Notes 47 Transforming Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
advertisement

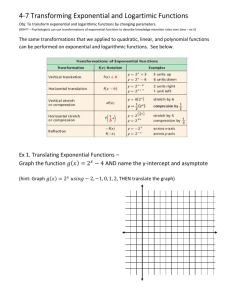
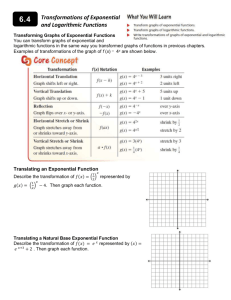
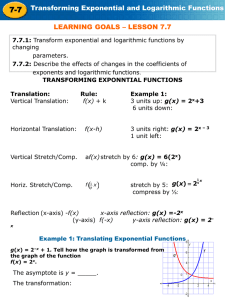
Notes 4­7 Transforming Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: ­ Transform exponential and logarithmic functions by changing parameters ­ Describe the effects of changes in the coefficients of exponential and logarithmic functions Who uses this? Psychologists can use transformations of exponential functions to describe knowledge retention rates over time. 1 You can provide the same transformations on exponential functions as you performed on polynomial, quadratic and linear functions... 2 Ex. Make a table of values, and graph the function asymptote. Tell how the graph is transformed from the graph X Describe the Y ­2 ­1 0 1 2 3 3 Ex. Graph the exponential function. Find the y­intercept and the asymptote. Describe how the graph is transformed from the graph of its parent function. a. 4 b. 5 Try These: Ex. Graph the exponential function. Find the y­intercept and the asymptote. Describe how the graph is transformed from the graph of its parent function. a. b. 6 Because a log is an exponent, transformations of logarithmic functions are similar to transformations of exponential functions. 7 Ex. Graph each logarithmic function. Find the asymptote. Then describe how the graph is transformed from the graph of its parent function. a. 8 b. 9 Try These: Ex. Graph the logarithmic function. Find the asymptote. Then describe how the graph is transformed from the graph of its parent function. a. 10 Ex. Write each transformed function. a. of is translated 2 units right, compressed vertically by a factor and reflected across the x­axis is translated 1 unit left and 3 units up and horizontally b. stretched by a factor of 5. 11 Try These: Ex. Write the transformed function when units left and stretched vertically by a factor of 2. is translated 3 12 Ex. A group of students retake the written portion of a driver's test after several months without reviewing the material. A model used by psychologists describes where a is the retention of the material by the function the average score at time t (in months). Describe how the model is transformed from its parent function. Then use the model to predict the number of months when the average falls below 70. 13