Unit Plan Accenuate the Negative
advertisement
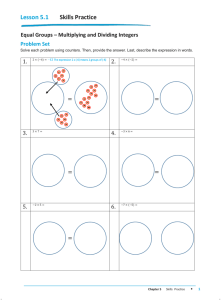
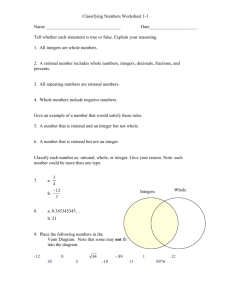
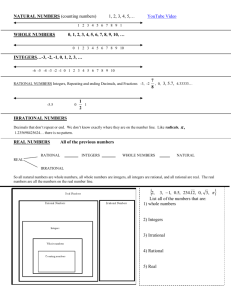
Unit Plan Template Unit Author: Sarah Bindl & Jim Braemer ~ 7th Grade Math The Wisconsin Standards that will be addressed are: http://www.corestandards.org/the-standards/mathematics/grade-7/the-number-system/ Mathematics » Grade 7 » The Number System 1. Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0..Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Understand subtraction of rational numbers as adding the additive inverse, p – q = p + (–q). Show that the distance between two rational numbers on the number line is the absolute value of their difference, and apply this principle in real-world contexts. Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers.2. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts.Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts.Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers. Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats.3. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers.1 Student Objectives/Learning Outcomes/Benchmarks: 1.)Compare and order positive and negative rational numbers and locate them on a number line. 2.) Understand the relationship between a positive or negative number and its opposite. 3.)Develop algorithms for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers 4.)Graph points in all 4 quadrants 5.) Use parenthesis and rules for the order of operations in computations Procedures: Briefly describe what you will attempt to accomplish each week of the Unit. Week 1: Students will gain an understanding of positive and negative integers by comparing and ordering integers in the context of money, temperature, and sports. Week 2: Students will develop algorithms for adding and subtracting integers and learn to apply these algorithms to real life situations. Week 3: Students will use their knowledge of positive and negative integers to graph ordered pairs on a four quadrant coordinate grid. Students will develop algorithms for multiplying and dividing integers and learn to apply these algorithms to real life situations. Week 4: Students will solve multi-step problems using the order of operations and algorithms for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers. Click here to enter text. Click here to enter text. Approximate Time Needed/Start Date: Start date: September 3 – first week of October Prerequisite Skills: Students will need to have an understanding of basic addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division facts using positive integers. Unit Overviewe Unit Plan Title: Accentuate the Negative Curriculum-Framing Questions Essential Course Question: What numbers are integers and how do we order them? What is the relationship between a positive or negative number and its opposite? What strategies do we use to add, subtract, multiply and divide integers? What is the order of operations? How are positive and negative integers used in real life situations? Unit Objective: We will explore this unit so that students extend their knowledge of negative numbers and explore ways to use negative numbers in solving problems. Unit Summary: Accentuate the Negative focuses on number sense and applications of the four operations on integers. Accommodations for Differentiated Instruction Resource Student: EEN support, modified ACE packets, CASH tutoring, after school tutoring, one-on-one aid from classroom teacher. Non-Native English Speaker: Modified ACE packets, classroom ELL support Gifted Student: Extensions, enrichment, higher level practice opportunities, Most difficult First Student Assessment: Formal: Classroom discussions, individual student observations, student questions, group work, individual practice, student surveys, classroom participation, student interviews Summative: Unit Assessment