Presentation Documents
advertisement

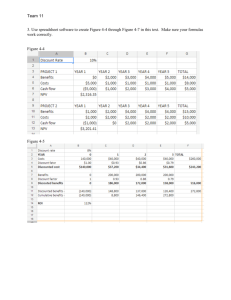
The Project Selection Process Session 3 Presented by Chris Upfold and Mark Maritz Acknowledgements Project Management in Practice, Mantel, J., Meredith, J., Shafer, S., and Sutton, M., (2011) Information Technology Project Management, Revised 6th edition, Schwalbe, K., (2011) Effective Project Management, Clements and Gido, (2006) Project Management, A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling and Controlling, Kerzner, H., 2002 Basic PAGDP 2014 Business Calculations, Zidel, D., (2001) Your Turn to Throw! PAGDP 2014 Methods for Selecting Projects • Focus on competitive strategy and broad organizational needs. • Perform net present value analysis or other financial projections. • Use a weighted scoring model. • Implement a balanced scorecard. • Address problems, opportunities, and directives. (maybe no choice) • Consider project time frame. • Consider project priority. PAGDP 2014 Aligning Projects with Business Strategy • Most organizations cannot undertake most of the potential projects identified because of resource limitations and other constraints. • An organization’s overall business strategy should guide the project selection process and management of those projects. PAGDP 2014 Pyramid for the Project Selection Process: 4 stages We need to start here first! PAGDP 2014 Focusing on Competitive Strategy and Broad Organizational Needs Competitive strategies: Cost leadership: Attract customers primarily because products or services are inexpensive. Examples include Macro, McDonalds, Pep stores. Focus: Develop products and services for a particular market niche. Examples include Bang & Olufsen, Bentley Broad organizational needs: People agree there is a need for a project, they will make funds available, and there is a strong will to make the project succeed. PAGDP 2014 Performing Financial Projections Financial considerations are often an important aspect of the project selection process, BUT, not in isolation. Three important methods include: Net Present Value analysis (NPV) Return on Investment (ROI) Payback analysis (how long to break even / make money) PAGDP 2014 Some alternative evaluation methods: Weighted Scoring A weighted scoring model is a tool that provides a systematic process for selecting projects based on many criteria. To create a weighted scoring model: Identify criteria important to the project selection process. Assign a weight to each criterion (so they add up to 100 percent). Assign numerical scores to each criterion for each project. Calculate the weighted scores by multiplying the weight for each criterion by its score and adding the resulting values. PAGDP 2014 Weighted Scoring PAGDP 2014 Problems, Opportunities, and Directives Problems are undesirable situations that prevent an organization from achieving its goals. These problems can be current or anticipated. (Equipment Breakdown: Walmer Park substation) Opportunities are chances to improve the organization. Directives are new requirements imposed by management, government, or some external influence. Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA) / National Credit Act (NCA) or new environmental legislation PAGDP 2014 What about the program mix? Aggregate Plan deals with product and process development projects Not a single project that determines the organisations long term success BUT a series of aligned projects that make-up the project portfolio. 3 classifications -Derivative Projects (incremental improvements) -Breakthrough Projects (new generation) -Platform Projects (new platform but existing technology) -R&D (basic technology to develop new knowledge) PAGDP 2014 Aggregate Project Plan Extensive product changes Minor product changes R&D Projects Extensive process Change Breakthrough Projects e.g. new generation products Platform Projects somewhere inbetween derivative and breakthrough Minor Process Change PAGDP 2014 Derivative projects Aggregate Project Plan Extensive product changes Minor product changes Internal Project (circles) Extensive process Change Size indicates Project size Minor Process Change PAGDP 2014 Strategic Alliance Projects (squares) Session Summary An organization’s overall business strategy should guide the project selection process and management of those projects. The four-stage planning process helps organizations align their projects with their business strategy. Several methods are available for selecting projects: Financial methods (net present value, return on investment, and payback) Weighted scoring models Aggregate Planning Balanced scorecards Addressing problems, opportunities, and directives Project time frame Project priority PAGDP 2014