Place Value - Kitwell Primary School
advertisement

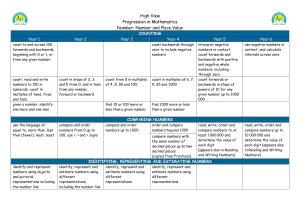
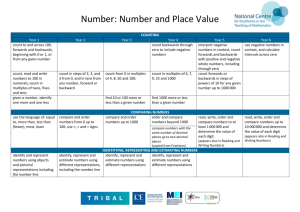
Place Value COUNTING Year 1 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning w ith 0 or 1, or from any given number Year 2 count in steps of 2, 3, and 5 from 0, and in tens from any number, forward or backward count, read and w rite numbers to 100 in numerals; count in multiples of tw os, fives and tens Year 3 count from 0 in multiples of 4, 8, 50 and 100; Year 4 count backw ards through zero to include negative numbers find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number count in multiples of 6, 7, 9, 25 and 1000 Year 5 interpret negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards with positive and negative w hole numbers, including through zero Year 6 use negative numbers in context, and calculate intervals across zero count forwards or backwards in steps of pow ers of 10 for any given number up to 1000 000 find 1000 more or less than a given number given a number, identify one more and one less use the language of: equal to, more than, less than (fewer), most, least compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100; use <, > and = signs identify and represent numbers using objects and pictorial representations including the number line identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations, including the number line read and w rite numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and w ords. read and w rite numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in w ords recognise the place value of each digit in a tw o-digit number (tens, ones) COMPARING NUMBERS compare and order numbers up order and compare numbers read, w rite, order and compare to 1000 beyond 1000 numbers to at least 1 000 000 and compare numbers with the same determine the value of each digit number of decimal places up to (appears also in Reading and Writing two decimal places Numbers) (copied from Fractions) IDENTIFYING, REPRESENTING AND ESTIMATING NUMBERS identify, represent and estimate identify, represent and estimate numbers using different numbers using different representations representations READING AND WRITING NUMBERS (including Roman Numerals read and w rite numbers up to 1 read Roman numerals to 100 (I read, w rite, order and compare 000 in numerals and in w ords to C) and know that over time, numbers to at least 1 000 000 and tell and write the time from an the numeral system changed to determine the value of each digit analogue clock, including using include the concept of zero and (appears also in Comparing Numbers) Roman numerals from I to XII, place value. read Roman numerals to 1 000 (M) and 12-hour and 24-hour clocks and recognise years written in Roman (copied from Measurement) numerals UNDERSTANDING PLACE VALUE recognise the place value of recognise the place value of each digit in a three-digit number each digit in a four-digit number (hundreds, tens, ones) (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones) find the effect of dividing a oneor two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as units, tenths and hundredths (copied from Fractions) read, w rite, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit (appears also in Reading and Writing Numbers) recognise and use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents (copied from Fractions) read, w rite, order and compare numbers up to 10 000000 and determine the value of each digit (appears also in Reading and Writing Numbers) read, w rite, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit (appears also in Understanding Place Value) read, w rite, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit (appears also in Reading and Writing Numbers) identify the value of each digit to three decimal places and multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 where the answers are up to Place Value three decimal places (copied from Fractions) ROUNDING round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1 000 round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number (copied from Fractions) use place value and number facts to solve problems solve number problems and practical problems involving these ideas. PROBLEM SOLVING solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and w ith increasingly large positive numbers round any number up to 1 000 000 to the nearest 10, 100, 1 000, 10 000 and 100 000 round decimals with two decimal places to the nearest whole number and to one decimal place (copied from Fractions) round any w hole number to a required degree of accuracy solve problems which require answers to be rounded to specified degrees of accuracy (copied from Fractions) solve number problems and practical problems that involve all of the above solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above