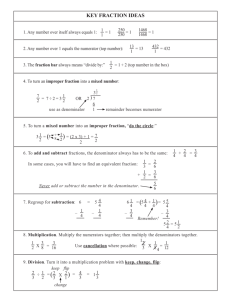
Okehampton Primary School Mathematical
advertisement

Okehampton Primary School Mathematical Vocabulary Glossary This booklet is designed to provide you with information on the different terms used in mathematics. If you have any questions please speak to either your child’s class teacher or Miss Gee or Mrs Palmer (Subject Leaders) Okehampton Primary School Basic operations Addition is bringing two or more numbers (or things) together to make a new total. Other words that will be used are: plus, add, sum, increase, total. Subtraction is taking one number away from another. Other terms that will be used are: subtract, minus, less, difference, decrease, take away, deduct. Multiplication is in its simplest form repeated addition. Other terms that the children will be taught to use are: multiply, product, by, times, lots of. Division is sharing things equally or grouping into sets of the same size. Other terms the children will use are: divide, quotient, goes into, how many times. Odd - An odd number is any whole number that cannot be divided by two exactly. Even - An even number is any whole number that can be divided by 2 exactly. Estimate - When you make an estimate you judge the amount without measuring or calculating. Acute angle - An acute angle measures between o° and 90°. Acute angled triangle - An acute angled triangle has all three angles less than a right angle. Adjacent - Adjacent means lying next to, or side by side. Algebra - An area of maths where numbers are represented by letters. Algorithm - An algorithm is the method you use to work out the answer to a calculation. Analogue clock - A clock with the numbers 1 to 12 around the face. Angle - An angle is the amount of turning between two lines, meeting at a point. Angles can be measured in degrees. Arc - An arc is part of the circumference of a circle. Area - Area is the total surface of a shape. Area is measured in square centimetres (cm²), square metres (m²), and square kilometres (km² ). Axis - An axis is the horizontal or vertical line on a graph. Many graphs have two axes; a horizontal axis and a vertical axis. Bar graph - A bar graph is a graph using bars to show quantity or numbers. The bars are all the same thickness and can be vertical or horizontal. Base - The base of a shape is the part on which it stands. Breadth - The breadth is the distance from one side to the other. It is sometimes called the width. The breadth is usually the shorter length when measuring the length and breadth. Calculation - A calculation is when you have to work out the answer to a problem. Capacity - Capacity is the amount a container can hold. It is usually measured in litres and millilitres. Carroll diagram - A Carroll diagram is used for sorting and takes the form of a grid. One part of the grid is the opposite of the other. Centilitre (cl) - A centilitre is one hundredth of a litre. There are 10 millilitres in 1 centilitre. Centimetre (cm) - A centimetre is one hundredth of a metre. There are ten millimetres in 1 centimetre. Centre of rotation - The point around which an object is rotated. Circumference - The circumference is the distance around a circle. It is the perimeter of a circle.. Common factor - A common factor is a number that divides two or more other numbers exactly. Common denominator - A common denominator is a multiple of the denominators of two or more fractions. 12 is the common denominator of thirds and quarters. Complementary angles - Two angles that add up to 90°. Composite - A composite is a number with more than two factors. Concave - Concave means curving inwards like a cave. It is the opposite of convex. Cone - A cone is a 3 dimensional shape. It has a flat base and the top comes to a point. It has curved edges. Conical shapes look like cones. Concentric circles - Concentric circles are circles of different sizes but they have the same centre point. Consecutive - Consecutive means when one number follows another number in an unbroken sequence. 7,8,9,10 are consecutive whole numbers. 12,14,16,18,20 are consecutive even numbers. Convert - Convert means you change something from one thing to another. 140 cm converts to 1.4 metres. Convex - Convex means curving outwards. It is the opposite of concave.. Co-ordinates - Co-ordinates are two numbers or letters that describe a position on a map, graph or chart. You write the horizontal co-ordinate first and the vertical co-ordinate second. Cube - A cube is a 3D shape which has 6 square faces, 8 vertices and 12 edge. Cuboid - A cuboid is a 3D shape which has 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. Cylinder - A cylinder is a 3D shape which has 2 flat faces and one curved face. Data - Data is a collection of information or facts. Decagon - A decagon is a 2D shape that has 10 straight sides. Decahedron - A decahedron is any 3D shape that has 10 flat faces. Decimal number - 124.75 This decimal number is made up of 1 hundred, 2 tens, 4 ones 7 tenths and 5 hundredths. Decimal point - The point between a whole number and a decimal fraction. Degree - A degree is a unit of measuring for measuring the size of an angles. It is also a unit used to measure temperature. Denominator - The denominator is the bottom number in a fraction. Face - A flat surface on a 3D shape is called a face. The base of a shape is also a face. Factor - A whole number that divides exactly into another. Fraction - Fractions are usually parts of something. A fraction has a denominator and a numerator. The denominator tells you the number of equal parts and the numerator tells you the number of the parts you are working with.. Fraction as a quotient - When you divide two numbers the quotient is the result. If you divide a larger number into a smaller number the quotient is a fraction. Fraction as a ratio - A fraction can be expressed as a ratio between two numbers. Four out six apples were ripe. The fraction of ripe apples was 2/3. Frequency - Frequency is the number of times a particular item appears in a set of data. Geometry - Geometry is the area of maths that looks at shape and space. Gram (g) - Grams are used to weigh things. There are 1000 grams in a kilogram. Graph - A graph is a drawing, chart, diagram or picture used to record information about something. Heptagon - A heptagon is a polygon that has 7 straight sides. Hexagon - A hexagon is a 2D shape that has 6 straight sides. Hexahedron - A hexahedron is a 3D shape that has 6 flat faces. Improper fraction - An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is larger than its denominator. An improper fraction is worth more than one. Integer - An integer is a whole number. It can be positive or negative. Zero is an integer. Intersect - Lines intersect when they cross over one another. Intersecting lines can be straight or curved. Inverse - Inverse means to reverse something. The inverse of addition is subtraction and the inverse of multiplication is division. Isosceles Triangle - An isosceles triangle has two sides that are the same length. Two angles of an isosceles triangle are also the same. Kilogram (kg) - A kilogram is used for weighing. There are 1000 grams in a kilogram. Kilometre (km) - Long distances can be measured in kilometres. There are 1000m in 1km. Length - Length is the measurement along a line or curve. When you measure the length and width of an object the length is usually longer than the width. Litre (l) - volume and capacity are measured using litres. It is usually used for measuring liquids. Mass - Mass is the amount of matter or material in an object. Mass can be measured in grams, kilograms and tonnes. Mean - The mean is an average. It is calculated by adding together all the quantities and then dividing the total by the number of quantities. Median - Median is another type of average. To find the median write out the quantities in order. The median is the quantity that has the middle value. Metre (m) - Metre is the metric unit used to measure length or distance. Millilitre (ml) - A millilitre is used to measure a small capacity or volume. There are 1000 millilitres in 1 litre. Millimetre (mm) - A millimetre is used to measure a small length or distance. Mode - The mode of a set of numbers/quantities is found by the number or quantity that occurs the most. Multiple - A multiple is lots of the same number or quantity. Multiples are like multiplication tables. The sixth multiple of 7 is 42. Multiply - When you multiply a number you increase something a number of times. Four multiplied by two equals 8. Net - A net is a flat shape that can be folded into a 3D shape. Nonagon - A nonagon is any 2D shape that has nine straight sides. Number sentence - A number sentence is a mathematical sentence. It can be expressed through words or numbers and symbols. 6 + 4 = 10. Numerator - The numerator is the number above the line on a fraction. It tells you how many equal parts there are. Oblique - Lines that are not horizontal or vertical are called oblique. Oblong - An oblong is a shape that is longer than it is wide. Obtuse angle - An obtuse angle is an angle that is between 90° and 180°. Octagon - An octagon is a shape that has 8 sides. Octahedron - An octahedron is a 3D shape that has 8 flat faces. Operation - Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are the four mathematical operations. Ordinal - Ordinal numbers show the place or position of something, i.e. 1st, 2nd or 10th. Parallel - Lines that are the same distance apart no matter how long they are called parallel lines. At no point do parallel lines cross. Parallelogram - A parallelogram is a 4 sided shape that has its opposite sides parallel to each other. Pentagon - A pentagon is a 2D shape that has 5 sides. Perimeter - The perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. Perpendicular - Two things are perpendicular when they meet each other at right angles. Pie - chart - A pie - chart is a graph where the information is shown as a circle. The different parts of the circle represents a different quantity. Place - value - This is the value of a digit depending on its position in a number. Plane - A plane is a flat surface. It can be vertical, horizontal or oblique. Plane shapes - 2D shapes are plane shapes. They are flat and only have two dimensions. Polygon - A polygon is any 2D shapes with 3 or more straight sides. Polyhedron - A polyhedron is any 3D shape that has been made from polygons. Prime number - A prime number is a number that has exactly 2 factors. These factors are one and itself. Prism - A prism is a 3D shape with two parallel, identical bases. Probability - probability is the chance of something happening. Product - When you multiply two numbers together your answer is called the product. Quadrilateral - A quadrilateral is a polygon that has four sides. The four angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360°. Quotient - The quotient is the answer to a division problem. It can be a whole number, a fraction, a mixed number or a decimal. Radius - The radius is the distance from the centre of a circle to its circumference. Range - The range is the difference between the lowest and the highest score. You may need to know the range when you are working out the averages of numbers. Ratio - A ratio is a way of comparing two or more values. Reflex angle - A reflex angle is an angle between 180° and 360°. Right - angle - A right angle measures 90°. Scale - A scale is a set of points on a line used for measuring. You can see a scale on maps, jugs, thermometers or rulers. Scalene triangle - A scalene triangle is a triangle which has no sides the same length. All of its angles are a different size as well. Square number - A square number is a number that you get when you multiply a number by itself. Sum - You get the sum when you add two or more numbers together. Symmetry - An object is symmetrical if one half is a mirror image of the other. Tangram - A tangram is a puzzle which is made up of triangles, squares and a rhombus cut out of a square. These shapes can then be used to make another shape. Tessellation - When you tessellate, you put shapes together without leaving any gaps. Tessellation is a tiling pattern. Tetrahedron - A tetrahedron is a 3D shape which has four faces and where each face is a triangle. Trapezium - A trapezium is a 4 sided shape that has one pair of sides that are parallel. Triangle numbers - 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21… are all triangle numbers. The difference between the triangle numbers increase by one each time. Triangular prism - A triangular prism is a prism that has triangular ends. Triangular pyramid - A triangular pyramid is a pyramid with a triangle base. Unit - Units are used in measuring. Litre is a unit of capacity. Kilogram is a unit of mass. Kilometre is a unit of distance. Vertex - A vertex is the point where two or more lines meet in an object or shape. Volume - Volume is the amount of space taken up by a solid shape. Volume is measured using cubic units. Vulgar fraction - A vulgar fraction is a fraction that has a numerator smaller than a denominator. Width - The width is the distance from one side to another. X - axis - The x-axis is the horizontal axis of a graph. Y - axis - The y-axis is the vertical axis of a graph.