Aplia, Inc.: Assignments
Page 1 of 5
ECON 651 - Economic Analysis for Managers
Welcome Bryon Gaskin! If you're not Bryon, please click here.
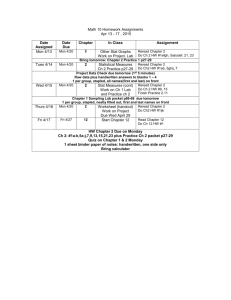
WEEK 2
08.30.04
WEEK 3
09.06.04
Due Date
Assignment
Mon, 08.30.04
04:00 PM
How to use online problems in practice mode.
Mon, 08.30.04
04:00 PM
How to use online problems in graded mode.
Introductory Practice Problem Set
Introductory Graded Problem Set
Thu, 09.09.04
11:00 PM
Consumer Behavior I
Thu, 09.09.04
11:00 PM
Preparing for the Price Ceilings and Price Floors
Experiment
Covers consumer behavior, including utility curves, indifference
maps, marginal rate of substitution, and budget constraints.
09.15.04
Type Status
Score
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
Practice only
Complete
16/22
N/A
N/A
Complete
Not graded yet
Complete
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Provides instruction for trading in the experiment with the
same name.
Thu, 09.09.04
11:00 PM
Thu, 09.09.04
11:00 PM
Analyzing Price Ceilings and Floors
A correct calculation of the range of possible surplus losses that
can be caused by price controls.
Do Cheap U.S. Corn Exports Impoverish Mexico's
Farmers?
Do cheap, subsidized U.S. corn exports impoverish Mexico's
farmers? The article gives two simple, but opposing, answers to
this question. The article does not provide enough information
to choose between the two opposing answers. But we can use
economics to examine the arguments offered in support of
each answer.
WEEK 4
09.13.04
Thu, 09.09.04
11:00 PM
Individual and Market Demand I
Mon, 09.13.04
04:00 PM
Price Elasticity of Demand
Mon, 09.13.04
04:00 PM
The World Health Organization claims that millions of lives
could be saved if countries increased cigarette taxes by 10%.
Supply and Demand I
Covers both sliding along and shifting of demand and supply
curves as well as equilibrium determination of market-clearing
price and quantity.
Tue, 09.14.04
04:00 PM
Supply and Demand II
Thu, 09.16.04
11:00 PM
Price Ceilings and Floors: Experiment
Thu, 09.16.04
11:00 PM
Consumer Behavior II
Thu, 09.16.04
11:00 PM
WEEK 5
09.20.04
This problem set demonstrates the methods at which individual
and market demand is established. It then covers economic
tools that help describe and analyze demand curves such as
elasticity and surplus.
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
Covers both sliding along and shifting of demand and supply
curves as well as equilibrium determination of market-clearing
price and quantity.
An experimental market for used books with limits on the
prices at which you can trade.
Covers consumer behavior, including utility curves, indifference
maps, marginal rate of substitution, and budget constraints.
Individual and Market Demand II
This problem set demonstrates the methods at which individual
and market demand is established. It then covers economic
tools that help describe and analyze demand curves such as
elasticity and surplus.
Production I
This problem set will help you understand firms' production
decisions involving inputs. You will learn about production with
one and two variable inputs including substitution between two
inputs.
Production II
This problem set will help you understand firms' production
decisions involving inputs. You will learn about production with
one and two variable inputs including substitution between two
inputs.
The Cost of Production in the Short Run I
This problem set will introduce you to firms' costs and cost
functions. You will learn about different types of costs and how
a profit-maximizing firm minimizes costs of production.
The Cost of Production in the Short Run II
This problem set will introduce you to firms' costs and cost
functions. You will learn about different types of costs and how
a profit-maximizing firm minimizes costs of production.
http://econ.aplia.com/af/servlet/assignmentadmin?action=showStudentList&ctx=jhorowitz-0003
9/15/2004
Aplia, Inc.: Assignments
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.20.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 6
09.27.04
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
The Cost of Production in the Long Run I
The Cost of Production in the Long Run II
This problem set will introduce you to firms' costs and cost
functions. You will learn about different types of costs and how
a profit-maximizing firm minimizes costs of production.
The Analysis of Competitive Markets I
In this problem set, you will be asked a series of questions
about the impact of government policy on markets. These
impacts depend upon the particular policy implemented, but
are measured by changes in consumer and producer surplus.
These changes, called "welfare effects" help us to weigh the
pros and cons of any particular policy initiative.
The Analysis of Competitive Markets II
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply I
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
In this problem set, you will be asked a series of questions
about the impact of government policy on markets. These
impacts depend upon the particular policy implemented, but
are measured by changes in consumer and producer surplus.
These changes, called "welfare effects" help us to weigh the
pros and cons of any particular policy initiative.
This problem set is designed to help you understand the
mechanics of the perfectly competitive market. The relationship
between the firm and its market is emphasized; you will need
to use supply and demand equations to determine equilibrium
prices, which individual firms must then take as given. You will
need to determine how profitable firms are, and then use that
information about profitability to make predictions about entry
and exit. Finally, you will consider the long-run position of the
perfect competitor.
Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply II
This problem set is designed to help you understand the
mechanics of the perfectly competitive market. The relationship
between the firm and its market is emphasized; you will need
to use supply and demand equations to determine equilibrium
prices, which individual firms must then take as given. You will
need to determine how profitable firms are, and then use that
information about profitability to make predictions about entry
and exit. Finally, you will work with the long-run industry
supply curve, and learn about gains that accrue to the supplier
in a perfectly competitive industry.
Preparing for the Taxes and Welfare Experiment
Prepares students for trading in the experiment with the same
name.
Taxes and Welfare: Experiment
Adds taxes on buyers and sellers to the basic supply and
demand experiment.
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
Analyzing Taxes and Welfare
Sun, 10.03.04
04:00 PM
The Market for Organs
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
N/A
N/A
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
This problem set will introduce you to firms' costs and cost
functions. You will learn about different types of costs and how
a profit-maximizing firm minimizes costs of production.
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 09.27.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 8
10.11.04
Page 2 of 5
Tests understanding of the main lessons in the Taxes and
Welfare experiment, including the effects of taxes on prices,
quantity, and gains for buyers and sellers.
Every year, thousands of Americans die waiting for an organ
transplant. Congress considered a bill that would provide a
financial incentive for people to donate vital organs.
China: Time to "Steel" Monopsony Lessons from
Japan?
You are probably familiar with the monopoly model: a single
seller in an industry with many buyers restricts output to raise
its price and profits. The monopsony model is less frequently
studied: a single buyer of a competitive industry's output
restricts its use of this good to lower the price it pays for the
good, thereby increasing its profits. Both models have wider
application than the pure examples of each. This news analysis
considers competition between Chinese steel mills for iron ore
and how the mills could save money by colluding when they
bargain with iron ore producers.
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Market Power: Monopoly I
Covers markets in which there is one seller and many buyers
(monopoly). Explores the behavior, consequences, and
regulation of the seller with market power.
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Market Power: Monopoly II
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Pricing with Market Power I
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.11.04
Covers markets in which there is one seller and many buyers
(monopoly). Explores the behavior, consequences, and
regulation of the seller with market power.
Covers the different pricing schemes firms use to increase
profits when they have market power.
Pricing with Market Power II
Covers the different pricing schemes that firms use to increase
profits when they have market power.
Monopsony I
http://econ.aplia.com/af/servlet/assignmentadmin?action=showStudentList&ctx=jhorowitz-0003
9/15/2004
Aplia, Inc.: Assignments
WEEK 9
10.18.04
04:00 PM
This problem set covers markets in which there is one buyer
and many sellers (monopsony).
Mon, 10.11.04
04:00 PM
Monopsony II
Mon, 10.18.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.18.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.18.04
04:00 PM
This problem set covers markets in which there is one buyer
and many sellers (monopsony).
Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly I
In this problem set, you will learn about market structures
characterized by imperfect competition (that fall somewhere
between pure monopoly and perfect competition). You will see
how the different market structures lead firms to different price
and output choices, and the effect these have on profits.
Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly II
In this problem set you will learn about market structures
characterized by imperfect competition (that fall somewhere
between pure monopoly and perfect competition). You will see
how the different market structures lead firms to different price
and output choices, and the effect these have on profits.
Basic Game Theory and Competitive Strategy I
This problem set covers some basic strategies firms use when
competing. You will learn how a firm's decisions are shaped by
its competitor's strategy.
Mon, 10.18.04
04:00 PM
Basic Game Theory and Competitive Strategy II
Sun, 10.24.04
04:00 PM
Introduction to Basic Price Discrimination
Sun, 10.24.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 10
10.25.04
Page 3 of 5
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
This problem set covers some basic strategies firms use when
competing. You will learn how a firm's decisions are shaped by
its competitor's strategy.
Combines explanation and problems to teach basic price
discrimination, including its definition, the conditions needed
for its success, perfect sorting, and group pricing.
Introduction to Advanced Price Discrimination
Combines explanation and problems to teach advanced price
discrimination, including second-degree price discrimination as
practiced through non-uniform pricing and menu pricing.
Advanced Game Theory and Competitive Strategy
I
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
N/A
N/A
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
This problem set covers more complex strategies firms use
when competing. You will learn how firms can influence their
competitor's strategies, and how firms use different strategies
to achieve different goals.
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
Advanced Game Theory and Competitive Strategy
II
This problem set covers more complex strategies firms use
when competing. You will learn how firms can influence their
competitor's strategies, and how firms use different strategies
to achieve different goals.
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 10.25.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 11
11.01.04
Mon, 11.01.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.01.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.01.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.01.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 12
11.08.04
Mon, 11.08.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.08.04
Markets with Asymmetric Information I
This problem set covers some of the most common examples
of market failures caused by asymmetric information.
Markets with Asymmetric Information II
This problem set covers some of the most common examples
of market failures caused by asymmetric information.
Preparing for the Market for Lemons Experiment
Prepares students for the Market for Lemons experiment.
A Market for Lemons: Experiment
Play the role of a buyer or seller in this online market for low
and high quality MP3 players.
Analyzing a Market for Lemons
Reinforces concepts learned in the Market for Lemons
experiment.
Labor I
Applies supply and demand in the context of the labor market.
Labor II
Tests understanding of the factors that affect employment and
wages.
Markets for Factor Inputs I
This problem set examines different market structures for
factors of productions, with an emphasis on labor as a factor of
production.
Markets for Factor Inputs II
This problem set examines different market structures for
factors of productions, with an emphasis on labor as a factor of
production.
Investment, Time, and Capital Markets I
This problem set teaches you how to determine what future
profits are worth today. Once you learn this, you will be able to
understand how firms and consumers make capital investment
decisions.
Investment, Time, and Capital Markets II
http://econ.aplia.com/af/servlet/assignmentadmin?action=showStudentList&ctx=jhorowitz-0003
9/15/2004
Aplia, Inc.: Assignments
WEEK 13
11.15.04
Page 4 of 5
04:00 PM
This problem set teaches you how to determine what future
profits are worth today. Once you learn this, you will be able to
understand how firms and consumers make capital investment
decisions.
Mon, 11.15.04
04:00 PM
General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency Equilibrium in Exchange I
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Not graded yet
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
Not started
Practice only
N/A
N/A
You will learn how changes in one market can affect the
markets of goods that are complements or substitutes. You will
also learn more about efficiency and what conditions are
necessary to ensure efficient markets.
Mon, 11.15.04
04:00 PM
General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency Equilibrium in Exchange II
You will learn how changes in one market can affect the
markets of goods that are complements or substitutes. You will
also learn more about efficiency and what conditions are
necessary to ensure efficient markets.
WEEK 14
11.22.04
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
Regulation of Sulfur Dioxide Emissions I
Examination of the effects of regulation of sulfur dioxide
pollution caused by electricity generation on marginal social
and private costs and benefits, production and consumption,
and use of pollution-reduction methods.
Regulation of Sulfur Dioxide Emissions II
Tests understanding of the effects of regulation of sulfur
dioxide pollution caused by electricity generation on marginal
social and private costs and benefits, production and
consumption, and use of pollution-reduction methods.
General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency Equilibrium in Production II
You will learn about efficiency in production and input markets.
Also, you will see the benefits resulting from trade between two
countries.
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency Equilibrium in Production I
You will learn about efficiency in production and input markets.
Also, you will see the benefits resulting from trade between two
countries.
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.22.04
04:00 PM
WEEK 15
11.29.04
Mon, 11.29.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.29.04
04:00 PM
Externalities and Public Goods I
This problem set will show you some of the common reasons
that market failure occurs for public goods, common goods,
and in the presence of externalities.
Externalities and Public Goods II
This problem set will show you some of the common reasons
market failure occurs for public goods, common goods, and in
the presence of externalities.
Market Solutions to Pollution
The new Chicago Climate Exchange, which creates and trades
credits in greenhouse gases, is similar to the sulfur dioxide
allowance program established by the U.S. Congress. Both
programs build new markets to limit pollution at the lowest
cost and create incentives to develop better and cheaper ways
to decrease pollution.
Preparing for the Tragedy of the Commons
Experiment
Prepares students for the Tragedy of the Commons
experiment.
Mon, 11.29.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.29.04
04:00 PM
Mon, 11.29.04
04:00 PM
Analyzing Tragedy of the Commons
Reinforces concepts learned in the Tragedy of the Commons
experiment.
Tragedy of the Commons: Overfishing the Oceans
Technological advances in catching fish and continual increases
in world demand for fish protein lead to nonsustainable
harvests of wild fish. Common property rights provide no
incentives for individual fishing firms to consider the long-term
consequences of their short-term actions: existing common
property rights fail to reward individual efforts to conserve fish
populations. In this news analysis, you will study the problem
of overfishing and use basic economic tools to understand how
shifts in supply and demand affect overfishing.
Tragedy of the Commons: Experiment
Illustrates the inefficiency of resources that are not priced and
mechanisms such as gifts or auctions of rights that can solve
the inefficiency. Also shows the efficiency and distributional
effects of various government policies.
Note: Scores for practice problem sets do not count towards your grade and are not reported to your professor.
Terms and Conditions | Privacy Notice | Security Notice | Aplia Support
http://econ.aplia.com/af/servlet/assignmentadmin?action=showStudentList&ctx=jhorowitz-0003
9/15/2004
Aplia, Inc.: Assignments
Page 5 of 5
Copyright © 2001-2004 Aplia Inc. All rights reserved.
http://econ.aplia.com/af/servlet/assignmentadmin?action=showStudentList&ctx=jhorowitz-0003
9/15/2004