Chapter Two Study Guide - Windsor C
advertisement

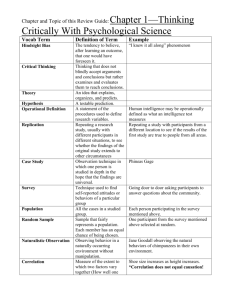
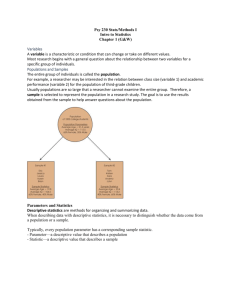
Chapter Two Study Guide Research Methods Instructions: Answer all Key Questions and define terms in your own words when possible. Definitions in the readings are often better than the margin definitions Key Question: How do psychologists develop new knowledge? Core Concept: Scientific Method: Empirical Investigation: Theory: Hypothesis: Operational Definitions: Random Presentation: Independent Variable: Dependent Variable: Data: Replicate: Clinical Research 1. 2. Experimental Correlational (e.g., observational, survey, clinical) Types of Psychological Research A. Experimental Method: Confounding or Extraneous Variables: Controls: Random Assignment: Ex-post Facto: B. Correlational Study: C. Survey Method: 1 D. Naturalist Observation: E. Case Study: (Not in book) A case study is one type of observational data collection technique in which one individual is studied in-depth in order to identify behavioral, emotional, and/or cognitive qualities that are universally true, on average, of others. Case studies often include face-to-face interviews, paper and pencil tests, and more F. Longitudinal Study: G. Cross-sectional Study: H. Cohort-sequential Study: ***************************************************************************************** Personal Bias: Expectancy Bias: Single-Blind Study: Double -Blind Study: Placebo: Placebo Effect: Random Sample: Ethics In Research Institutional Review Board: (IRB) Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee: (IACUC): Deception: Good and Bad? Animal Studies Questions Science Can Not Answer p.39 The scientific methods in not appropriate for answering questions that cannot be put to an objective, empirical test. Some examples…. Ethics: What are the ethical issues involved in animal research Values: Which culture had the best attitude towards work/leisure? Morality: When is it morally acceptable to go to war? Preferences: Is rap music better than blues music? Aesthetics: Was Picasso more creative than Van Gogh Existential Issues: What is the meaning of life? Religion: How do people of faith explain natural disasters? Law: What should the speed limit be on a highway 2 STATISTICS Descriptive and Inferential Key Question: How Do We Make Sense Of The Data? Core Concept: A. Descriptively … B. Inferentially … Frequency Distribution: Histogram: 1. Descriptive Statistics Descriptive Statistics: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Measures of Central Tendency…or averages The central point around which the scores seem to cluster Mean: Median: Mode: Range: Mean, Median, Mode, Range All are descriptive statistics and measures of central tendency Standard Deviation: Normal Distribution: Statistical Significance: Correlation: Correlation Coefficient: 3 2. Inferential Statistics Inferential Statistics: Random Sample: Representative Sample: Significant Difference: Indicated by notation p < .05 ========================================================================== Notes Five Steps of the Scientific Method 1. Develop a hypothesis 2. Perform a controlled test 3. Gather objective data 4. Analyze the results 5. Publish, criticize, and REPLICATE the results The independent variable is the thing that someone actively controls/changes; while the dependent variable is the thing that changes as a result. For example……… --In a study of how different dosages of a drug are related to the severity of symptoms of a disease, a measure of the severity of the symptoms of the disease is a dependent variable. --The administration of the drug in specified doses is the independent variable. --Researcher will compare the different values of the dependent variable (severity of the symptoms) and attempt to draw a conclusion. The Experimental Method Basic Purpose: to explore cause and effect How Conducted: manipulate one or more factors, use random assignment What is Manipulated?: the independent variables Weaknesses: Sometimes not feasible Results may not generalize to other contexts Not ethical to manipulate certain variables Correlational Study Basic Purpose: To detect naturally occurring relationships To assess how well one variable predicts another How Conducted: compute statistical association, sometimes among survey responses What is Manipulated?: nothing Weaknesses: does not specify cause and effect 4 ************************ Other Terms to Know ************************. Pseudoscience: fake science…has not survived trial by the scientific method Experimental group: Those in the study that get the special treatment, such as a new drug Control group: Those in the study that get the placebo Quantified: Concepts that are measured and expressed as numbers. Often presented in graph form. This type of data is generally obtained when you conduct experimental research. False Consensus Effect: The tendency to overestimate others’ agreement with us. Example: Vegetarians will think more people are vegetarians that will meat eaters. Scatterplots: A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. --The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. --The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation Correlation Coefficient: A number between –1 and +1 expressing a degree of relationship between two variables 1. If people have high scores on one variable also have high scores on another, the correlation is positive The Correlation Coefficient is also positive ex: +.03 2. If people have high scores on one variable, but low on another, the correlation is negative The Correlation Coefficient is also negative…(less than 0) 3. Zero means there is no relationship between scores **Does NOT tell about cause and effect Simply gives information on the direction and strength of the relationship Significant Difference: Psychologists accept a difference between groups to be ‘real’ or significant when the probability that in might be due to chance is less than 5 in 100 Indicated by notation p < .05 p<.05 = chance of very little influence p<.01 = (less 1-100) more strict p<.001 = (less 1-100) more strict APA Psychological Academic Paper Outline 1. Abstract 2. Introduction 3. Method 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. References 5