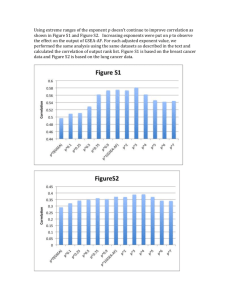
2 *Scatterplots 3 *Negative Correlation 4 *Positive Correlation 5 No
advertisement

8th Grade 2 *Scatterplots Probability & Statistics 3 *Negative Correlation 4 *Positive Correlation 5 No Correlation 6 *Box & Whisker Plot 7 *Histogram 8 *Experimental Probability 9 *Theoretical Probability Additions 10 *Independent Probability 11 *Dependent Probability Scatterplots A graph with points plotted to show a relationship between two variables Back to List Negative Correlation Negative Correlation: As one variable increases, the other decreases. Examples: •The more minutes in the freezer the lower the temperatures. Back to List •The more miles driven the fewer gallons of gas left in the tank. Positive Correlation Positive Correlation: As one variable increases, so does the other. Examples: •The more gas used the higher the miles driven. Back to List •The more minutes spent walking on the treadmill the more calories burned. No Correlation No Correlation: As one variable increases, you cannot tell what the other is doing. Examples: •Being in a higher grade level has no effect on the number of homework assignments. Back to List •Driving a further distance to work does not mean you will go through more traffic lights. Box & Whisker Plot A graph that shows how far apart and how evenly data are distributed Example: Back to List Histogram • A bar graph that shows the number of times data occur within certain ranges or intervals Example: Back to List Experimental Probability • The ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials or times the activity is performed Number of times outcomes occurs Total number of trials Example: If you roll a die 12 times and get a four five times, the experimental probability of getting a four is 5 Back to List 12 Theoretical Probability • A comparison of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible equally likely outcomes number of favorable outcomes possible Number of possible equal likely outcomes Example: the theoretical probability of getting a four 1 on a die is because there is 1 four 6 Back to out of 6 possible outcomes. List Independent Probability • events that do not have any influence on the occurrence or nonoccurrence of another event; Example • The probability of tossing tails on a coin, spinning blue on this spinner, and rolling a 2 on a number cube is Back to List 1 2 x 1 4 x 1 6 = 1 48 Dependent Probability • Two events are dependent if the outcome or occurrence of the first affects the outcome or occurrence of the second so that the probability is changed. Example When drawing two marbles at random from the bag below, what is the probability that they will both striped. 5/10 since there 4/9 since there are only 4 are 5 striped out of 10 total Back to List 5 x 10 striped left out of 9 total since you took one striped one out. 4 9 = 20 90 2 = 9