STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

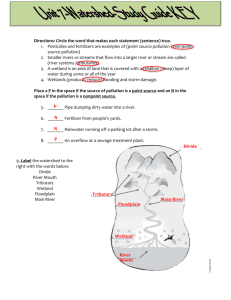
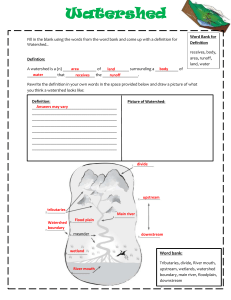
Name: __________________________ STUDY GUIDE Science/Key/Block # __________ Date: _________ WATERSHED TEST(S) / Complete sentences are not required for this assignment. You should use your notes to complete all questions. Watersheds / Parts of a Watershed 1. Define a watershed and what does it mean that we live in the Chesapeake Bay watershed? A watershed is the land that water flows over as surface runoff, collecting into Rills, Streams, and Rivers before flowing into a larger body of water. Living in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed means that all the water that falls onto this area will eventually end up in Chesapeake Bay 2. Most of the water in Loudoun County flows into which river that is a tributary to the Chesapeake Bay? ___Potomac__________________________ 3. Which six states, along with the District of Columbia, make up the Chesapeake Bay Watershed? ___Deleware ____________ ____New York_______________ ____Pennsylvania________ ___Maryland_____________ ____West Virginia____________ _____Virginia_____________ 4. Define tributary and name three tributaries (other than the Potomac) to the Chesapeake Bay. Smaller stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. 1) Susquehanna 2) James 3) York 4) Rappahannok 5. What do we call the rainfall that flows over the ground instead of soaking into the ground? ____Surface runoff____________________________ 6. Which tributary to the Chesapeake Bay is the largest (brings the most fresh water)? ___Susquehanna_________________________ 7. What do we call the highest point or elevation in a watershed that divides one watershed from another? ____Ridgeline or Divide_________________________________ 8. What is a floodplain and where is it located? (draw a picture too) Flat border area around a river channel that the river periodically floods. 9. Rocks experience changes in temperature that causes them to crack. Is this an example of erosion or weathering? _____Weathering____________________ 10. Acid rain eats away at statues. Is this an example of physical or chemical weathering? ___Chemical______________________________ 11. What is the difference between erosion and weathering? Weathering is breaking big things into small things. Erosion is moving earth with wind or water. Environmental Influences and Wetlands 12. Which type of load causes turbidity in water? ____Suspended Load_____________________ 13. What materials are sediments made of? Small rock fragments and bits of dirt/sand 14. Give two reasons why water runoff is a problem for our watershed? 1) Excess sediment can kill off some living things 2) Carries pollutants into the Bay 15. Explain how vegetation along a stream affects runoff. Absorbs some excess water and nutrients. Helps to slow erosion. 16. If a river has more energy what happens to the landscape and the turbidity of the water? More erosion and increased water turdibity 17. What is a wetland and what are two categories of wetlands? An area where the soil is covered by water. 1) Coastal 2) Inland 18. Why are wetlands called a transition zone from open water to dry land? Wetlands are where the open water meets the land. 19. What are 3 types of wetlands? ___Swamp___________ / _____Bog__________ / _____Marsh_________ 20. What are 3 functions of a wetland that helps the health of the Chesapeake Bay? 1) Flood control 2) habitat for living things 3) filtration of water (absorb excess nutrients) 21. Define abiotic factors and give three examples of abiotic factors in a river. Non-living factors that affect the health of an ecosphere. 1) Temperature 2) Turbidity 3) Dissolved Oxygen 4) Nitrogen and Phosphorous content 5) Salinity 6) Light 7) Pollution 22. Of all the water quality tests, which one is a test of a biotic factor?___Dissolved Oxygen______ Estuaries and Conservation 23. What is an estuary? Place where freshwater and saltwater mix! 24. Name three things that can cause the water quality in the Chesapeake Bay (estuary) to decrease. 1. Excess nutrients from fertilizers, such as nitrogen and phosphorous compounds, in the water (main cause). These nutrients cause algae to grow out of control. This makes it hard for underwater grasses to grow, reducing the supply of oxygen to decrease. 2. The destruction of natural habitats for plants and animals, including wetlands. 3. Toxic chemicals and increased sediment (dirt) in the water. 25. What is the largest estuary in the US? _Chesapeake Bay________________ 26. Give two reasons estuaries are important for humans. 1) Cultural Benefits (recreation, science, education) 2) Economic Benefits (tourism, fishing) 3) Transportation Benefits (harbors and ports) 27. Completely explain how oxygen can be depleted (used up) in a body of water. There are two basic reasons. 1) Turbidity blocks sunlight from reaching Submerged Aquatic Vegitation. 2) Excess nutrients cause algae to bloom, which causes turbidity. When the algae dies and decays, bacteria that decompose the algae uses oxygen. 28. Define salinity and explain how the levels can change in an estuary. Salinity = amount of dissolved salt in the water. Changes as the amount of freshwater coming into the Bay changes due to rain. 29. How can pH be measured and what is the pH scale for an acid, base, and a neutral substance? pH is measured with special paper or test kits. Acids have a pH of 0-6, Bases have a pH of 8-14, neutral is a pH of 7 (pure water is neutral) 30. What problems do farms create for the watershed? Runoff from farms adds excess nitrogen and phosphorus to the water. 31. What is the difference between point and non-point source pollution and give two examples for each. 1) Point source pollution = pollution comes from one polluter and can be easily identified . Examples: an industry is releasing toxic waste or a sewage treatment plant is leaking 2) Non-point source pollution is not easily identified, because there may be many contributors to the pollution Examples: fertilizers, nutrients, pesticides from farms; oil and paint from housing developments or city areas; spilled gasoline at gas stations Runoff can be reduced by adding materials, such as vegetation, wood chips or gravel to allow the water to soak into the ground. 32. List three ways non-point source pollution can be reduced. 1) Using cleaning products and fertilizers without phosphorus 2) Testing your car for oil leaks 3) Manure containment on farms 4) Silt fences around construction sites 1 How much of the Earth’s water is salt water (percent)? 97% 2 What is a Submerged Aquatic Vegetation, and give two reasons they are important to the Bay. Plants that live on the bottom of the Bay and never are exposed to the air. 1) Provide habitat for living organisms 2) Add dissolved oxygen to the water 3 1) Name and define three types of pollutants. Sediment pollution – sediments suspended in the water 2) Toxic pollution – Gasoline, oil, pesticides, industrial discharge, etc. 3) Thermal pollution – hot water resulting from water runoff from paved surfaces 4 Which water quality test (standard) is the most important test for the health of a water ecosystem? Dissolved Oxygen 5 What is a nutrient, how does it get into the water, where does it come from, and what does it cause? 1) A nutrient is a compound (nitrates and phosphates) that is necessary for all living organisms. 2) Nutrients get into the water through runoff 3) Nutrients come from fertilizers, animal wastes, and detergents (phosphates) 4) Nutrients cause algae to bloom.