalSubtropical average of rainfall per year 25-60 Tall grass Short grass Human Impact humid and very wet dry and with hotter summers and colder winters The land is being divided for farming and urban development. A lot of grasslands have disappeared because of the building of power plants. Bibliography http://www.geography.learnontheinternet.co.uk/topics/savanna.html http://bostonsciencecommunications.com/index/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/biomes.jpg http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/glossary/gloss5/biome/deserts.html http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/savanna.htm http://www.marietta.edu/~biol/biomes/temprain.htm http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/savanna.htm http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/rainforest.htm http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/taiga.htm http://the-taiga-biome.weebly.com/human-influences.html http://desertbiomes.weebly.com/human-impacts.html http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/tundra.htm http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/grasslands.htm http://grasslandsbiome3.weebly.com/human-impact.html