Physcial Science-Electricity and Magnetism.doc
advertisement

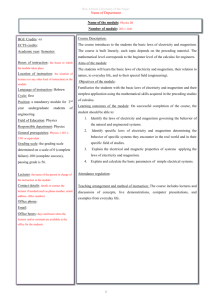
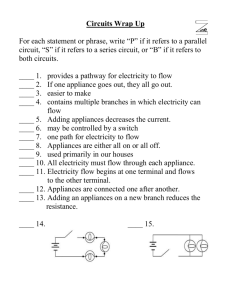
HARNETT COUNTY HIGH SCHOOLS Course: Physical Science Title of Unit: 3.3 Electricity, magnetism and their relationship Timeframe: 4 days Content Area Standard(s): PSc.3.3 Understand electricity and magnetism and their relationship. PSc.3.3.1 Summarize static and current electricity. PSc.3.3.2 Explain simple series and parallel DC circuits in terms of Ohm’s law. PSc.3.3.3 Explain how current is affected by changes in composition, length, temperature, and diameter of wire. PSc.3.3.4 Explain magnetism in terms of domains, interactions of poles, and magnetic fields. PSc.3.3.5 Explain the practical application of magnetism. Unpacked PSc.3.3.1 • Identify interactions between charged objects - opposite charges attract and like charges repel. • Compare the three methods of charging objects: conduction, friction, and induction – explain the re-distribution or transfer of electrons for each method for both positively and negatively charged objects. • Compare static and current electricity related to conservation of charge and movement of charge (without calculations.) PSc.3.3.2 • Interpret simple circuit diagrams using symbols. • Explain open and closed circuits. • Apply Ohm’s law and the power equation to simple DC circuits: and. VIR= PVI= • Compare series and parallel circuits. Conceptually explore the flow of electricity in series and parallel circuits. (Calculations may be used to develop conceptual understanding or as enrichment.) • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and resistance. PSc.3.3.3 • Explain how the wire in a circuit can affect the current present – for a set voltage, the current in a wire is inversely proportional to its resistance (more current exists where resistance is low); the resistance of a material is an intensive property called resistivity; increasing the length of a wire increases the resistance; increasing the temperature increases the resistance; increasing the diameter of a wire decreases its resistance. • Explain using a cause-and-effect model how changes in composition, length, temperature, and diameter of a wire would affect the current in a circuit. PSc.3.3.4 • Describe the characteristics and behaviors of magnetic domains. • Explain the attractions of unlike poles and the repulsion of like poles in terms of magnetic fields. Explain magnetic fields produced around a current-carrying wire and wire coil (solenoid). • Explain the relationship between strength of an electromagnet and the variance of number of coils, voltage, and core material. PSc.3.3.5 • Explain the relationship between electricity and magnetism in practical applications such as generators and motors – the process of electromagnetic induction in electric generators that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy; transformation of electric energy to mechanical energy in motors. • Extrapolate other practical applications such as security cards (ATM, credit or access cards), speakers, automatic sprinklers, traffic signal triggers, seismometers, battery chargers, transformers, AC-DC adapters. Reading Standard(s): 3. Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or exceptions defined within the text. 5. Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms 7. Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g., a table or chart) and translate information expressed visually or mathematically (e.g., in an equation) into words. Writing Standard(s): 1. Write arguments focused on disciplinespecific content. a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. 2. Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. e. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective. Speaking and Listening(s): Comprehension and Collaboration 1. Initiate and participate effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grades 9–10 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively. Math Practice(s): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Model with mathematics. Use appropriate tools strategically. Attend to precision. Look for and make use of structure. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Technology Standard(s): HS.TT.1.1 HS.TT.1.2 Use appropriate technology tools and other resources to access information (multidatabase search engines, online primary resources, virtual interviews with content experts). Use appropriate technology tools and other resources to organize information (e.g. online note-taking tools, collaborative wikis). HS.TT.1 Use technology and other resources for assigned tasks. HS.TT.1.3 Use appropriate technology tools and other resources to design products to share information with others (e.g. multimedia presentations, Web 2.0 tools, graphics, podcasts, and audio files). Learning Experiences: Students create series and parallel circuits Practice problems for calculating variables in Ohm’s law. Demonstrate electromagnet and electroscope Project Goals and Description of Unit: This unit demonstrates the relationship of electricity and magnetism. By the end of this unit students will be able to: -identify series and parallel circuits; calculate resistance, current, and voltage. - discuss how to detect the flow of electrical currents. -research magnetic domains and explain practical applications. Essential Questions: 1. How does electricity affect our everyday lives? 2. What precautions must be taken when working with an electrical system? 3. How does a compass work? Vocabulary: Static electricity Current electricity AC/DC current Battery Voltage (potential difference) current resistor Ohm’s Law Conductor Insulator Parallel circuits Series circuit Domain Magnetic field Poles Permanent magnet Temporary magnet Electromagnet Instructional Resources (print materials, technology): Magnets, light bulbs, switches, batteries, compass, wires, balloons, silk or wool cloth Websites: http://www.kids-science-experiments.com/stuckonyou.html (static electricity lab)[C3,5] http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/outreach/8thgradesol/SeriesParallelFrm.htm [C6] http://cstephenmurray.com/worksheets.htm[A2] http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc[C3] http://serc.carleton.edu/sp/compadre/interactive/examples/14204.html[B6] http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/category/physics/electricity-magnets-andcircuits[B4] http://www.woodlands-junior.kent.sch.uk/revision/science/electricity.htm[C2] Website resource: khanacademy.com SAS (access via the Harnett County Schools homepage) 3.3.1 Summarize static and current electricity. Investigate and analyze the nature of static electricity and the conservation of electrical charge: Positive and negative charges. Opposite charges attract and like charges repel. Analyze the electrical charging of objects due to the transfer of charge. Static Electricity, Inquiry 41 PSc.3.3.2 Explain simple series and parallel DC circuits in terms of Ohm’s law PSc.3.3.3 Explain how current is affected by changes in composition, length, temperature, and diameter of wire. Lab: Building Circuits, Web Lesson 972 Lab: Conduction, Web Lesson 272 Series circuits. Lab: Building Circuits, Web Lesson 972 Parallel circuits. Lab: Building Circuits, Web Lesson 972 PSc.3.3.4 Explain magnetism in terms of domains, interactions of poles, and magnetic fields. PSc.3.3.5 Explain the practical application of magnetism. Investigate and analyze magnetism and the practical applications of the characteristics of magnets. Permanent magnets. Lab: Natural Magnets & Electromagnetism, Web Lesson 1004 Electromagnetism. Magnetism & Its Uses, Web Lesson 448 Lab: Natural Magnets & Electromagnetism, Web Lesson 1004 Lorentz Force and Induction, Web Lesson 480 Movement of electrical charges. Magnetism & Its Uses, Web Lesson 448 Lab: Natural Magnets & Electromagnetism, Web Lesson 1004 Lorentz Force and Induction, Web Lesson 480 Facilitator’s Role: Ensure all students are conscious of all laboratory safety rules. Allow students to design and create parallel and series circuits through experimentation. Provide lectures and guided practice activities to provided information needed for students to be successful in this unit. Assessment: Formative assessment: Assess students’ ability to construct series and parallel circuits and using variables to calculate Ohm’s law. Completed daily based on learning targets and criteria for success Ticket out the door Think-Pair-Share Peer Assessment Writing Summary of learned concepts Parking Lot to allow students to ask questions Summative assessment: Create an assessment that requires students to calculate, draw and/or analyze graphs and discuss the mathematical relationship of V=IR, P=IV. Students will demonstrate an understanding the concepts of static electricity. Students will distinguish between the characteristics of parallel and series circuits. http://www.cstephenmurray.com/worksheets.htm#ch6[A1,C2,C3] 7:1 - Types of Circuits and Ohm's Law 6:2 - Circuits and Symbols 6:1 - Electric Charge **the above worksheets can be used to assist in creating summative assessments* Notes and Additional Information: To add and/or check for new materials check the following: http://harnettcountyhighschools.wikispaces.com/Science