Number and Operations—Fractions
advertisement

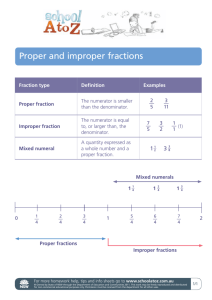
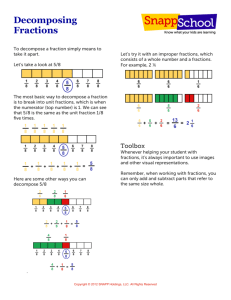
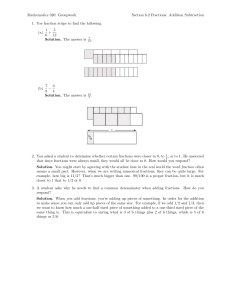
DATE NAME Parts and Wholes 1. P In a tangram … M • 2 small triangles (S) cover a medium triangle (M) L What fraction of each shape is covered by a single small triangle? S • 2 small triangles (S) cover a square (SQ) SQ • 2 small triangles (S) cover a parallelogram (P) S L • 4 small triangles (S) cover a large triangle (L) a) d) b) c) e) f ) 2. What fraction of the shape is shaded? Explain how you know. a) b) c) d) 3. What fraction of the trapezoid is covered by a single small triangle? Show your work. 4. If a) F-76 = red and = blue, approximately what fraction of each flag is shaded red? Explain. b) c) d) Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION NAME DATE Fraction Strips 2 3 4 6 1 2 3 6 3 4 6 8 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION 3 5 6 10 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 F-77 DATE NAME Investigating Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (1) NOTE: The blocks shown here are not actual size! hexagon triangle rhombus trapezoid Euclid’s bakery sells hexagonal pies. They sell pieces shaped like triangles, rhombuses, and trapezoids. 1. a) Shade 2 5 pies. 6 b) How many pieces did you shade? c) Write an improper fraction from the amount of pie shade. 2. M ake a model of the pies below with pattern blocks. (Place the smaller shapes on top of the hexagons). Then write a mixed number and improper fraction for each group of pies. a) b) c) Mixed Number: Mixed Number: Mixed Number: Improper Fraction: Improper Fraction: Improper Fraction: 3. U se the hexagon as the whole pie. Use the triangles, rhombuses, and trapezoids as the pieces. Make a pattern block model of the fractions below. Then sketch your models on the grid. a) 2 1 b) 1 1 1 6 d) 1 2 c) 2 2 3 e) 3 f )11 g) 5 h)10 2 3 F-78 6 3 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION 2 DATE NAME Investigating Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (2) 4. Using the trapezoid as the whole pie, and triangles as the pieces, make a pattern block model of the fractions. Sketch your models on the grid. The first one is done for you. a) 5 b) 7 c) 1 2 d) 2 1 3 3 3 3 Draw sketches (using the hexagon as the whole) to answer the questions. 5. Which fraction is greater: 1 5 or 9 ? 6 6 6. Which fraction is greater: 2 1 or 14 ? 6 6 9. How much larger than a whole is 4 ? 10. Crystal ate 2 of a pie each day for 4 days in a 3 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION 6 8. How much larger than a whole pie is 7 of a pie? 7. Draw a picture to show 3 − 1 . 6 11.Ahmed ate 1 1 pies during the week. 12.Alice ate 3 2 pies in January. 3 Jill ate 1 of a pie each day for a week. Who ate more pie? 3 row. How much did she eat altogether? 3 6 How many third-sized pieces did she eat? Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 F-79 DATE NAME Pattern Blocks Triangles Squares Rhombuses Trapezoids COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION Hexagons F-80 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 DATE NAME COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION Equivalent Fractions Memory (1) 1 2 3 5 1 3 2 4 6 10 3 9 1 4 3 7 2 5 3 12 6 14 6 15 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 F-81 DATE NAME F-82 2 3 3 4 3 8 8 12 9 12 6 16 5 8 7 8 4 5 10 16 21 32 16 20 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION Equivalent Fractions Memory (2) DATE NAME COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION Equivalent Fractions Memory (3) 7 9 5 6 6 7 56 72 45 54 36 42 4 9 5 11 7 12 28 63 55 121 63 108 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 F-83 DATE NAME Organized Lists Many problems in mathematics and science have more than one solution. Some problems involve two quantities. To make sure you don’t miss any possible solutions, list the values of one of the quantities in increasing order. 1. Fill in the number of pennies, nickels, dimes, or quarters you need to make each amount. a) Make 17¢ b) Make 45¢ c) Make 23¢ dimes pennies nickels 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 d) Make 32¢ pennies nickels dimes e) Make 65¢ quarters pennies 0 0 1 1 2 2 pennies f ) Make 85¢ pennies quarters pennies 3 2. Ben wants to find all the ways he can make 60¢ using quarters and nickels. He lists the number of quarters in increasing order. Why did he stop at 2 quarters? quarters nickels 0 1 2 a) 90¢ using dimes and nickels b) 25¢ using quarters and dimes 4. Alicia wants to find all the ways she can make 70¢ using quarters and dimes. Which entry in her chart won’t work? Put an “ ” in the “dimes” column for that row. quarters dimes 0 1 2 5. Make a chart to show all the ways to make 85¢ using quarters and dimes. F-84 Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION 3. Make a chart to show all the ways you can make the given amount. DATE NAME Always, Sometimes, or Never True (Numbers) A B If you multiply a three-digit number by a one-digit number, the answer will be a three-digit number. If you subtract a three-digit number from 999 you will not have to regroup. The product of two numbers is greater than the sum. D E F If you divide a number by itself the answer will be 1. The product of 0 and a number is 0. Mixed numbers are larger than improper fractions. G H I The product of two even numbers is an even number The product of two odd numbers is an odd number. When you divide an even number by 4, the remainder is 0. J K L When you round to the nearest thousands place, only the thousands digit changes. When you divide, the remainder is less than the number you are dividing by. To multiply a fraction by a whole number, you multiply the numerator and denominator by the number. M N Five times a number is even. Improper fractions are greater than 1. C O If you have two fractions, the one with the smaller denominator is the larger fraction. 1. C hoose a statement from the chart above and say whether it is always true, sometimes true, or never true. Give reasons for your answer. What statement did you choose? Statement Letter This statement is… COPYRIGHT © 2013 JUMP MATH: TO BE COPIED. CC EDITION Always True Sometimes True Never True Explain: 2. Choose a statement that is sometimes true, and reword it so that it is always true. What statement did you choose? Statement Letter Your reworded statement: 3. Repeat Questions 1 and 2 with different statements. Blackline Master — Number and Operations—Fractions — Teacher’s Guide for AP Book 5.1 F-85