notes
advertisement

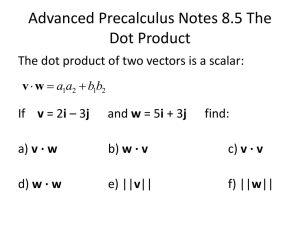
6.006 IntroductiontoAlgorithms Lecture1:DocumentDistance Prof.ErikDemaine YourProfessors Prof.ErikDemaine Prof.Piotr Indyk Prof.Manolis Kellis Your TAs KevinKelley JosephLaurendi DavidWen Tianren Qi NicholasZehender Your Textbook Administrivia • • • • • • • • • Handout: Course information Webpage:http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.006/spring11/ Signupforrecitationifyoudidn’tfilloutformalready Sign up for problemsetserver: https://alg.csail.mit.edu/ SignupforPiazzza accounttoask/answerquestions: http://piazzza.com/ Prereqs: 6.01(Python), 6.042(discretemath) Grades: Problem sets (30%) Quiz1 (20%;Mar.8@7.30–9.30pm) Quiz2 (20%;Apr.13@7.30–9.30pm) Final (30%) Lectures&Recitations;Homeworklabs;Quizreviews Read collaboration policy! Today • Classoverview – What’sa(good)algorithm? – Topics • DocumentDistance – Vectorspacemodel – Algorithms – Pythonprofiling&gotchas What’sanAlgorithm? • Mathematicalabstractionof computerprogram • Well‐specifiedmethodforsolving acomputationalproblem – Typically,afinitesequence ofoperations • Descriptionmightbestructured English,pseudocode,orrealcode • Key: no ambiguity http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Euclid_flowchart_1.png al‐Khwārizmī (c.780–850) • “al‐kha‐raz‐mi” http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Al‐Khwarizmi http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Abu_Abdullah_Muhammad_bin_Musa_al‐Khwarizmi_edit.png al‐Khwārizmī (c.780–850) • “al‐kha‐raz‐mi” • Fatherofalgebra – TheCompendious BookonCalculationby Completionand Balancing(c.830) – Linear&quadratic equations:someofthe firstalgorithms http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Al‐Khwarizmi http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Image‐Al‐Kit%C4%81b_al‐ mu%E1%B8%ABta%E1%B9%A3ar_f%C4%AB_%E1%B8%A5is%C4%81b_al‐ %C4%9Fabr_wa‐l‐muq%C4%81bala.jpg EfficientAlgorithms • Wantanalgorithmthat’s – Correct – Fast – Smallspace – General – Simple – Clever EfficientAlgorithms • Mainlyinterestedinscalability asproblemsizegrows WhyEfficient Algorithms? • Savewaittime,storageneeds,energy consumption/cost,… • Scalability=win – Solvebiggerproblemsgivenfixedresources (CPU,memory,disk,etc.) • Optimizetraveltime,scheduleconflicts,… HowtoDesignan Efficient Algorithm? 1. Definecomputational problem 2. Abstract irrelevant detail 3. Reducetoaproblemyoulearnhere (or6.046oralgorithmicliterature) 4. 5. 6. 7. Elsedesignusing“algorithmictoolbox” Analyzealgorithm’sscalability Implement & evaluate performance Repeat(optimize,generalize) Modules&Applications 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction BinarySearchTrees Hashing Sorting GraphSearch Shortest Paths Dynamic Programming NumbersPictures(NP) 9. Beyond Document similarity Scheduling Filesynchronization Spreadsheets Rubik’s Cube Google Maps Justifyingtext,packing,… Computingπ,collision detection,hardproblem Folding,streaming,bio Document Distance • Giventwodocuments, howsimilararethey? • Applications: – Findsimilardocuments – Detectplagiarism/ duplicates – Websearch (one“document”isquery) http://www.google.com/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Mirrors_and_forks/ Document Distance • Howtodefine “document”? • Word =sequenceof alphanumeric characters • Document= sequenceofwords – Ignorepunctuation& formatting Document Distance • Howtodefine “distance”? • Idea: focuson sharedwords • Wordfrequencies: – =# occurrencesofword indocument VectorSpaceModel [Salton, Wong, Yang 1975] • Treat each document – Onecoordinate as a vector of its words foreverypossibleword ‘dog’ • Example: – – 1 =“thecat” =“thedog” • Similaritybetweenvectors? – Dotproduct: ‘the’ 1 1 ‘cat’ http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=361220 VectorSpaceModel [Salton, Wong, Yang 1975] • Problem: Dotproductnotscaleinvariant • Example1: ‘dog’ – – – =“thecat” =“thedog” 2 1 • Example2: – – – =“thecatthecat” =“thedogthedog” 0 1 ‘the’ 1 2 2 ‘cat’ http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=361220 VectorSpaceModel [Salton, Wong, Yang 1975] • Idea: Normalizeby#words: ‘dog’ 1 ‘the’ • Geometricsolution: anglebetweenvectors – 0=“identical”, ∘ 1 1 ‘cat’ =orthogonal(nosharedwords) http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=361220 Algorithm 1. 2. 3. 4. Read documents Split eachdocument into words Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) Compute dot product Algorithm 1. Read documents 2. Split eachdocument into words – re.findall(‘\w+’, doc) – Buthowdoesthisactuallywork? 3. Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) 4. Compute dot product Algorithm 1. Read documents 2. Split eachdocument into words – Foreachlineindocument: Foreachcharacterinline: Ifnotalphanumeric: Addpreviousword (ifany)tolist Startnewword 3. Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) 4. Compute dot product Algorithm 1. Read documents 2. Split eachdocument into words 3. Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) a. Sortthewordlist b. Foreachwordinwordlist: – Ifsameaslastword: Incrementcounter – Else: Addlastwordanditscountertolist Resetcounterto0 4. Compute dot product Algorithm 1. 2. 3. 4. Read documents Split eachdocument into words Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) Compute dot product: Foreverypossibleword: Lookupfrequencyineachdocument Multiply Addtototal Algorithm 1. 2. 3. 4. Read documents Split eachdocument into words Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) Compute dot product: Foreverywordinfirstdocument: Ifitappearsinseconddocument: Multiplywordfrequencies Addtototal Algorithm 1. 2. 3. 4. Read documents Split eachdocument into words Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) Compute dot product: a. Startatfirstwordofeachdocument(insortedorder) b. Ifwordsareequal: Multiplywordfrequencies Addtototal c. Inwhicheverdocumenthaslexically lesserword,advancetonextword d. Repeatuntileitherdocumentoutofwords Algorithm 1. Read documents 2. Split eachdocument into words 3. Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) a. Initializeadictionarymappingwordstocounts b. Foreachwordinwordlist: – Ifindictionary: Incrementcounter – Else: Put0indictionary 4. Compute dot product Algorithm 1. 2. 3. 4. Read documents Split eachdocument into words Count wordfrequencies(documentvectors) Compute dot product: Foreverywordinfirstdocument: Ifitappearsinseconddocument: Multiplywordfrequencies Addtototal PythonImplementations PythonProfiling Culprit Fix PythonImplementations docdist1 docdist2 docdist3 docdist4 docdist5 docdist6 docdist7 docdist8 initialversion addprofiling replace+ withextend countfrequenciesusingdictionary splitwordswithstring.translate changeinsertion sorttomergesort nosorting, dotproductwithdictionary split wordsonwholedocument, notlinebyline 192.5 sec 126.5sec 73.4 sec 18.1sec 11.5sec 1.8sec 0.2sec ExperimentsonIntelPentium4,2.8GHz,Python2.6.2,Linux2.6.18. Document1(t2.bobsey.txt)has268,778lines,49,785words,3,354distincts. Document2(t3.lewis.txt)has1,031,470lines,182,355words,8,530distincts. Don’tForget! • Webpage: http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.006/spring11/ • Signupforrecitationifyoudidn’talready receivearecitationassignmentfromus • Sign up for problemsetserver: https://alg.csail.mit.edu/ • SignupforPiazzza accounttoask/answer questions:http://piazzza.com/