Echinodermata
advertisement

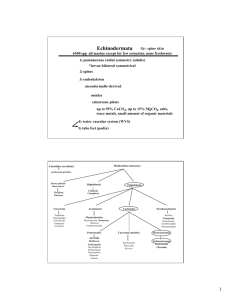
Echinodermata Echinodermata • • • • • • • • Approx. 6,000 known species; all marine Deuterostomes Pentamerous radial symmetry Endoskeleton – calcareous ossicles Tricoelomate Water-vascular system Mutable connective tissue Reproduction – External Fertilization, larval If radially symmetrical – why placed so “high” on evolutionary tree? • Radial symmetry is secondarily derived trait – Evolutionary influences? – Benthic lifestyle • Water-vascular system • Bilateral symmetry in larvae • Metamorphose to radial Endoskeleton • Composed of ossicles • Ossicles linked or diffuse • Small or large plates – one of features that distinguishes classes Mutable Connective Tissue • Dermis, extracellular matrix • Changes in Ca+2 concentration • Rigidity through matrix • Movement of urchin spines Regeneration • Most echinoderms capable of regeneration • Totipotent cells • Mutable connective tissue – Brittle star losing arm – Cucumbers regurgitating viscera Tricoelomate • Three pair of coelomic pouches (characteristic of deuterostomes) • One forms water vascular system Water-Vascular System • Point of inflow • Series of canals (formed from mesocoel) • Tube feet • Functions by changing pressure Water-Vascular System • Ampulla • Muscle/suction • Adhesion largely chemical • Release Circulatory System • Closed • “ebb and flow” • Lymph system – Tiedemann’s bodies – linked to WVS Class Asteroidea • Sea Stars • 1,500 known species • Central disc, radiating arms • Ossicles – connected, shape varies w/ sp. • Pedicellariae (see Fig. 28-10 an 28-11) defense • Mucus secretion and cilia – keep surface clean Cross Section (Arm) Digestive System Class Ophiuroidea • Brittle Stars, Basket Stars • 2,000 known species • Central disc, arms distincly set off • Ossicles – Plates • “Vertebrae” in arms • Lack pedicellariae and cilia Calcareous plates and shields Locomotion • Most mobile of Echinodermata • “rowing” Class Echinoidea • • • • • Urchins, sand dollars ~950 known species Name means “like a hedgehog” No arms, circular or oval in shape Some members have secondary bilateral symmetry • Ossicles – flattened and sutured to form a test Spines • • • • Primary (long) and secondary (short) Ball and socket Movement by muscular sheath Mutable connective tissue locks in place Water Vascular System • Essentially like a sea stars • Madreporite is a modified genital plate • Circumpharyngeal ossicles and muscles • Protrusible • Highly muscularized • Used of grazing Holothuroidea • Sea cucumbers • 1,200 species • Greatest habitat diversity of Echinoderms • Most 10 – 30 cm • Range 5 mm – 2 m • 1/3 species live deep ocean (90% biomass Holothuroidea • Elongate on oralaboral axis • No arms • Buccal podia • Micro-ossicles