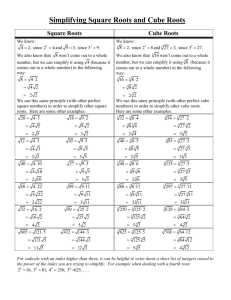
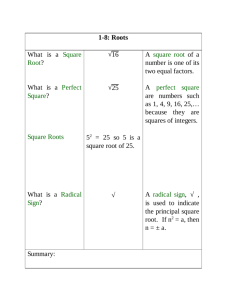
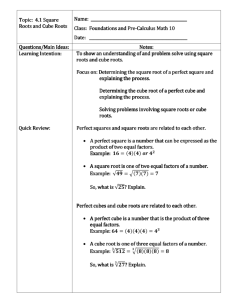
Three Cube Roots of Unity & Four Fourth Roots of Unity Exercise 4.4
advertisement

Three Cube Roots of Unity & Four Fourth Roots of Unity
Three Cube Roots & Four Fourth Roots of a Number
Exercise 4.4
1. Find the three cube roots of: 8, -8, 27, -27, and 64
(I) 8
Solution:
Let x be a cube root of 8
1
∴ x = 3 8 = (8) 3
1
x 3 = ((8) 3 )3
x3 = 8
x3 − 8 = 0
( x)3 − (2)3 = 0
( x − 2)( x 2 + 2 x + 4) = 0
x−2= 0
x2 + 2x + 4 = 0
x=2
−2 ± (2) 2 − 4(1)(4)
x=
2(1)
−2 ± −12
2
−2 ± −(4)(3)
x=
2
−2 ± 2 − 3
x=
2
2(−1 ± 3i )
x=
2
−1 + 3i
x = 2(
)
2
x=
−1 ± 3i
)
2
−1 − 3i
x = 2(
)
2
Q w = −1 + 3i
x = 2w
x = 2 w2
2
Q w2 = −1 − 3i
2
2
Hence, three cube roots of 8 are: {2, 2 w, 2 w }
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
⇒
x = 2(
Prepared by Bilal
(II) -8
Solution:
Let x be a cube root of -8
1
∴ x = 3 −8 = (−8) 3
1
3 3
x = ((−8) )
x 3 = −8
x3 + 8 = 0
( x)3 + (2)3 = 0
( x + 2)( x 2 − 2 x + 4) = 0
x+2=0
x2 − 2x + 4 = 0
3
x = −2
x=
−(−2) ± (−2) 2 − 4(1)(4)
2(1)
2 ± −12
2
2 ± −(4)(3)
x=
2
2 ± 2 −3
x=
2
2(1 ± 3i )
x=
2
1 + 3i
x = 2(
)
2
−1 − 3i
x = −2(
)
2
x=
x = −2 w 2
1 ± 3i
x = 2(
)
2
1 − 3i
x = 2(
)
2
−1 + 3i
x = −2(
)
2
⇒
x = −2 w
Q w = −1 + 3i
2
Q w2 = −1 − 3i
2
Hence, three cube roots of -8 are: {−2, −2w, −2 w2 }
(III) 27
Solution:
Let x be a cube root of 27
1
∴ x = 3 27 = (27) 3
1
x 3 = ((27) 3 )3
x 3 = 27
x 3 − 27 = 0
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
( x)3 − (3)3 = 0
( x − 3)( x 2 + 3 x + 9) = 0
x −3= 0
x 2 + 3x + 9 = 0
−3 ± (3) 2 − 4(1)(9)
x=
2(1)
x=3
−3 ± −27
2
−3 ± −(9)(3)
x=
2
−3 ± 3 −3
x=
2
3(−1 ± −3)
x=
2
3(−1 ± 3i )
−1 ± 3i
⇒
x=
x = 3(
)
2
2
−1 + 3i
−1 − 3i
x = 3(
)
x = 3(
)
2
2
x = 3w
x = 3w2
Hence, three cube roots of 27 are: {3,3w,3w2 }
x=
(IV) -27
Solution:
Let x be a cube root of -27
1
∴ x = 3 −27 = (−27) 3
1
x 3 = ((−27) 3 )3
x 3 = −27
x 3 + 27 = 0
( x)3 + (3)3 = 0
( x + 3)( x 2 − 3 x + 9) = 0
x+3= 0
x 2 − 3x + 9 = 0
x = −3
x=
−(−3) ± ( −3) 2 − 4(1)(9)
2(1)
3 ± −27
2
3 ± −(9)(3)
x=
2
x=
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
3 ± 3 −3
2
3(1 ± −3)
x=
2
3(1 ± 3i )
1 ± 3i
⇒
x=
x = 3(
)
2
2
1 + 3i
1 − 3i
x = 3(
)
x = 3(
)
2
2
−1 − 3i
−1 + 3i
x = −3(
)
x = −3(
)
2
2
x = −3w
x = − 3w 2
Hence, three cube roots of -27 are: {−3, −3w, −3w2 }
x=
(V) 64
Solution:
Let x be a cube root of 64
1
∴ x = 3 64 = (64) 3
1
x 3 = ((64) 3 )3
x 3 = 64
x 3 − 64 = 0
( x)3 − (4)3 = 0
( x − 4)( x 2 + 4 x + 16) = 0
x−4= 0
x 2 + 4 x + 16 = 0
x=4
x=
−4 ± (4) 2 − 4(1)(16)
2(1)
−4 ± −48
2
−4 ± −(16)(3)
x=
2
−4 ± 4 − 3
x=
2
4(−1 ± 3i )
−1 ± 3i
⇒
x=
x = 4(
)
2
2
−1 + 3i
−1 − 3i
x = 4(
)
x = 4(
)
2
2
x = 4w
x = 4 w2
Hence, three cube roots of 64 are: {4, 4w, 4w2 }
x=
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
2. Evaluate:
(i) (1 + w − w2 )8
(iv) (
(ii) w28 + w29 + 1
−1 + −3 9 −1 − −3 7
) +(
)
2
2
(v) (−1 + −3)5 + (−1 − 3)5
(i) (1 + w − w2 )8
Solution:
(1 + w − w2 )8
Add and subtract w2
(1 + w − w2 )8 = (1 + w + w2 − w2 − w2 )8
= (1 + w + w2 − 2 w2 )8
= (0 − 2w2 )8
= 256w16
= 256( w3 )15 w
= 256(1)15 w
= 256w
(ii) w28 + w29 + 1
Solution:
w28 + w29 + 1 =
=
=
=
(iii) (1 + w − w2 )(1 − w + w2 )
( w3 )9 w + ( w3 )9 w2 + 1
(1)9 w + (1)9 w2 + 1
w + w2 + 1
0
Q 1 + w + w2 = 0
Q w3 = 1
Q w + w2 + 1 = 1 + w + w2 = 0
(iii) (1 + w − w2 )(1 − w + w2 )
Solution:
(1 + w − w2 )(1 − w + w2 )
Add and subtract w2 in the 1st bracket, and add and subtract w in the 2nd bracket.
(1 + w − w2 )(1 − w + w2 )
= (1 + w + w2 − w2 − w2 )(1 + w − w − w + w2 )
= (1 + w + w2 − 2 w2 )(1 + w + w2 − 2 w)
= (0 − 2w2 )(0 − 2w)
= (−2 w2 )(−2w)
= 4w3
=4
−1 + −3 9 −1 − −3 7
) +(
)
2
2
Solution:
(iv) (
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
(
−1 + −3 9 −1 − −3 7
) +(
)
2
2
= ( w ) 9 + ( w 2 )7
Qw=
−1 + −3
−1 − −3
, w2 =
2
2
= ( w3 )3 + w14
= ( w3 )3 + ( w3 )4 w2
= (1)3 + (1)4 w2
= 1 + w2
= −w
−1 + −3 7 −1 − −3 7
) +(
)
2
2
Then solution:
−1 + −3 7 −1 − −3 7
=
(
) +(
)
2
2
=
=
=
=
If (
( w)7 + ( w2 )7
( w3 ) 2 w + w14
( w3 ) 2 w + ( w3 )4 w2
w + w2
−1
(v) (−1 + −3)5 + (−1 − 3)5
Solution:
Multiply and divide by “2” with both the brackets.
−1 + −3 5
−1 − −3 5
= (2 ×
(−1 + −3)5 + (−1 − 3)5
) + (2 ×
)
2
2
= (2 × w)5 + (2 × w2 )5
= 32 w5 + 32 w10
= 32 w3 w2 + 32( w3 )3 w
= 32(1) w2 + 32(1) w
= 32 w2 + 32 w
= 32( w2 + w)
= 32(−1)
= −32
3. Show that:
(i) x 3 − y 3 = ( x − y )( x − wy )( x − w2 y )
Solution:
x 3 − y 3 = ( x − y )( x − wy )( x − w2 y )
x 3 − y 3 = ( x2 − wxy − xy + wy2 )( x − w2 y )
x 3 − y 3 = ( x3 − w2 x2 y − wx2 y + w3 xy2 − x2 y + w2 xy2 + wxy2 − w3 y3 )
Rearranging we have,
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
x3 − y3
x3 − y3
x3 − y3
x3 − y3
x3 − y3
= ( x3 − w2 x2 y − wx2 y − x2 y + w3 xy2 + w2 xy2 + wxy2 − w3 y3 )
= x3 − x2 y ( w2 + w + 1) + xy2 ( w3 + w2 + w) − w3 y3
= x3 − x2 y ( w2 + w + 1) + wxy2 ( w2 + w + 1) − w3 y3
= x3 − w3 y3
= x3 − y 3
Proved.
(ii) x 3 + y3 + z3 − 3 xyz = ( x + y + z )( x + wy + w2 z )( x + w2 y + wz )
Solution:
x 3 + y3 + z3 − 3 xyz = ( x + y + z )( x + wy + w2 z )( x + w2 y + wz )
Take L.H.S
= ( x + y + z )( x + wy + w2 z )( x + w2 y + wz )
= ( x + y + z )( x 2 + w2 xy + wxz + wxy + w3 y2 + w2 yz + w2 xz + w4 yz + w3 z2 )
= ( x + y + z )( x 2 + xy ( w2 + w) + xz ( w + w2 ) + yz ( w2 + w) + w3 y2
= ( x + y + z )( x 2 + xy (−1) + xz (−1) + yz (−1) + (1) y2
= ( x + y + z )( x 2 − xy − xz − yz + y2 )
= x 3 − x 2 y − x2 z − xyz + xy2 + x2 y − xy2 − xyz − y2 z + y3 + x2 z − xyz − xz2 − yz2 + y2 z
= x 3 + y 3 + z 3 − 3 xyz Proved.
(iii) (1 + w)(1 + w2 )(1 + w4 )(1 + w8 ) …… 2n factors = 1
Solution:
(1 + w)(1 + w2 )(1 + w4 )(1 + w8 )
…… 2n factors
2
2
(1 + w)(1 + w )(1 + w)(1 + w )
…… 2n factors
2
3
2
3
(1 + w + w + w )(1 + w + w + w )
…… 2n factors
2
2
(1 + w + w + 1)(1 + w + w + 1)
…… 2n factors
(0 + 1)(0 + 1)
…… 2n factors
(1)(1)
…… 2n factors
2n
(1)
1
Proved.
4. If w is a root of x 2 + x + 1 = 0 , show that its other root is w2 and prove that w3 = 1.
Solution:
If w is the root of the equation x 2 + x + 1 = 0 then,
→ Equation (A)
w2 + w + 1 = 0
Now, to prove that its other root is w2 , Replace x by w2 ,
( w2 )2 + w2 + 1 = 0
x2 + x + 1 = 0 ⇒
Add and subtract w2 .
( w2 )2 + w2 + w2 + 1 − w2 = 0
( w2 )2 + 2 w2 + 1 − w2 = 0
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
( w2 + 1)2 − w2 = 0
( w2 + 1 + w)( w2 + 1 − w) = 0
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
From Equation (A) w2 + 1 + w = 0 , therefore
(0)( w2 + 1 − w) = 0
⇒ ( w2 )2 + w2 + 1 = 0 → Equation (B)
Hence, w2 is also a root of x 2 + x + 1 = 0 .
Now, to prove w3 = 1 subtract Equation (A) from B.
( w2 )2 + w2 + 1 = 0
_ w2 ± w ± 1 = 0
w4 − w = 0
w( w3 − 1) = 0
As, w ≠ 0
w3 − 1 = 0
w3 = 1
Proved.
5. Prove that complex cube roots of −1 are
9
1 + 3i
1 − 3i
and
; and hence prove that
2
2
9
1 + −3 1 − −3
+
= −2
2 2
Solution:
Let x be the cube root of −1 , therefore
1
x = 3 −1 = (−1) 3
x 3 = −1
x3 + 1 = 0
( x)3 + (1)3 = 0
( x + 1)( x 2 − x + 1) = 0
x +1 = 0
x2 − x + 1 = 0
−(−1) ± 1 − 4
x = −1
x=
2(1)
1 ± −3
2
1 ± 3i
x=
2
1 + 3i
x=
2
x=
1 − 3i
2
1 + 3i 1 − 3i
Hence, three cube roots of −1 are: {−1,
,
}
2
2
x=
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
9
9
1 + −3 1 − −3
→ Equation (C)
Now, we have to prove,
+
= −2
2
2
−1 + −3
−1 − −3
As we know that: w =
and
w2 =
2
2
1 − −3
1 + −3
−w =
− w2 =
2
2
Hence, equation (C) becomes:
( −w ) + ( −w)
2 9
9
= −2
Take R.H.S
( −w ) + ( −w)
2 9
9
3 6
3 3
6
3
− w18 − w9 = −( w ) − ( w ) = −(1) − (1) = −2
Proved.
6. If w is a cube root of unity, form an equation whose roots are 2w and 2w2 .
Solution:
To form an equation, whose roots are 2w and 2w2 , we have
Q If 2w is a root
⇒ x = 2w ⇒ x − 2 w = 0
( x − 2 w)( x − 2 w2 ) = 0
⇒ x = 2 w2 ⇒ x − 2 w2 = 0
Is 2w2 is a root
x 2 − 2 w2 x − 2 wx + 4 w3 = 0
x 2 − 2 x ( w2 + w) + 4 w3 = 0
Q w2 + w = −1 , w3 = 1
x 2 − 2 x (−1) + 4(1) = 0
Answer
x2 + 2x + 4 = 0
7. Find four fourth roots of: 16, 81, and 625
(i) 16
Solution:
Let x be a fourth root of 16, therefore,
x = 4 16
x = 16
1
4
14
( x) = 16
4
x = 16
x 4 − 16 = 0
4
4
( x ) − ( 4)
2 2
2
=0
( x 2 + 4)( x 2 − 4) = 0
x2 + 4 = 0
x 2 = −4
x = ± −4
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
x2 − 4 = 0
x2 = 4
x=± 4
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
x = ±2
x = ± 4i
x = ±2i
Hence four fourth roots of 16 are: 2, −2, 2i, −2i
(ii) 81
Solution:
Let x be a fourth root of 81, therefore,
x = 4 81
1
4
x = 81
14
( x) = 81
4
x = 81
x 4 − 81 = 0
4
4
( x ) − ( 9)
2 2
2
=0
( x + 9)( x − 9) = 0
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
x2 + 9 = 0
x2 − 9 = 0
x 2 = −9
x2 = 9
x = −9
x= 9
x = ±3
x = 9i
x = ±3i
Hence, four fourth roots of 81 are: 3, −3,3i, −3i
2
2
(iii) 625
Solution:
Let x be a fourth root of 625, therefore,
x = 4 625
1
x = 625 4
1
( x) = 625 4
4
x − 625 = 0
4
4
( x ) − ( 25)
2 2
2
=0
( x 2 + 25)( x 2 − 25) = 0
x 2 + 25 = 0
x 2 = −25
x = −25
x = 25i
x = ±5i
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
x 2 − 25 = 0
x 2 = 25
x = 25
x = ±5
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
Hence, four fourth roots of 625 are: 5, −5,5i, −5i
8. Solve the following equations:
(i) 2 x 4 − 32 = 0
Solution:
2 x 4 − 32 = 0
2( x 4 − 16) = 0
x 4 − 16 = 0
( x 2 ) 2 − (4)2 = 0
( x 2 + 4)( x 2 − 4) = 0
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
x2 + 4 = 0
x2 − 4 = 0
x 2 = −4
x2 = 4
x = −4
x= 4
x = ±2
x = 4i
x = ±2i
Hence, solution set = {2, −2, 2i, −2i}
(ii) 3 y 5 − 243 y = 0
Solution:
3 y 5 − 243 y = 0
3 y ( y 4 − 81) = 0
3y = 0
y 4 − 81 = 0
y=0
( y 2 )2 − (9)2 = 0
( y 2 + 9)( y 2 − 9) = 0
y2 + 9 = 0
y 2 = −9
Q a 2 − b2 = ( a + b)( a − b)
y2 − 9 = 0
y2 = 9
y = ± −9
y=± 9
y = ±3i
y = ±3
Hence, solution set = {0,3, −3,3i, −3i}
(iii) x 3 + x 2 + x + 1 = 0
Solution:
x3 + x2 + x + 1 = 0
x 2 ( x + 1) + 1( x + 1) = 0
( x + 1)( x 2 + 1) = 0
x +1 = 0
x2 + 1 = 0
x = −1
x 2 = −1
x = ± −1
Q i 2 = −1
x = ± i2
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal
x = ±i
Hence, solution set = {−1, i, −i}
(iv) 5 x 5 − 5 x = 0
Solution:
5 x5 − 5 x = 0
5 x( x 4 − 1) = 0
5x = 0
x4 −1 = 0
x=0
( x 2 ) 2 − (1)2 = 0
( x 2 + 1)( x 2 − 1) = 0
x2 + 1 = 0
x2 −1 = 0
x 2 = −1
x2 = 1
x = ±i
x = ±1
{0,1,
−
1,
i
, −i}
Hence, solution set =
Mathematics Notes for First Year (Class 11)
Prepared by Bilal