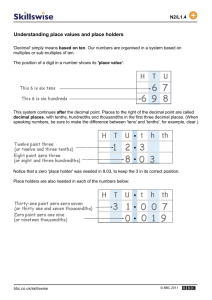
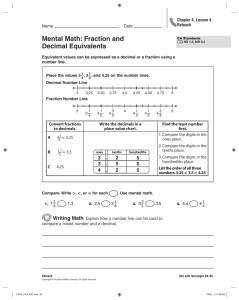
Decimal Place Value p. 22
advertisement

Medications and Math Bob Warner, MS, RN Your Mission if you choose to accept it • Math Competency Scores needed • NUR105 • NUR106 • NUR205 • NUR206 85% or better 90% or better 95% or better 100% Mission Possible Your Responsibility & Accountability • Calculate with Confidence, 6th edition • Chapters 1 – 22, 25….1st year • Chapters 23 – 24…2nd year • Accurate calculation of medication dosages is a critical and necessary skill for nurses. Serious harm can come to patients from math errors. Medication Routes include Decimal Place Value p. 29 • The first place to the right of the decimal is tenths. • The second place to the right of the decimal is hundredths. • The third place to the right of the decimal is thousandths. • In the calculation of medication dosages it is necessary to consider only three figures after the decimal point (thousandths) (e.g., 0.375 mg). Decimal Place Value p. 29 • When there is no whole number before the decimal point, it is important to place a zero in front of it. This will emphasize its value and prevent errors in interpretation. .15…..NO 0.15….YES • The source of many medication errors is misplacement of a decimal point or incorrect interpretation of a decimal value. No Decimal Point • When the amount is a whole number, do NOT use a decimal point with trailing zeroes 15.0…..NO 15….YES • The source of many medication errors is misplacement of a decimal point or incorrect interpretation of a decimal value. Rounding Off Decimals p. 37 • Some syringes are marked in tenths and some, in hundredths. Rounding Off Decimals p. 37 • To ensure accuracy, most calculation problems require that you carry your division at least two decimal places (hundredths place) and round off to the nearest tenth. Rounding Off Decimals Guideline Do Not Round until the FINAL Answer step Rounding Off Decimals p. 37 • To express an answer to the nearest tenth, carry the division to the hundredths place (two places after the decimal). If the number in the hundredths place is 5 or greater, add one to the tenths place. If the number is less than 5, drop the number to the right of the desired decimal place. Which is bigger? And Rounding • 2.001 2.01 • 0.13 0.31 • 45.9345 • 100.42 • 100.63 Equivalents Metric 5 ml 15 ml 30 ml 1000 ml = 1 L 1 mg = 1000 mcg 1 gm = 1000 mg 1 kg = 1000 gm Household 1 tsp 1 Tbs 1 oz 2.2 lbs Calculating Intake & Output p. 100 Abbreviations p. 149 -158 • Need to memorize the most common abbreviations • P. 149 -150 • Be careful of the Do Not Use & Error-Prone Lists • p. 151, 156 - 158 Proportions Chapter 14 Outer terms are the extremes, Inner terms are the means. The product of the means equals the product of the extremes Step 1 5 : 25 :: 10 : 50 Step 2 5 x 50 = 25 x 10 Ratio-Proportion Chapter 14 Step 1 _5_ 25 = _10_ 50 Cross multiply Step 2 5 x 50 = 25 x 10 Formula Method Chapter 15 Desired Have x Quantity Dimensional Analysis Chap. 16 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XKCZn5MLKvk&feature=player_em bedded#! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JreBcC2b0Mk IV Flow Rate: mL/hour p. 520 Amount of solution (mL) Time in hours = mL/hour IV Tubing IV Flow Rate: gtts/min p. 523 Amount of solution (mL) x drop factor = gtts/min Time in minutes Let’s Do Some Math Problems Order: Lopressor 25 mg b.i.d. Available: Lopressor 50 mg/tablet Order: Coumadin 7.5 mg po daily Available: Coumadin 5 mg/tablet Order: Penicillin 750,000 units IV stat Available: Penicillin 1,000,000 units/10 mL Order: Kanamycin 300 mg IM Directions on label: Add 2.7 mL sterile water = 1 g/3 mL Order: Benadryl 30 mg po every 6 hours prn Available: Benadryl 12.5 mg/5 mL Order: Hydrochlorothiazide 0.05 g Available: Hydrodiuril (Hydrochlorothiazide) 25 mg/tablet Infuse 1 L normal saline (NS) in 8 hours. How many mL/hr? Infuse 1,000 mL NS in 8 hours. Drop factor is 20 gtt/mL. How many gtts/min?