A Fraction of your Life By: Bryan Pashong
advertisement

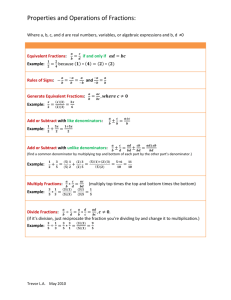
A Fraction of Your Life! 6th Grade (5 Day Unit Plan) *Fraction Bars* *Foam Shapes* *TI Interactive* *National Library Virtual Manipulatives* *Computers/Online* *Graphing Calculators* BRYAN PASHONG I2T2 WORKSHOP DECEMBER 2ND 2007 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS A) Overview of 5 Day Unit Page 3 B) Objectives of 5 Day Unit Page 4 C) NYS Standards & NCTM Standards Page 4-5 D) Materials Used Page 5 E) Resources Used Page 6 F) Day One: Fraction Introduction Visual Exploration of Part vs. Whole with Fraction Bars Common Denominator Page 7 G) Day Two: Equivalent Fractions / Comparing Fractions Finding Factors / Finding LCM’s Page 9 H) Day Three: More Fraction Bars Shapes and Fractions Adding Fractions Subtracting Fractions Page 11 I) Day Four: Multiplying Fractions Multiplying Fractions for Real Life Settings Page 14 J) Day Five: Problem Solving with Fractions Using Fractions in Everyday Life Page 17 2 OVERVIEW OF UNIT Day Description Materials *Fraction Introduction *Common Denominator *Visual Exploration of part vs. whole with fraction bars An introduction and exploration of fractions will be taught including definitions, representations, how to read them and finding common denominators. *Math Notebooks *Overhead & Transparencies *Fraction Bars *Computer Access *National Library of Virtual Manipulatives 2 *Equivalent Fractions *Comparing Fractions *Finding Factors *Finding LCM's Students will use the program TI Interactive to explore how fractions can be compared and find their equivalencies. They will also find factors to help compare fractions and then be able to find the Lowest Common Multiples (LCM). *Math Notebooks *Computer Lab *Overhead & Transparencies *TI Interactive Program *National Library of Virtual Manipulatives 3 *More Fraction Bars *Shapes and Fractions *Adding Fractions *Subtracting Fractions Students will use a variety of manipulatives to explore more with fractions; including part vs. whole and a variety of shapes. They will learn how to add and subtract fractions with both same and different denominators. *Math Notebooks *Fraction Bars *Shapes *Overhead & Transparencies *Multiplying Fractions *Convert Mixed Fraction to Improper Fractions *Add, Subtract, Multiply with mixed numbers *Begin Real Life Explore Students will use websites, graphing calculators, and paper/pencil to see the many ways of multiplying fractions with like and unlike denominators and how to add, subtract, multiply mixed fractions. *Math Notebooks *Graphing Calculators *Computer Access *Various Websites *Overhead & Transparencies *Problem Solving with Fractions *Using Fractions in Everyday Life Students will learn to solve a variety of word problems which incorporated fractions in real-life settings. They will see the important role that they play in everyday life. Lastly they will complete a hands-on activity to explore the relationship between fractions, proportions, and M&M's. *Math Notebooks *Various Websites *M&M's 1 4 5 Lesson Title 3 OBJECTIVES OF UNIT Students will: • Use common denominators when comparing and ordering fractions. • Learn how to find the simplest form of a fraction. • Recognize the idea that the whole is made of several parts. • Recognize fractions in everyday life. • Express which fractions are equivalent to each other. • Use fraction bars to add and subtract fractions with like and unlike denominators • See parts of fractions and the relationships between halves, thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, eighths, ninths, tenths, and twelfths with fraction bars. • Add and subtract fractions with common and unlike denominators without using manipulatives. • Use various computer websites, especially NVLM, to learn about various components of fractions. NYS STANDARDS • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 5.N.5 Compare and order fractions including unlike denominators (with and without the use of a number line.) 5.N.19 Simplify fractions to lowest terms. 5.N.20 Convert improper fractions to mixed numbers, and mixed numbers to improper fractions. 5.N.22 Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators. 6.PS.3 Interpret information correctly, identify the problem, and generate possible strategies and solutions. 6.PS.13 Model problems with pictures/diagrams or physical objects. 6.PS.14 Analyze problems by observing patterns. 6.RP.1 Recognize that mathematical ideas can be supported using a variety of strategies. 6.RP.2 Understand that mathematical statements can be supported, using models, facts, and relationships to explain their thinking. 6.R.1 Use physical objects, drawings, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations. 6.CN.1 Understand and make connections and conjectures in their everyday experiences to mathematical ideas. 6.N.3 Connect and apply mathematical information to solve problems. 6.CN.4 Understand multiple representations and how they are related. 6.CN.6 Recognize and provide examples of the presence of mathematics in their daily lives. 6.N.16 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators. 6.N.17 Multiply and divide fractions with unlike denominators. 6.N.18 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide mixed numbers with unlike denominators NCTM STANDARDS 4 • Number and Operations Standard o Understanding numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems. Grades 6-8: Compare and order fractions. . . o Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates Grade 6-8: Select appropriate methods and tools for computing with fractions…mental computation, estimation, calculators or computers, and paper and pencil, depending on the situation, and applying the selected methods. • Problem Solving Standard o Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving. o Solve problems that arise in mathematics and in other contexts. o Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to solve problems. • Representation Standard o Select, apply, and translate among mathematical representations to solve problems. o Use representations to model and interpret physical, social, and mathematical phenomena. MATERIALS USED • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Math Notebooks Computer Lab/ Access Overhead Unit Overhead Transparencies Overhead Markers Fraction Bars Foam Shapes Various Websites o www.nlvm.com (National Library of Virtual Manipulatives) o http://ali.apple.com/ali_sites/ali/lessonideas/DayWithFractions.html (Video on Everyday Life Fractions) TI Interactive Program Graphing Calculators “M&M's” Various Worksheets Middle Grades Math, Prentice Hall Middle Grades Math Workbook, Prentice Hall RESOURCES USED 5 • • • • • • • • • • Prentice Hall, Middle Grades Math, Authors: (Susan Chapin, Mark Illingworth, Marsha Landau, Joanna Masingila, Leah McCracken), Chapters: 4,5 (Pages 146, 147, 149, 195, 208, 209, 228, 229) Copy Right Date: 2001 Prentice Hall, Middle Grades Math Workbook, (Part of Book Above) Page: 28 TI Interactive www.yahoo.com www.wikipedia.com http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/vlibrary.html (National Library of Virtual Manipulatives) Utah State University http://score.kings.k12.ca.us/lessons/ (M&M’s) Kings County Office of Education http://mathforum.org/paths/fractions/frac.recipe.html (Recipe) http://ali.apple.com/ali_sites/ali/lessonideas/DayWithFractions.html (Video on Everyday Life Fractions) Apple Learning Interchange http://math.rice.edu/~lanius/Patterns/ (Fraction Shapes Sheet) Cynthia Lanius DAY ONE OF UNIT PLAN *Fraction Introduction* 6 *Visual Exploration of Part vs. Whole with Fraction Bars* *Common Denominator* (A) Daily Objectives: • Students will learn what fractions are, how to read them, how to find a common denominator, and the representations of them through fraction bars. (B) Daily Outline: • On the overhead show the following: • Fraction Definition: any part of a unit, or a quotient of a numbers, e.g. ¾ • A fraction is read by stating a part out of a whole, a number divided by another number, or one number over another number, or as a one number: e.g. “Three parts out of Four whole parts” “Three divided by Four” “Three over Four” or most commonly “Three Fourths.” The numerator = top & denominator = bottom. • Mixed Number Definition: the sum of a whole number and a proper fraction, e.g. “You could have two entire cakes and three quarters of another cake. The whole and fractional parts of the number are written next to each other: 2 + ¾ = 2 ¾. • Students are to be given fraction bars and make discoveries such as: o Find which bar is equal to a whole, or = 1 o Find which bar is equal to three quarters, or = ¾ o Find which bar is equal to a half, or = ½ o Find which bar is equal to one quarter, or = ¼ o Find which bar is equal to one eight, or = ⅛ • Students should make discoveries realizing that ½ + ½ = 1, ¾ + ¼ = 1, etc . . . • Finding a Common Denominator o Process: You must find a number that is similar in multiple between each of the two denominators 3/4 + 3/5 where the denominators are 4 and 5. These have a common multiple of 20. In most cases, such as here you just multiply 4*5 = 20. This doesn’t not always give the solution in lowest terms though • Reducing: When a fraction has a numerator and a denominator that can be divided by the same number then they can be reduced or placed into lowest terms. For example: !2$ !1$ """# %%%& = """# %%%& 6 3 ! 3 $ !1$ %% = "" %% """# 12 %& "# 4 %& ! 20 $ ! 2 $ %% = "" %% """# 50 %& "# 5 %& true true true *Both 2 and 6 can be divided by 2* *Both 20 and 50 can be divided by 10* *Both 3 and 12 can be divided by 3* (C) Daily Student Handouts: (including supporting screenshots or graphics that assist the student in completion of tasks), transparencies (optional), and homework (if not from textbook) • Homework Assignment(s): 7 o Online Explore: “National Library of Virtual Manipulatives” Students are to complete: “Fractions-Adding” (Under Grades 6-8) where they can practice exploration to adding and finding common denominators with fractions and visual aids. o Practice Workbook: “Math for Middle Grades” (Prentice Hall) Students are to complete: Practice 4-1, Relating Fractions to Models. (D) Daily Answer Keys: • Homework Assignment(s): o Online Explore: Answers are self corrected through website. o Practice Workbook Answers: 1) 3/4 2) 7/12 3) 1/4 4) 3 3/4 5) 1 5/6 6) 2 2/3 7) 1 1/2 8) 9/25 9) 2 2/5 10) a)7/12 b) 5/12 11-14) Answers may vary 15) 5/26 16) Answers may vary DAY TWO OF UNIT PLAN *Equivalent Fractions* + *Comparing Fractions* 8 *Finding Factors* + *Finding LCM’s* (A) Daily Objectives: • Students will use the TI Interactive math program to explore how fractions can be compared and find their equivalencies. It will show a relationship between finding factors and LCM (Lowest Common Multiple) of the denominators. (B) Daily Outline: • On the overhead show the following: • Read “Think and Discuss” on page 147 in “Middle Grades Math” (Prentice Hall): o “Suppose you and a friend do volunteer work at the animal shelter. Both of you are at the shelter today. You volunteer every third day and your friend volunteers every fourth day. After how many days will both be at the center on the same day?” • So, you will see each other at the shelter on the twelfth day. The diagram represents the multiple numbers of each 3 and 4. A Multiple of a number is the product of the numbers and a nonzero whole number. The LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two numbers is the least number that is a multiple of both. The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12. o Have students figure out what the multiple of 6 and 9 are: 6: 6,12,18,24,30 9: 9,18,27,36 Therefore 18 is the LCM of 6 and 9 • Showing equivalency in shaded bars of same size • • Diagram A: 3/4 is shaded f Diagram B: 6/8 = 3/4 is shaded Diagram C: 12/16 = 6/8 = 3/4 • A Factor is a whole number that divides another whole number with no remainder 9 o This can be found by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same number: i.e. ! 2 $ '! 2 $ ! 4 $ """ %%% """ %%% = """ %%% #" 3 &% #" 2 &% #" 6 &% o Two is factor of 4 and 6. And 6 is a common denominator of 2 and 3 • Lastly students will use the TI Interactive Program to practice and explore equivalent fractions, adding, and subtracting o By using the INSERT, MATH BOX, function- students can type in a fraction and then automatically have answer appear to check after solving themselves. It is imperative that students are shown the proper way to type in parenthesis, adding, and subtraction signs. (C) Daily Student Handouts: (including supporting screenshots or graphics that assist the student in completion of tasks), transparencies (optional), and homework (if not from textbook) • Homework Assignment(s): o Online Explore: “National Library of Virtual Manipulatives” Students are to complete: “Fractions-Comparing” & “FractionsEquivalent” (Under Grades 6-8) where they can practice making comparison between fractions and explore their equivalencies. The interactive setup also allows students to change the number of pieces the fraction is divisible by to see which factors of the denominator will match up. o Textbook: “Math for Middle Grades” (Prentice Hall) Students are to complete: Page 149, #1-4, 7-9, 13, 17-19, 25-27 (D) Daily Answer Keys: • Homework Assignment(s): o Textbooks Answers 1) 1,17 2) 1,2,36,9,18 3) 1,2,4,8,16,32 4) 1,2,3,6,7,14,21,42 7) 7,14,21,28,35 8) 4,8,12,16,20 9) 9,18,27,36,45 13) Answers may vary 17) 12 18) 36 19) 40 25) 30 26) 45 27) 48 DAY THREE OF UNIT PLAN 10 *More Fraction Bars* *Shapes and Fractions* *Adding Fractions* *Subtracting Fractions* (A) Daily Objectives: • Students will use manipulatives (fraction bars and shapes) to explore more fraction representations. They will compare the shapes as fractions of another shape. They will learn how to add and subtract fractions with same and different denominators. (B) Daily Outline: • Hand out the fraction bars to students again and have them get reacquainted. • Explain that models can help you understand more of the meaning of fractions. • Break the class (ideally take 20 students for an even number) into halves and then have half of the students stand and the other half sit. • Now break the class into thirds: Have a third of the class stand up, then have another third stand up to have two thirds standing, and then the last third to have three out of three standing or a whole. • This can be repeated for fourths, fifths, etc • Have students work with a partner using shapes to complete “Fraction Shapes” (SEE SHEET BELOW) and #1-3 on page 144 of the textbook. Here they will see part vs. whole representations. o Page 144 ANS: 1) a) 2 b) ½ 2) a) 6 b) 1/6 3) a) 3 b) 1/3 o “Fraction Shapes” ANS: 1) 2 2) 3 3) 2 4) 6 5) 3 6) 1 ½ 7) 1/6 8) 1/3 9) ½ 10) 2/3 • • On the overhead show the following: Adding Fractions With Same Denominator: o Process: Add the top two numerators together and place over the denominator which stays the same number. You are adding two parts of a same equal whole together. • • 3 1 4 4 2 6 + = + = 5 5 5 8 8 8 Adding Fractions With Different Denominators: o Process: You must first find a common denominator, and then you add just the same as your would for fractions of same denominators. ! 18 $ ! 10 $ 28 3 2 6!3 5!2 28 14 + = + "" %% + "" %% = = ! ! # & # & 5 6 56 65 " 30 % " 30 % 30 30 15 Adding Fractions With Fraction Bars: o Have students add fractions with the bars, seeing that: 11 • • ½+½=1 • ¾+¼=1 • 1/6 + 5/6 = 1 • ½+¼=¾ • 1/3 + 1/3 = 2/3 Subtracting Fractions With Same Denominators: o Process: When fractions have the same denominator you subtract the second numerator from the first numerator, and place that answer over the denominator (which is the same as the original two fractions.) !3$ !2$ """# %%%& - """# %%%& 5 5 !3$ !2$ """# %%%& - """# %%%& 8 8 ! 7 $ ! 4 $ %% - "" """# %% 11 %& "# 11 %& 1 5 1 8 3 11 ! 5 $ ! 2 $ %% - "" """# %% 12 %& "# 12 %& 1 4 *Notice in last example on far right that 5-2 = 3 over 12, but when reduced = 1/4 Subtracting Fractions With Different Denominators: o Process: When fractions have different denominators you must first find a common denominator, make the fractions equivalent, and then subtract the fractions as you would above. For example: !3$ !1$ "" %% - "" %% #" 5 &% #" 4 &% --> !7$ !3$ "" %% - "" %% #" 8 &% #" 5 &% --> ! 3$4 % ! 1$5 % "" " & "#" 20 &&&'& - "#"" 20 &'&& --> ! 7$5 % ! 3$8 % "" " & "#" 40 &&'&& - ""#" 40 &'&& --> ! 12 $ ! 5 $ "" %-" % #" 20 %&% "#" 20 %&% = ! 35 $ ! 24 $ "" %-" % #" 40 %&% "#" 40 %&% = ! 7 $ "" % #" 20 %&% ! 11 $ "" % #" 40 %&% (C) Daily Student Handouts: (including supporting screenshots or graphics that assist the student in completion of tasks), transparencies (optional), and homework (if not from textbook) • Homework Assignment(s): o Textbook: “Math for Middle Grades” (Prentice Hall) Students are to complete: Page 195, #1-10, #14-23 (D) Daily Answer Keys: • Homework Assignment(s): o Textbook Answers: 1) 5/7 6) 1 27/40 2) 4/5 7) 1 3/10 3) 1 1/6 8) 2 4) 3/4 9) 1 3/4 5) 1 5/8 10) 1 17/24 14) 3/5 15) 3/5 16) 8/15 17) 1/2 18) 1/2 19) 5/12 20) 1/2 21) 1/6 22) 7/20 23) 5/12 Name:__________________________ Date:______ 12 Fraction Shapes 1. How many are in ? 6. How many = ____ 2. How many are in ? = _____ are in Based on these relations, ? = _____ 7. If 3. How many in are = 1, = ___ . ? = _____ 8. If = 1, = ___ . 4. How many are in ? = ______ 9. If = 1, = ___ . 5. How many are in ? = _____ 10. If = 1, = ___ . DAY FOUR OF UNIT PLAN 13 *Multiplying Fractions* *Multiplying Fractions for Real Life Settings* (A) Daily Objectives: • Students will be introduced to the multiplication of fractions, being able to multiply when like/unlike denominators and mixed fractions are present. They will explore various websites which enable students to practice multiplication skills. Lastly students will explore the internet to find how fractions play a role in everyday life. (B) Daily Outline: • To multiply fractions you must multiply the numerator of the first fraction by the numerator of the second fraction to produce the new numerator in the answer. The denominator of the first fraction must be multiplied by the denominator in the second fraction to then produce the new denominator in the answer. • On the overhead show the following: o Shorter form:(Top * Top)/(Bottom * Bottom) = (TopTop)(BottomBottom) ! 7 $ '! 2 "" %% "" #" 8 &% #" 3 ! 2 $ '! 5 $ """ %%% """ % # 6 & # 12 %%& 5 36 • ! 1 $ '! 3 $ """ %%% """ %%% #5& #8& 3 40 $ ! 14 $ %% = "" % &% #" 24 %&% ! 13 $ ' ! 2 $ """ % " % # 14 %%& ""# 2 %%& 13 14 ! """ 2 + # ! 3 $ $ '! """ %%% %%% """ 3 + # 4 && # ! 4 $$ """ %%% %%% # 7 && 275 28 When adding, subtracting, or multiplying mixed numbers you must first create an improper fraction, or a fraction where the numerator is larger than or equal to its denominator: o 1) By converting the mixed number to an improper fraction you can then find a common denominator and add, subtract, or multiply as normal. First you multiply the denominator by the whole number and then add the numerator, and place that number over the original denominator. This creates an improper fraction, where the numerator is larger than the denominator. SUBTRACTION EXAMPLE: ADDITION EXAMPLE: 14 ! ! $$ """ 3 + """ 4 %%% %%% "# "# 5 &% &% ! ! 2 $$ " """ %%% %%% 2 + " - ""# "# 5 &% &% 5!"# 3 $% + 4 19 3!"# 2 $% + 2 So... ! 19 $ %% ""# " 5 &% 4!"# 3 $% + 1 So... ! 12 $ "" % #" 5 %&% 5!"# 2 $% + 2 12 ! ! $$ """ 2 + """ 2 %%% %%% "# "# 3 &% &% Then... ! 19 $ ! 12 $ """ %-" % #" 5 %&%% ""#" 5 %&%% And... !7$ ! $ "" %% = 1 + "" 2 %% #" 5 &% #" 5 &% 8 13 7 5 ! ! 1 $$ " """ %%% %%% 3 + " + ""# "# 4 &% &% So... !8$ ""# %%& "3% So... ! 13 $ "" % #" 4 %&% ! 8 $ ! 13 $ """# %%%& + """# %%%& Then... " 3 % " 4 % 71 12 ! 71 $ ! $ %% = 5 + "" 11 %% ""# & #" 12 &% And… " 12 % MULTIPLICATION EXAMPLE: ! ! $$ ! ! $$ "" 5 + "" 2 %% %% '"" 2 + "" 1 %% %% "# "# 3 &% &% #" "# 6 %& %& ! 17 $ ! 13 $ "" % " % "#" 3 %%&% + ""#" 6 %%&% So... • 3! "# 5$% + 2 47 6 17 6! "# 2$% + 1 13 ! 47 $ ! $ "" %% = 7 + "" 5 %% # & #" 6 &% And... " 6 % Students will be given graphing calculators to explore multiplication of fractions and also introducing them the concept of converting fractions to decimals and vice versa. (C) Daily Student Handouts: (including supporting screenshots or graphics that assist the student in completion of tasks), transparencies (optional), and homework (if not from textbook) • Homework Assignment(s): o Online Explore: Students are to: Find one recipe online that contains fractions and print it out to bring to class. o Textbook: “Math for Middle Grades” (Prentice Hall) Students are to complete: Page 208, #13-17 Page 209 #25-32, #45 (D) Daily Answer Keys: • Homework Assignment(s): 15 o Online Assessment: Will be based on the recipe brought to class o Textbook Answers 13) 1 1/8 14) 4/15 15) 4/25 16) 3 17) 15 25) 7 1/8 26) 15 27) 18 28) 22 2/9 29) 7 1/3 30) 3 1/4 31) 4/5 32) 28 45) 34.5lbs DAY FIVE OF UNIT PLAN 16 *Problem Solving with Fractions* *Using Fractions in Everyday Life* (A) Daily Objectives: • Students will learn how to read fractions within word problems. They will also discover that fractions play a major role in everyday life situations; recipes, shopping, time, percentages/proportions, taxes, etc. (B) Daily Outline: • Show the video from “iLife Lessons: A Day with Fractions - Elementary Math Lesson Idea.” This video shows some of the many ways fractions play a role in everyday life. o http://ali.apple.com/ali_sites/ali/lessonideas/DayWithFractions.html • Next as a class complete the following three word problems o “Bill, Joe, and Diana went shopping for new sneakers. The sign said, ‘All sneakers are 1/5 off of the original price.’ If the pair that Diana wanted was originally $80, how much are they now?” ANS: $80 * (1/5) = 1$6 $80 - $16 = $64 o “John worked on his homework for 40 minutes, while in the mean time his friend had already finished. He told John, ‘I finished my homework in a quarter of the time that it took you. How long did the homework take for John’s friend to complete? ANS: 40minutes * (1/4) = 10 minutes o “When Ashley received her paycheck she figured out that 1/8 of her original pay was taken out for taxes and other deductions. If her original pay was $350, then how much money was taken out? how much did she actually get to take home? (Round to the nearest hundredths place) ANS: $350*(1/8) = $43.75[out] $350-$43.75 = $306.25[home] • Now take your recipe that you found online for homework the night before and say you are having 30 people over for dinner. The recipe may only be based on a ten person serving, so now you want to triple it (in lowest terms.) When they are finished have them quadruple the recipe (in lowest terms.) Have them hand in and check for accuracy. ORIGINAL MYSTERY RECIPE: 1 C butter/margarine, softened 2 C granulated sugar 4 eggs 2 t vanilla 1 1/3 C flour 3/4 C Hershey's Cocoa 1 t baking powder 1/2 t salt 2/3 C chopped nuts, optional 6 ounces of cream cheese TRIPLED: 3 Cups 6 Cups 12 Eggs 6 Teaspoons 4 Cups 2 1/4 Cups 3 Teaspoons 1 1/2 Teaspoons 2 Cups 18 Ounces QUADRUPLED: 4 Cups 8 Cups 16 Eggs 8 Teaspoons 5 1/3 Cups 3 Cups 4 Teaspoons 2 Teaspoons 2 2/3 Cups 24 Ounces 17 1/3 C granulated sugar 3/4 t vanilla • 1 Cup 2 1/4 Teaspoons 1 1/3 Cups 3 Teaspoons Now pass out a bag of “M&M’s” to each student with the worksheet below and have them follow the directions at the top. Then have them create a fractional piece for each color. (C) Daily Student Handouts: (including supporting screenshots or graphics that assist the student in completion of tasks), transparencies (optional), and homework (if not from textbook) • Transparency Diagram of “M&M’s” Chart: SEE SHEET BELOW • Homework Assignment(s): o “M&M’s” Continued: Students are to find the fraction by color to the whole bag of “M&M’s.” They are also to turn each fraction into a percentage and a decimal. o Textbook: “Math for Middle Grades” (Prentice Hall) Students are to complete: Page 146 #10 Page 228 #12-14 Page 229 #6 (D) Daily Answer Keys: • Homework Assignment(s): o M&M’s Continued: Answers will depend on answers found in class o Textbook Answers: 10) a) 2,4,8 b) Each denominator is twice preceding c) 1/16, 1/32 12) $32 13) 40 rows 14) 4 people 6) D Name:__________________________ Date:________ 18 M&M's ® Without opening or touching your bag of "M&M's", estimate how many are inside and record below. Predict how many of each color you will have. (If your estimated total is 10 "M&M's" in your bag then your total prediction of "M&M's" colors should also add to 10.) Then open your bag and find your actual total and how many you have of each color. Record your results below. Estimated total= Colors: Prediction: Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Dark Brown Total= Actual total= Actual Amount: Now show the Fractional Number of M&M’s by color below: Red: Orange: Yellow: Green: Blue: Dark Brown: 19