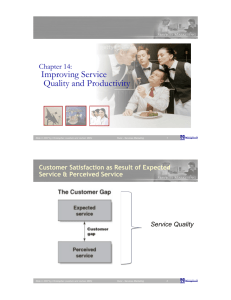
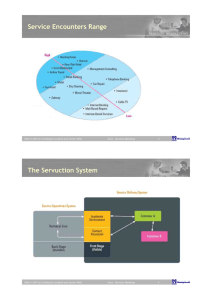
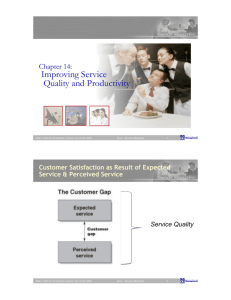
What is productivity? Integrating Service Quality and Productivity
advertisement

What is productivity? ! Efforts you put into work and the final result ! Efficiency ! How many service you produce in a certain amount of time ! Productivity vs. Service Quality ! Productivity is cost related ! Quality is perceived Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 12 Integrating Service Quality and Productivity Strategies " Quality and productivity are twin paths to creating value for both customers and companies " Quality focuses on the benefits created for customers; productivity addresses financial costs incurred by firm " Importance of productivity: ! Keeps costs down to improve profits and/or reduce prices ! Enables firms to spend more on improving customer service and supplementary services ! Secures firm’s future ! May impact service experience Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 13 What can you do to increase productivity in your business? Discuss with your neighbor (don’t have to be your group member) ! Train your employee better ! Partnering with companies (Gas-station, …) ! Specialized jobs for just serving in a bar ! Partnering with a parking lot to keep the tables full Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 14 Improving Service Productivity: (1) Operations-driven Strategies " Control costs, reduce waste " Set productive capacity to match average demand " Automate labor tasks " Upgrade equipment and systems " Train employees " Broadening array of tasks that a service worker can perform " Leverage less-skilled employees through expert systems " Service process redesign Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 16 Improving Service Productivity: (2) Customer-driven Strategies " Change timing of customer demand ! By shifting demand away from peaks, managers can make better use of firm’s productive assets and provide better service " Involve customers more in production ! Get customers to self-serve ! Encourage customers to obtain information and buy from firm’s corporate websites " Ask customers to use third parties ! Delegate delivery of supplementary service elements to intermediary organizations Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 17 Generic Productivity Improvement Strategies " Typical strategies to improve service productivity: ! Careful control of costs at every step in process ! Efforts to reduce wasteful use of materials or labor ! Replacing workers by automated machines ! Installing expert systems that allow paraprofessionals to take on work previously performed by professionals who earn higher salaries " Although improving productivity can be approached incrementally, major gains often require redesigning entire processes ? Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz ? Kunz - Services Marketing ? 18 Long Waiting Times May Indicate Need for Service Process Redesign (Fig 14.8) Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 19 Questions When Developing Strategies to Improve Service Productivity " How to transform inputs into outputs efficiently? " Will improving quality hurt productivity? " Will improving productivity hurt quality? " Are employees or technology the key to productivity? " Can customers contribute to higher productivity? Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 20 Tools to Analyze and Address Service Quality & Profitability Problems " Pareto Chart ! Separating the trivial from the important. Often, a majority of problems is caused by a minority of causes (i.e. the 80/20 rule) " Fishbone diagram ! Cause-and-effect diagram to identify potential causes of problems " Blueprinting ! Visualization of service delivery, identifying points where failures are most likely to occur Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 21 When Does Improving Service Reliability Become Uneconomical? (Fig 14.7) Satisfy Target Customers through Service Recovery Service Reliability 100% Optimal Point of Reliability: Cost of Failure = Service Recovery A B C Small Cost, Large Improvement Satisfy Target Customers through Service Delivery as Planned D Large Cost, Small Improvement Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Investment Assumption: Customers are equally (or even more) satisfied with the service recovery provided than with a service that is delivered as planned. Kunz - Services Marketing 22 Cause-and-Effect Chart for Flight Departure Delays (Fig 14.5) Facilities, Equipment Arrive late Oversized bags Customers Customers Frontstage Front-Stage Personnel Personnel Procedures Procedures Delayed check-in Aircraft late to Gate agents procedure gate cannot process fast enough Mechanical Acceptance of late Failures passengers Late/unavailable Late pushback airline crew Delayed Departures Late food service Other Causes Weather Air traffic Late cabin cleaners Poor announcement of departures Late baggage Weight and balance sheet late Late fuel Materials, Materials, Supplies Supplies Backstage Personnel Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Information Kunz - Services Marketing 23 Cause-and-Effect Chart for Flight Departure Delays (Fig 14.5) Facilities, Equipment Arrive late Oversized bags Customers Customers Frontstage Front-Stage Personnel Personnel Procedures Procedures Delayed check-in Aircraft late to Gate agents procedure gate cannot process fast enough Mechanical Acceptance of late Failures passengers Late/unavailable Late pushback airline crew Delayed Departures Late food service Other Causes Weather Air traffic Late cabin cleaners Poor announcement of departures Late baggage Weight and balance sheet late Late fuel Materials, Materials, Supplies Supplies Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Backstage Personnel Information Kunz - Services Marketing 25 When Does Improving Service Reliability Become Uneconomical? (Fig 14.7) Satisfy Target Customers through Service Recovery Service Reliability 100% Optimal Point of Reliability: Cost of Failure = Service Recovery A B C Small Cost, Large Improvement Satisfy Target Customers through Service Delivery as Planned D Large Cost, Small Improvement Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Investment Assumption: Customers are equally (or even more) satisfied with the service recovery provided than with a service that is delivered as planned. Kunz - Services Marketing 26 What Happens, When, in What Sequence? Time Dimension in Augmented Product (Fig 3.3) Reservation Parking Get car Check out Internet Check in Internet Use room USE GUESTROOM OVERNIGHT internet Porter Meal Before Visit Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Pay TV Room service Time Frame of An Overnight Hotel Stay (Real-time service use) Kunz - Services Marketing 27 Blueprinting the Restaurant Experience: A Three Act Performance " Act 1: Prologue and Introductory Scenes " Act 2: Delivery of Core Product ! Cocktails, seating, order food and wine, wine service ! Potential fail points: Menu information complete? Menu intelligible? Everything on the menu actually available? ! Mistakes in transmitting information a common cause of quality failure— e.g. bad handwriting; poor verbal communication ! Customers may not only evaluate quality of food and drink, but how promptly it is served, serving staff attitudes, or style of service " Act 3: The Drama Concludes ! Remaining actions should move quickly and smoothly, with no surprises at the end ! Customer expectations: Accurate, intelligible and prompt bill, payment handled politely, guest are thanked for their patronage Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 28 Developing a Blueprint Define big picture before drilling down to obtain a higher level of detail " Identify key activities in creating and delivering service " Which persons are involved? " Distinguish between front stage and backstage " Clarify interactions between customers and staff, and support by backstage activities and systems (key elements of the script). " Identify potential fail points; take preventive measures; prepare contingency " Develop standards for execution of each activity— times for task completion, maximum wait times, and scripts to guide interactions between employees and customers Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 29 Key Components of a Service Blueprint 1. Identify principal customer actions 2. Front-stage actions by customer-contact personnel 3. Identify & define scripts (detailed) 4. Define standards for front-stage activities 5. Specify physical evidence 6. Line of interaction (customers and front-stage personnel) 7. Line of visibility (between front stage and backstage) 8. Backstage actions by customer contact personnel 9. Support processes involving other service personnel 10. Support processes involving IT - Identify fail points and risks of excessive waits - Set service standards and do failure-proofing (detailed) - Points to improve profitability (e.g. SST) Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 30 Exercise " Develop a detailed blueprint for your service company Including customer actions, Front-stage actions, scripts (detailed), standards, physical evidence, Line of interaction, Line of visibility, Backstage actions, Support processes involving other service personnel, Support processes involving IT, Fail Points, Waiting time " E-mail me till Monday your blueprint (e.g. ppt, photo, scan) Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 31 Developing a Blueprint Define big picture before drilling down to obtain a higher level of detail " Identify key activities in creating and delivering service " Which persons are involved? " Distinguish between front stage and backstage " Clarify interactions between customers and staff, and support by backstage activities and systems (key elements of the script). " Identify potential fail points; take preventive measures; prepare contingency " Develop standards for execution of each activity— times for task completion, maximum wait times, and scripts to guide interactions between employees and customers Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 33 Benefits of Blue Printing " Provides a platform for innovation. " Recognizes roles and interdependencies among functions, people, and organizations. " Transfers and stores service knowledge. " Designs moments of truth from the customer s point of view. " Suggests critical points for measurement and feedback in the service process " Clarifies competitive positioning " Provides understanding of the ideal customer experience. Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 34 Where are Failure points, Standards, Physical evidence Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 35 Different Services – Different Flow Charts (Blueprints) People Processing – Stay at Motel Park Car Check In Possession Processing – Repair a DVD Player Spend Night in Room Breakfa st Maid Makes up Room Check Out Collec t Weat her Data View Presentation of Weather Forecast Meteorologists Input Data to Models and Creates Forecast from Output Technician Examines Player, Diagnoses Problem Breakfa st Prepare d TV Weatherperso n Prepares Local Forecast Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Return, Pick up Player and Pay Leave Store (Later) Play DVDs at Home Technician Repairs Player Information Processing – Health Insurance Mental Stimulus Processing – Weather Forecast Turn on TV, Select Channel Travel to Store Confirm Plans for Picnic Learn about Options Select Plan, Complete Forms University and Insurance Company Agree on Terms of Coverage Kunz - Services Marketing Pay Insurance Coverage Begins Customer Information Entered in Database 36 Printed Policy Document s Arrive Setting Service Standards " Service providers should design standards for each step sufficiently high to satisfy and even delight customers ! Standards may include time parameters, script for a technically correct performance, and prescriptions for appropriate style and demeanor ! Must be expressed in ways that permit objective measurement " First impression is important as it affects customer’s evaluations of quality during later stages of service delivery ! Research by Marriott Hotels indicates that four of five top factors contributing to customer loyalty come into play during the first 10 minutes of service delivery " Customer perceptions of service experiences tend to be cumulative " For low-contact service, a single failure committed front stage is relatively more serious than in high-contact service ! Viewed more seriously because there are fewer subsequent opportunities to create a favorable impression Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 37 Improving Reliability of Processes by Failure Proofing " Analysis of reasons for failure often reveals opportunities for failure proofing to reduce/eliminate future risk of errors " Need fail-safe methods for both employees and customers " Errors include: ! Treatment errors—human failures during contact with customer ― e.g., lack of courteous or professional behavior, failure to acknowledge, listen to, or react appropriately to the customer ! Tangible errors—failures in physical elements of service ― e.g., noise pollution, improper standards for cleaning of facilities and uniforms, equipment breakdown " Goal of fail-safe procedures is to prevent errors such as: ! Performing tasks incorrectly, in the wrong order, too slowly ! Doing work that wasn’t requested in the first place " See Service Perspectives 8.1 – Poka Yokes Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 38 Where might be possibility to redesign this process? Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 39 Redesigning Service Processes Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 40 Why Redesign? " Not profitable anymore " Rising Quality issues (e.g. waiting time) " Revitalizes process that has become outdated " Changes in external environment make existing practices obsolete and require redesign of underlying processes ! Creation of brand-new processes to stay relevant " Rusting occurs internally ! Natural deterioration of internal processes; creeping bureaucracy; evolution of spurious, unofficial standards - Extensive information exchange - Data redundancy - High ratio of checking or control activities to value-adding activities, increased exception processing - Customer complaints about inconvenient and unnecessary procedures Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 41 Process Redesign: Approaches and Potential Benefits " Eliminating non-value-adding steps " Delivering direct service " Bundling services " Redesigning physical aspects of service processes " Shifting to more customer participation Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 42 Process Redesign: Approaches and Potential Benefits (1) (Table 8.1) " Eliminating non-value-adding steps ! Streamline front-end and back-end processes of services with goal of focusing on benefit-producing part of service encounter ! Eliminate non-value-adding steps ! Improve efficiency ! More customized service ! Differentiate company " Delivering direct service ! Bring service to customers instead of bringing customers to provider ! Improve convenience for customers ! Productivity can be improved if companies can eliminate expensive retail locations ! Increase customer base Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 43 Process Redesign: Approaches and Potential Benefits (2) (Table 8.1) " Shifting to self-service ! Increase in productivity and service quality ! Lower costs and perhaps prices ! Enhance technology reputation ! Greater convenience " Bundling services ! Involves grouping multiple services into one offer, focusing on a welldefined customer group ! Often has a better fit to the needs of target segment ! Increase productivity ! Add value for customers through lower transaction costs ! Customize service ! Increase per capita service use Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 44 Process Redesign: Approaches and Potential Benefits (3) (Table 8.1) " Redesigning physical aspects of service processes ! Focus on tangible elements of service process; include changes to facilities and equipment to improve service experience ! Increase convenience ! Enhance the satisfaction and productivity of front-line staff ! Cultivate interest in customers ! Differentiate company Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 45 Levels of Customer Participation " Customer Participation ! Actions and resources supplied by customers during service production and/or delivery ! Includes mental, physical, and even emotional inputs " Three Levels ! Low—Employees and systems do all the work - Often involves standardized service ! Medium—Customer inputs required to assist provider - Provide needed information and instructions - Make some personal effort; share physical possessions ! High—Customer works actively with provider to co-produce the service - Service cannot be created without customer’s active participation - Customer can jeopardize quality of service outcome (e.g., weight loss, marriage counseling) Slide © 2007 by Christopher Lovelock and Jochen Wirtz Kunz - Services Marketing 46