Teaching the ADDITION & SUBTRACTION of Integers
advertisement

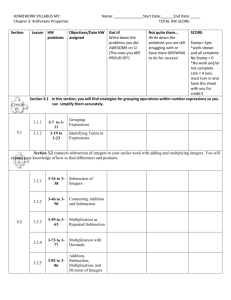
Teaching the ADDITION & SUBTRACTION of Integers 1. Using Counters • 2 colours, one for positive and the other for negative • based on the “zero principle” – adding “opposite” integers gives zero Example: (+1) + (-1) = 0 • • Addition – relatively straight forward, upon understanding of zero principle Subtraction – more involved, often requires the “addition of zero” before subtraction can take place Example: (+5) – (+7) cannot be performed using only 5 red chips, thus we need to add 2 red and 2 blue chips (“zero principle”) and then subtract the 7 red chips, leaving 2 blue chips remaining … thus (+5) – (+7) = (-2). 2. Using Number Lines <----------|----|----|----|----|----|----|----------> -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 • Use arrows above a number line to illustrate addition and subtraction • Addition – e.g. (-5) + (-2) – find the first number on the number line, then draw an arrow from that number going LEFT # units if adding a NEGATIVE number (thus becoming less positive) or RIGHT if adding a POSITIVE numbers (becoming more positive), where # units is “2” in this example Subraction – e.g. (-5) – (-2) – now what?? What does it mean to SUBTRACT a NEGATIVE number? … the number is becoming less negative and thus move to the RIGHT ☺ Example: (-5) – (+2) – here you move LEFT because you are subtracting a positive number and thus becoming less positive. • 3. Using “Rules” (without manipulatives) • Once addition of integers is understood, you could teach subtraction of integers as a rule: • “To subract an integer, add its opposite” Example: (+5) – (+7) = (+5) + (-7) = (-2) Questions to think about: • Which method is best? • Should all methods be taught? • What does it mean to understand addition/subtraction of integers? • Can students understand the model and yet, not be able to do the arithmetic? • How much practice is required? • What about “5 - 7”? Does the "-" sign mean “take away” or is it tied to the number 7, as (-7)? Addition & Subtraction Using Number Lines A. Illustrate the following additions: 1. (+5) + (+2) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2. (-3) + (+7) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3. (+8) + (-7) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 4. (-6) + (-4) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B. Illustrate the following subtractions: 1. (+5) - (+2) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2. (+5) - (+10) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3. (+5) - (-2) = <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 4. Additional Examples: <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---> -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10