Activity Studying Prime and Composite Numbers
advertisement
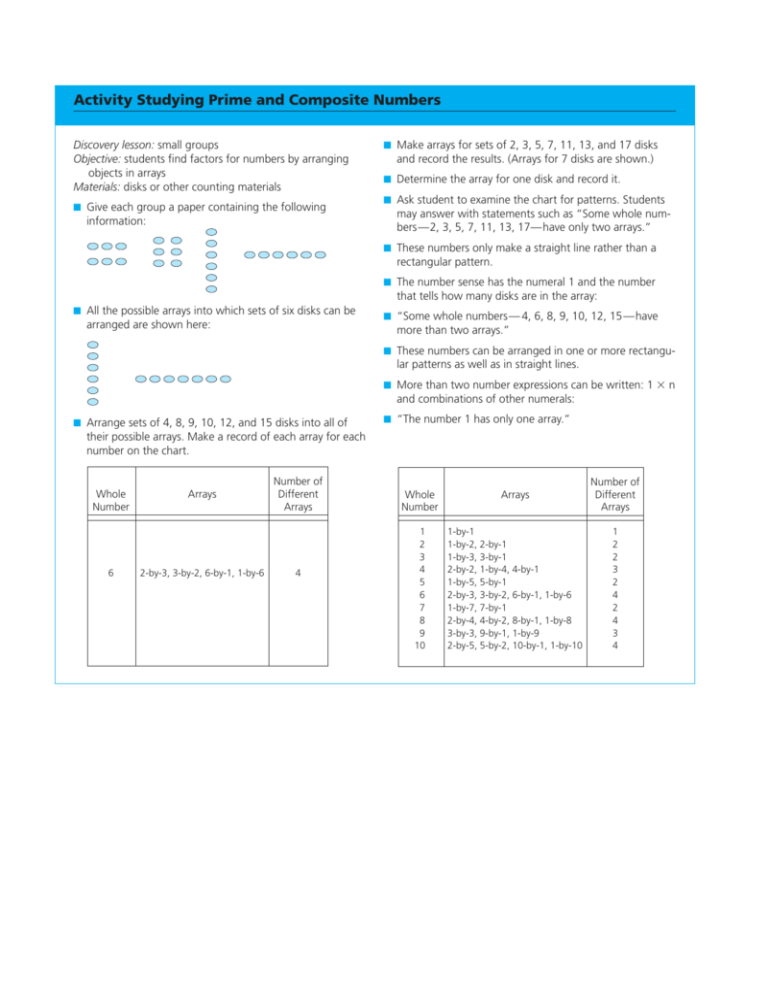
Activity Studying Prime and Composite Numbers Discovery lesson: small groups Objective: students find factors for numbers by arranging objects in arrays Materials: disks or other counting materials 䡲 Give each group a paper containing the following information: 䡲 Make arrays for sets of 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and 17 disks and record the results. (Arrays for 7 disks are shown.) 䡲 Determine the array for one disk and record it. 䡲 Ask student to examine the chart for patterns. Students may answer with statements such as “Some whole numbers—2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17—have only two arrays.” 䡲 These numbers only make a straight line rather than a rectangular pattern. 䡲 The number sense has the numeral 1 and the number 䡲 All the possible arrays into which sets of six disks can be arranged are shown here: that tells how many disks are in the array: 䡲 “Some whole numbers— 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15—have more than two arrays.” 䡲 These numbers can be arranged in one or more rectangular patterns as well as in straight lines. 䡲 More than two number expressions can be written: 1 ⫻ n and combinations of other numerals: 䡲 Arrange sets of 4, 8, 9, 10, 12, and 15 disks into all of 䡲 “The number 1 has only one array.” their possible arrays. Make a record of each array for each number on the chart. Whole Number 6 Arrays 2-by-3, 3-by-2, 6-by-1, 1-by-6 Number of Different Arrays 4 Whole Number Arrays Number of Different Arrays 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1-by-1 1-by-2, 2-by-1 1-by-3, 3-by-1 2-by-2, 1-by-4, 4-by-1 1-by-5, 5-by-1 2-by-3, 3-by-2, 6-by-1, 1-by-6 1-by-7, 7-by-1 2-by-4, 4-by-2, 8-by-1, 1-by-8 3-by-3, 9-by-1, 1-by-9 2-by-5, 5-by-2, 10-by-1, 1-by-10 1 2 2 3 2 4 2 4 3 4