Acid Rain - Wild about Bio
advertisement

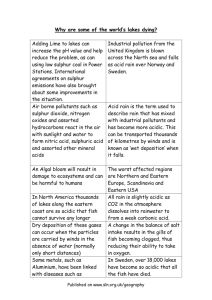
Human Impact – Effects of Acid Rain NGSSS: SC.912.L.17.20 Predict the impact of individuals on environmental systems and examine how human lifestyles affect sustainability. AA Background: (Source: www.epa.gov) The burning of fossil fuels during the industrialization of the world has caused many negative environmental impacts. Acid rain is a broad term used to describe several ways that acids fall out of the atmosphere. A more precise term is acid deposition; which has two part wet and dry. Wet deposition refers to acidic rain, fog, and snow. The strength of the effects depend on many factors, including how acidic the water is, the chemistry and buffering capacity (the ability to neutralize acidic compounds) of the soils involved, and the types of fish, trees, and other living things that rely on the water. Dry deposition refers to acidic gases and particles. The wind blows these acidic particles and gases onto buildings, cars, homes, and trees. Scientists discovered, and have confirmed, that sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are the primary causes of acid rain. In the U.S., about 2/3 of all SO 2 and 1/4 of all NOx comes from electric power generation that relies on burning fossil fuels like coal. Acid rain occurs when these gases react in the atmosphere with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form various acidic compounds. Sunlight increases the rate of most of these reactions. The result is a mild solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3). Acid rain is measured using a scale called pH. The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. It ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral. A pH less than 7 is acidic, and a pH greater than 7 is basic. Mixing acids and bases can cancel out their extreme effects; much like mixing hot and cold water can even out the water temperature. Normal rain is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves in it, so it has a pH of about 5.5. In recent years, the most acidic rain falling in the US has a pH of about 4.3. Acid deposition has a variety of effects, including damage to forests and soils, fish and other living things, materials, and human health. Acid rain also reduces how far and how clearly we can see through the air, an effect called visibility reduction. Problem Statement: How does the concentration of vinegar affect the germination of radish seeds? Safety: Handle solutions carefully to avoid spills. The simulated “acid rain” solution may cause irritation and should be rinsed off promptly if it comes into contact with the sun. Wear goggles at all times. If any of the solutions get into your eye, flush the eye with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention. Vocabulary: pH, acid, base, germination, concentration, acid rain, fossil fuels, environment Materials (per group): graduated cylinder filter paper medicine droppers pH meter 5 Petri dishes water vinegar (acetic acid) 25 radish seeds Procedures: 1. Label one Petri dish for each of the following treatments: 100%, 75%, 50%, 25%, and 0%. 2. Place two pieces of filter paper into each dish. 3. Create the acid vinegar solutions. Use the following measurements: 4. Add 5 ml of acid solution to the appropriate Petri dish. 5. Place 5 seeds in each treatment. 6. Place the Petri dishes in the box in front of the room. 7. Uses the pH meter to measure the acidity of each of the 5 solutions provided for the testing, and record each reading in the chart. 8. After 5 days, remove the Petri dishes and check to see how many seeds have germinated (sprouted). 9. Record your data in the chart. Note any changes in the appearance of the seeds. Observations/Data: Percentage of Vinegar pH # of Radish Seeds Germinated Changes in Appearance 10% 5% 2% 1% 0% Data Analysis: Create a line graph using the data from the table above; make sure to label your axis(s) and include the units of measurements. Effects of pH on the Germination of Radish Seeds Results: 1. Identify the relationship between pH and vinegar concentration. 2. Is vinegar an acid? Explain how that can be inferred from this activity. 3. Compare your results with the class; were there any differences in the germination or pH by lab group? Is so, speculate on possible reasons for these differences. 4. Under which vinegar concentration did the seeds germinate best? Is this consistent with your expectations? 5. Predict how the results of this experiment can be used to explain the effects of acid rain on our environment. 6. Explain how acidic water can harm aquatic plants and animals. Conclusion: Write a lab report using the “Power Writing Model 2009” answering the following questions: What was investigated? Was the hypothesis supported by the data? What were the major findings? How did your findings compare with other researchers? What possible explanations can you offer for your findings? What recommendations do you have for further study and for improving the experiment? What are some possible applications of the experiment?