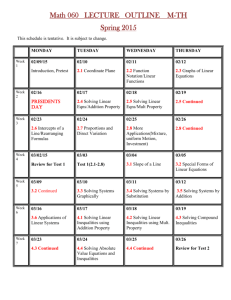
9-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors A. Definitions 1. Factors
advertisement

9-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors A. Definitions 1. Factors – two numbers that multiply to give you the product. Ex 1: find the factors of 48 2. Prime numbers – whole number whose only factors are 1 and itself. Ex 2: is 23 prime? 3. Composite numbers – Whole number that is not prime. Ex 3: Find the prime factorization of 150. 4. Prime factors - when a whole number is expressed as the product of factors that are all prime. Ex 4: find the prime factorization of the following. a.) 84 b.) -132 5. Greatest common factor – the greatest number that is a factor of two integers. Ex 5: What is the greatest common factor of: a.) 84 and 70? b.) 27a 2b and 15ab 2 c HW: Algebra 9-1 p. 477-479 21-27 odd, 30-31, 33-61 odd, 70-71, 72-86 9-2 Factoring Using the Distributive Property A. Factoring 1. Regular 3 x 2 + 75 x can be factored to 3 x( x + 25) by doing the reverse of distribution. Ex 1: Factor by distribution each polynomial a.) b.) c.) d.) 12mn 2 − 18m 2 n 2 = 6 x 2 + 12 x = 28a 2b + 56abc 2 20abc + 15a 2 c − 5ac 2. Also you can do the reverse of FOILing, called factoring by grouping. Ex 2: Factor a.) 5 y 2 − 15 y + 4 y − 12 b.) 20ab − 35b + 36a − 63 c.) 3 x3 + 2 xy − 15 x 2 − 10 y d.) a 2 − ab − 7b + 7a e.) 3a 2 − 2ab + 10b − 15a B. Solving Equations 1. If two things multiplied together equal zero, one of them has to be zero. ab = 0 Ex 3: solve a.) ( x − 2)(4 x − 1) = 0 b.) 12 y 2 = 4 y HW: Algebra 9-2 p. 484-486 17-39 odd, 44, 46, 49-59 odd, 64-74, 76-81 9-3 Factoring Trinomials A. Factoring 1. To factor trinomials, you do the reverse of FOILing, sometimes you may have to try a few different ways. Ex 1: Factor the following a.) ( x 2 + 7 x + 10) b.) ( x 2 − 12 x + 27 ) c.) ( y 2 + 3 y − 18 ) d.) ( a 2 − a − 6) e.) ( x 2 − 2 x − 48) B. Solving equations by Factoring 1. Get everything over to one side, factor and then solve each part. Ex 2: solve x 2 + 2 x = 15 HW: Algebra 9-3 p. 493-494 17-34, 37-53 odd, 54, 64-65, 70-76, 78-83 9-4 Factoring Trinomials ax 2 + bx + c = 0 A. Factoring 1. First put what two things multiply to give you ax 2 . 2. Then put what two things multiply to give you c. Example 1: Factor a.) 5 x 2 + 27 x + 10 b.) 7 x 2 + 22 x + 3 c.) 2 x 2 + 9 x + 9 d.) 24 x 2 − 22 x + 3 e.) 4 x 2 + 24 x + 32 B. Solve equations by Factoring Example 2: Solve a.) 3 x 2 + 13 x − 10 = 0 b.) 18b 2 − 19b − 8 = 3b 2 − 5b HW: Algebra 9-4 p. 499-500 14-30, 32-33, 35-47 odd, 54-70 9-5 Factoring Difference of Squares A. Factor a 2 − b 2 1. Foil ( x − 7)( x + 7) 2. When you need to factor something that looks like a 2 − b 2 , it factors to a difference of squares. Ex 1: Factor a.) m 2 − 64 b.) 3b3 − 27b c.) (2 x 4 − 32) d.) 6 x 3 + 30 x 2 − 24 x − 120 B. Solve equations by factoring Ex 2: Solve each equation a.) x 2 = 25 4 b.) r − =0 25 2 c.) 48 y 3 = 3 y HW: Algebra 9-5 p. 505-506 16-32, 34-44, 53-70