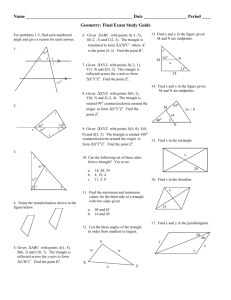
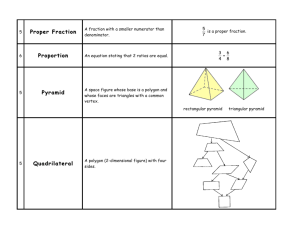
Geometry Chapter 1 Vocabulary coordinate
advertisement

Geometry Chapter 1 Vocabulary coordinate - The real number that corresponds to a point on a line. point - Has no dimension. It is usually represented by a small dot. bisect - To divide into two congruent parts. coplanar points - Points that lie on the same plane. straight edge - A construction tool used to draw segments. A ruler without marks. compass - A construction tool used to draw arcs. ray - Part of a line that consists of a point, called an initial point, and all points on the line that extend in one direction. obtuse angle - An angle with measure between 90° and 180°. angle - Consists of two different rays that have the same initial point. intersection - The set of points that two or more geometric figures have in common. postulate - Rules that are accepted without proof. Also called axioms. acute angle - An angle with measure between 0° and 90°. linear pair - Two adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. plane - Extends in two dimensions. It is usually represented by a shape that looks like a tabletop or wall. line - Extends in one dimension. It is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads to indicate that it extends without end in two directions Geometry Chapter 2 Vocabulary postulates - Rules that are accepted without proof. Also called axioms. hypothesis - The "if" part of a conditional statement. conclusion - The "then" part of a conditional statement. inverse - The statement formed when you negate the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement. contrapositive - The statement formed when you negate the hypothesis and conclusion of the converse of a conditional statement. biconditional statement - Contains the phrase "if and only if." theorem - A true statement that follows as a result of other true statements. definition - Uses known words to describe a new word. inductive reasoning - A process that includes looking for patterns and making conjectures. converse - The statement formed by switching the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. conjecture - An unproven statement that is based on observations. negation - The negative of a statement. It is symbolized by ~. Geometry Chapter 3 Vocabulary perpendicular - Two lines that intersect to form a right angle. two column proof - A type of proof written as numbered statements and reasons that show the logical order of an argument. skew lines - Two lines that do not intersect and are not coplanar. corresponding angles - Two angles that are formed by two lines and a transversal and occupy corresponding positions. linear pair - Two adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. exterior angles - Two angles that are formed by two lines and a transversal and that lie outside the two lines on opposite sides if the transversal. complement angles - The sum of the measures of two angles 90°. consecutive interior angles - Two angles that are formed by two lines and a transversal and that lie between the two lines on the same side of the transversal. supplement angles - The sum of the measures of two angles 180°. same side interior angles - Consecutive interior angles. flow proof - A type of proof that uses arrows to show the flow of a logical argument. Statements are connected by arrows to show how each statement comes from the ones before it, and each reason is written below the statement it justifies. alternate interior angles - Two angles that are formed by two lines and a transversal and that lie between the two lines on opposite sides of the transversal. Geometry Chapter 4 Vocabulary legs - The sides that form the right angle. base - The noncongruent side of an isosceles triangle that has only two congruent sides. corollary - A statement that can be proved easily using a theorem or a definition. isosceles triangle - Has at least two congruent sides. congruent segments - Segments that have the same length. equiangular triangle - A triangle with three congruent angles. scalene triangle - A triangle with no congruent sides. midpoint - The point that divides, or bisects, a segment into two congruent segments. vertex - Each of the three points joining the sides of a triangle. right angle - An angle with measure equal to 90°. equilateral triangle - A triangle with three congruent sides. Geometry Chapter 5 Vocabulary point of congruency - The point of intersection of two concurrent lines. median - A segment whose endpoints are a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. intersect - To have one or more points in common. incenter - The point of concurrency of the angle bisectors of a triangle. midpoint - The point that divides, or bisects, a segment into two congruent segments. altitude - The perpendicular segment from a vertex of a triangle to the opposite side or to the line that contains the opposite side. equidistant - The distance from each point is the same. circumcenter - The point of concurrency of the perpendicular bisectors of the triangle. congruent segments - Segments that have the same length. concurrent lines - Three or more lines that intersect in the same point. centroid - The point of concurrency of the medians of a triangle. midsgement - A segment that connects the midpoints of two sides of a triangle. orthocenter - The point of concurrency of the lines containing the altitudes of a triangle Geometry Chapter 6 Vocabulary vertex - Each endpoint of a side of a polygon. isosceles trapezoid - A trapezoid with congruent legs. equiangular polygon - A polygon with all its interior angles congruent. parallelogram - A quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. regular polygon - A polygon that is equilateral and equiangular. diagonal - A segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon. equidistant - The distance from each point that is the same. kite - A quadrilateral that has two pairs of consecutive congruent sides, but in which opposite sides are not congruent. convex polygon - A polygon such that no line containing a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. rectangle - A parallelogram with four right angles. equilateral polygon - A polygon with all its sides congruent. base angles - The two pairs of angles whose common side is the base of the trapezoid. square - A parallelogram with four congruent sides and four right angles. polygon - A plane figure that meets the following two conditions. (1) It is formed by three or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoint are collinear. (2) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint Geometry Chapter 7 Vocabulary rotational symmetry - Iif the figure can be mapped onto itself by a rotation of 180° or less. preimage - The original figure in the transformation of a figure in a plane. isometry - A transformation that preserves lengths. Also called rigid transformation. terminal point - The ending point of a vector. rotation - A type of transformation in which a figure is turned about a fixed point. composition - The result when two or more transformations are combined to produce a single transformation. An example is a glide reflection. image - The new figure that results from the transformation of a figure in a plane. transformation - The operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. frieze pattern - A pattern that extends to the left and right in such a way that the pattern can be mapped onto itself by a horizontal translation. Also called a border pattern. vector - A quantity that has both direction and magnitude, and is represented by an arrow drawn between two points. parallel lines - Two lines that are coplanar and do not intersect. corresponding angles - Two angles that are formed by two lines and a transversal and occupy corresponding positions. Geometry Chapter 8 Vocabulary image - The new figure that results from the transformation of a figure in a plane. angle bisector - A ray that divides an angle into two adjacent angles that are congruent. means - The middle terms of a proportion. slope - The ratio of the vertical change (the rise) to the horizontal change (the run) of a nonvertical line. congruent segments - Segments that have the same length. side-angle-side (SAS) - If an angle of one triangle is congruent to an angle of a second triangle and the lengths of the sides including these angles are proportional, then the triangles are similar. scale factor - The ratio of the lengths of two corresponding sides of two similar polygons. extremes - The first and last terms of a proportion. transformation - The operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. enlargement - A dilation with k > 1. proportion - An equation that equates two ratios. angle-angle - If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar. ________ Similarity Postulate. preimage - The original figure in the transformation of a figure in a plane. Geometry Chapter 9 Vocabulary special right triangles - Right triangles whose angle measures are 45°-45°-90° or 30°-60°-90°. magnitude - The distance from the initial point to the terminal point. converse - The statement formed by switching the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. altitude - The perpendicular segment from a vertex of a triangle to the opposite side or to the line that contains the opposite side. proportion - An equation that equates two ratios. equal vectors - Two vectors that have the same magnitude and direction. Pythagorean triple - A set of three positive integers a, b, and c that satisfy the equation c2 = a2 + b2. equilateral triangle - A triangle with three congruent sides. parallel vectors - Two vectors that have the same or opposite directions. equiangular triangle - A triangle with three congruent angles. direction - Is determined by the angle that the vector makes with a horizontal line. Geometry Chapter 10 Vocabulary secant segment - A segment that intersects a circle in two points, with one point as an endpoint of the segment. tangent segment - A segment that is tangent to a circle at an endpoint. secant line - A line that intersects a circle in two points. locus - The set of all points that satisfy a given condition or a set of given conditions. intercepted arc - The arc that lies in the interior of an inscribed angle and has endpoints on the angle. semi circle - An arc whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter of the circle. diameter - A chord that passes through the center of the circle. The distance across a circle, through its center. tangent line - A line that intersects a circle in exactly one point, called the point of tangency. tangent circle - Circles that intersect in one point. exterior points - All points of the plane that are outside a circle. circle - The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point, called the center. interior points - All points of the plane that are inside a circle. Geometry Chapter 11 Vocabulary convex polygon - A polygon such that no line containing a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. circumference - The distance around a circle. major arc - The measure of an arc where the difference between 360° and the measure of its associated minor arc. circle - The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point, called the center. polygon - A plane figure that meets the following two conditions. (1) It is formed by three or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoint are collinear. (2) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. trigonometric ration - A ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. minor arc - The measure of an arc where the measure of its central angle. geometric probability - A probability that involves a geometric measure such as length or area. regular polygon - A polygon that is equilateral and equiangular. NGON - A polygon with number of sides n. apothem - The distance from the center of a polygon to any side of the polygon. concave - A polygon that is not convex. arc length - A portion of the circumference of a circle. Geometry Chapter 12 Vocabulary polyhedron - A solid that is bounded by polygons, called faces, that enclose a single region of space. right cone - A cone with a vertex that lies directly above the center of the base. polygon - A plane figure that meets the following two conditions. (1) It is formed by three or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoint are collinear. (2) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. right cylinder - A cylinder such that the segment joining the centers of the bases is perpendicular to the bases. oblique prism - A prism whose lateral edges are not perpendicular to the bases. edge - A line segment formed by the intersection of two faces of a polyhedron. scale factor - The ratio of the lengths of two corresponding sides of two similar polygons. platonic solids - Five regular polyhedra, named after the Greek mathematician and philosopher Plato, including a regular tetrahedron, a cube, a regular octahedron, a regular dodecahedron, and a regular icosahedron. right cone - A prism whose lateral edges are perpendicular to both bases. cylinder - A solid with congruent circular bases that lie in parallel planes. hemisphere - Half of a sphere, formed when a great circle separates a sphere into two congruent halves. prism - A polyhedron with two congruent faces, called bases, that lie in parallel planes. sphere - The locus of points in space that are a given distance from a point, called the center. net - A two-dimensional representation of all the faces of a polyhedron.