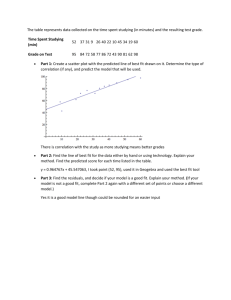
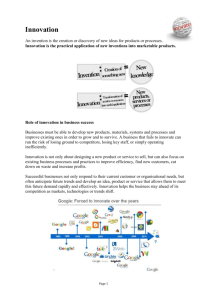
Fawaz hamidi presentation
advertisement
Shaping Business Strategy Through Competitive Intelligence Strategic Use of Intellectual Property Information This project is funded by the EU Strategic Planning Process This project is funded by the EU Business Strategy Definition • • • • “A course of action including the specification of resources required, to achieve a specific objective” Strategy is the means for achieving the business objectives. Plans a company uses to gain competitive advantage over competitors in a market. An advantage that a firm has over its competitors, allows it to generate greater sales or margins and/or retain more customers than its competition. Business Strategy External alignment Competitive position Internal alignment Business Strategy Formulation the match between the organization’s strategy and its industry structure IOT centers on the relationship between an organization’s Implementation internal aspects and its strategy RBV 2 INTEGRATION Michael Porter Generic Strategy Options Competitive Advantage Cost Competitive Broad Target Scope Narrow Target Differentiation Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus Successful business strategy requires awareness about the company’s external environment, including its customers, competitors, industry structure, competitive forces, etc… The Strategic Planning Process Feedback Objectives Environmental Scan: External & Internal Strategy Alternatives Strategy Formulation Strategy Choice Structuring Implementing Results Strategy Implementation Feedback Goal / Objectives Environmental Scan Strategy Alternatives Strategy Choice Structuring Implementing Results The Strategic Planning Process CI:IP Strategy Formulation Products / Markets Processes Strategy Implementation Strategy Formulation Process Environmental Scan External Environment PEST: •Political •Economic •Social •Technology / RD Macro Environment Industry Structure: Porter’s 5 Forces Model BARRIERS TO ENTRY Absolute cost advantages Proprietary learning curve Access to inputs Government policy Economies of scale Capital requirements Brand identity Switching costs Access to distribution Expected retaliation Proprietary products SUPPLIER POWER Supplier concentration Importance of volume to supplier Differentiation of inputs Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation Switching costs of firms in the industry Presence of substitute inputs Threat of forward integration Cost relative to total purchases in industry DEGREE OF RIVALRY -Exit barriers -Industry concentration -Fixed costs/Value added -Industry growth -Intermittent overcapacity -Product differences -Switching costs -Brand identity -Diversity of rivals -Corporate stakes BUYER POWER Bargaining leverage Buyer volume Buyer information Brand identity Price sensitivity Threat of backward integration Product differentiation Buyer concentration vs. industry Substitutes available Buyers' incentives THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES -Switching costs -Buyer inclination to substitute -Price-performance trade-off of substitutes Traditional Competitor’s Analysis: Sources of competitor data “BENCHMARKING” Looking at World-Class Competitors World-class competitors are proving that the best way to match your rivals' strengths is to, well, copy them. Not only is it both legal and ethical, the practice is virtually mandatory for any company that hopes to be considered a “world-class competitor”. Benchmarking is: The formal process of measuring, and comparing a company's operations, products, and services against those of top performers (both within and outside that company's primary industry). The aim of this process is to identify the leading companies' secrets to success, and copy them. Benchmarking as a management practice, has been growing explosively as it directs a company's focus outside its own walls, and is aimed directly at the marketplace and the competition The Competitive Intelligence Cycle Planning & Direction Feedback Collection Dissemination Source: Society for Competitive Intelligence Professionals Analysis “Competitive Intelligence is a systematic and ethical program for gathering, analyzing, and managing external information that can affect your company's plans, decisions, and operations” Competitive Intelligence Sources Sources of CI (by extent of use) High Use • Trade journals • External (on-line) databases • External hard copy documents • Employees • Industry experts • Trade organizations Moderate Use • Sales representatives • Customers • Internal documents • Internal databases / CD-ROM • Telephone interviews Low Use • Government records • Direct observations • Clipping services • Security analysis • Competitors (contact directly) • Personal interviews • Suppliers Very Little Use • Product purchasing • Freedom of information act • Focus groups • Case studies • Mail questionnaires 2002 Society of Competitive Intelligence Professionals Based on the Society of Competitive Intelligence Professionals 1997 Salary Survey Competitive Intelligence is a process which gives insight on the future direction of the market. This process involves stages from data to information to intelligence. “Competitive Intelligence is a systematic and ethical program for gathering, analyzing, and managing external information that can affect your company's plans, decisions, and operations” Difference Between Competitive Analysis and Benchmarking Competitive Analysis Benchmarking State of Mind Catch up with Competitor Over take competition Reach Excellence Methodology Measure Performances Compare costs Quantity Gaps Understand Mechanisms Compare Processes Indentify Positive Solutions Sphere of activity Direct Competitors Sector-based comparisons Inter-sector-based comparisons competitors or not Source of Information Sector-based analysis of competitors Leader Companies in their sector Fields of Application Enter field of Activity Organization / Product One method / one Function The Strategic Planning Process Feedback Objectives Environmental Scan: External & Internal Strategy Alternatives Strategy Formulation Strategy Choice Structuring Implementing Results Strategy Implementation Strategy Formulation Process Environmental Scan: Internal Environment Strengths and Weaknesses: RBV: Tangible & Intangible Intangibles: R&D, IP, HR, Internal Processes, L&G BSC: L&G, Internal Processes 28 Intellectual Property Strategic Resources Innovation • Patents • Utility models Brand • Trademarks Design • Industrial Designs Analysis of Intellectual Property portfolios of competitors may reveal a great deal about the competitors’ strategies. 28 Comparative advantage Input costs Less Relevant Competitive advantage Innovation More Important Innovation Process 1 Introduce Change to • Market Need / Problem recognition • Idea Generation 2 Products Services 3 • R&D / Feasibility (Technical and Financial) Processes • Implementation 4 • Commercialization 5 Marketable Value Added To introduce change to products, services, or processes with added value to the market through the management of knowledge, sciences, and technology. Financial The Balanced Scorecard Customer Internal Business Processes Learning and Growth Feedback Goal / Objectives Environmental Scan Strategy Alternatives Strategy Choice Structuring Implementing Results The Strategic Planning Process CI:IP Strategy Formulation Products / Markets Processes Strategy Implementation Thank You