Plate Tectonics Unit Test - High School Science
advertisement
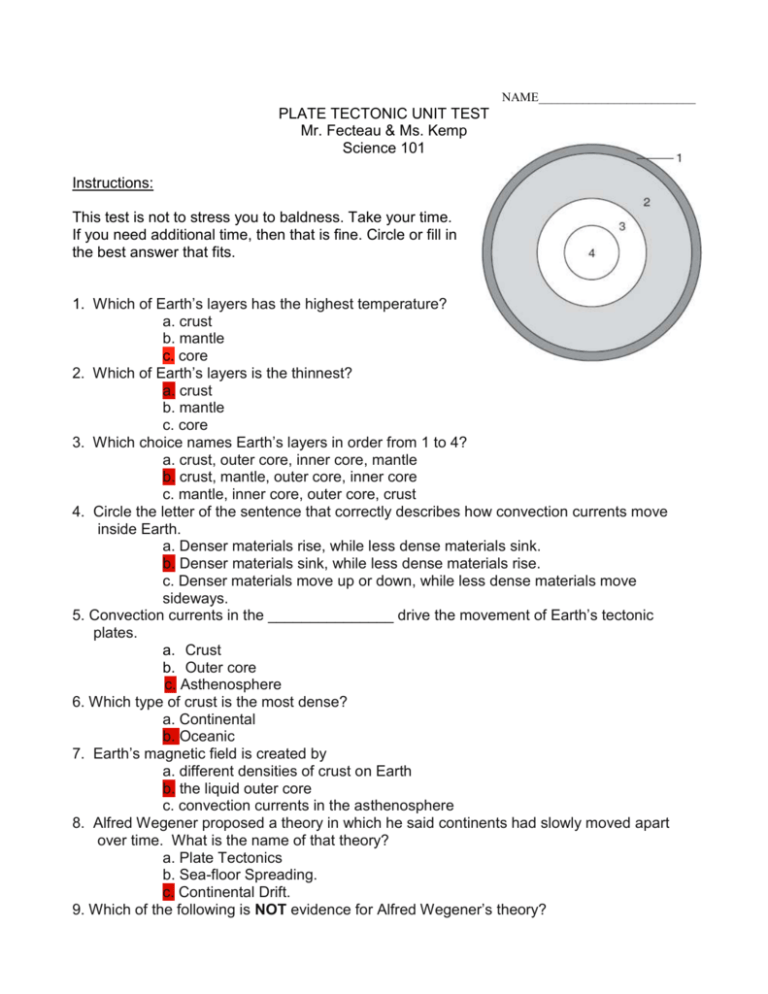
NAME_________________________ PLATE TECTONIC UNIT TEST Mr. Fecteau & Ms. Kemp Science 101 Instructions: This test is not to stress you to baldness. Take your time. If you need additional time, then that is fine. Circle or fill in the best answer that fits. 1. Which of Earth’s layers has the highest temperature? a. crust b. mantle c. core 2. Which of Earth’s layers is the thinnest? a. crust b. mantle c. core 3. Which choice names Earth’s layers in order from 1 to 4? a. crust, outer core, inner core, mantle b. crust, mantle, outer core, inner core c. mantle, inner core, outer core, crust 4. Circle the letter of the sentence that correctly describes how convection currents move inside Earth. a. Denser materials rise, while less dense materials sink. b. Denser materials sink, while less dense materials rise. c. Denser materials move up or down, while less dense materials move sideways. 5. Convection currents in the _______________ drive the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates. a. Crust b. Outer core c. Asthenosphere 6. Which type of crust is the most dense? a. Continental b. Oceanic 7. Earth’s magnetic field is created by a. different densities of crust on Earth b. the liquid outer core c. convection currents in the asthenosphere 8. Alfred Wegener proposed a theory in which he said continents had slowly moved apart over time. What is the name of that theory? a. Plate Tectonics b. Sea-floor Spreading. c. Continental Drift. 9. Which of the following is NOT evidence for Alfred Wegener’s theory? a. Continents match up like pieces of a puzzle. b. Tropical plant fossils are found in cold regions today. c. There is evidence that all plates move in the same directions. 10. What is the name of Alfred Wegener’s supercontinent? a. Gondwana b. Pangaea c. Eurasia 11. Subduction is a recycling of Earth’s crust which happens a. During an earthquake. b. at mid ocean ridges. c. under folded mountains (volcanoes). 12. A boundary where two plates push together (head to head) is called a a. divergent boundary. b. convergent boundary. c. transform boundary. 13. At which type of plate boundary do earthquakes occur? a. convergent b. divergent c. transform d. all of the above 14. The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the point at which an earthquake occurs is called the a. focus b. epicenter 15. Which plate boundary feature is most likely to cause the formation of volcanoes? a. earthquakes b. compression c. subduction d. stress 16. What is the name of the region of volcanoes which surrounds the Pacific Ocean? a. Mid Atlantic Ridge b. Ring of Fire c. Hot Spot 17. Which of the following is a hot spot volcano? a. Mt. Saint Helens, Washington b. Mauna Loa, Hawaii Thinking about Plate Tectonics ~*use the picture below to answer the following*~ 18. Interpreting Diagrams: Which kind of plate boundary occurs at A? a. convergent boundary b. divergent boundary c. transform boundary 19. Interpreting Diagrams: Which kind of plate boundary occurs at C? a. convergent boundary b. divergent boundary c. transform boundary 20. Applying Concepts: Which process happens at boundary A? a. sea-floor spreading b. subduction c. converging 21. Applying Concepts: Which process happens at boundary C? a. sea-floor spreading b. subduction c. converging Thinking about Earthquakes 22. What is the difference between P and S wave arrival times in each city? (Subtract P waves from S waves) a.) Chicago: _______min._______sec. b.) Savannah: _______min._______sec. c.) Seattle: _______min._______sec. 23. Use your answers from the previous question to determine each city’s distance from epicenter? Hint: (Plot your answers by looking at the left side, numbered 1 - 9 minutes, on the graph. Once you have found the time, follow the graph’s horizontal line across until it intersects the bold graph line. This will provide you with the amount of km from the epicenter.) a.) Chicago: _________km b.) Savannah: _________km c.) Seattle: _________km 24. Measuring: Draw circles on the map to show the distance from Chicago, Savannah, and Seattle to the earthquake’s epicenter. *Roughly 1 inch = 1000km 25. Interpreting Diagrams: Place an “E” on the map at the earthquake’s epicenter. Thinking about Volcanoes 26. Interpreting Diagrams: What kind of plate boundary is shown in the diagram? a. divergent boundary b. convergent boundary c. transform boundary 27. Inferring: What causes magma to form at this plate boundary? a. The oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate and melts. b. The continental plate gets warmer and melts. c. The continental plate pushes magma up from the mantle. ~* SHORT ANSWER *~ 28. Describe in complete detail two reasons as to why the plate tectonic theory is supported -puzzle like fit of continents -fossils matching across oceans 29. Why is seismic activity such a constant occurrence near Japan? -many plate boundaries converge in area -plates are constantly moving 30. Describe the different kinds of plate tectonic boundaries and what happens at each type of plate boundary -convergent -divergent -transfor 31. What do you think the world would be like if there were no plate boundaries? -answers may vary... 32. Write your own question that you would like to explain and answer it. -Answers may vary 33. Draw a normal fault and explain it. ~*ANSWER KEY*~ 1. __C__ 2. __A___ 3. __B___ 4. __B___ 5. __C___ 6. __B___ 7. __B___ 8. __C___ 9. __C___ 10. __B___ 11. __C___ 12. __B___ 13. __C___ 14. __B__ 15. __C__ 16. __B___ 17. __B___ 18. __B___ 19. __A___ 20. __A___ 21. __B___ 22. a.)3min 20sec b.) 4min 5sec c.) 2min 25sec 23. a.) 2000km b.) 2650km c.) 1400km 24. See Figure 25. See Figure 26. __B___ 27. __A___ 28. See Question 29. See Question 30. See Question 31. See Question 32. See Question 33. See Question Sources: Test: http://www.google.com/search?client=safari&rls=en&q=plate+tectonic&ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF8#sclient=psy&hl=en&client=safari&rls=en&biw=953&bih=641&source=hp&q=plate+tectonic+test&aq=f&aqi=g2 &aql=&oq=&pbx=1&bav=on.2,or.r_gc.r_pw.&fp=56f4866b51aaf71c