Topic 4 - Conceptua Math
advertisement

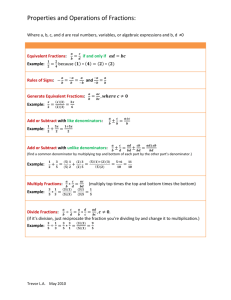
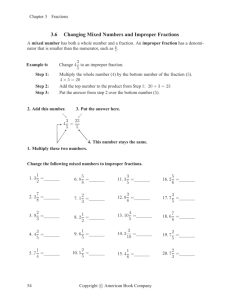
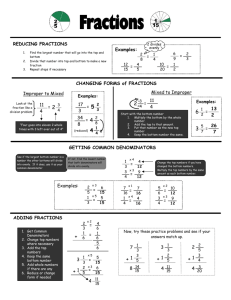
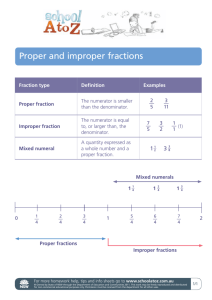
In Class Reference Sheet Big Idea 4: Fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators (same size parts) can be added or subtracted. Topic 4: Apply Your Knowledge Key Concept: Addition and subtraction of fractions can be used to solve a variety of problems. Prior Knowledge: 1. Understands part/whole relationships. 2. Writes mixed numbers and improper fractions Activity 1: Improper Fractions with Pattern Blocks Description Students use pattern blocks to model improper fractions. Vocabulary Preparation for Learning Teacher/Student Dialogue Indicators of Understanding * Content: area, shape, fractional part Process: drag, click, fill Provide students with pattern blocks. Have student take out a hexagon and cover it with trapezoids. Ask students to provide the fractions represented by the trapezoids (1/2). • Rephrase the problem stating that the trapezoid represents 1 whole. How many wholes are there in the hexagon? (2) • Ask students to cover the hexagon with triangles. If the hexagon represents 2 wholes, what does each triangle represent? (thirds) How many thirds in all? • Tell students that they need to identify the whole first and then the fractional parts. Open the Unitizing with Pattern Blocks tool. • Select a grey area and place it on the grid, making sure to lock the grid. • Set the value of the grey area as a fractional representation greater than 1 whole. • Review the process terms of drag and click as you demonstrate. • Ask: “How many triangles does it take to cover the design? How many wholes are in this design? How many parts does ___ cover?” • Again, have students first identify the whole then the fractional parts. While students are working in the software, be sure to circulate and ask: • How is this area divided? • What is the sum of the fractional parts? • Is there a different way you could show the same fraction? Can determine the whole (unit). Writes the value of a fractional part of a whole when the whole is defined. Uses addition strategies to check that the sum of all parts is equal to the whole. * Indicators of Understanding are in addition to the formative assessment at the end of each activity. • • • www.conceptuamath.com © 2010 Conceptua Math LLC 1 In Class Reference Sheet Big Idea 4: Fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators (same size parts) can be added or subtracted. Topic 4: Apply Your Knowledge Key Concept: Addition and subtraction of fractions can be used to solve a variety of problems. Prior Knowledge: 1. Understands part/whole relationships. 2. Writes mixed numbers and improper fractions. Activity 2: Mixed Numbers with Pattern Blocks Description Students use pattern blocks to model mixed numbers. Vocabulary Content: area, shape, fractional part, value, unknown Process: drag, blocks, create, overlap Preparation for Learning Teacher/Student Dialogue Indicators of Understanding * Review Activity 1, reminding students that an improper fraction can be written as a mixed number. Open the Unitizing with Pattern Blocks tool. • Select a grey area and place it on the grid, making sure to lock the grid. • Create a grey area of a hexagon and set the value to 2. • Review the process terms of drag and click as you demonstrate. • Ask: How many wholes are in this design? How many triangles do we need to cover the whole? Cover 5 parts of the wholes with blue. Have students determine what improper and mixed number is represented. • Discuss how finding the whole can help you determine the value or number for each colored part of the shape. • Show multiple examples assisting students in first determining the whole and then the value of each colored part. While students are working in the software, be sure to circulate and ask: • What part is equal to one whole? How many triangles create a whole? • How many wholes are in that model? How many parts? • How many groups of __(numerator) can you get from __(denominator)? How many times does __(numerator) go into __(denominator)? Can determine the whole (unit). Determines the value of a fractional part when more than one whole is provided. • Uses addition to check that the sum of all parts is equal to the given unit number. * Indicators of Understanding are in addition to the formative assessment at the end of each activity. • • www.conceptuamath.com © 2010 Conceptua Math LLC 2 In Class Reference Sheet Big Idea 4: Fractions and mixed numbers with like denominators (same size parts) can be added or subtracted. Topic 4: Apply Your Knowledge Key Concept: Addition and subtraction of fractions can be used to solve a variety of problems. Prior Knowledge: 1. Understands part/whole relationships. 2. Writes mixed numbers and improper fractions. Activity 3: Challenge: Improper Fractions & Mixed Numbers Description Students synthesize their knowledge of adding and subtracting mixed numbers and improper fractions with like denominators to determine the missing elements of a given equation. Vocabulary Content: proper fractions, improper fractions, mixed numbers, convert, equation Preparation for Learning Teacher/Student Dialogue Indicators of Understanding * Process: complete, missing, fill Review key vocabulary and model usage during lesson. Play Mystery Equation: • Show students an equation using mixed numbers with like fractions that has two parts missing. • Have students work in groups to figure out the missing parts. • Encourage students to use a variety of models, manipulatives, and mathematical strategies to figure out and check their solution. • Have students share. Discuss and compare the strategies of different groups. • Repeat with a variety of equations. Help students to learn and apply the inverse operations of addition and subtraction to find the missing parts. • Encourage students to begin with what they know. For example first fill in the denominators (these are all like fractions). While students are working in the software, be sure to circulate and ask: • What mathematical strategies are you using to complete these equations? • What would a model for this equation show? How can you use the model to assist you? Solves addition and subtraction problems with mixed numbers and improper fraction with like denominators. • Uses mathematical strategies and models to complete equations with missing elements. • Uses mathematical terms to explain his/ her mathematical thinking as he/she determines missing elements of an equation. * Indicators of Understanding are in addition to the formative assessment at the end of each activity. • www.conceptuamath.com © 2010 Conceptua Math LLC 3