Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications Lab Class Week 5
advertisement

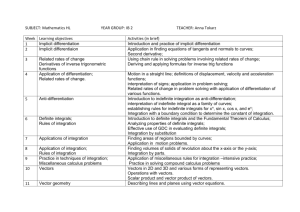
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications Lab Class Week 5 School of Computer Science & Informatics Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Vector operators Definition (Vector Addition, Subtraction and Scalar Multiplication in Rn ) Let v and w be two vectors in Rn and k a real number. The following rules are well-defined: v + w = (v1 + w1 , v2 + w2 , . . . , vn + wn ). v − w = (v1 − w1 , v2 − w2 , . . . , vn − wn ) kv = (kv1 , kv2 , . . . , kvn ). These rules coincide with the geometrical interpretation for two-dimensional vectors (see previous definitions). 2 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Vector Addition, Subtraction and Scalar Multiplication in MATLAB MATLAB directly supports vector addition, subtraction and scalar multiplication: >> v=[1 2 5]; >> w=[3 -1 1]; >> v+w ans = 4 1 6 >> v-w ans = -2 3 4 >> 3 * v ans = 3 6 15 >> w*(-1) ans = -3 1 -1 3 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Scalar product Definition (Scalar product) Given two vectors v and w in Rn with components (v1 , v2 , . . . , vn ) and (w1 , w2 , . . . , wn ). We define the scalar product (or (standard) inner product, dot product) of v and w as v.w or hv, wi = n X vi wi i=1 Note what the scalar product does: It takes two vectors and assigns them a real number. Problem (Scalar product) Work out the scalar product of vectors v = (1, 2) and w = (2, 3) Note the notations v.w and hv, wi are equivalent. We use the v.w notation. 4 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Scalar product using MATLAB MATLAB provides a vector function dot that computes the dot product of two vectors (of any, identical dimension). >> v = [3 2 -1] >> w = [2 -1 1] >> dot(v, w) ans = 3 >> sum(v.*w) ans = 3 dot(v, w) is equivalent to sum(v.*w) note v.*w is an array multiplication that returns a vector of the same size. 5 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Properties of scalar products Theorem (Cauchy-Schwarz inequality) Let v and w be vectors in Rn Then they satisfy the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality |v.w| ≤ kvkkwk. Theorem (Angle Between Two Vectors) If n = 2, 3 we even have the relation v.w = kvkkwk cos(θ) We call θ the angle between v and w . 6 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Euclidean norm of a vector Definition (Euclidean norm of a vector) For a vector v ∈ Rn we define its norm as √ kvk = v.v This norm is called the Euclidean norm of the vector v. The Euclidean norm of a vector coincides with the length of the vector in R2 and R3 . v2 y (v1, v2) !v! v v1 x By Pythagoras’ Theorem, kvk = q √ v12 + v22 = v.v 7 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Euclidean norm of a vector in MATLAB The default behaviour of MATLAB function norm for a given vector input is to return the Euclidean norm (also called 2-norm): >> v = [3 4] >> norm(v) ans = 5 >> sqrt(dot(v, v)) ans = 5 8 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration The Vector Cross Product Besides the scalar product that maps two vectors from Rn to R we also need a product that maps two vectors from Rn to a vector in Rn . Definition (The vector cross product in R2 ) We define the vector cross product of v, w ∈ R2 as a mapping × : R2 × R2 7→ R with v × w = v1 w2 − v2 w1 The vector product in R2 is anti-symmetric, i.e. v × w = −w × v 9 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration The Vector Cross Product (cont.) Definition (The vector cross product in R3 ) We define the vector cross product of v, w ∈ R3 as a mapping × : R3 × R3 7→ R3 with v2 w3 − v3 w2 v × w = v3 w1 − v1 w3 . v1 w2 − v2 w1 The vector product in R3 is also anti-symmetric, i.e. v × w = −w × v The vector cross product has very useful properties, especially: for finding orthogonal vectors in R3 . for area and volume calculations in R2 and R3 respectively. 10 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Vector cross products in MATLAB MATLAB provides a vector function cross to compute the cross product of two vectors in R3 : >> v=[1 2 3]; >> w=[-1 1 2]; >> cross(v, w) ans = 1 -5 3 11 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Differentiation in MATLAB Derivative of a poly() structure - polyder(), Poly Diff Eg.m >> a = [ 3 6 9 ] ; % 3 x ˆ2 + 6 x + 9 >> k = p o l y d e r ( a ) k = 6 6 >>b = [ 1 2 0 ] ; >> k = p o l y d e r ( b ) % x ˆ2 + 2 x k = 2 2 >> k = p o l y d e r ( a , b ) %(3x ˆ2 + 6 x + 9 ) ( x ˆ2 + 2 x ) k = 12 36 42 18 MATLAB code for this at Poly Diff Eg.m 12 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Symbolic Differentiation in MATLAB Symbolic Derivative via diff(), Symb Diff Eg.m >>syms x ; % Declare f (x) >>f = x ˆ2 + 2∗ x +1; % Differentiate f (x) >>d f = d i f f ( f ) a n s = 2∗ x + 2 MATLAB code for this at Symb Diff Eg.m 13 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Computing and Plotting Tangent to a Curve Symb Diff Eg.m continued % G r a d i a n t a t ( x0 , y0 ) x0 = 1 ; y0= 5 ; % compute m + c ( y−a x i s I n t e r c e p t ) m = s u b s ( d f , x0 ) ; c = y0 − m∗ x0 ; %D e c l a r e t a n e q n = m∗ x + c ; %P l o t f ( x ) and t a n g e n t a t ( x0 , y0 ) e z p l o t ( t a n e q n ,[ −50 5 0 ] ) ; h o l d on ; e z p l o t ( f ,[ −50 5 0 ] ) ; MATLAB code for this at Symb Diff Eg.m 14 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Symb Diff Eg.m Output x2 + 2 x + 1 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 −50 −40 −30 −20 −10 0 x 10 20 30 40 50 15 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Stationary Points in MATLAB MATLAB Example:Stationary point eg.m syms x f = x ˆ3 −3∗x ˆ2 −9∗x + 2 ; df = d i f f ( f ) ; % 1 st d e r i v a t i v e d f 2 = d i f f ( d f ) ; %2nd d e r i v a t i v e % f i n d Turning p o i n t s % n e e d d o u b l e ( ) from c o n v e r t s y m b o l i c v a r i a b l e t u r n p t s x = double ( s o l v e ( df ) ) ; t u r n p t s y = double ( subs ( f , t u r n p t s x ) ) ; max min = d o u b l e ( s u b s ( d f 2 , t u r n p t s x ) ) ; .... P l o t R e s u l t s ( s e e S t a t i o n a r y p o i n t e g .m f i l e ) Full MATLAB code at: Stationary point eg.m 16 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Stationary point eg.m Output x3 − 3 x2 − 9 x + 2 600 400 200 0 Max Min −200 −400 −600 −800 −1000 −1200 −10 −8 −6 −4 −2 0 x 2 4 6 8 10 17 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration MATLAB Integration: poly() Integrals MATLAB lets you integrate poly() Polynomials: polyint() and trapz() >> p = [ 1 0 0 ] % p = x ˆ2 % Indefinite Integral >> p o l y i n t ( p ) % Ans = x ˆ3/3 ans = 0.3333 0 0 0 % Definite I n t e g r a l ( via numerical integration ) >> t r a p z ( −6:6 , p o l y v a l ( p , − 6 : 6 ) ) ans = 146 18 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration MATALB Example: Area Under Graph (1) MATLAB Code to solve and plot above example: integral area.m % d e c l a r e f u n c t i o n and p l o t syms x plot range = [ −10 ,10]; it f = x ˆ2; ezplot (f , plot range ); h o l d on ; % define definite integral i n t l i m i t s = [−6 6]; limits % Integrate intf = int ( f ) % Indefinite Integral % Definite Integral via Indefinite result i n t v a l i n d = int ( f , i n t l i m i t s (1) , i n t l i m i t s (2)) 19 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration MATALB Example: Area Under Graph (2) integral area.m Cont. % I d i o t Check ! D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l v i a I n d e f i n i t e r e s u l t subs ( i n t f , i n t l i m i t s (2)) − subs ( i n t f , i n t l i m i t s (1)) % not r e a l l y a n e c e s s a r y b i t o f code as %Def . I n t i s t h e way t o do i t ! % S e t up p l o t range = i n t l i m i t s ( 1 ) : 0 . 1 : i n t l i m i t s ( 2 ) ; y = s u b s ( f , r a n g e ) ; %s a m p l e v a l u e s on c u r v e % Shade a r e a b e l o w t h e c u r v e area ( range , y , ’ FaceColor ’ , [ 0 , 0 , 1 ] , ’ LineStyle ’ , ’ none ’ ) ; Note: area()- useful plot function to shade areas of given graph values. MATLAB code for this at integral area.m 20 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Example: Area Between Two Curves (1) MATLAB Code: integral area between.m % declare functions syms x plot range = [ −3 ,3]; f 1 = −x ˆ2 + 6 ; f 2 = x ˆ2 − 2∗ x + 2 ; % Find Points of I n t e r s e c t i o n of cur ves r o o t s i n t e r s e c t = s o r t ( double ( s o l v e ( f1 − f2 ) ) ) ; % Definite Integral area intersect = i n t ( f 1 − f2 , r o o t s i n t e r s e c t ( 1 ) , r o o t s i n t e r s e c t ( 2 ) ) 21 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration Example: Area Between Two Curves (1) integral area between.m Cont. % S e t up p l o t range = r o o t s i n t e r s e c t ( 1 ) : 0 . 1 : r o o t s i n t e r s e c t ( 2 ) ; y = s u b s ( f 1 , r a n g e ) ; %s a m p l e v a l u e s on c u r v e f 1 % Shade Are a f 1 area ( range , y , ’ FaceColor ’ , [ 0 , 0 , 1 ] , h o l d on ; ’ LineStyle ’ , ’ none ’ ) % ’ r u b out ’ a r e a a b o v e t h e c u r v e y = s u b s ( f 2 , r a n g e ) ; %s a m p l e v a l u e s on c u r v e f 2 area ( range , y , ’ FaceColor ’ , [ 1 , 1 , 1 ] , ’ L i n e S t y l e ’ , ’ none ’ ) % Plot funtions e z p l o t ( f1 , p l o t hf2 = e z p l o t ( f2 s e t ( hf2 , ’ Color ’ over p l o t range range ); , plot range ); , ’ black ’ ) ; MATLAB code for this at integral area between.m 22 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration MATLAB Example: Area Under x-axis (1) MATLAB Code: integral area under.m % declare function syms x plot range = [ −5 ,5]; i n t l i m i t s = [ −3 ,3]; f = x ˆ3; % Definite Integral via Indefinite result int area = int ( f , i n t l i m i t s (1) , i n t l i m i t s (2)) % WRONG ( f o r A rea ) ! Answer i s ZERO % F o r x ˆ3 n e e d t o s p l i t a t x = 0 % E x e r c i s e : W r i t e a g e n e r a l f u n c t i o n t o work t h i s p o i n t o u t . % Do Area P r o p e r l y i n t a r e a = abs ( i n t ( f , i n t l i m i t s ( 1 ) , 0 ) ) + abs ( i n t ( f , 0 , i n t l i m i t s ( 2 ) 23 / 24 Vectors Calculus: Differentiation Calculus: Integration MATLAB Example: Area Under x-axis (2) MATLAB Code: integral area under.m % S e t up p l o t range = i n t l i m i t s ( 1 ) : 0 . 1 : 0 ; y = s u b s ( f , r a n g e ) ; %s a m p l e v a l u e s on c u r v e % Shade a r e a b e l o w t h e c u r v e area ( range , y , ’ FaceColor ’ , [ 1 , 0 , 0 ] , h o l d on ; ’ LineStyle ’ , ’ none ’ ) ; range = 0 : 0 . 1 : i n t l i m i t s ( 2 ) ; y = s u b s ( f , r a n g e ) ; %s a m p l e v a l u e s on c u r v e % Shade a r e a b e l o w t h e c u r v e area ( range , y , ’ FaceColor ’ , [ 0 , 0 , 1 ] , ’ LineStyle ’ , ’ none ’ ) ; %p l o t f u n c t i o n h f =e z p l o t ( f , p l o t r a n g e ) ; s e t ( hf , ’ Color ’ , ’ black ’ ) ; MATLAB code for this at integral area under.m 24 / 24