COURSE INFORMATION
advertisement

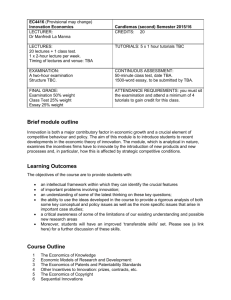
IT STRATEGY COURSE COURSE OBJECTIVE The goal of this course is to help the student become skilled in the creation of value through the management of information and information technology. INSTRUCTOR INFORMATION Professor David E. Pingry, McClelland Professor of Management Information Systems and Economics READINGS Course materials (including readings, cases and spreadsheets) are listed below and will be available from two sources: Harvard Business Online – marked with $ Other articles - marked with @ COURSE OUTLINE CLASS TOPICS Class 1 Introduction and Overview Class 2 IT Framework Class 3 Information Economics Class 4 Information Economics Class 5 Class 6 Information Economics Information Economics ASSIGNMENTS $ (optional) Information Technology Management From 19602000 (Nolan) @ Mastering the Three Worlds of Information Technology (McAfee) @CRM Alignment Case (Pingry) @CRM Spreadsheet (Pingry) @An Unusual Way to Run a Ski Business (Freedman) $Harrah’s (Case 1) @Six Decisions your IT People Shouldn’t Make @IT Doesn’t matter (Carr) @Modeling the ‘IT Value Paradox’ (Thatcher and Pingry) @What Determines IT Spending Priorities (Hoon, Pingry, and Thatcher) @Investing in IT makes a competitive difference (McAfee and Brynjolfsson) @Beyond Valuation: “Options Thinking” in IT Project Management (Fichman, Keil, and Tiwana) Class 7 Information Economics Class 8 Information Economics Class 9 Decision Support/Business Intelligence/Analytics @A Theory of DSS Evaluation (Marsden and Pingry) Class 10 Decision Support/Business Intelligence/Analytics @Competing on analytics (Davenport) @CRM Done Right @Preventing the Premature Death of Relationship Management @Avoid the Four Perils of CRM Class 11 Decision Support/Business Intelligence/Analytics $Business Intelligence Software at SYSCO (Case 2) Class 12 Economics of Design @Science of Design (Simon) IT Strategy Course, Pingry, Page 1 of 2, 3/3/2016 Class 13 Class 14 Economics of Design Economics of Design Class 15 Midterm Examination Class 16 Organizational Alignment and Boundaries Class 17 Organizational and IT Alignment: Structure and Boundaries Class 18 Organizational and IT Alignment: Structure and Boundaries Class 19 Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Class 20 Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Class 21 Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Class 22 Class 23 @Generating an optimal information system: PMAX-SDLC and the redirection of MIS research (or how to help Joe eat salmon) (Marsden and Pingry) Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Class 24 Organization and IT Alignment: Incentives and Contracting Class 25 Intellectual property, open source, privacy, standards etc. Class 26 Intellectual property, open source, privacy, standards etc. Class 27 Summary and Overview Class 28 Final Examination @The Nature of the Firm (Coase) @Electronic Markets and Electronic Hierarchies (Malone, Yates, and Benjamin) @Electronic Markets Hypothesis Redux: Where are We Now? (Glassberg and Merhout) @Managing the Knowledge Supply Chain: An Organizational Learning Model of Information Technology Offshore Outsourcing (Cha, Pingry, and Thatcher) @Principal Agent Spread Sheet @The Cost of High-Powered Incentives: Employee Gaming in Enterprise Software Sales (Larkin) @Managing J Pierrepont Finch (Isaac and Pingry), @JP Finch Spreadsheet $Strategic Outsourcing at Bharti Airtel Limited and Strategic Outsourcing at Bharti Airtel Limited. One Year Later. (Case 3) @ Research Commentary: Introducing a Third Dimension in Information Systems Design – The Case for Incentive Alignment (Ba, Stallaert, Whinston) @Software patents: the good, the bad, and the messy (Thatcher and Pingry) @Privacy, Economics, and Price Discrimination on the Internet (Odlyzko) CASE DISCUSSION AND PRESENTATION Cases are an important aspect of this class, but to be successful it relies on active and meaningful participation of class members. Everyone should read and be prepared to discuss the assigned case. A list of relevant discussion questions will be made available. Your two page write-up should specifically respond to these questions. During the discussion, you should be prepared to participate and present your analysis of these issues. Many of the issues in the case do not have a definitive answer. What is important is a logical analysis leading to some clear insight and recommendation, where appropriate. IT Strategy Course, Pingry, Page 2 of 2, 3/3/2016