Section 2 - 1 Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Fractions
advertisement

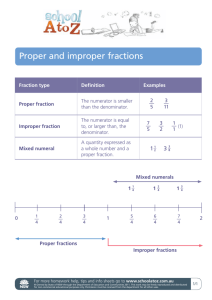
Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Section 2 - 1 Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Fractions – equal parts of the whole. Numerator – TOP = number of parts Denominator – BOTTOM = number of parts the whole is divided into. Proper Fraction = Numerator is LESS than the Denominator. Improper Fraction = Numerator is GREAT than or EQUAL to the Denominator. Mixed Numbers = SUM of a Whole Number and a Fraction. Procedure – Changing a Mixed number to an Improper Fraction 1) Multiply the Whole Number by the Denominator. 2) Add the result to the Numerator. 3) Keep the Denominator = ∗ 5 10 ∗ 8 + 5 80 + 5 85 10 = = = 8 8 8 8 15 ∗ 2 + 1 31 1 = 15 = 2 2 2 Procedure – Changing Improper Fraction to Mixed Number 1) Divide Numerator by Denominator. 2) Whole Number = Quotient Numerator = Remainder Denominator or Divisor = Denominator 1 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION 14 4 =24=2 5 5 7 95 =47=4 22 22 Section 2 – 2 Prime Numbers and Factorization AxB =C A and B are FACTORS of C Factorization: of 12 1x12 of 17 1x17 2x6 3x4 2x2x3 Find all the FACTORS of 72 1 * 72 a) left side gets bigger 2 * 36 b) right side gets smaller 3 * 24 c) let small numbers find larger numbers 4 * 18 d) where numbers pass stop NO reason to find numbers twice 5 * ___ e) Factors = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 72 6 * 12 f) Always starts with “1” and ends with “Number” 7 * ___ 8*9 Divisibility RULES By 2 - number ends in a 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 (even) 1. 84 YES 2. 59 NO 3. 998 YES 4. 2225 NO By 3 – sum of the digits is divisible by 3 5. 111 = 1+1+1 = 3 ÷ 3 = 1 6. 1111 = 1+1+1+1 = 4 ÷ 3 = 1 R 1 7. 309 3+0+9=12 ÷ 3 = 4 2 ALEKS –Chapter TWO YES NO YES Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) 8. 17216 By 10 – ends with a 0 17. 305 18. 300 19. 847 20. 8760 By 5 – ends in 0 or 5 21. 5780 22. 3427 23. 34678 24. 7775 By 7 – no rule just divide Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION 1+7+2+1+6=17÷3=5 R 2 NO NO YES NO YES YES NO NO YES PRIME NUMBER – is a whole number greater than “1” that has ONLY TWO factors, itself and “1”. PRIMES from “2” to “157” 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, [13x13=169] 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157 COMPOSITE NUMBER – is a whole number greater than “1” that is not PRIME. Note: “0” and “1” are NEITHER prime or composite. PRIME FACTORIZATION – the factorization in which every factor is a prime number. Every number has JUST ONE unique prime factorization. Factor out “2s”, then “3s”, then “5s”, etc. 3 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Factor Tree 220 220 11 10 22 2 5 2 20 2 11 10 2 5 220 220 2 4 55 2 2 5 110 2 11 55 5 11 Successive Division – divide by primes until a prime remains. 220 2 = 110 110 2 = 55 55 5 = 11 220 = 2 * 2 * 5 * 11 = 22 * 5* 11 168 2 84 2 42 2 21 3 4 7 2 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 7 = 23 * 3 * 7 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION 990 10 2 99 5 3 33 3 11 2 * 3 * 3 * 5 * 11 = 2 * 32 * 5 * 11 Determine if Prime, Composite, or Neither 39 3*13 Composite 0 Neither 41 1*41 Prime Section 2 – 3 SIMPLIFYING TO LOWEST TERMS Equivalent Fractions = equal each other. 3 2 1 = = 6 4 2 Determining if Equivalent " = if a * d = b * c then equivalent if NOT then $. ! # %& '( , ( 5 )* )* + %% -( '( 13*11 [ ] 24*6 143 [ ] 144 $ 9*24 [ ] 4*54 = 216 [ ] 216 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Simplifying to LOWEST TREMS /∗0 / 0 / / = = ∗ = ∗1= 1∗0 1 0 1 1 . 1) Prime factor the numerator and denominator. 2) Cancel any common factors in both. 3) Multiply remaining factors in the numerator and denominator. 15 3∗5 3 5 3 3 = = ∗ = ∗1= 35 5∗7 7 5 7 7 2 ∗ 13 2 2 26 = = = 3 ∗ 5 ∗ 13 3∗5 15 195 150 2 ∗ 3 ∗ 5 ∗ 5 2 ∗ 5 10 = = = 105 3∗5∗7 7 7 Greatest Common Factor – the largest factor of both the Numerator and Denominator. (If you see it; prime factorization always works.) '2 = (∗3 &, = &∗%& = %- = %- = &+ & ,5 (∗, = &∗% +∗%- 3 '4'43 , '4'4&4& %& % = 13 + = = 3 &4& = 3 , (Just divide) % + (When you run out of factors, you can always multiply by 1). Simplifying factors of 10, 100, 1000, etc 630 63 10 63 = ∗ = 190 19 10 19 1300 13 100 1 ∗ 13 1 = ∗ = = 52000 520 100 13 ∗ 40 40 6 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION 21 1000 21 3∗7 3 21000 = ∗ = = = 35 1000 35 5∗7 5 35000 (You can cancel the same number of trailing ZEROs in both the Numerator and Denominator. Joanne planted 77 seeds and 55 sprouted. Geoff (Jeff) planted 140 seeds and 80 sprouted. a) What fraction sprouted for Joanne? What fraction sprouted for Geoff? b) Who had a greater portion sprout? Section 2 – 4 Procedure: a) b) Joanne = 33 25 = -∗%% 3∗%% 2 = - 3 '∗( ( Geoff = = = = %(5 %( '∗3 3 As the Denominators are the same, Just compare Numerators. Joanne did better. Multiplication of Fractions and Applications Multiplying Fractions (Note NOT Mixed numbers) Multiply Numerators = new Numerator Multiply Denominators = new Denominators 0 ∗0 ∗ = / /∗ 1 1 1 1 1∗1 1 6 = ∗ = = 2 4 2 4 2∗4 8 2 5 10 ∗ = 3 9 27 7 7 11 77 ∗ 11 = ∗ = 12 12 1 12 7 -- ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Multiplying and Simplifying Fractions multiplying) (Often easier to do before 4∗7 7 7 4 28 ∗ = = = 20 3 60 4 ∗ 15 15 7 4 7∗4 7 7 ∗ = = = 20 3 4 ∗ 5 ∗ 3 3 ∗ 5 15 2∗3∗3∗5 1 6 15 ∗ = = = 25 18 5 ∗ 5 ∗ 2 ∗ 3 ∗ 3 5 5 (when you run out of factors “* by 1”) 2 9∗2 3∗3∗2 6 97 8 = = = 15 15 3∗5 5 3 4 6 3∗2∗2∗3∗2 1 1 7 87 87 8 = = = 16 9 5 2 ∗ 2 ∗ 2 ∗ 2 ∗ 3 ∗ 3 ∗ 5 2 ∗ 5 10 Order of Operations 4 4 4 16 ( )' = ∗ = 3 3 3 9 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 ( ∗ )& = ( )& = ∗ ∗ = 5 12 10 10 10 10 1000 % AREA of a Triangle A = ∗ ;< ∗ = >ℎ = ' % % ' b = 8m, h = 5m A = ∗ 8 ∗ 5 = 20 = 20 ' ' ( b = 2 ft, h = 6 & % ( A = ∗ 26 ∗ 6 = ' & KITE (page128) 8 ALEKS –Chapter TWO ( & 6 ' % BH = /ℎ ' Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) base = %% ' & + = ' %( ' Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION = 76 ℎ >ℎ = 26 Kite = 2*triangle % A = 2* ∗ 76 ∗ 26 = 14ft2 ' Section 2 – 5 Division of Fractions and Applications Procedure: Reciprocal / 1 1 → → → → → / 1 1 ! % ∗ = 1 ∗ = 1 $ 0 / $ 0 ! 7 10 → 10 7 1 4 → →4 4 1 7→ 1→ 9 7 1 → 1 7 1 →1 1 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Division of Fractions – to divide by a Fraction, you multiply by the reciprocal of the fraction (divisor). 4 3 4 5 20 = ∗ = 5 7 3 21 7 2 1 2 5 10 = ∗ = 3 5 3 1 3 1 2 1 5 5 = ∗ = ( 1 < CD 61 D ℎ 0 C0D) 4 5 4 2 8 3 9 3 10 3∗2∗5 5 = ∗ = = 8 10 8 9 2∗4∗3∗3 12 15 1 3∗5 3 15 10 = ∗ = = 4 10 4∗2∗5 8 4 12 20 5 4∗5∗5 25 20 = ∗ = = 5 1 12 4∗3 3 Order of Operations 3 6 1 3 3 14 6 2 = ∗ = ∗ =2 7 14 7 2 14 7 3 4 8 4 3 3 9 ( )' = ( ∗ )' = ( )' = 7 3 7 8 14 196 ' 2 2 2 Recipe requires package 20 − − − − … 5 5 5 Of chips for each batch of Repeated sub = Cookies. How many batches 2 5 can be made with 20 20 = 20 ∗ 5 2 packages? = 50 /0ℎ< 10 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) '- Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION - yd ditch will be filled with yd ' ( lengths of pipe. How many segments are needed? School will cost $20,000,000 to & build. State will pay of cost. School district sells bonds to cover ( of non-state costs? a) state costs? b) non-state costs? c) district bond sales? % of police department is female. & of these were promoted. What fraction were promoted Section 2 – 6 numbers 25 5 − − 2 4 25 5 = 2 4 5 − … 4 25 4 ∗ = 10 2 5 & ) of $20,000,000 of = times 3 ∗ $20,000,000 = $12,000,000 5 b) $20,000,000-$12,000,000 = $8,000,000 ( c) ∗ $8,000,000 = $6,400,000 - ' 3 1 2 1 2 2 6 = ∗ = 3 7 3 7 21 Multiplication and Division of MIXED Procedure: a) Change each Mixed number to a Fraction. b) Multiply or Divide c) Convert back to Mixed if needed. 5 23 35 23 ∗ 7 161 5 3 74 8 75 8 = 7 8 7 8 = = = 26 5 6 5 6 6 6 6 1 7 33 40 3 ∗ 11 ∗ 2 ∗ 20 716 8 73 8 = 7 8 7 8 = = 60 2 11 2 11 2 ∗ 11 11 ALEKS –Chapter TWO Basic College Mathematics (ALEKS) Chapter TWO – FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION 1 43 10 43 ∗ 2 ∗ 5 215 2 77 8 (10) = 7 8 7 8 = = = 71 6 6 1 2∗3 3 3 1 5 31 17 31 6 31 ∗ 2 ∗ 3 62 11 710 8 72 8 = 7 8 7 8 = ∗ = = =3 3 6 3 6 3 17 3 ∗ 17 17 17 4 24 8 5 8∗5 5 2 84 =8 = ∗ = = =1 5 5 1 24 8 ∗ 3 3 3 4 112 8 112 1 14 ∗ 8 14 5 12 8 = = ∗ = = =1 9 9 1 9 8 9∗8 9 9 & Recipe requires 2 cups of flour. ( % How much flour for 2 recipes? & % 2 ∗2 = ( ' %% ( - ∗ = ' -2 3 = 6 cups 2 ' Costs $2 to wrap a present. Ribbon $2 – nothing to the problem. 2 ft long is used for each present. Repeated sub 2 How many presents can be wrapped with 168 ft roll? 12 5 168 21 168 2 = 8 1 8 168 8 = ∗ 1 21 21 ∗ 8 ∗ 8 = = 64 21 ALEKS –Chapter TWO