Even number
advertisement

FINITE STATE MACHINES
(AUTOMATA)
Switch Example 1
Think about the On/Off button
Switch Example 1
The corresponding Automaton
Off
Push
On
Push
Input:
Push Push Push Push
Vending Machine Example 2
Vending machine dispenses Cola for $0.45
Vending Machine Example 2
Input:
D Q Q D
45
is final state
Input Accepted
Example 3
11
0
1
0,1
1
0111
111
1
0
0
1
The machine accepts a string if the process
ends in a final state
Example 3
1
0
Input Symbols
states
1
q1
0
q0
0,1
final states (F)
0
q12
The machine accepts a string if the process
start state (q0) ends in aqfinal
states
state
3
Definitions
An alphabet S is a finite set of symbols
(in Ex3, S = {0,1})
A string over S is a finite sequence of elements
of S (e.g. 0111)
For a string s, |s| is the length of s
The unique string of length 0 will be denoted
by ? and will be called the empty string
The reversal of a string u is denoted by uR.
Example: (banana)R = ananab
Definitions
The concatenation of two strings is the string
resulting from putting them together from left to
right. Given strings u and v, denote the
concatenation by u .v, or just uv.
Example:
jap . an = japan, QQ . DD = QQDD
Q1: What’s the Java equivalent of
concatenation?
Q2: Find a formula for |u .v |?
The + operator
on strings
|u .v | = |u |+|v |
Definitions
If S is an alphabet,
S * denotes the set of all strings over S.
A language over S is a subset of S *
i.e. a set of strings each consisting of
sequences of symbols in S.
Examples
Example1: in our vending machine we have
Σ = { D, Q }
Σ∗ = {λ,
D, Q,
DD, DQ, QD, QQ,
DDD, DDQ, DQD, DQQ, QDD, QDQ, QQD, QQQ,
DDDD, DDDQ, … }
L = { u∈Σ∗ | u successfully vends }
Example2: in our switch example we have
Σ = { Push}
Σ∗ = {λ,
Push,
Push Push,
Push Push Push,
Push Push Push Push, … }
L = { Pushn | n is odd }
Definitions
A finite automaton is a 5-tuple M = (Q, S, δ, q0, F)
Q is the set of states
S is the alphabet
δ is the transition function
q0 ∈ Q is the start state
F ⊆ Q is the set of final states
L(M) = the language of machine M
= set of all strings machine M accepts
Definitions
State Diagram
a
and Table
a
b
q0
q1
b q2
a
Q = {q0 , q1 , q2 }
Σ = {a, b}
F = {q2 }
b
δ
a
b
q0
q0
q1
q1
q0
q2
q2
q2
q2
FINITE STATE MACHINES
(AUTOMATA)
Deterministic Finite Automata
(DFA)
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata with
empty move (?-NFA)
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata
(NFA)
Deterministic & Nondeterministic
Non-Deterministic
Deterministic
B
B
E
E
A
A
H
H
C
C
G
F
D
G
E
G
F
D
I
G
I
E
One choice
Multi choice è Backtrack
Deterministic & Nondeterministic
Deterministic
Non-Deterministic
B
a
A
a
C
a
A
C
a
D
From ONE state machine can go to
another ONE state on one input
One choice
From ONE state machine can go to
MANY states on one input
Multi choice
Deterministic
Computation
Non-Deterministic
Computation
reject
accept or reject
accept
DETERMINISTIC FINITE AUTOMATA
(DFA)
Definitions
A DFA is a 5-tuple M = (Q, S, δ, q0, F)
Q is the set of states
S is the alphabet
δ : Q × S ? Q is the transition function
q0 ∈ Q is the start state
F ⊆ Q is the set of accept states
L(M) = the language of machine M
= set of all strings machine M accepts
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)
Example 1
0
0
1
0
1
1
is not final state
Input Rejected
1
1
0
0 1
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)
Example 1
0
0
1
0
1
1
Q:
What kinds of bit-strings are accepted?
A: Bit-strings that represent binary even
numbers.
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)
Example 2
0
1
1
q1
0
q2
q3
0,1
010 reject
11
accept
010100100100100
010000010010
reject
λ
accept
reject
Exercise
q0
L(M) = {0,1}*
∅
0,1
Exercise
0
0
1
q0
q1
1
L(M) = { w | w has an even number of 1s}
Exercise
Build an automaton that accepts all and only those
strings that contain 001
1
q
0,1
0
0
1
q0
0
q00
1
q001
Exercise
Strings over {a,b} containing even number of a’s and odd number of b’s.
q0 = Even(a).Even(b)
q1 = Even(a).Odd(b)
Σ*
q2 = Odd(a).Even(b)
q3 = Odd(a).Odd(b)
Even(a)
Odd(a)
Even(b) Odd(b) Even(b) Odd(b)
b
q0
a
a
a
a
q2
q1
b
b
b
q3
Exercise
Strings over {a,b,c} that has the form (ab)*c
q0 = End(b)
q1 = End(a)
Σ*
valid prefix
q2 = End(c)
q3 = Error
invalid prefix
End(a) End(b) End(c)
q0
c
q2
a
b
q1
a,c
b
a,b,c
q3
a,b,c
Exercise
Design with a friend a machine that tells
us when a base-10 number is divisible by 3.
What should your alphabet be?
How can you tell when a number is divisible
by 3?
Answer
0,3,6,9
1 mod 3
1,4,7
2,5,8
0 mod 3
2,5,8
0,3,6,9
1,4,7
2,5,8
2 mod 3
0,3,6,9
1,4,7
Exercise
0,3,6,9
0 mod 3
1,4,7
2,5,8
0,3,6,9
2,5,8
1 mod 3
2,5,8
1,4,7
2 mod 3
Find the formal description
of this automaton.
0,3,6,9
1,4,7
Answer
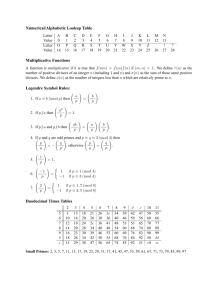
Q = { 0 mod 3, 1 mod 3, 2 mod 3 }
Σ = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }
q0 = 0 mod 3
F = { 0 mod 3 }
( rename: {q0, q1, q2} )
d :Q × Σ → Q
d ( q 0 , 2 ) = q 2 , d ( q 0 ,9 ) = q 0 , d ( q 1 , 2 ) = q 0 ,
d ( q 1 ,7 ) = q 2 , d ( q 2 ,3 ) = q 2 , d ( q 2 ,5 ) = q 1 .
Question
: d(qi, j) = ?
d( qi , j ) = q( i + j ) mod 3