Math - Oak Meadow
advertisement

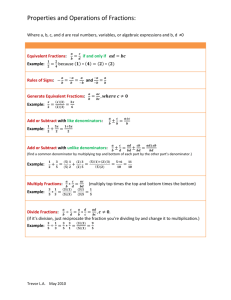
Lesson Grade 7 Contents Introduction................................................................... vii Lessons Lesson 1: Common Denominators................................. 1 Finding the Lowest Common Denominator Lesson 2: LCDs in Mixed Numbers................................. 9 Borrowing With Mixed Numbers and LCDs Lesson 3: Multiplying Simple Fractions........................ 17 Multiplying Whole Numbers by Fractions Multiplying by Fractions in Word Problems Multiplying Mixed Numbers Canceling Fractions Lesson 4: Dividing Fractions.......................................... 27 Dividing Whole Numbers and Fractions Dividing Mixed Numbers Dividing Whole Numbers and Mixed Numbers Why You Invert and Multiply to Divide Lesson 5: Decimal Fractions ......................................... 39 Hundredths Thousandths Comparing Decimals Adding Decimals Lesson 6: Subtracting Decimals..................................... 49 Subtracting Decimals and Whole Numbers Multiplying Decimals Multiplying Larger Decimals Multiplying Decimals and Whole Numbers iii Lesson Contents Grade 7 Math Lesson 7: Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers........ 61 Dividing With Dividends Less Than One Dividing Decimals With Remainders Lesson 8: Dividing Decimals By Decimals.................... 73 Dividing Whole Numbers by Decimals Lesson 9: Exponents....................................................... 83 Square Roots Lesson 10: Order of Operations.................................... 93 Addition and Subtraction Parentheses Lesson 11: Three Ways to Indicate Multiplication.... 103 Order of Operations with Multiplication and Division Lesson 12: Multiplying Decimals by 10, 100, and 1000................................................................... 113 Dividing Decimals by 10, 100, and 1000 Percents Finding a Percent of a Number Lesson 13: Converting Common Fractions to Decimals............................................................... 125 Converting Decimals to Percents Lesson 14: Using Percents in Word Problems............ 133 Finding Percents in Word Problems Lesson 15: Remainders in Dividing Decimals............. 143 Repeating Decimals Factors of Whole Numbers Lesson 16: Finding Missing Numbers in Addition..... 151 Finding Missing Numbers in Subtraction Missing numbers in Multiplication and Division Lesson 17: Order of Operations With Exponents...... 161 Three Ways to Indicate Division Fractions in Order of Operations Lesson 18: First Semester Exam................................... 173 iv Oak Meadow Grade 7 Math Lesson Contents Lesson 19: Negative Numbers..................................... 181 Directions and the Number Line Adding and Subtracting Signed Numbers Adding Signed Numbers Subtracting Signed Numbers Lesson 20: Multiplying Signed Numbers.................... 193 Dividing Signed Numbers Lesson 21: Finding the mean and the Median........... 201 Finding the Mode and Range Lesson 22: The Metric System..................................... 211 Reading a Centimeter Ruler Meters and Kilometers Lesson 23: Probability.................................................. 223 Probability of a Series Chance Lesson 24: Addition Rule of Equations....................... 231 The Addition Rule With Negative Numbers Lesson 25: Division Rule For Equations..................... 239 The Multiplication Rule For Equations Lesson 26: Ratios.......................................................... 247 Proportions Lesson 27: Using Proportions in Word Problems...... 257 Converting Units in Proportions Lesson 28: Formulas..................................................... 265 Transforming Formulas Lesson 29: Pi and the Circumference of a Circle........ 273 Pi and the Area of a Circle Lesson 30: Measuring Weight With Metrics.............. 281 Measuring Liquids With Metrics Lesson 31: Trillions in Place Value............................... 289 Prime Numbers Oak Meadow v Lesson Contents Grade 7 Math Lesson 32: Sequences................................................... 297 Functions Lesson 33: Angles.......................................................... 305 Perpendicular Lines and Right Angles Types of Angles Measuring Angles Triangles Classifying by Angles Classifying by Sides Sum of the Angles Area of a Triangle Lesson 34: Using a Compass....................................... 319 Drawing an Equilateral Triangle Polygons Lesson 35: Geometric Solids........................................ 329 Volume of Solids Lesson 36: Second Semester Exam............................. 337 Appendix........................................................................ 347 Answer Keys for Skill Practice and Application Practice B-tests vi Oak Meadow Lesson Grade 7 1 Common Denominators When we are adding or subtracting fractions whose denominators are the same, we simply add or subtract the numerators, and the denominator remains the same. But in many operations with fractions, the denominators are not the same. When this is the case, we can’t just add or subtract the numerators; we have to rename one or both of the fractions by finding what is called a common denominator. This is a number that can be divided evenly by both denominators in the problem. When we’re looking for a common denominator for two fractions in a problem, there are several ways to find this. 1. Use the largest denominator in the problem 2.Multiply the two denominators 3.Compare the multiples of both denominators and choose the lowest multiple that both fractions have in common To begin, we’ll look at the first two approaches: 1. Use the largest denominator in the problem Example 1: 3 1 8 4 Step 1: U sing the largest denominator in the problem doesn’t always work, but this is the approach we try first, because it’s the easiest. In this example, the largest denominator is 8 and the smallest denominator is 4. Does 4 go into 8 evenly? Yes, 4 x 2 = 8, so 8 will be our common denominator. 1 Lesson 1 Grade 7 Math Common Denominators (continued) Step 2: Write the fractions in vertical format and add the equal sign and the common denominator. Since the top fraction isn’t changing, write that as is: 3 3 = 8 8 1 = 4 8 Step 3: Look at the denominator in the bottom fraction. Say to yourself, “4 goes into 8 two times.” Look at the numerator in the bottom fraction and say, “Two times 1 is 2.” Write the 2 2 above the 8 in the bottom fraction to create the fraction 8 , then subtract as usual: 3 3 = 8 8 1 2 = 4 8 1 8 That approach will work well with some problems, and it’s the one you should always try first because it’s the easiest. But if you find a problem that won’t work with this approach, then try the next approach: 2.Multiply the two denominators Example 2: 2 3 + 3 4 Step 1: In this problem we can’t use the largest denominator, because 3 won’t divide evenly into 4, so we’ll try the second approach: we’ll multiply the two denominators. In this example, we would multiply 3 by 4 and get 12. This is the common denominator. 2 Oak Meadow Grade 7 Math Lesson 1 As before, write the problem in a vertical format and add the equal sign and a common denominator: 2 = 3 12 3 + = 4 12 Common Denominators (continued) Step 2: Look at the denominator in the top fraction and say, “How many times does 3 go into 12?” The answer is 4, so you then say, “4 times 2 is 8” and you put the 8 above the 12, 8 to create 12 . 2 8 = 3 12 3 + = 4 12 Step 3: Look at the denominator in the bottom fraction and say, “How many times does 4 go into 12?” The answer is 3, so you then say, “3 times 3 is 9” and you put the 9 above the 12, to 9 make 12 . Then add as usual, and reduce the fraction to lowest terms: 12 2 8 = 3 12 3 9 + = 4 12 17 5 = 1 12 12 Practice these two approaches to finding common denominators in the following Skill Practice. When you’re finished, we’ll review the third approach to finding common denominators. Oak Meadow 3 Lesson 1 Grade 7 Math Common Denominators (continued) Finding the Lowest Common Denominator Multiplying the two denominators will always give you a common denominator, but often this denominator will be quite large and must be reduced to lowest terms at the end of the problem. To avoid having to reduce fractions at the end of the problem, you always look for the lowest common denominator, or LCD. Sometimes, the first two approaches will give us the LCD. If not, we use a third approach: 3.Compare the multiples of both denominators and choose the lowest multiple that both fractions have in common Example 1: 1 1 + 4 6 Step 1: A s usual, we first look to see if we can use the largest denominator in the problem as a common denominator, but we find that this doesn’t work. We can’t divide 4 into 6 evenly. So we try the second approach: we multiply the two denominators. We can do this, but we end up with 24 for a denominator. Since the numbers are small, we think there may be a smaller denominator, so we compare the multiples of the two denominators: Multiples of 4:4 8 12 16 20 24 28 Multiples of 6:6 12 18 24 30 36 42 We find that 24 is a multiple of both denominators, but 12 is also a multiple, and since 12 is a lower number, we choose that as the lowest common denominator. Step 2: Once we’ve found the LCD, we complete the problem as usual: 1 3 = 4 12 1 2 + = 6 12 5 12 4 Oak Meadow Grade 7 Math Math 7 Skill Practice A Lesson 1 - 4 Lesson 1 SKILL PRACTICE A Reduce answers to the lowest terms. Reduce answers to lowest terms 1. 4. 7. 10. 2 3 − − − − 41 2. + 7 8 1 2 3. 3 4 − 21 2 4 − 31 3 4 2 3 5. 3 5 + 21 6. 4 5 1 2 8. 2 5 + 130 9. 3 4 1 3 11. Oak Meadow + 3 4 5 8 12. + 1 2 3 8 4 16 + 1 4 5 Lesson 1 Math 7 Lesson 1 - 6 Skill Practice B Grade 7 Math SKILL PRACTICE B Find the lowest common denominator anddenominator solve. Find the lowest common and solve 1. 4. 7. 10. 6 3 8 − + − − 61 2. + 1 6 1 9 3. 3 4 + 130 5 6 − 34 5 6 1 8 5. 3 8 + 152 6. 1 6 1 8 8. 5 8 + 172 9. 3 8 1 12 11. − 1 4 1 10 12. − 3 4 5 6 2 9 + 56 Oak Meadow Grade 7 Math Math 7 Lesson 1 - 7 Lesson 1 REVIEW 1 Lesson 1 Review Reduce all fractions in answers to lowest Reduce all fractions in terms. answers to lowest terms 1. − 3 5 1 3 2. 5,0 8 9 × 375 3. 6. 1 2 4 1 5 2 4. 1 5 + 170 5. 7. 1 3 + 34 8. 7 1 1 0 6 10. 307 ×294 Oak Meadow 11. − − 3 4 1 2 2 4 1 6 9. 12. 1 8 2 3 − + 125 + 59 5 6 1 9 7 Lesson 1 Grade 7 Math Lesson 1 Review continued 13. Simon orders books for The Book Barn. He ordered 175 copies of a new bestseller at a cost of $12 per copy. What was the total cost of the 175 books he ordered? 14. The Ferndale Kiwanis Club bought 700 Christmas trees to sell at 5 locations throughout Ferndale. If they distribute the trees equally to each location, how many trees will be available at each location? 15. Ali is buying furniture, and the salesman says she will have to pay $35 a month for 24 months to buy what she wants. When she completes all her monthly payments, how much will she have paid for the furniture? 16. The Spaghetti Factory is giving its employees a year-end bonus, and $7,800 has been set aside to distribute equally to all employees. If there are 24 employees, how much will each employee receive? 8 Oak Meadow